2022 Vol. 39, No. 3
2022, 39(3): 465-474.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210373
Abstract:
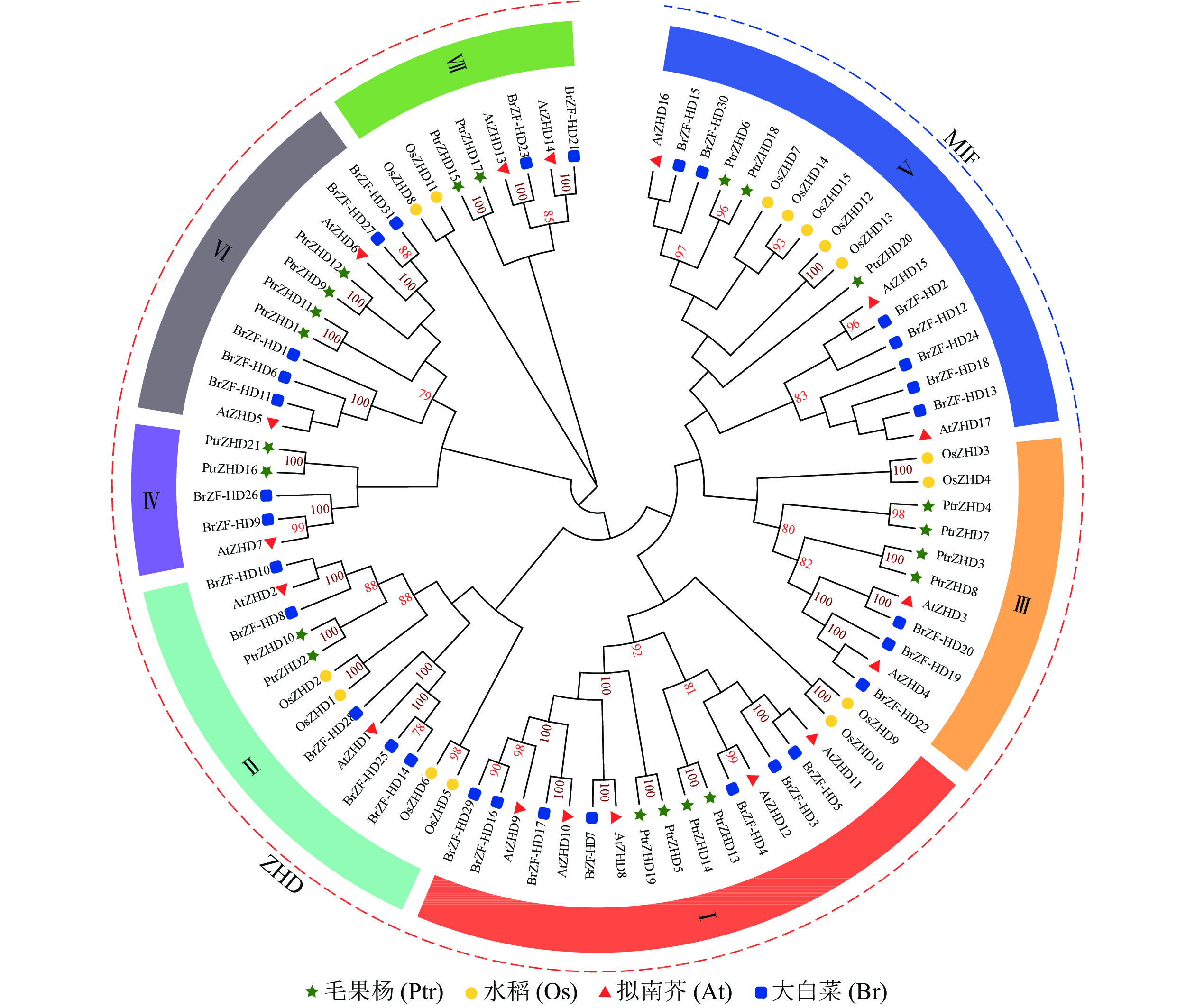
Objective With an investigation of the bioinformatics information of the ZHD gene family of Populus trichocarpa (PtrZHD) and an analysis of the expression characteristics of this gene family under drought stress, This study is aimed to provide reference for exploring the functions of PtrZHD in drought stress. Method Bioinformatics was used to identify all members of the ZHD gene family in P. trichocarpa at the genome-wide level before an analysis was conducted of their evolution, physicochemical properties, gene structure, conserved Motifs, cis-acting elements of the promoter and expression characteristics. Result The ZHD gene family of P. trichocarpa consisted of 21 members, which could be divided into 7 subfamilies. There were 8 pairs of homologous genes in the ZHD gene family of P. trichocarpa, and the Ka/Ks value of each pair of homologous genes was far lower than 1. Though with different physicochemical properties, PtrZHD gene family members had relatively conservative structures, all containing Motif 1. Different numbers of hormone and abiotic stress response elements were found in the promoter regions of PtrZHD gene family members with various response elements among different genes. One, seven and thirteen members of the PtrZHDs gene family were preferentially expressed in the root, stem and leaf tissues of P. trichocarpa, respectively. The response of PtrZHD gene family members to drought stress was tissue-specific and time-specific with the expression levels of each member of ZHD gene family being different in root, stem and leaf tissues, yet with the increase of drought stress time, they all showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. Conclusion Different members of the PtrZHD gene family had different responses to drought stress, indicating that they might regulate the response of P. trichocarpa to drought stress. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 475-485.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210385
Abstract:
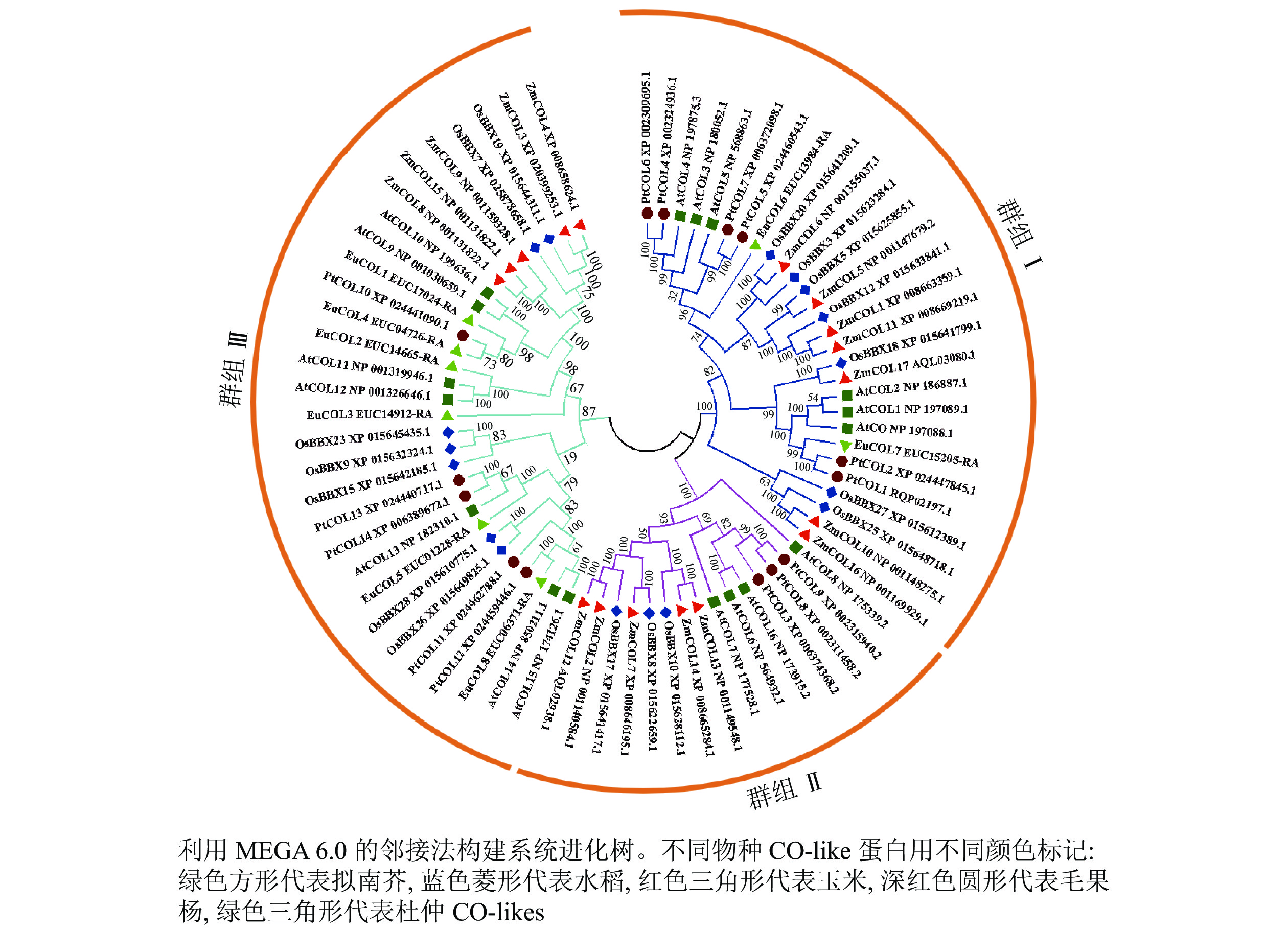
Objective This study aims to reveal the distribution and expression pattern of CONSTANS-like in Eucommia ulmoides genome. Method Bioinformatics method was used to identify the CONSTANS-like gene family of E. ulmoides and analyze its physicochemical properties, evolutionary relationship, gene structure, promoters and expression patterns. Result A total of 8 EuCOL genes (EuCOL1−EuCOL8) were identified in E. ulmoides genome, composed of 315−469 amino acid residues. Their isoelectric point distribution range was 5.10−6.47 and the molecular weight was 35.21−52.65 kDa. Subcellular localization predicted that they were all located in the nucleus and were hydrophilic proteins, distributed on 8 chromosomes. EuCOL gene family was divided into two subfamilies (Group Ⅰ and Group Ⅲ), containing 2 and 6 EuCOLs proteins, respectively, the motifs of the same subfamily were similar. EuCOL genes were simple in structure and contained multiple photoperiodic response elements in their promoters. Expression pattern analysis showed that the expression level of EuCOLs was relatively low during the development of E. ulmoides leaves, the expression level of EuCOL7 was the highest in gutta-percha formation, and the expression characteristics of family members were different. Protein interaction prediction showed that EuCOL7 could interact with multiple photoperiod responsive proteins. Conclusion The CONSTANS-like gene family of E. ulmoides contains a typical CCT and B-box domain, which may be involved in leaf development and gutta-percha formation. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 56 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 486-494.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210471
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to investigate the family members of phosphorus transporter Ⅰ (PHTⅠ) protein of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) and analyze their expression patterns. Method With the employment of the bioinformatics, the PHTⅠ family members of Moso bamboo were identified before an analysis was conducted of the regulatory elements of gene promoters, the physicochemical properties of coding proteins, gene structure, conserved motifs of amino acids, gene positions on chromosomes, tissue expression specificity, gene adaptive evolution and phylogeny. Result PHTⅠ family of Moso bamboo consisted of 20 members distributed on ten chromosomes in the cell membrane and each gene contained 1 to 2 introns while the PePHTs promoter sequence contained elements of abiotic stress such as drought and low temperature and hormone response elements such as Gibberellic acid. Most PHTⅠ from Ph.edulis were basic proteins with the range of molecular weight of PePHTs between 48.61 and 76.37 kDa and that of the theoretical isoelectric point between 6.84 and 9.30. The hydrophobicity value of all PePHTs was greater than zero, indicating that all the proteins in this family were hydrophobic. In terms of gene adaptive evolution, the ω value of most PePHTs genes were lower than zero, indicating that most genes were under negative selection pressure. PePHTs had different expressions in different tissues, which indicated that PePHTs played different roles in the growth and development of Moso bamboo. PePHTs were clustered in the first Ⅰ subfamily, preferentially in the same branch as rice (Oryza sativa). Conclusion PHTⅠ family plays an important role in the absorption and transport of phosphorus in plants and the results of this study have provided a favorable theoretical foundation for a further analysis of the functions of the PHTⅠ family genes in Moso bamboo. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 45 ref. ]
2022, 39(3): 495-504.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210433
Abstract:
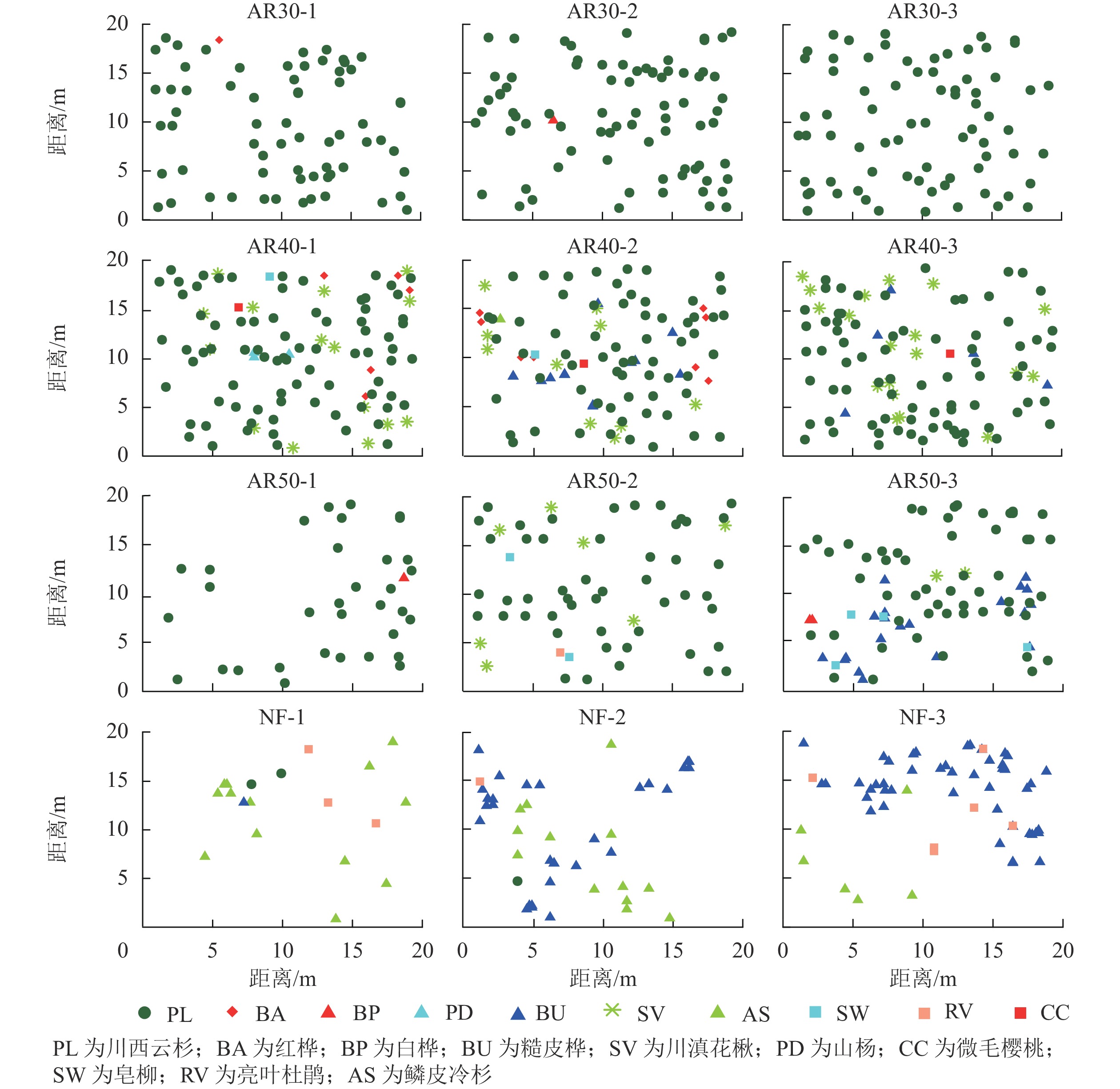
Objective As an important component of forest resources in western Sichuan, the area and standing volume of Picea likiangensis var. rubescens (PL) plantations are increasing with the implementation of the national project Converting Farmland to Forest. This study aims to analyze the spatial distribution pattern and interspecific correlation between natural forest and plantation in Daofu County, so as to reveal community dynamic change and succession law of plantation community. Method The typical sampling method used to set up 12 fixed plots to measure the central position coordinates, diameter at breast height (DBH), height and crown width of each living tree. The univariate Ripley’s L(t) function and bivariate Ripley’s L12(t) function in point pattern analysis were used to analyze the spatial distribution pattern of plantation and natural forest colony, and the spatial correlation between tree species in the community. Result (1)With the increase of restoration years, the population density of PL gradually decreased, while the number of community species gradually increased. (2)The spatial distribution pattern of living trees was generally random in plantations but was aggregated in natural forests. (3)The spatial correlation between PL and other broad-leaved tree species was not significant in plantations, while the main tree species in the natural forest community were not correlated on a small scale but negatively correlated on a large scale. Conclusion After 50 years of artificial restoration, there are still distinct differences between PL plantations and natural forests in community spatial distribution pattern and interspecific correlation, and the process of ecological restoration is slow. It is suggested that the structure of plantations could be optimized and improved by combining thinning measures and planting dominant tree species of natural forests, so as to accelerate the succession process from plantations to natural forests. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 35 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 505-515.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210330
Abstract:
Objective The objective of this study is to evaluate the stability of 9 typical forest communities in Xianrendong National Nature Reserve, Liaoning Province, and to analyze the main influencing factors. Method Taking the survey data of 9 typical forest communities in the reserve as the data source, the population regenerative potential, basic community characteristics, species diversity, population niche overlap, litter characteristics and soil fertility of 9 forest communities were compared, and a stability evaluation system was constructed based on the above 6 indicators and 44 factors. The subordinate function value method in fuzzy mathematic was used to evaluate the stability of each forest community. Result (1) Pinus densiflora+Quercus acutissima-Parthenocissus tricuspidata+Zanthoxylum schinifolium-Amphicarpaea edgeworthii+Cardamine leucantha had the best regeneration potential, species diversity and soil fertility. The average value of basic characteristics of growth and development of P. densiflora-Rubus crataegifolius+Z. schinifolium-Carex callitrichos var. nana community was the highest. The niche overlap of the 9 communities was similar, and the litter accumulation and water holding capacity of Q. dentata+Q. acutissima-Indigofera kirilowii+Corylus heterophylla-Artemisia keiskeana+C. callitrichos var. nana community were the best. (2) The stability ranking of the 9 forest communities from high to low was P. densiflora+Q. acutissima-P. tricuspidata+Z. schinifolium-A. edgeworthii+C. leucantha, Q. dentata+Q. acutissima-I. kirilowii+C. heterophylla-A. keiskeana+C. callitrichos var. nana, Q. acutissima+Q. variabilis-Z. schinifolium+C. heterophylla-C. callitrichos var. nana, P. densiflora-Lindera obtusiloba+Rhododendron micranthum-C. callitrichos var. nana, P. densiflora-Z. schinifolium-C. callitrichos var. nana, Q. mongolica+P. densiflora-R. crataegifolius+R. micranthum-C. callitrichos var. nana, Q. mongolica-R. crataegifolius-C. callitrichos var. nana, P. densiflora-R. crataegifolius+Z. schinifolium-C. callitrichos var. nana and Q. dentata+P. densiflora-C. heterophylla-C. callitrichos var. nana. (3) Among the 6 forest community stability indicators, the load coefficient of population regenerative potential, species diversity and soil fertility was the largest in the first principal component. Conclusion There are significant differences in the stability of the 9 typical forest communities in Xianrendong National Nature Reserve, and the main influencing factors are regenerative potential, species diversity and soil fertility. [Ch, 10 tab. 31 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 516-523.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210350
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the characteristics and laws of litter decomposition in mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest and evergreen broad-leaved forest during acid rain in Jinyun Mountain, is aimed to provide scientific basis for the optimization of forest management and the guidance in forest stand allocation. Method With two typical forests of Jinyun Mountain in Chongqing selected, four acid rain simulation experiments with different concentrations were conducted. Then, with the employment of the Olson negative exponential decay model, the decomposition rate of litter of two forest stands was assessed, and the laws of litter decomposition in two typical forest stands under simulated acid rain were analyzed. Result (1) After a six-month decomposition, in comparison, the mass residue rate of the mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forest treated with acid rain of pH 4.50(ck), pH 4.00, pH 3.25, and pH 2.50 was higher than those of the evergreen broad-leaved forest under the same conditions by 4.60%, 3.78%, 4.22% and 5.39%. (2) The time for the control group to reach half-life and full-life of litter decomposition in the coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest was 1.62 a and 6.98 a whereas that for evergreen broad-leaved forest was 1.29 and 5.56 a; the time for the material loss rate to reach 50% and 95% for the coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest litter under different concentrations of acid rain is 1.47−2.00 a and 6.35−8.43 a whereas that for the evergreen broad-leaved forest is 1.23−1.50 a and 5.33−6.48 a. (3) The k values of the mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests treated with ck, pH 4.0, pH 3.25, and pH 2.5 were 0.43, 0.47, 0.40, and 0.35, respectively while those of the evergreen broad-leaved forest were 0.54, 0.56, 0.51, and 0.46, respectively, and the overall k value shows a downward trend as the pH value of the treatment decreases. (4) The simulated acid rain with pH 4.00 in the study area promoted the decomposition of litter in the forest to a certain extent whereas the simulated acid rain with pH 2.50 and pH 3.25 inhibited the decomposition of falling objects in different forests to a certain extent. Conclusion In Jinyun Mountain of Chongqing, simulated acid rain of different concentrations had a significant effect on the decomposition rates of litters in the two typical stands and the decomposition rate of evergreen broad-leaved forest was higher than that of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 32 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 524-530.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200523
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to better utilize and preserve the wild resources of Nanmu (Phoebe). Method With the employment of tally and quadrat method, an investigation was conducted of the distribution, habitation and population of Phoebe species in Qingyuan County of Zhejiang Province. Result P. chekiangensis, P. bournei, and P. sheareri were found in Qingyuan County with a total of 23 distribution areas detected covering streets in nine townships. P. chekiangensis and P. bournei were mostly distributed below the altitude of 800 meters whereas P. sheareri enjoyed the largest horizontal distribution span with the altitude possibly reaching up to 1 250 meters, but a relatively small population size. The wild resources of Phoebe in the counties are scarce with most populations located either in fengshui woods or protected areas with Fagaceae and Lauraceae as the main dominant and constructive species. Conclusion The endangerment of Nanmu mainly attribute to frequent human activities and their unique demand of light. [Ch, 5 tab. 21 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 531-539.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210473
Abstract:
Objective To improve the estimation accuracy of forest aboveground biomass, this study is aimed to conduct an uncertainty analysis, trying to figure out the percentage error of estimating forest aboveground biomass by remote sensing and the causes behind. Method With factors extracted from remote sensing images and combined with the data of Pinus densata from field surveys, three types of aboveground biomass estimation model were established, namely Multiple Linear Regression (MLR), Gradient Boost Regression Tree (GBRT), and Random Forest (RF), before the uncertainty of sample plot scale and three models was measured and analyzed. Result (1) The uncertainty of tree biomass model for P. densata is 16.43%, and the uncertainty of the scale up to the sample plot is 7.07%; (2) The residual uncertainty of the MLR model is 34.86%, the parameter uncertainty is 21.30% whereas the total uncertainty combined with the sample plot uncertainty is 41.45%. (3) In the non-parametric model of the GBRT modeling estimates, the total uncertainty of the aboveground biomass is 23.12%, and the RF is 19.42%. Conclusion Among the three remote sensing models, the uncertainty of the non-parametric model is obviously lower than that of the parametric model. Compared with the uncertainty of the sample plot scale, the remote sensing estimation model has a great effect on the accuracy of the aboveground biomass estimation. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 26 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 540-546.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210457
Abstract:
Objective Given the significant environmental improvement after the implementation of ecological projects in the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi, this study is aimed to investigate the effect of ecological projects on vegetation improvement so as to provide reference for ecological construction and development countermeasures. Method With the Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI images in the growing season from 2000 to 2019 collected, the DBEST algorithm was used to detect breakpoints in the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time series before a multi-stage trend analysis method was proposed to analyze the temporal and spatial dynamic of the vegetation change in Fu County, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. Result Results of break-point detection showed that 66.47% of the breakpoints showed a change magnitude of NDVI lower than 0.2, mainly distributed in the western and northeastern areas and the vegetation was relatively stable without drastic changes; 33.53% of the breakpoints showed a change magnitude of NDVI higher than 0.2 with areas having more than 4 breakpoints accounting for only 5.88% and they were concentrated on roads and rivers with frequent changes in vegetation due to human activities. Results of trend analysis showed that for areas with a break-point change magnitude of NDVI higher than 0.2, the improved area accounted for 24.57% whereas the degraded area only accounted for 2.12%; Featured with a large time distribution span and a strong spatial heterogeneity, the current trends started before 2014, revealing the diversity and complexity of vegetation changes in Fu County; A trend of improvement was detected in all the four main types of forest land in Fu County, namely wood land, sparse wood land, shrub land and young afforested land with the improved area accounting for 96.23% of the total wood land. Conclusion Recent years have witnessed an overall improvement trend of the vegetation in the study area, showing the positive impact exerted by ecological construction projects and further ecological countermeasures should be formulated taking into consideration in accordance the differences in spatial characteristics of vegetation changes in Fu County from 2000 to 2019 as well as local circumstances. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 25 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 547-553.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210455
Abstract:
Objective With an investigation of the flowering dynamics of Styrax obassia, this study is aimed to reveal the basic characteristics of its breeding system for a better understanding of its biological characteristics so as to provide theoretical basis for cross breeding and habitat protection of S. obassia as well as technical support for the application and popularization of urban landscaping. Method Observations were made of the flower dynamic characteristics, floral structure and insect visiting characteristics before the pollen viability and stigma receptivity were determined employing TTC staining and benzidine hydrogen peroxide method whereas the breeding line type was determined using hybridization index (OCI) and pollen ovule ratio (P/O). Result (1) With a single flowering period of about 3 to 5 days, the flowering period of S. obassia is from mid-April to early May with April 15 to 18 being the initial flowering period, April 19 to 26 being the full flowering period and April 27 to May 2 being the final flowering period. (2) With the racemes drooping, its flowering sequence was divided into 2−3 segments from the base of the pedicel to the apex and the average number of florets in 30 racemes was (25.3±1.8). (3) The pollen vigor was the strongest one day after flowering, and the mature time of male and female stamens partially coincided, with a P/O of (646.30±64.35) and an OCI of 4. (4) The flower visiting insects mainly include Apis cerana and Camponotus japonicus. Conclusion The flowering period of S. obassia began in mid-April and ended in early May with the bloom lasting for a week and the breeding system is featured with facultative outcrossing and pollinator and is partially self-compatible. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 25 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 554-561.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210421
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the variation patterns of physiological indices of seedless Diospyros lotus during fruit development and ripening, is aimed to provide a theoretical basis for the further utilization of such resources. Method With fruits of seedless D. lotus of different stages collected, a survey was conducted of the variation patterns of tannin, total polyphenols and flavonoids, anthocyanins, sugar and pectin composition, as well as the activity of pectin degrading enzyme before an analysis was conducted of the correlation. Result During the fruit development and ripening there was a constant decrease in the contents of soluble tannin and anthocyanin and a gradual increase in the contents of insoluble tannin, starch, fructose, glucose, sugar-acid ratio, water soluble pectin and ironic soluble pectin whereas there was first an increase and then a decrease in the contents of total polyphenols, flavonoids, titratable acids and covalent soluble pectin content. There was a significant increase in the activities of polygalacturonase and pectate lyase at the later stage of fruit ripening (P< 0.05). There was a significant positive correlation between the contents of water soluble pectin and ironic soluble pectin and the activities of polygalacturonase and pectate lyase (P<0.01), a significant negative correlation between the contents of covalent soluble pectin and the activities of polygalacturonase and pectate lyase (P< 0.05) and a significant positive correlation between the contents of starch, fructose and glucose and the contents of water soluble pectin, ironic soluble pectin as well as the activities of polygalacturonase and pectate lyase (P< 0.01). Conclusion During the development and ripening of seedless D. lotus, the content of soluble tannin gradually decreased to below the edibility threshold while polygalacturonase and pectate lyase enzymes were involved in the catalytic degradation of pectin components in the cell wall, which led to the change of pectin components, the increase of soluble sugar content and the change of active components in the fruit. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 29 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 562-570.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210296
Abstract:
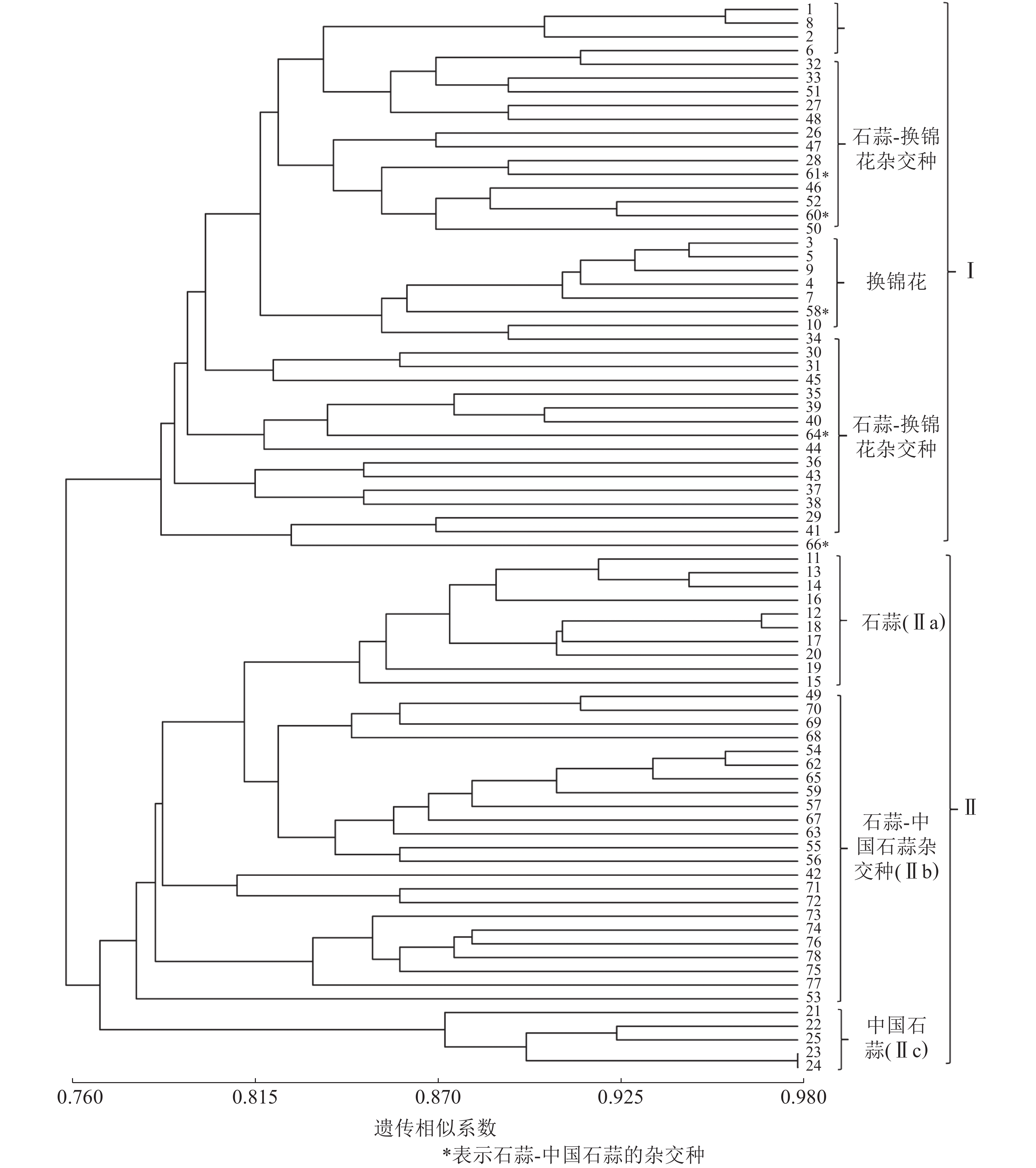
Objective This study is aimed to identify the authenticity of F1, an interspecific hybrids among Lycoris. Method With 78 samples collected of F1, an interspecific hybrids among L. radiata, L. chinensis and L. sprengeri, expressed sequence tag simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) was employed to construct their molecular identification cards before an analysis was conducted of their genetic relationships. Result fluorescence labeled EST-SSR primers yielded 92 amplified bands that averaged 6.13 per pair; polymorphism information (PIC) was 0.629 2 to 1.000 0 and averaged 0.913 7. The authenticity identification rate of primers SSR203+SSR115 for the F1 generation of L. radiata-L. sprengeri and L. chinesis-L. radiata was 96.30% and 96.15%, respectively. UPGMA cluster analysis showed that the genetic similarity coefficients of parents (L. radiata, L. chinensis and L. sprengeri) and their hybrids ranged from 0.76 to 0.98, and with the similarity coefficient being 0.77, the 25 parents and 53 hybrids could be clusted into 2 groups, namely group Ⅰ and group Ⅱ. Group Ⅰ included L. sprengeri parents and hybrids between L. radiata and L. sprengeri whereas group Ⅱ, including L. radiata, L. chinensis and the hybrids between L. radiata and L. chinensis, could be divided into three subclades: Ⅱa, Ⅱb and Ⅱc. The unique molecular identity cards of 78 Lycoris parents and hybrids were constructed based on the fluorescent EST-SSR genotypes coding. Conclusion Fluorescence labelled EST-SSR can be used for early identification of interspecific hybrids in Lycoris, which can provide important reference for variety identification and cross breeding of Lycoris. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 26 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 571-581.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210453
Abstract:
Objective This study is designed to explore the response mechanism of urban bird habitat based on urban forest structure with birds as indicators, so as to optimize urban forest structure and improve the ecological service function of urban forest patches. Method Taking Hefei City as the study area, 21 urban forest patches with an area of 0.5−2.5 hm2 were selected as sample plots. The characteristics of plant community and structure were investigated by sampling method, and the composition of bird community in selected sample plots was observed and recorded in the form of fixed sample line and sample point in autumn. Combined with ArcGIS and satellite images, the relevant indicators of urban forest tree species composition, space, infrastructure and landscape structure were quantified, and correlation analysis, principal component analysis and regression analysis were used to clarify the potential relationship with urban bird richness, abundance, Shannon index and Pielou evenness. Result (1) 90 species of vegetation belonging to 51 families and 76 genera were recorded. 38 species of birds in 22 families and 8 orders were recorded, accounting for 10.08% of the recorded bird species in Hefei, and 1213 birds were counted by maximum retention method. The dominant species of urban birds were Pycnonotus sinensis, Cyanopica cyana and Passer montanus, and the bird composition between patches had a high similarity, with an average similarity of 0.588. (2) Non-parametric rank sum test showed that there was no obvious difference in bird community with or without water area, and the composition of urban forest tree species, space, infrastructure and landscape structure had different degrees of impact on bird indicators. (3) Principal component analysis showed that the factors affecting bird richness could be classified into three aspects: the amount of resources and potentially available resources of urban forest patches, the richness and diversity of trees, and the resource enrichment degree of patches per unit area, and the equations of bird richness and bird abundance could be obtained by further analysis. Conclusion The attraction of urban forest to urban birds depends on multiple structural levels. The indicators that can reflect the amount of resources and the potentially available resources of urban forest, tree richness and diversity, and resource enrichment degree per unit area are important factors affecting bird habitat. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 26 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 582-589.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210456
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to clarify the latest distribution range of Tragopan caboti population in Wuyanling National Nature Reserve of Zhejiang, so as to provide help for the evaluation of previous conservation work and development of future conservation plan. Method Transect survey and infrared camera survey were used to investigate the field distribution in all protection stations in the reserve from 2019 to 2020. Through field investigation and ArcGIS image interpretation, the distribution range of T. caboti was determined by comprehensively analyzing the forest vegetation type, altitude, topography and other related factors around the distribution point. Result A total of 69 distribution points of T. caboti were found in Shuangkengkou, Beipai, Huangqiao and Yangxi protection stations, with a distribution area of 24.9, 15.2, 10.7, and 4.5 km2 respectively. The distribution points of T. caboti were mainly in coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests and broad-leaved forests, and less in other vegetation types. The altitude range was 670−1 550 m, which was wider than the altitude range of 800−1 400 m previously reported. Compared with the core region, the distribution of T. caboti was relatively large in the edge area of broad-leaved forest, and its population distribution showed edge effects. T. caboti-dependent plant Daphniphyllum macropodum was not found in the low altitude and Yangxi areas, indicating that there was no complete correlation between current population distribution and D. macropodum. Among the four distribution areas, Shuangkengkou, Beipai and Huangqiao were geographically connected, and the population of T. caboti might be the result of reproduction and diffusion of the original population in Wuyanling, while the distribution area of Yangxi was distant from Wuyanling, and its population could be identified as an independent population. Conclusion After long-term protection, the habitat environment of T. caboti in Wuyanling National Nature Reserve has been restored on a large spatial scale, the habitat fragmentation has been significantly altered, and the population distribution of T. caboti has been greatly expanded, which shows that the conservation measures taken in the reserve for a long time have achieved positive results. Further follow-up research should be carried out on phenomena such as edge effect and scientific countermeasures should be taken in future work. [Ch, 2 tab. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 590-597.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210407
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to reveal the categorization of ant species and their distribution patterns in the Upper Yarlung Zangbo Valley and southwest slope of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and accumulate scientific data for biodiversity conservation of hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Method With the employment of the sample-plot method, an investigation is conducted of the distribution patterns of ant species in the two locations mentioned above. The distribution charaters including habitats, foraging and nesting sites of ant species are compared with the method of collecting frequency analysis. Result A total of 19 species belonging to 2 subfamilies and 8 genera of Formicidae were recognized, of which 13 species belonging to 2 subfamilies and 8 genera were from Upper Yarlung Zangbo Valley whereas 15 species belonging to 2 subfamilies and 8 genera were from southwest slope of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. These two areas are abundant in cold-tolerant species but short of heat-tolerant ones. The species richness of ants was extremely significantly positively correlated with canopy density and shrub coverage (P<0.01), and extremely significantly negatively correlated with litter thickness and altitude (P<0.01), but had insignificant correlation with herbal and ground coverage. Different ant species had different preferences in habitats, but most individuals foraged on the ground and nested under stone or in soil. Conclusion The distribution of ant species was mainly affected by altitude and habitat conditions whereas their choice of habitats, sites of foraging and nesting was mainly affected by food resources, environmental stability and the quantity of heat. [Ch, 6 tab. 26 ref.]
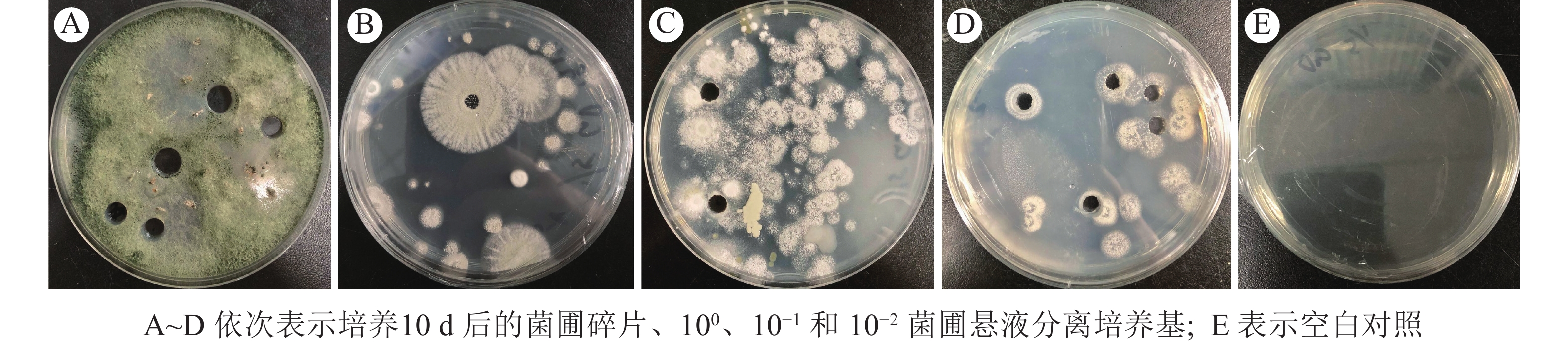
2022, 39(3): 598-606.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210478
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation into how Odontotermes formosanus fungus-combs microorganisms influence the growth of Termitomyces heimii, is aimed to provide an experimental reference for further research on the micro-ecology of the termite combs, and make contribution to the artificial cultivation of Termitomyces. Method First, oligotrophic medium was employed to separate microorganisms in the fungus-combs. As for bacterium, with an exploration conducted of how bacterial fermentation broth influences the growth of T. heimii, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the newly formed soluble carbohydrates in the fermentation broths to clarify the relationship between bacterium and T. heimii. In terms of fungi, co-culture was used to detect the interaction between T. heimii and other fungi in the combs. Result Eight species of bacteria and 12 species of fungi were isolated from the fungus-combs where a large number of spores of T. heimii were distributed. Firmicute separated promoted the growth of T. heimii, under the influence of which, knots were formed in the hyphae and the growth rate of the hyphae partly increased by 0.033 cm·d−1 (P<0.01). By contrast, Proteobacteria inhibited the growth of T. heimii, with a significant inhibitory effect displayed by Burkholderia sp. (undetermined) under the influence of which, T. heimii could hardly grow. As was shown in the HPLC analysis, a large amount of soluble carbohydrates were newly produced in the bacterial fermentation broths, indicating that the bacterium in the fungus-combs had the ability to degrade lignocellulose and convert it into oligosaccharides. Other fungi in the fungus-combs inhibited the growth of T. heimii and once the fungus-combs died out, fungi such as mold quickly occupied the combs. Conclusion 78.9% of the bacterium isolated from termite combs benefits T. heimii, while all the fungi isolated inhibit its growth, implying that the microorganisms of O. formosanus fungus-combs have a significant effect on T. heimii. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 18 ref.]
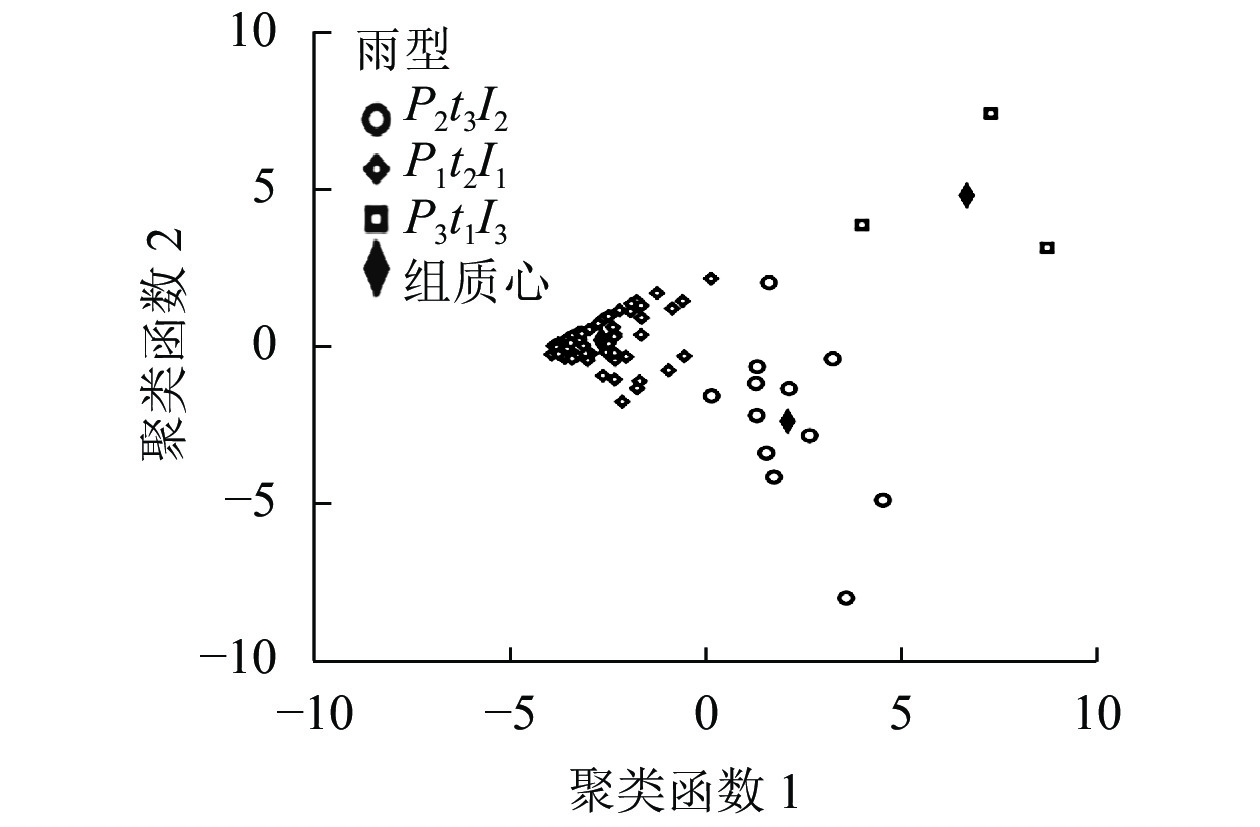
2022, 39(3): 607-615.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210429
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the effects of different natural rainfall patterns on runoff process. Method According to the quantitative characteristics of rainfall and the concentration period of rainfall peaks, the natural rainfall in the upper reaches of Miyun Reservoir was classified into two levels, and the runoff characteristics under different rain patterns and process rain patterns were investigated. Result (1) According to P (precipitation ), t (rainfall duration) and I30 (maximum 30 min rainfall intensity), the rainfall in the study area could be divided into three patterns: P2t3I2 rain (medium rainfall, long duration and medium rainfall intensity), P1t2I1 rain (light rainfall, medium duration and light rainfall intensity) and P3t1I3 rain (heavy rainfall, short duration and heavy rain intensity). P1t2I1 rain pattern had the highest frequency in the study area. The occurrence frequency of the four process rain patterns ranging from large to small was uniform, pre-peak, post-peak, and mid-peak. (2) The runoff characteristics under different rainfall patterns were significantly different. In terms of single rainfall, P3t1I3 had the largest single runoff production capacity, while P2t3I2 had the largest contribution rate to runoff. (3) Rainfall patterns of different processes had significant effects on runoff characteristics, and the rainfall concentrated in the early rainfall period was most likely to produce runoff. (4) Rainfall had the greatest impact on runoff depth. I30 had a great impact on runoff depth, runoff coefficient and runoff depth peak, and the impact on runoff depth peak was greater than that on runoff depth. Conclusion The characteristics of slope runoff are highly sensitive to rainfall patterns and process rainfall patterns. Using reasonable rainfall pattern division method to study the relationship between rainfall patterns and runoff can improve the accuracy of hydraulic erosion research. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 616-624.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210348
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to reveal the effects of different restoration communities on understory species diversity and soil physical and chemical properties in the dry-hot valley of the Red River. Method The plant communities of Schleichera oleosa, Dodonaea viscosa, Cassia siamea, Pistacia weinmannifolia and natural secondary sparse shrub and grass artificially restored for 15 years in the dry-hot valley of the Red River were taken as the objects, the species composition, diversity characteristics and soil physical and chemical properties of understory herbaceous plants were studied by using typical plots and random sampling methods. Result (1) A total of 60 species of vascular plants were found in different restoration communities, belonging to 20 families and 49 genera, of which the dominant families were Leguminosae, Compositae, Gramineae, and Euphorbiaceae. (2) Among the four artificial restoration communities, the Richness index, Shannon-Wiener diversity index and dominance index of P. weinmannifolia were significantly higher than those of natural secondary sparse shrub and grass (P<0.05). (3) The similarity degree of species composition between the four artificial restoration communities and the sparse shrub and grass was at a moderate dissimilarity level. (4) The soil organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium of the four artificially restored plant communities were significantly lower than those of sparse shrub and grass (P<0.05). Conclusion There are significant differences in understory species diversity and soil physical and chemical properties among different restoration communities in the dry-hot valley of the Red River. Compared with the natural secondary sparse shrub and grass, the artificial restoration community can increase the species diversity in a relatively short period of time, but cannot quickly restore soil nutrients. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 35 ref.]
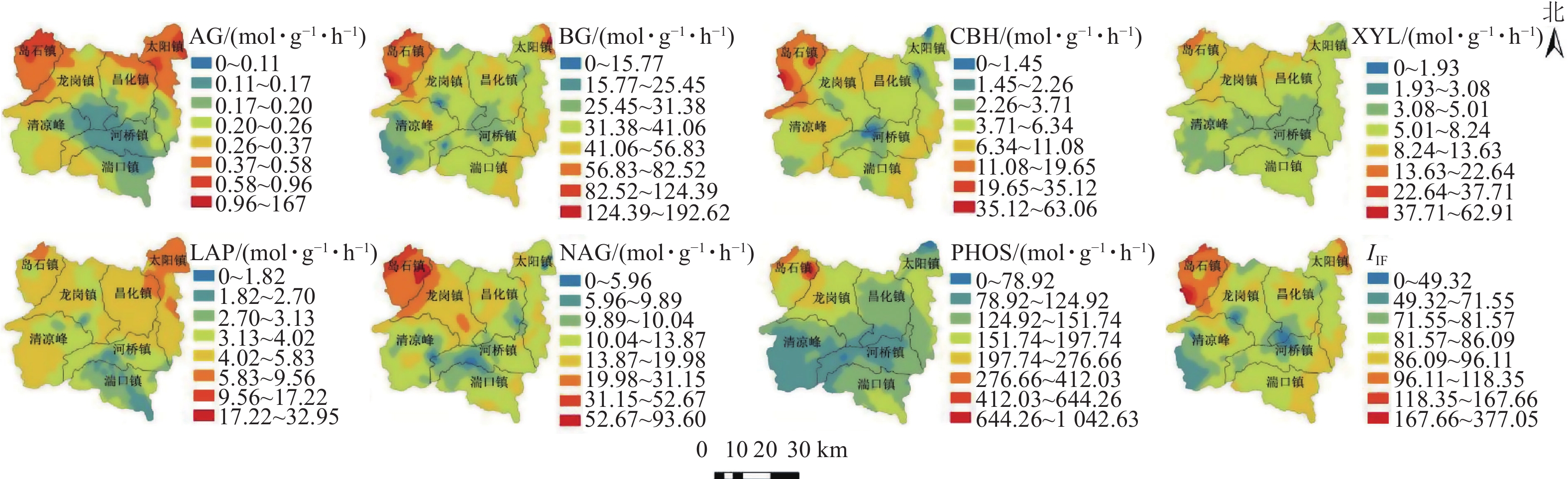
2022, 39(3): 625-634.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210417
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the spatial distribution characteristics of soil hydrolase activity and soil fertility in Caya cathayensis forests. Method 259 sample plots were selected from the main C. cathayensis producing areas in Lin’an District of Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province to determine the main fertility indicators and the activities of 7 hydrolases such as α-glucosidase (AG), β-glucosidase (BG), cellobiosidase (CBH), xylosidase (XYL), leucine amino peptidase (LAP), N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG), and acid phosphatase (PHOS). Principal component analysis, geostatistical analysis, pearson correlation analysis, and redundancy analysis were used to analyze the soil fertility as well as the spatial variation of 7 hydrolase activities and their influencing factors. Result The spacial structure ratios [C0/(C+C0) ] of AG, BG, CBH, LAP, NAG, XYL, and PHOS were 55%, 42%, 56%, 49%, 66%, 47% and 78% respectively, and the global Morans’I (Ig) was greater than 0. Available N, available P, available K, and organic matter in the rich soil accounted for 64%, 56%, 23% and 45%, respectively, and the average pH was 5.76. The soil fertility of 58.7% of the sample plots was below average. Most of the C. cathayensis plots were in level Ⅲ and Ⅳ, while only 32.7% of the plots were in levelⅠand Ⅱ. Conclusion Among the 7 soil hydrolases, AG, BG, CBH, LAP, NAG, and XYL have moderate spatial autocorrelation, and their variation is jointly affected by human interference and topographic structure factors. PHOS has weak spatial autocorrelation, and its spatial distribution is mainly affected by human interference. The activities of 7 hydrolases have spatial correlations and similar high and low clustering. High value aggregation occurs near Daoshi town while low value clustering occurs near Qingliangfeng town and the boundary of Heqiao, Longgang and Changhua towns. Soil pH, organic matter and available N are the key factors affecting the high and low value clustering of hydrolase activity. The results of soil fertility index classification and comprehensive fertility score show that most soil nutrients are sufficient to support the normal growth of C. cathayensis forests, but the comprehensive fertility needs to be improved. [Ch, 3 fig. 5 tab. 32 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 635-643.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210437
Abstract:
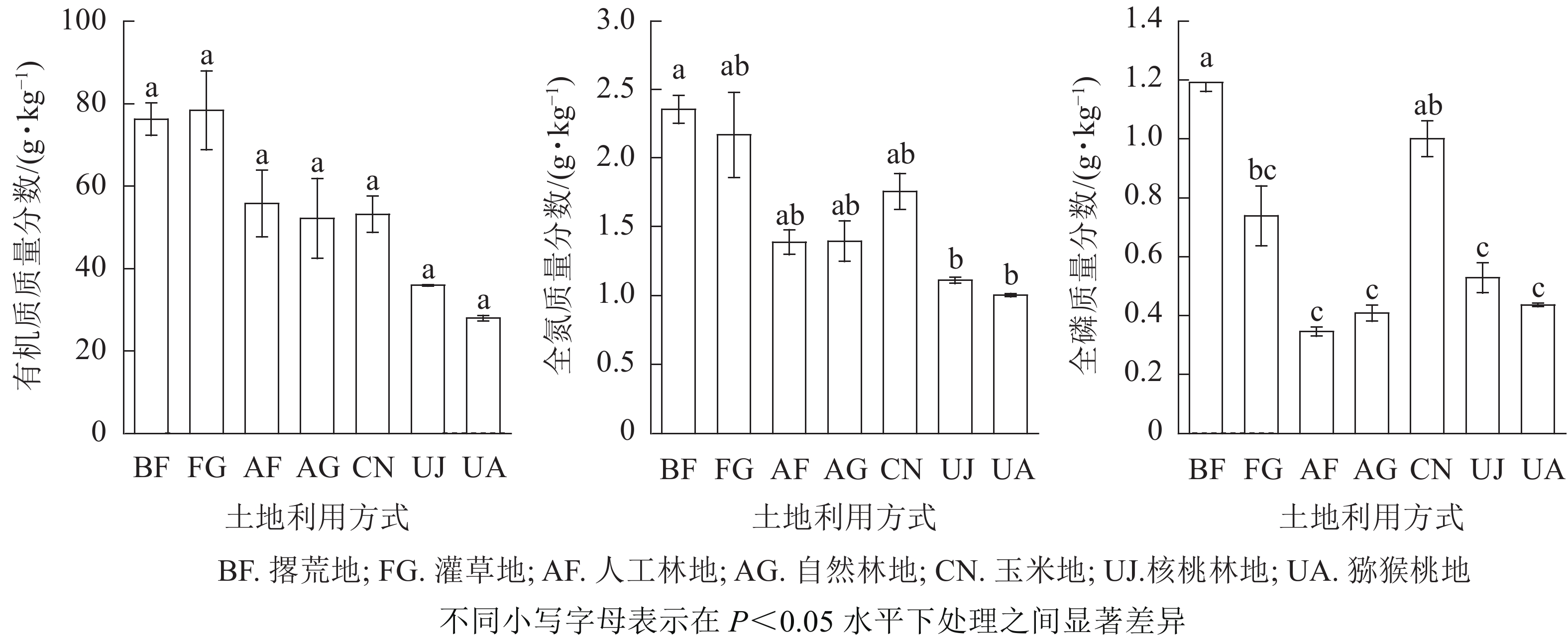
Objective This study aims to explore the characteristics of soil fertility and heavy metal pollution under different land use modes and the relationship between soil nutrients and heavy metals. Method Abandoned land, shrub land, artificial forest land, natural woodland, Zea mays field, Juglans regia woodland, and Actinidia chinensis land in Sanguang Rocky Desertification Comprehensive Control Demonstration Area in Xichou County of Yunnan Province were taken as the research objects, and the mass fractions of soil nutrients and heavy metals were measured and analyzed. Result The mass fractions of soil organic matter, total nitrogen and total phosphorus under natural restoration mode were significantly higher than those under other land use modes (P<0.05). The soil of shrub land (IFI=0.915) and abandoned land (IFI=0.913) was more fertile, while the soil of A. chinensis land (IFI=0.485) and J. regia land (IFI=0.501) was poor. Under different land use modes, the risk of heavy metal pollution was the lowest (IR=66.91) in shrub land, and the highest (IR=169.16) in A. chinensis land. Correlation analysis showed that the effect of soil nutrient content on heavy metal content was different with different land use modes, and was more significant in shrub and grass field, artificial forest and natural forest land (P<0.05), but insignificant in abandoned land and crop planting land (P>0.05). Conclusion Areas with strong natural attributes have high soil fertility and low risk of heavy metal pollution, indicating that human disturbance is an important factor affecting vegetation restoration in rocky desertification areas. Human disturbance should be appropriately reduced to better improve soil nutrients. [Ch, 3 fig. 8 tab. 29 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 644-652.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210438
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to investigate whether biochar prepared from different raw materials can alleviate the stress effect of long-term heavy metal pollution on soil microbial activity, so as to provide scientific basis for biochar remediation of contaminated soil. Method Three kinds of biochar prepared from bamboo leftover (BB), Carya cathayensis peels (PB) and Zea mays straw (CB) were added to the long-term lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) contaminated soil at a ratio of 3% (biochar soil mass ratio) respectively. The changes of soil nutrients, available mass fraction of heavy metals, soil microbial activity under short-term application of biochar were analyzed. Result The addition of three kinds of biochar did not affect the total amount of heavy metals in soil, but significantly (P<0.05) reduced the mass fraction of extractable Pb and Cd in soil calcium chloride (CaCl2). Compared with ck, BB, PB and CB significantly (P<0.05) decreased CaCl2-extractable Pb concentration by 69%, 84% and 72%, and CaCl2-extractable Cd by 26%, 63% and 36%, respectively. PB treatment was significantly (P<0.05) lower than BB and CB treatments. PB and CB significantly increased soil pH (0.79 and 0.51 pH units), soil organic carbon (37% and 74%) and total nitrogen (12% and 41%), respectively, but BB addition had no significant effect. BB, PB and CB significantly (P<0.05) increased the total amount of phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) in soil by 33%−56%, gram-positive bacteria by 30%−41%, gram-negative bacteria by 40%−66%, actinobacteria by 34%−52% and fungi by 33%−79%, respectively, but there was no significant difference among the three treatments (except that the total amount of phospholipid fatty acids in PB and CB treatment was significantly higher than that in BB treatment). The three biochar treatments significantly increased the activity of dehydrogenase (2−6 times), but did not affect the soil basal respiration, while PB treatment significantly (P< 0.05) decreased the bacterial stress index (13.9%) and increased the substrate induced respiration rate. Conclusion PB and CB can be used as a better modifier to decrease heavy metal availability and restore the number and activity of soil microorganisms. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 29 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 653-661.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210467
Abstract:
Objective 16 out of 26 key lakes in Wuhan Economic Development Zone (Hannan District) have water quality worse than Class Ⅳ standard. The purpose is to study the pollution characteristics of 6 heavy metals and phosphorus in the sediment, analyze and determine the appropriate dredging depth, which is of great significance to the prevention and control of similar small and micro water pollution and environmental dredging in this area. Method Taking Wujin Port as an example through 2 sets of experiments, the pollution characteristics of heavy metals and phosphorus in the sediment of Wujin Port were analyzed: (1) Stratified samples were taken from the sediment in the depths of 0−60 cm at 3 points, and the contents and the distribution pattern of 6 heavy metals( Cu, Hg, As, Pb, Cd and Ni ) were analyzed. Geo-accumulation index and potential ecological risk index method were used to analyze and evaluate the pollution characteristics and risks of heavy metals in the sediment. (2) Comprehensive pollution index method was used to analyze and evaluate the phosphorus content in the sediment of polluted layer (0−15 cm), transition layer (15−30 cm) and normal layer (30−50 cm) at 3 points, and the soluble active phosphorus (SRP) and total phosphorus (TP) in the sediment were analyzed through analytical experiments. Result With regard to the heavy metal pollution characteristics in the sediment, the contents of heavy metals decreased with the increase of depth, those in 40−50 cm tended to be stable, and those below 50 cm were close to the soil background value or the soil environmental quality Level Ⅱ standard. Geoaccumulation index (Igeo) showed that the degree of heavy metal pollution was mostly mild to moderate, and the potential ecological risk index value was less than 40, so the risk was low. The pollution characteristics of phosphorus in the sediment showed that TP content in polluted layer, transition layer and normal layer displayed an obvious decreasing law. The concentration of SRP and TP released from polluted layer and transition layer was higher than that from the original overlying water. SRP and TP released from the normal layer in both short term and long term were the lowest. Conclusion The pollution in the sediment of Wujin Port is mainly concentrated in polluted layer and transition layer. Cu and Pb are the main ecological risk factors, but they are at low ecological risk. In order to better remove endogenous pollution, it is determined that the optimal dredging depth of the small and micro water body in Wujin Port is 40 cm, based on the comprehensive analysis of the pollution characteristics of heavy metals and phosphorus in the sediment. [Ch, 3 fig. 6 tab. 14 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 662-670.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210335
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the optimal amount of sawdust during landfill sludge fermentation so as to improve the potential of sludge in landscaping. Method Three groups of fermentation materials, i.e. C/N20(T1), C/N25(T2), and C/N30(T3), were prepared by using sludge from a landfill in Hangzhou as the main raw material and sawdust as a conditioning agent. Through batch aerobic fermentation, the changes of physical and chemical indicators such as temperature, pH, conductivity, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and heavy metal forms were analyzed. Result The fermentation was a typical medium temperature fermentation (30~45 ℃). During the fermentation process, there was a significant difference in temperature between different sawdust additions (P<0.05), and the pH increased first and then decreased, which was significantly affected by sawdust amount while the conductivity was less affected. The ammonium nitrogen loss rates for T1, T2 and T3 after the fermentation were 30%, 47%, and 42%, respectively, and the nitrate nitrogen rates increased by 8.25, 6.27, and 3.85 times, indicating that the addition of sawdust had a great impact on nitrogen. The growth rates of total phosphorus for T1, T2 and T3 were 7.0%, 11.8%, and 10.8%, respectively, and the proportions of available phosphorus were 8%, 9%, and 9%, respectively. The growth rates of total potassium were 27%, 36%, and 44%, and the proportions of available potassium were 8%, 12%, and 17%, respectively, among which there was a significant difference in total potassium between T1 and T2 (P<0.05). The bioavailability of Cu for T1, T2 and T3 increased from 32%, 38%, and 40% to 72%, 74%, and 74%, and the bioavailability of Zn for T1, T2 and T3 increased from 84%, 85%, and 86% to 96%, 98%, and 97%, respectively. There were significant differences in bioavailable and oxidized Cu and Zn under different sawdust addition levels (P<0.05). The fermentation products of the three groups had no toxicity to plant growth (IG>80%), but the toxicity of T2 was significantly greater than that of T3 (P<0.05). Conclusion The pH, nitrogen, potassium, bioavailable Cu, stable Zn, and seed germination index in the fermentation process are significantly affected by the amount of sawdust (P<0.05). The indicators of the three treatments are all in line with the GB/T 23486−2009 limit standard for argillaceous alkaline soil for landscaping, of which T2 has the most reference value for sawdust control in fermentation process. [Ch, 6 fig. 4 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 671-678.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210377
Abstract:
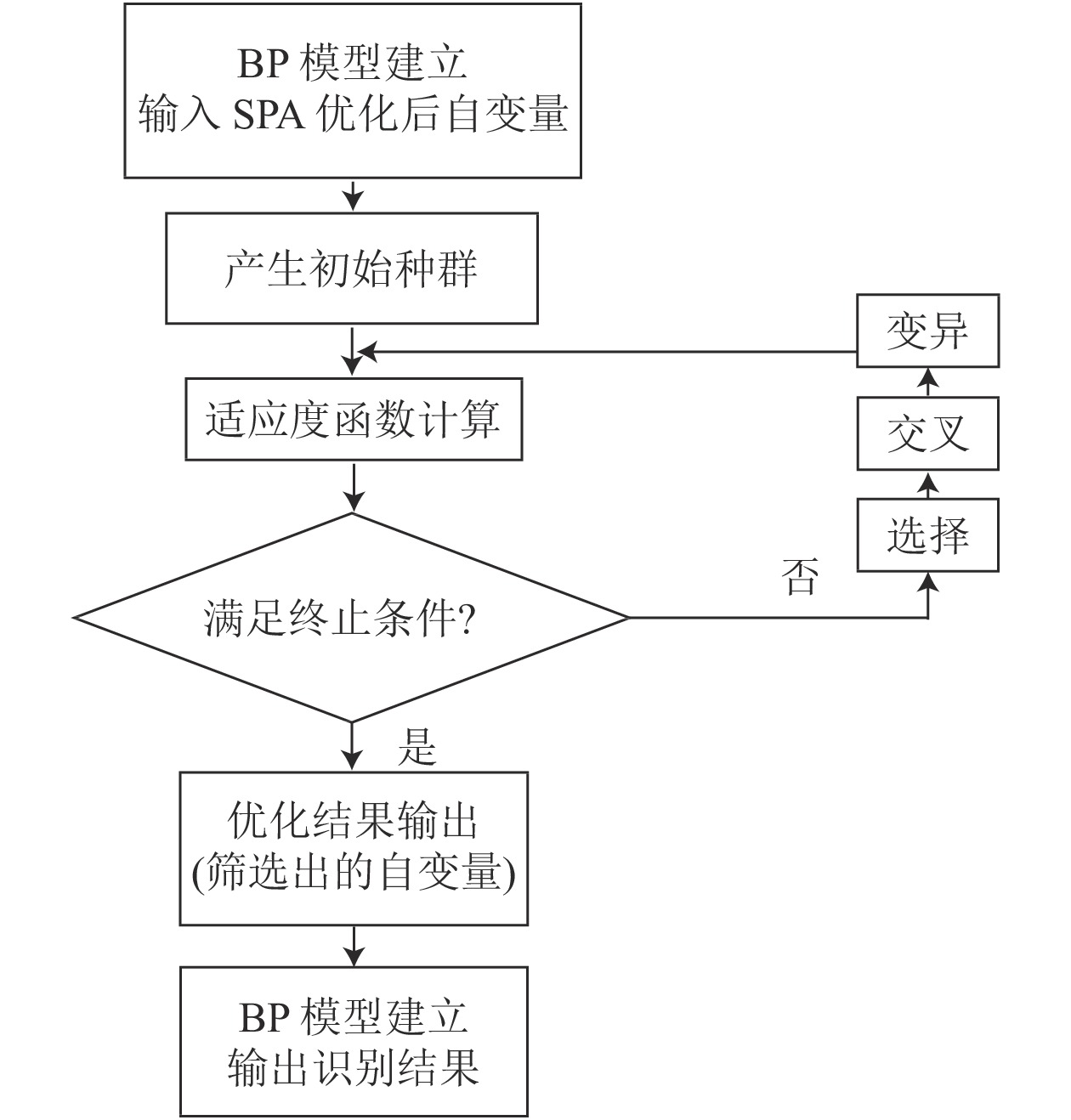
Objective The purpose of this study is to explore the effect of BP neural network identification under different pretreatment and feature extraction methods based on visible/near infrared spectroscopy technology, with 10 wood species as objects. Method The LabSpec 5000 spectrometer produced by American ASD company was used to collect the spectrograms of 10 species of wood, which were pretreated by moving average method, moving average method + multiplicative scattering correction(MSC), average method+standard normal variable transformation (SNV), Savitzky-Golay convolution smoothing algorithm (S-G filter), S-G filter+MSC and S-G filter+SNV. Meanwhile, principal component analysis(PCA), successive projections algorithm(SPA), and SPA combined with genetic algorithm(GA) were used for feature extraction respectively. The extracted features were combined with BP neural network for wood identification test. Result When SPA and GA were combined to extract spectral features, the moving average+SNV method had the best preprocessing effect. When absorption peak was used as the initial waveband (Winitial=1 445 nm) and the number of absorption peaks (Ntot=9) as the number of features, the identification rate was high, and the number of features mostly decreased to about 1/2 of the number of feature values extracted by SPA. The average identification speed of BP neural network significantly increased. The average identification rate of the 10 wood species was 98.0%, and the identification rate of 7 of them reached 100.0%. Conclusion Under the pretreatment of moving average method+SNV, the combined use of SPA and GA in spectral feature extraction can improve not only the accuracy of wood identification by BP neural network, but also the identification speed. [Ch, 3 fig. 6 tab. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 679-686.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210356
Abstract:
Objective This paper, with an investigation of the impact of COVID-19 on the ecotourism consumption behaviors of visitors to Mount Tianmu National Nature Reserve of Zhejiang and an analysis of their ecotourism product preference in the post-pandemic era, is aimed to provide reference for the development of tourism in nature reserves. Method SPSS 23.0 statistical software was employed to analyze the significant differences in visitors’ ecotourism behavior and their demand characteristics in the nature reserves before and after the epidemic, the significant differences in their stated preference and revealed preference of ecotourism products after the epidemic as well as the effect of visitors’ stated preference of eco-tourism products on their revealed preference. Result (1) There was extremely significant difference in visitors’ tourism frequency and travel time after the COVID-19 outbreak, the impact of which on their channels of information, transportation means and tourist expenses was extremely significant, yet there was no significant impact on visitors’ other ecotourism needs and consumption behaviors. (2) After the COVID-19 outbreak, demographic characteristics of visitors such as gender, age, educational level, occupation and income exerted a significant impact on their stated preferences of some ecotourism products while age, educational level and occupation exerted significant impact on their revealed preference of some ecotourism products of Tianmu Mountain Reserve. (3) Visitors’ revealed preferences are significantly positively correlated with their stated preferences for ecotourism products of the reserve with the stated preferences of biological landscape and natural education exerting more significant impact than those of geological landscape and water landscape. Conclusion A series of development countermeasures were put forward to promote the quality of ecotourism products: innovative products were created to drive new tourist needs while intelligent ecotourism products and services were put forward to enhance visitors’ post-tourism experience, especially in sharing. [Ch, 6 tab. 24 ref.]
2022, 39(3): 687-694.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210143
Abstract:
The research and application of control technology of Lyonetia clerkella at home and abroad in recent years were reviewed and summarized in this paper. Chemical control, as the main control measure, has been widely used in the control of L. clerkella, but excessive use of pesticides has led to the increase of insecticide resistance, environmental pollution and killing of natural enemies. Therefore, it is necessary to utilize other sustainable control measures to reduce the use of chemical pesticides. In this paper, the biological characteristics, ecology and control technology progress of L. clerkella were summarized, and the new research direction was prospected. The progress in agriculture, ecology, biology, physics and pesticide control, as well as the factors affecting the control effect were summarized, and the differences of control methods at home and abroad were compared. For research and promotion of prevention and control technology of L. clerkella, besides agricultural prevention and control, the research and application of biological and ecological prevention and control technology, as well as physical prevention and control equipment should be emphasized, in particular, the development of multiple-species mating disruptants for L. clerkella and other main pests to simultaneously control a variety of pests in orchards. At the same time, special LED trapping lamp for L. clerkella should be developed to reduce the side effects of chemical control, so as to protect biodiversity and ensure social, economic and ecological benefits. [Ch, 1 tab. 60 ref.]
The research and application of control technology of Lyonetia clerkella at home and abroad in recent years were reviewed and summarized in this paper. Chemical control, as the main control measure, has been widely used in the control of L. clerkella, but excessive use of pesticides has led to the increase of insecticide resistance, environmental pollution and killing of natural enemies. Therefore, it is necessary to utilize other sustainable control measures to reduce the use of chemical pesticides. In this paper, the biological characteristics, ecology and control technology progress of L. clerkella were summarized, and the new research direction was prospected. The progress in agriculture, ecology, biology, physics and pesticide control, as well as the factors affecting the control effect were summarized, and the differences of control methods at home and abroad were compared. For research and promotion of prevention and control technology of L. clerkella, besides agricultural prevention and control, the research and application of biological and ecological prevention and control technology, as well as physical prevention and control equipment should be emphasized, in particular, the development of multiple-species mating disruptants for L. clerkella and other main pests to simultaneously control a variety of pests in orchards. At the same time, special LED trapping lamp for L. clerkella should be developed to reduce the side effects of chemical control, so as to protect biodiversity and ensure social, economic and ecological benefits. [Ch, 1 tab. 60 ref.]