2022 Vol. 39, No. 4
2022, 39(4): 695-704.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220236
Abstract:
Objective This paper aims to understand the effect of nitrogen (N) input on soil phosphorus (P) fraction and its transformation mechanism in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) plantation, so as to provide a reference for achieving efficient use of soil phosphorus in moso bamboo plantation. Method Moso bamboo plantation were used as research subjects, four N addition gradients (0, 30, 60, 90 kg·hm−2·a−1) were set and the bioavailable P method was used to determine P fractions (CaCl2-P, Citrate-P, Enzyme-P and HCl-P) in the topsoil (0−20 cm) and subsoil (20−40 cm). The effect of N input on P fraction of moso bamboo plantation and its relationship with available P and soil physicochemical properties were explored. Result Compared to the control group, nitrogen addition significantly increased CaCl2-P content (28.5%−63.3%) in all soil layers and Enzyme-P content (16.3%−33.6%) in the subsoil, and had no significant effect on the HCl-P content in the subsoil. Low N treatment significantly increased the Citrate-P content (43.5%) in the topsoil and the medium to high N treatment significantly increased the HCl-P content in the topsoil (101.0%−155.2%). In both the control and N addition treatments, the different phosphorus fractions were significantly higher in the topsoil than in the subsoil. Each soil P fractions in the topsoil were significantly and positively correlated with available P (P<0.05). Enzyme-P in the subsoil was only significantly and positively correlated with available P (P<0.01). N addition accelerated the conversion of soil bioavailable P to available P by decreasing soil pH, increasing soil organic carbon, microbial biomass phosphorus, acid phosphatase activity. Conclusion The input of N increased the bioavailability of soil phosphorus in moso bamboo plantation, which could provide scientific reference for efficient management of moso bamboo plantation in the context of global change. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 43 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 705-716.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210595
Abstract:
Objective The continuous expansion of Phyllostachys edulisin recent years has severely threatened the species diversity and ecosystem stability of the forest. Therefore, the research on the renewal and management of Ph. edulis forest has attracted extensive attention. The purpose of this study is to analyze the dynamic changes of species composition, tree species characteristics and species diversity in the natural restoration process of the community through clear cutting of Ph. edulis stands in Mount Tianmu, so as to promote the protection and restoration of species diversity. Method Based on the location monitoring data from 2018 to 2020 in the natural restoration process of the community after clear cutting in Mount Tianmu, the restoration characteristics of plant community, such as composition of family, genus and species, changes of dominant species, the functional characteristic composition of tree species and species diversity were studied. Result (1) The species composition was rich and varied sharply: 45 families, 86 genera, and 131 species were found in the arbor layer, 65 families, 137 genera, and 224 species in the shrub layer, and 45 families, 99 genera, and 135 species in the herb layer. Compared with 2018, there was little change in the arbor layer in 2020, but the number of species in the shrub layer and herb layer decreased rapidly, by 54.1% and 65.5%, respectively. (2) The dominant species in tree layer were deciduous species, and the absolute value of the annual average population size change rate of most dominant species exceeded 10%. The dominant species in shrub layer were Theaceae and Rosaceae. The dominant species in the herb layer were Cyperaceae and Gramineae. (3) After clear cutting, community was dominated by deciduous tree species, and the proportion of species and plants in the community was about 80% and 90% respectively. The proportion of species of different growth types and light-tolerant species had little change, but the number of plants of neutral and negative species increased significantly, withgrowth rates of 88.1% and 56.2% respectively. (4) The species diversity of tree layer had no significant difference with time and showed a slight upward trend. Shannon index and Margalef richness of shrub layer decreased significantly, and Pielou evenness increased significantly (P<0.05). Shannon diversity, Simpson Index and Margalef richness of herb layer decreased significantly, but Pielou evenness had no significant difference (P<0.05). Conclusion In the natural restoration process of the community after clear cutting, the species composition is rich and the restoration effect of species diversity is obvious. Therefore, clear cutting of Ph. edulis stands is a feasible method to restore and protect biodiversity in National Nature Reserveof Mount Tianmu, and can also be used to improve the ecosystem stability of the spreading area of subtropical Ph. edulis stands. [Ch, 10 tab. 35 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 717-726.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210562
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the differences of biomass and understory vegetation diversity in different stands, and to screen suitable and precious native broad-leaved tree species for subtropical plantations. Method Seven broad-leaved tree species (Cinnamomum platyphyllum, C. longepaniculatum, C. japonicum, C. camphora, Alnus cremastogyne, Toona sinensis and T. ciliata) were selected as the research objects in the common garden experiment in Chongzhou Base of Sichuan Agricultural University. The impact of tree species on biomass and understory vegetation diversity was quantified by measuring the average tree height, average diameter at breast height, and understory vegetation species of each tree species. Result There were significant differences in total plant biomass among different tree species (P<0.05). C. platyphyllum had the highest biomass, followed by A. cremastogyne and T. ciliata, and the lowest was C. japonicum. There were significant differences in the biomass of various organs of tree species (P<0.05), and the order from large to small was trunk, root, branch, and leaf. In general, the biomass of each organ of C. platyphyllum was the highest and the biomass of each organ of C. japonicum was the lowest. There were significant differences in the proportion of organ biomass to whole plant biomass among tree species (P<0.05), but there was no consistent rule in the size ranking among tree species. There was no significant difference in whole plant, leaf, branch and trunk biomass among different functional groups. However, the root biomass, proportion of root biomass and root shoot ratio of evergreen tree species were significantly higher than those of deciduous tree species (P<0.05), while the proportion of branch and trunk biomass was the opposite. The diversity of understory vegetation in deciduous tree stand was significantly higher than that in evergreen tree stand (P<0.05), and the Simpson index of understory herbaceous in T. ciliata, A. cremastogyne and T. sinensis stands were significantly higher than that of C. japonicum, C. camphora, C. platyphyllum and C. longepaniculatum stands (P<0.05). The Shannon-Wiener index of understory herbaceous in T. ciliata was significantly higher than that of the other six stands (P<0.05). Conclusion The cultivation of deciduous tree species in this area may be beneficial to the material circulation and understory vegetation diversity conservation of the plantation. Compared with other native tree species, the selection of A. cremastogyne and T. ciliata as breeding species may be more conducive to sustainable management of subtropical plantations. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 37 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 727-733.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220171
Abstract:
Objective Tree trunk sampling is destructive and difficult to obtain in comparison with soil and litter sampling. Therefore, small-size sampling is often used to estimate its composition. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the uncertainty in estimating mass fraction and reserve of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus (C, N, P) in trunks of different tree species caused by small-size sampling. Method Based on the data sets of C, N, and P concentrations of five dominant tree species in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests, including Pinus massoniana, Cunninghamia lanceolata, Schima superba, Quercus glauca, and Phyllostachys edulis (sampling size n=18−32), Bootstrap method was used to compare the estimated differences between small-size samples (n=3−5) and full samples (n=18−32). By weighing the relationship between sampling quantity and variation, the recommended sampling quantity of corresponding index and the estimation error range of different sampling quantities are given. Result The variation of C concentration of P. massoniana was significantly higher than that of other tree species. A small sample size of n =3−5 caused an estimation error of about ±10%, but only ± 5% for other tree species. For P. massoniana, the estimation error was −4% to 5% when the sample size was increased to 10. Conclusion It is suggested to appropriately increase the sampling quantity (n=5−10) to reduce the estimation error when estimating and evaluating C, N and P reserves of P. massoniana forest. If a small sample size of n=3−5 is used, an estimation error range of ±10% should be taken into account. When estimating C, N and P concentration of other tree species, the estimation error is within the acceptable range when n =4−5. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 734-741.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210431
Abstract:
Objective This study, based on the time series data of moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS) in Zhejiang Province, is aimed to estimate the aboveground biomass (AGB) of bamboo forest in Zhejiang Province to provide reference for remote sensing monitoring of bamboo carbon sink. Method The time series data of MODIS leaf area index (LAI), enhanced vegetation index (EVI) and ratio vegetation index (RVI) were taken as variables before they were screened by random forest model, and then the AGB of bamboo forest in the study area was estimated employing support vector regression (SVR) model. Result Of all the variables screened by random forest model, 43 had the greatest impact on bamboo forest AGB, and the SVR model constructed by radial kernel function based on them has the strongest prediction ability with its training accuracy and test accuracy being 0.76 and 0.72 while the root mean squared error (RMSE) being 5.15 and 8.03 Mg·hm−2 respectively. The average aboveground biomass of bamboo forest in Zhejiang Province was 7.85 Mg·hm−2 whereas the total aboveground biomass was 3.31×107 Mg. There was an evident diversity in the aboveground biomass of bamboo forest among the cities across Zhejiang Province among which the average aboveground biomass of bamboo forest in Huzhou City, Hangzhou City, Jinhua City, Shaoxing City and Ningbo City was greater than the provincial average value, with that of Huzhou City being the largest (13.56 Mg·hm−2) while that of Zhoushan City being the smallest (5.72 Mg·hm−2). Conclusion The SVR Model coupled with MODIS LAI, EVI, RVI time series data could serve to realize the high-precision estimation of bamboo forest AGB in Zhejiang Province. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 31 ref.]
Plant diversity in various sections of Jinsha River dry-hot valley under different site environments
2022, 39(4): 742-749.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210572
Abstract:
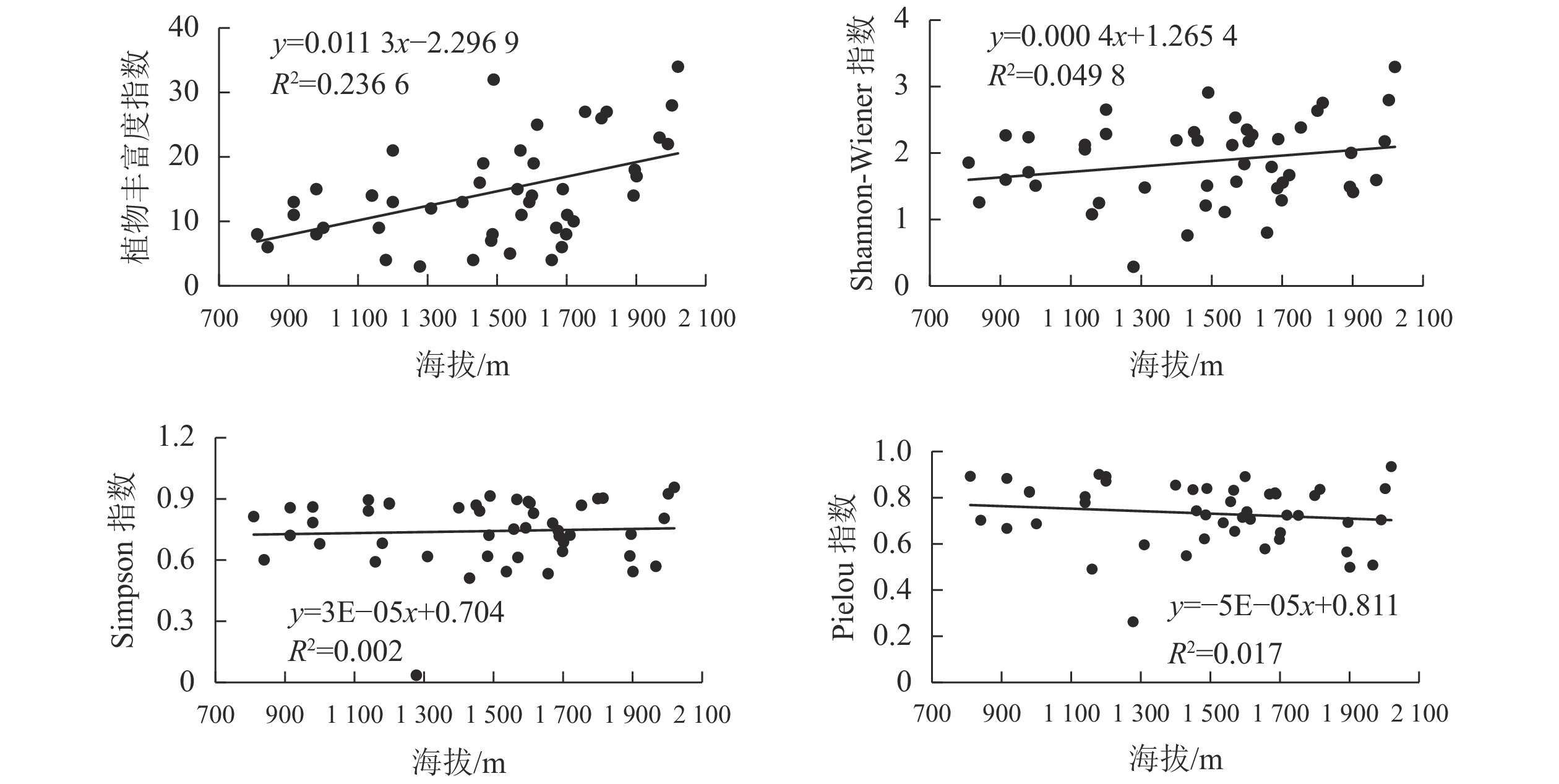
Objective This study is aimed at an investigation of the structural features and differences of the plant diversity in various sections of the dry-hot valley under different site environments so as to efficiently protect and restore the biological environment of Jinsha River dry-hot valley. Method With the employment of standard sample plot survey method, a survey was conducted of the plant species richness and diversity of 47 plots in the upper, middle and lower sections of the Jinsha River dry-hot valley. Result The plant species richness, diversity and uniformity of the Jinsha River dry-hot valley increased from the upper section to the lower one with the order of species richness being natural forest (20.56)>plantation (12.16)>sparse trees and shrubs (8.00) and no significant difference in diversity or uniformity between natural forest and plantation. The plant diversity tends to increase as the altitude increases with the plant diversity of shade slopes being significantly higher than that of sunny slopes (P<0.05). No significant differences have been found in diversity among the upper, middle and lower sections in the range of 800−1 400 m, while in the range of 1 400−2 000 m, the diversity in the middle section was lower than that in the lower section, but higher than the upper section. The plant diversity in the lower section was always higher than that in the middle section and the upper section of the same slope, and the Shannon-Wiener diversity index and Simpson diversity index in the lower section were significantly different from those of the upper section (P< 0.05). Conclusion There are significant differences in plant diversity in various sections of the Jinsha River dry-hot valley, with altitude and slope as main environmental influencing factors, and local plantation may increase the plant diversity. [Ch, 1 fig. 4 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 750-757.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210551
Abstract:
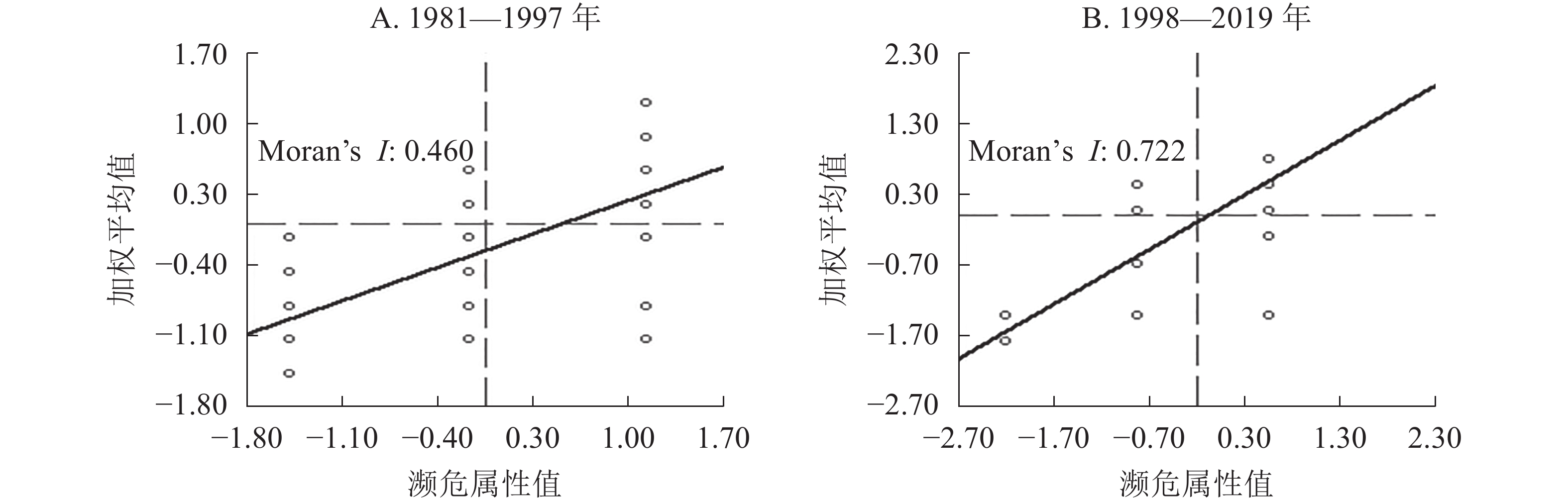
Objective This study, with an investigation of the scientific and standard identification of the migration of Orchidaceae, a protected and flagship group, in the Yangtze River Watershed, is aimed at an exploration of the spatial distribution of endangered orchids and the determination of key protected species and hot spots so as to serve the better research and protection of rare and endangered orchids. Method Taking the representative Orchidaceae plants in the Yangtze River Watershed from 1981 to 2019 as the research object, 130 species distribution points of 10 species including Neottianthe and Pleione were selected based on the field investigation and Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) database. Then, with the guidance of the theory of phytogeography and the conduct of a GIS spatial analysis, the spacial distribution of endangered orchids was investigated employing kernel density, Moran index and hot spot distribution. Result (1) The period between 1998 and 2019 witnessed the disappearance of Orchidaceae plants in Guangxi and Guizhou, a decrease in high-density areas of them in the Yangtze River Watershed, changes in the median density areas as well as their migration from central Sichuan to north Sichuan. (2) There was a significant positive correlation between the level of endangerment of Orchidaceae plants and their spatial location and the correlation between 1998 and 2019 was stronger than that of 1981−1997. (3) There was a shift of high risk areas: from 1981 to 1997, the high risk areas of Orchidaceae were mainly distributed in Guizhou and Hubei whereas from 1998 to 2019, they were mainly distributed in Hubei Province. Conclusion There have been changes in the distribution of Orchidaceae plants and a reduction in quantity which mainly attribute to global warming, infrastructure construction, illegal harvesting and excessive deforestation and in the future Hubei would become the focus of attention. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 31 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 758-764.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210307
Abstract:
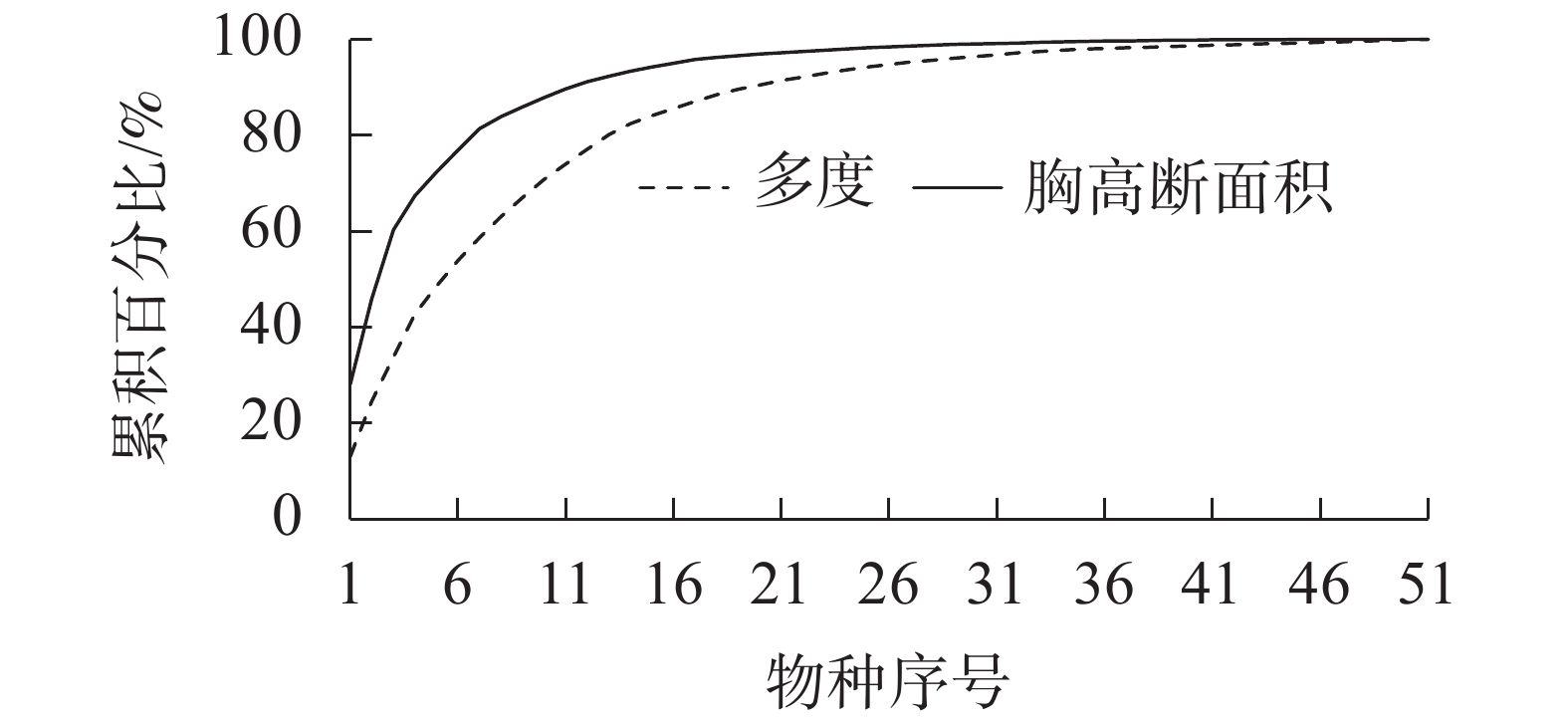
Objective With an analysis of the population and community characteristics of Carpinus tientaiensis, an extremely small population as well as its interactions with other trees species, this study is aimed to explore its endangerment mechanisms so as to propose workable protection strategies. Method Sampling method was first used to investigate the community characteristics in Shangshantou, Jingning She Nationality Autonomous County of Zhejiang Province, and indicators including the importance value, species abundance, distribution of the diameters at breast height (DBH) and inter-specific associations were analyzed. Result C. tientaiensis is one of the main dominant species in the community with the largest DBH 74.6 cm, ranking the third in importance value and accounting for 10.6% of the total tree species number, while 17.79% of the total basal area. Individuals with DBH of 1−4 cm and above 30 cm accounted for 90.00% and 66.11% of the total trees in the community respectively, while those with DBH of 4−20 cm only took up 7.91%. Strong inter-specific associations between C. tientaiensis and other species were found by means of association coefficient and percentage of co-occurrence whereas χ Conclusion Although C. tientaiensis, is one of the dominant species in the community, it has displayed population regeneration limitation with individuals with DBH at 4−20 cm found, thus faced with strong competition from other species. It was suggested that intermediate felling measures should be taken to reduce the competitive pressure of C. tientaiensis and necessary light environment should be provided for seedling settlement and tree growth. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 24 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 765-774.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210661
Abstract:
Objective This study, taking Gogestai Hanwula Nature Reserve as the research area, is aimed to investigate the distribution of macrofungi and its relationship with the local vegetation in five broad-leaved forests so as to provide plausible reference for the conservation of macrofungi in the future. Method First, macrofungi were collected from Betula platyphylla (Type Ⅰ), Quercus mongolica (Type Ⅱ), B. platyphylla-Tilia mongolica (Type Ⅲ), B. platyphylla-T. mongolica and B. platyphylla-Q. mongolica-Populus davidiana-B. dahurica (Type Ⅳ), and P. davidiana-Q. mongolica-B. dahurica (Type Ⅴ) in the nature reserve with the employment of random sampling and sample plot method. Then the collected specimens were identified from the perspectives of morphology and molecular chemistry before an analysis was conducted of the species distribution, diversity, community similarity and macrofungi-plant relationships. Result (1) There were 213 species of macrofungi in the reserve, which can be categorized into 2 phyla, 4 classes, 19 orders, 54 families, 119 genera. (2) There were a total of 8 dominant genera including Russula, Agaricus and Lepista. (3) Of the five vegetation types, Type Ⅳ wuranked the first in richness, diversity and evenness. (4) The diversity index and evenness index of tree layer, shrub layer and herb layer and the diversity index of tree layer and herb layer had significant influence on the indices of macrofungi. (5) The total vegetation coverage, herbage coverage, canopy closure and altitude were significantly correlated with the dominant genera of macrofungi. (6) The similarity between Type Ⅱ and Type Ⅳ was the highest (0.27) whereas the one between Type Ⅲ and Type Ⅳ and the one between Type Ⅰ and Type Ⅱ were the lowest (both being 0.14). (7) In terms of species clustering, with the distance coefficient being 25, they could be divided into two groups, while with the distance coefficient being 14, they could be divided into three clusters. Conclusion The diversity and similarity of plants affected the distribution of macrofungi to varying degrees, and the more similar the plant type was, the more similar the composition of macrofungi was. [Ch, 2 fig. 7 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 775-782.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210604
Abstract:
Objective The dump of open-pit mine in arid desert regionis easy to produces and (powder) dust and cause air pollution. The purpose of this study is to obtain the ratio of dominant dust retaining plants and species in the restoration community based on the simulation of Community Assembly by Trait Selection (CATS) model, and put forward the vegetation restoration strategy. Method A quadrat survey was conducted around the waste dump of Wuhai Xinxing Coal Mine in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Regionin August 2020 to determine the trait values at species and community levels, calculate the target values of functional traits, and substitute the dust retention function and root volume of plants into the model as two factors. Result The root volume of plant species was inversely proportional to the dust retention per unit leaf area. The root volume and soil water content was U-shaped. The simulation results showed that the highest relative abundance of each species was Salsola collina and Peganum harmala, with amedian of 0.41 and 0.32, respectively. Conclusion To plant S. collina and P. harmala in the dumping site with the relative abundance ratio of 6 to 4 is beneficial to dust detention, which can also explain some mechanical problems in vegetation restoration and provide reference for other studies. [Ch, 2 fig. 1 tab. 40 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 783-791.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210523
Abstract:
Objective The rocky desertification area in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River affects the ecological security of the whole basin. Under the comprehensive control of rocky desertification vigorously implemented by the state, the situation of rocky desertification has been significantly alleviated. But at present, there’s no evaluation method for eco-environmental quality in rocky desertification areas. The objective of this study is to carry out the real-time and quantitative evaluation of eco-environmental quality in rocky desertification areas. Method Based on Landsat 5, Landsat 7, and Landsat 8 satellite image data of Huize County, Yunnan Province in 2002, 2010, and 2018, the rocky desertification grades of the study area were divided, and the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) was used to quantitatively evaluate and analyze the eco-environmental quality of the study area. Result (1) From 2002 to 2018, the overall rocky desertification situation in Huize County was significantly improved, and the rocky desertification area decreased by 583.33 km2. (2) There was a significant positive correlation between rocky desertification and eco-environmental quality (r2=0.688−0.873), indicating that RSEI was effective in evaluating eco-environmental quality in rocky desertification areas. (3) In 2002, 2010, and 2018, the average RSEI value in the study area was 0.458, 0.490, and 0.488 respectively, and the overall eco-environmental quality was at a medium level. The area of eco-environmental quality optimization in 16 years accounted for 27.42% of the total county area, and the area of ecological deterioration accounted for 15.09%. (4) The contribution of dryness index to RSEI was increasing, and the first principal component load value changed from −0.029 to −0.622, which was an important factor restricting the optimization of eco-environmental quality of Huize County. Conclusion From 2002 to 2018, the rocky desertification situation in Huize County was significantly improved, and the eco-environmental quality was at a medium level. The dryness index was an important factor restricting the optimization of eco-environmental quality. The protection of rocky desertification areas should be emphasized in the future. [Ch, 8 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 792-799.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210547
Abstract:
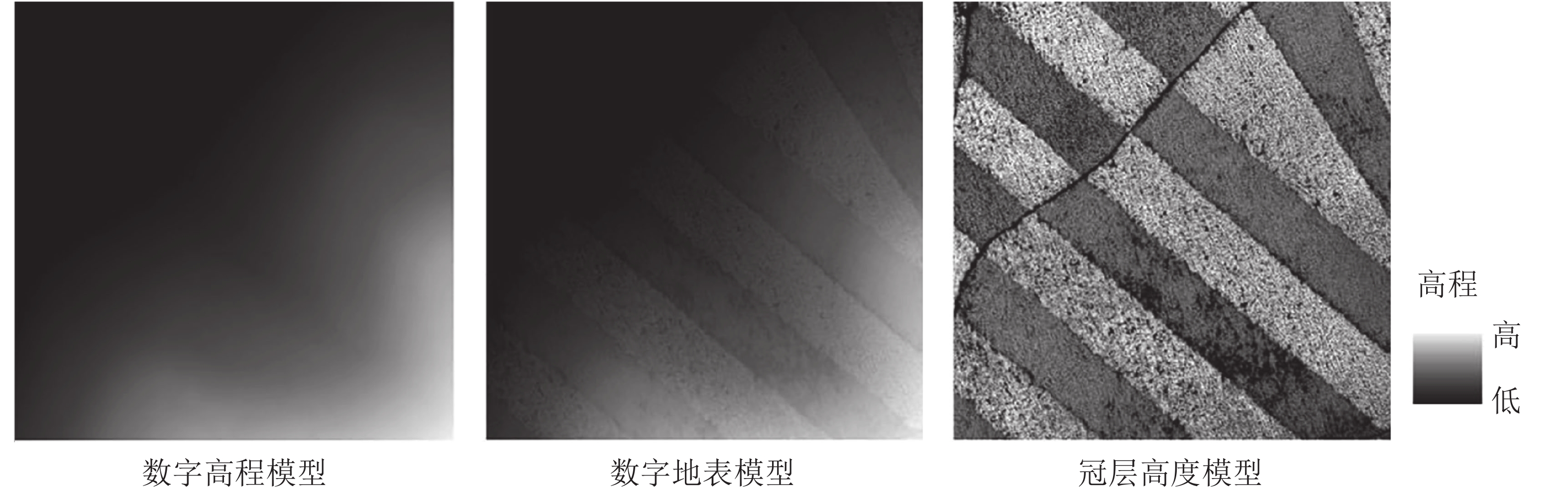
Objective Tree attributes are generally measured by obtaining the tree height and DBH using a method based on three-dimensional point cloud, which is featured with either low efficiency or high cost. To solve this problem, this study is aimed to propose a measuring method of multiple trees attributes based on Structure from Motion. Method Firstly, a smart phone was used to shoot a video of a scene with multiple trees before its key frame images were automatically extracted using the fixed-frame sampling and dHash algorithm; Secondly, such key frame images of the trees were processed on the basis of structure from motion (SfM) algorithm to obtain the original 3D point cloud of the scene; Thirdly, after the pre-procession and initial segmentation of the original 3D point cloud, the conditional European clustering algorithm is used to segment the 3D point cloud of multiple trees to extract the 3D point cloud of a single tree; Finally, the most value traversal method and ellipse fitting method were employed to deal with the tree 3D point cloud to realize the automatic measurement of tree height and DBH. Result Compared with real values, the mean relative errors of tree height and DBH measured using this method are 1.96% and 3.19%, the root mean square errors were 0.1333 m and 0.5337 cm whereas the correlation coefficients were 0.9879 and 0.9621 respectively. Conclusion This method, with high measurement accuracy of tree height and DBH, serves as a convenient and low-cost three-dimensional measurement method for multiple trees attributes. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 800-806.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210399
Abstract:
Objective With low identification accuracy of individual trees in Larix principis-rupprechtii forest with high canopy density employing high resolution images, this paper is aimed to confirm the strengths of airborne Laser Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) 3D point cloud data as an alternative with a workable method proposed. Method Based on the preprocessing of point cloud data, an improved Mean Shift with Gaussian kernel function (MSP) position recognition method on the basis of the spatial characteristics of airborne LiDAR point cloud was proposed. The comparison is made with other three commonly used methods: regional growing segmentation algorithm based on point cloud (RGP), local maximum method based on canopy height model (LMC) and multi-scale segmentation method based on CHM (MSC). Result Identification accuracy of the four methods is: MSP (89.30%)>LMC (85.60%)>RGP (77.50%)>MSC (70.00%), and MSC, the proposed method, displayed high average individual tree crown extraction accuracy (90.18%) and relatively low omission error and commission error rate: 8.7% and 8.0% respectively. Conclusion The proposed MSP has good applicability in high crown density L. principis-rupprechtii forest and provides a new way of extracting L. principis-rupprechtii forest structure parameters accurately on the basis of airborne LiDAR point clouds. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.]
Analysis and evaluation of growth and wood fiber characters of seven poplar clones in southern China
2022, 39(4): 807-813.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210481
Abstract:
Objective With an investigation of differences among wood fiber related traits and their correlation with growth traits among tested poplar (Populus) clones, this paper provides basic information and guidance for the targeted cultivation and selection as well as the utilization of high-quality poplar clones. Method Seven poplar clones, including XL-80, XL-86, XL-83, XL-58, XL-75, ZH-17 and I-69 (ck) with straight trunk and large growth were chosen before the principal component comprehensive score method was employed to evaluate the fiber traits of each clone with indexes including fiber length, fiber width, fiber length-width ratio, cellulose mass fraction and cellulose content per plant. Result The wood fiber length range of the seven poplar clones was 0.95−1.12 mm, all meeting the standard of intermediate fiber length 0.91−1.60 mm stipulated by the International Society of Wood Anatomy. The length to width ratio of fiber varied from 49.09 to 54.62, which is 63.67%−82.00% of the length to width ratio (30) required for paper making. The cellulose mass fraction varied from 53.06% to 59.66%, exceeding the basic requirement (40%) of paper making cellulose content. Fiber width was positively correlated with height, diameter at breast height (DBH) and biomass but not significantly (P> 0.05). Fiber length, fiber length-width ratio and cellulose mass fraction were negatively correlated with DBH, tree height and growth, respectively, but not significantly (P>0.05). Five clones with good traits were selected by principal component comprehensive score method, namely XL-80, XL-58, XL-86, ZH-17, and XL-83. Conclusion The five selected fiber clones have integrated the excellent characteristics of each character, which could maximize the utilization of poplar clones and provide more abundant genetic resources for poplar multi-objective breeding. [Ch, 6 tab. 24 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 814-820.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210517
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and discoloration law of knots in the Mytilaria laosensis plantation, so as to provide theoretical reference for the cultivation of clear wood. Method A total of 1 101 complete knots were obtained by knot analysis from 20 trees of 11-year old M. laosensis plantation in Experimental Center of Tropical Forestry in Pingxiang City of Guangxi. Result In the development age of the knots, the branches of M. laosensis mainly began to grow in the 1st and 2nd year, and the death peak came in the 2nd to 4th year (91.9%). These branches (87.2%) completely healed and formed knots in the 5th to 8th year after death, and the healing time of most of them (76.7%) was 3 to 6 years. More branches of M. laosensis died in the 2nd to 4th year, which was a critical period to control the formation of knots. In the vertical distribution, the number of knots increased first and then decreased sharply with the increase of tree height and they were mainly concentrated on the trunk with a height of 0−8.0 m. The discoloration length of knots was positively correlated with knot diameter and healing time (P<0.05), but negatively correlated with branch angle (P<0.05). Through stepwise regression, it was concluded that knot diameter, dead knot length, knot age and knot healing time were the key factors affecting knot discoloration length, and their correlation was very significant (P<0.01). Conclusion Pruning the trunk below 8.0 m for the first time 2−4 years after planting is beneficial to the cultivation of clear wood. Taking corresponding forest cultivation measures to reduce the base diameter of branches and the time required for knot healing will help ease the impact of knots on wood. [Ch, 7 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 821-829.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210651
Abstract:
Objective Floral organ development is an important factor affecting the ornamental value of flowers, and APETALA1 (AP1) genes regulate the formation of floral organs. This study aims to explore the important role of SvAP1 gene of Senecio vulgaris (Asteraceae) in floral organ formation, so as to reveal the regulatory mechanism of the complex inflorescence structure in Asteraceae. Method SvAP1 gene was cloned from S. vulgaris. The function of SvAP1 gene was predicted and analyzed by multiple sequence alignment, phylogenetic tree construction, qRT-PCR, overexpression vector construction, and histological staining observation. Result The open reading frame (ORF) of SvAP1 gene was 705 bp in length, and encoded 234 amino acids. Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis showed that SvAP1 gene belonged to AP1 subfamily of MADS-box gene, and the C-terminus had a conserved motif of paleoAP1. Tissue specific expression analysis of S. vulgaris showed that SvAP1 gene was expressed in both vegetative organs and inflorescences. Morphological observation and paraffin section analysis of transgenic Solanum nigrum showed that compared with wild S. nigrum, the pistil development of transgenic S. nigrum was abnormal, which was characterized by enlarged ovary and increased pistil-like tissue. Conclusion The overexpression of SvAP1 gene in S. nigrum affects the pistil development, which is different from the effect of over expression of class A gene in ABC model on floral organ development, that is, the stamens of transgenic S. nigrum have no obvious changes and the pistils aren’t transformed into sepal or leaf-like organs, which may be related to the complexity of the floral organ regulation mechanism and the inflorescence structure of S. vulgaris. In conclusion, SvAP1 gene may play an important role in floral organ formation as a characteristic gene of floral organ. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 35 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 830-837.
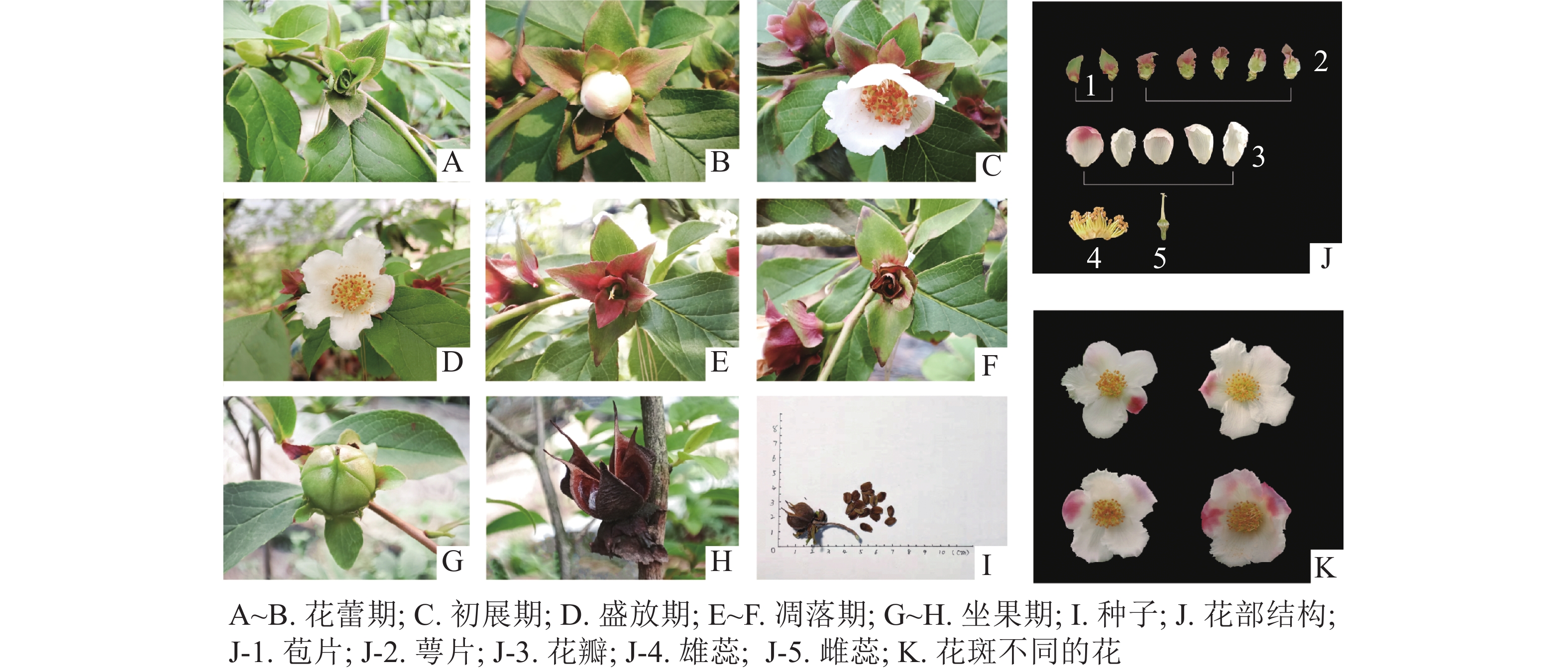
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210563
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to study the floral syndrome and breeding system of Stewartia rostrata, so as to provide a scientific basis for its population renewal, artificial reproduction and garden popularization and application. Method Taking 3-year-old S. rostrata as material, the characteristics of pollination biology and breeding system were observed and analyzed by observing the floral syndrome and insect visiting characteristics, measuring the pollen viability and stigma acceptability, and calculating the hybridization index (OCI) and pollen-ovule ratio (P/O). Result (1) The flowering period of the population was about 17 days from early May to mid and late May, and the single flowering period was about 2 days. (2) The pollen vitality reached the highest on the day of opening, and the single flower bloomed for 24−32 h , the corolla and stamens were easy to fall off, and the pollen was easy to lose vitality after falling off. (3) The stigma was receptive before flowering, lasting for 7 days. The strong pollen vitality and stigma receptivity had a meeting period of 1−2 days. (4) Stigma was higher than anther in bud stage, and anther was higher than stigma after flowering. Both before and after flowering, stamens and pistils had a certain spatial separation. (5) The OCl of S. rostrata was 4 and P/O was 2 108.0−195 525.0. The breeding system was mainly outcrossing and some self compatibility was required for pollination. (6) Bombus sp. was the main pollinator. Conclusion S. rostrata has short pollen life, single pollinating insect, and pollination is easily affected by cloudy and rainy weather, so the reproductive process is greatly limited. The floral syndromes such as centralized flowering mode, large amount of pollen, 5-lobed stigma and long receptive period are the basic manifestations of reproductive success. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 31 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 838-844.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210683
Abstract:
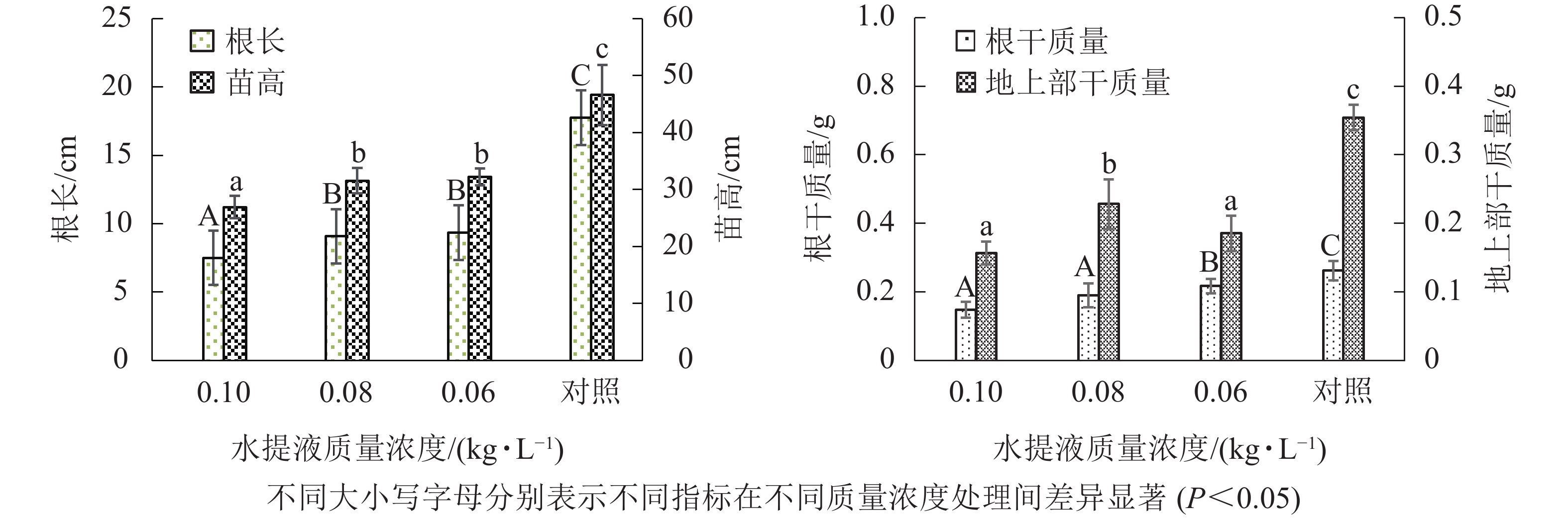
Objective The objective is to probe the relationship between toxicity of Brassica oleracea var. capitata and stubble obstacles, so as to provide a theoretical basis for establishing a reasonable crop rotation system. Method Taking the air-dried leaves of B. oleracea var. capitata as test materials, two crops species (Zea mays and Cucurbita pepo) with relatively high economic benefits and suitable for cultivation in cold and arid area of Shanxi were used as receptor. The effects of water extract from B. oleracea var. capitata leaves with four mass concentrations 0, 0.06, 0.08 and 0.10 kg·L−1 on the nutritional growth of the above two receptor crops were compared by indoor bioassay method, and the corresponding allelopathic effect index and comprehensive effect index were calculated. Result When the water extract concentration of B. oleracea var. capitata leaves was ≥0.06 kg·L−1, the growth of roots and shoots of potted Z. mays seedling could be significantly inhibited (P<0.05). The seedling height and root length of C. pepo were significantly reduced (P<0.05) only when the mass concentration of water extract of B. oleracea var. capitata leaves was 0.10 kg·L−1. At the same concentration, the allelopathic inhibition on root length of Z. mays was always greater than that on seedling height. For C. pepo, the allelopathic inhibition on root length was greater than that on seedling height when the water extract concentration of B. oleracea var. capitata leaves was ≥0.08 kg·L−1. When the mass concentration decreased to 0.06 kg·L−1, the allelopathic inhibition on root length was less than that on seedling height. According to the results of allelopathic comprehensive effect index, the allelopathic comprehensive inhibition on C. pepo was less than that on Z. mays. Conclusion C. pepo can be used in the rotation system of B. oleracea var. capitata to alleviate the obstacles caused by other toxicity. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 845-851.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210597
Abstract:
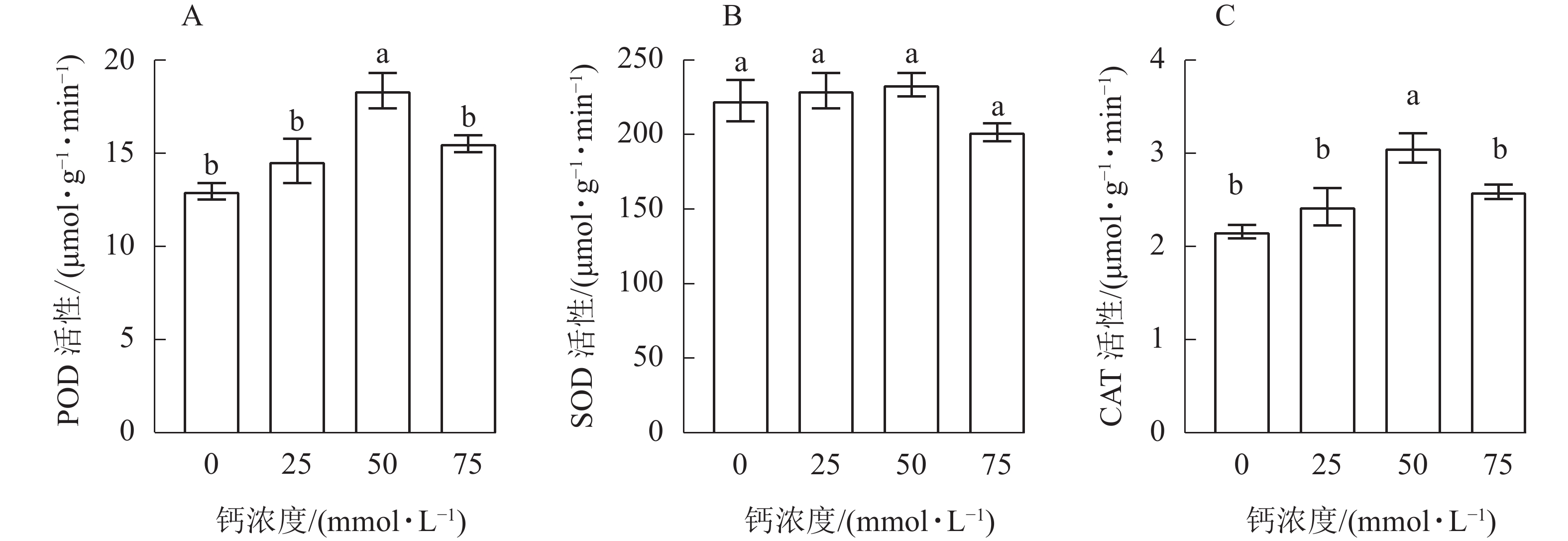
Objective This study, with an investigation of the effects of different calcium concentrations on leaf morphological indexes, chlorophyll content and enzyme activity of Fraxinus malacophylla seedlings, is aimed to better understand the growth and development of F. malacophylla seedlings under different calcium concentrations so as to further explore the environmental adaptability of F. malacophylla seedlings when treated with different calcium concentrations. Method With 1-year-old F. malacophylla seedlings selected as the materials, a research was conducted of the effects of 0 (ck), 25, 50, 75 mmol·L−1 calcium treatments on their leaf morphological indexes, chlorophyll content and enzyme activity. Result Different calcium concentrations had different effects on leaf morphological indexes, chlorophyll content and enzyme activity of F. malacophylla seedlings. When treated with different calcium concentrations, with the increase of calcium concentration, all indexes of leaf morphology and structure of F. malacophylla seedlings increased first and then decreased, except for specific leaf length and specific leaf area which increased, whereas leaf number, leaf biomass, specific leaf length, specific leaf area, chlorophyll content, catalase activity and peroxidase activity were significantly different from those in control (P<0.05). When the calcium concentration was more than 50 mmol·L−1, the treatment had no inhibitory effect on F. malacophylla seedlings, indicating that F. malacophylla seedlings responded favorably to medium-low calcium concentration. When the concentration of calcium was 75 mmol·L−1, it inhibited the growth and development of F. malacophylla seedlings, implying that too high a calcium concentration can inhibit the growth of F. malacophylla seedlings. When the calcium concentration was 50 mmol·L−1, the leaf morphological indexes, leaf related indexes, chlorophyll content and enzyme activity of F. malacophylla seedlings reached the maximum, and the growth and development of F. malacophylla seedlings were the best. Conclusion The optimal calcium concentration for the growth of F. malacophylla seedlings is 50 mmol·L−1 since too high a calcium concentration inhibits the growth, leaf chlorophyll mass fraction and leaf enzyme activity of F. malacophylla seedlings. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 852-859.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210525
Abstract:
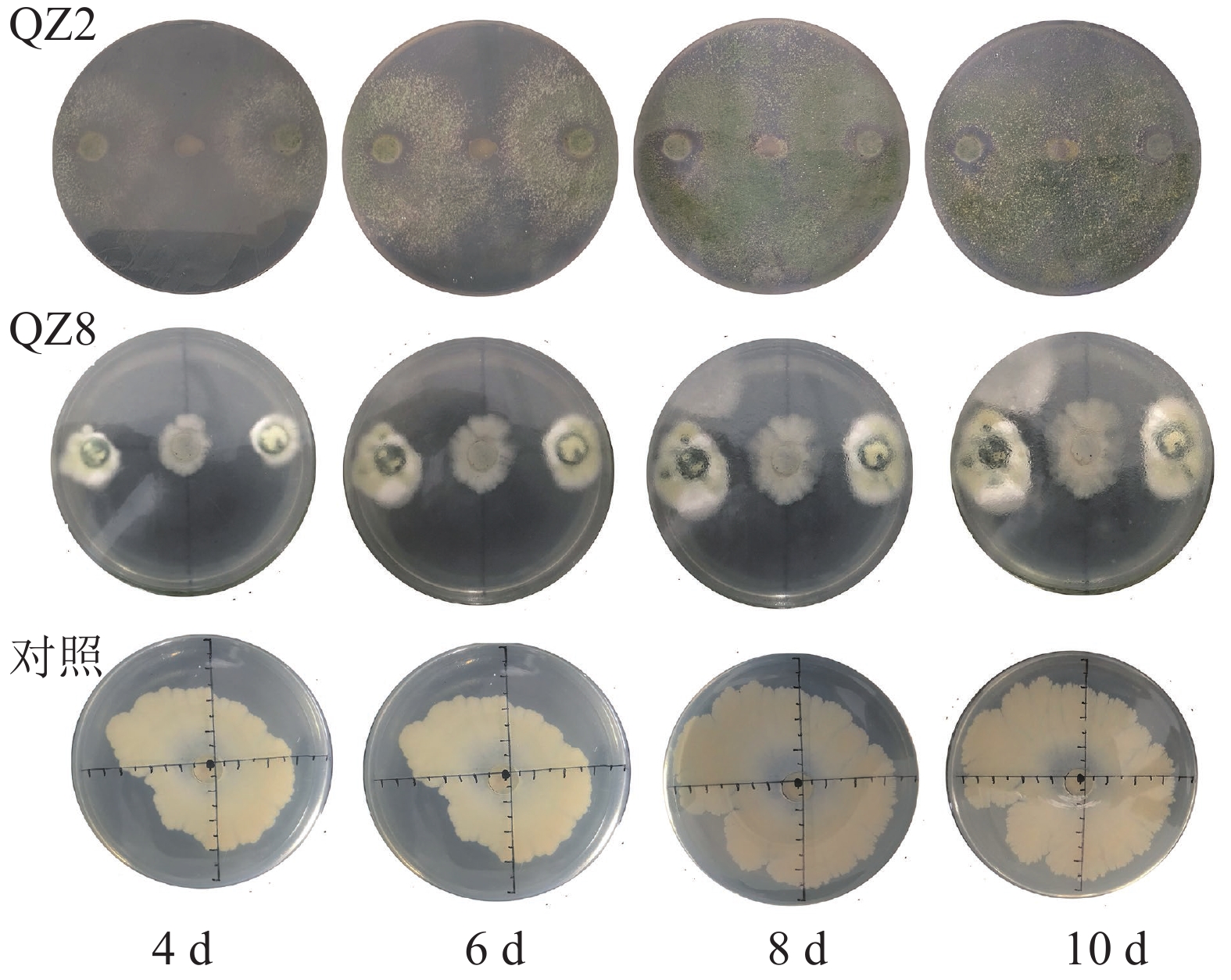
Objective This study aims to investigate the effect of two biocontrol strains Trichoderma asperellum QZ2 and Penicillium oxalicum QZ8 on Ralstonia solanacearum (bacterial blight for short) With the help of T. asperellum QZ2 and P. oxalicum QZ8 screened by our laboratory, the effect of two biocontrol strains on R. solanacearum was investigated. Hereinafter referred to as the biocontrol effect of bacterial blight. Method Using bacterial blight as the target, The the inhibition effect of biocontrol bacteria and their fermentation broth on the growth of bacterial bacterial blight was determined by plate culture method and growth curve method. Soil culture test and dilution coating method were used to determine the inhibitory effect of biocontrol bacteria on bacterial blight in soil. Result In plate confrontation culture experiment, test showed that QZ2 and QZ8 had significant inhibitory effects on bacterial blight (P<0.05), with inhibition rates of 80.9% and 45.9%, respectively. The plate culture with high temperature sterilized fermentation broth of QZ2 and QZ8 two biocontrol strains also showed significant inhibition effect on bacterial blight in plate culture (P<0.05), and the inhibition rates of QZ2 and QZ8 on bacterial blight reached were 33.3% and 34.8%, respectively. The fermentation broth on the growth of bacterial blight results showed that the D(600) value of the treatment was significantly lower than that of the control (P<0.05), and the inhibition effect of QZ2 was better than that of QZ8. Soil culture test results showed that the number of viable bacteria of R solanacearum in soil treated by with two biocontrol strains was significantly lower than that of ck (P<0.05). Conclusion The biocontrol strains of QZ2 and QZ8, which were extracted independently, had have significant inhibitory effects on bacterial blight wilt, and could can be positioned identified as potential biocontrol bacteria of tomato bacterial wilt. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 32 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 860-868.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210619
Abstract:
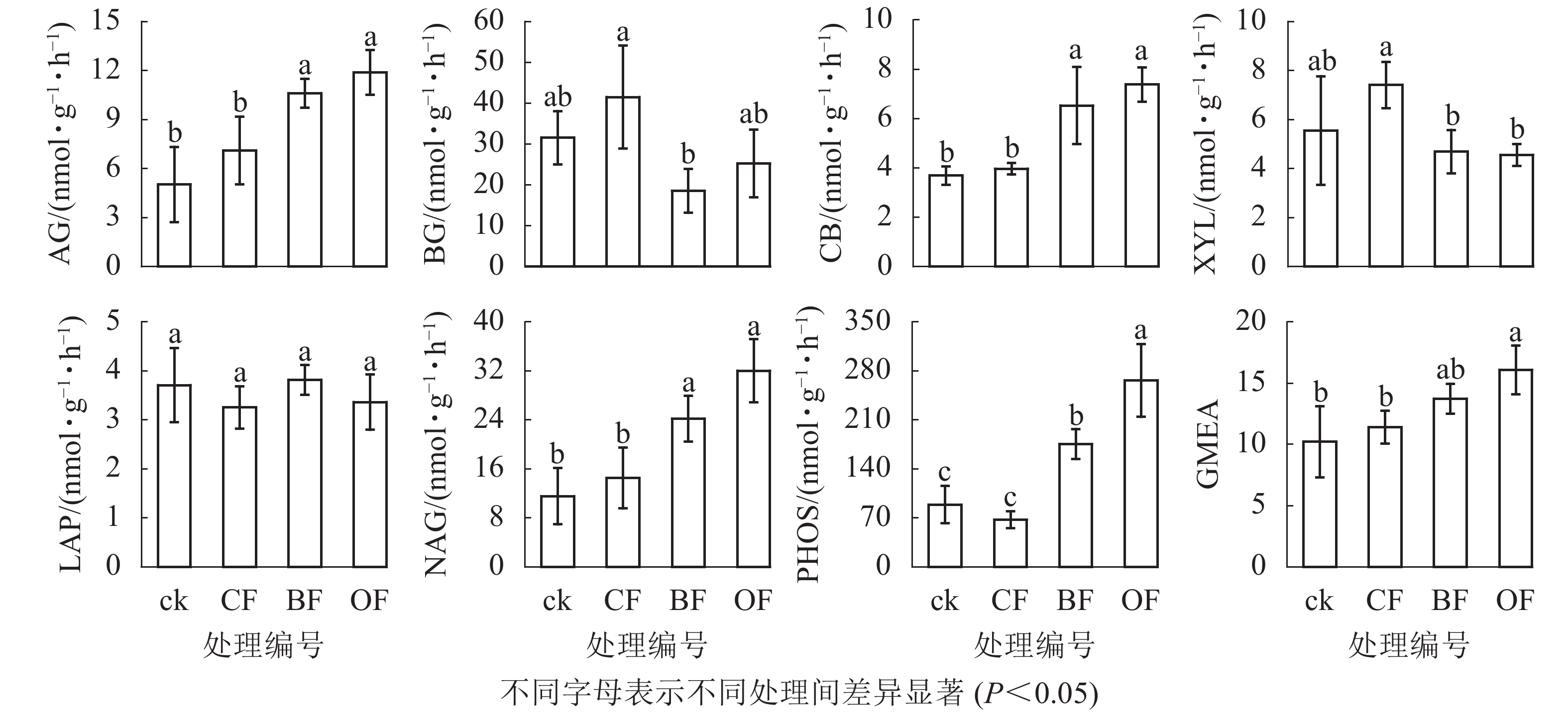
Objective The objective is to provide a scientific basis for improving rice paddy soil quality and for the application of new fertilizer, by investigating the effects of biochar-based fertilizer and organic fertilizer substituting chemical fertilizer partially on soil nutrients contents, microbial abundances and enzyme activities, and investigated the driving factors for soil enzyme activities. Method A field experiment was conducted in a typical rice paddy located in Hangjiahu Plain, which soil is Qingzini paddy soil. Four treatments, namely no fertilizer control (ck), conventional fertilizer (CF), biochar-based fertilizer (BF) and organic fertilizer substitution of 50% chemical fertilizer (OF), were laid out with the three fertilization treatments had consistent input of N, P and K amount. The field trail was initiated on June 2019 and soil sampling were collectted on November, 2019. Topsoils (0−20 cm) were sampled to investigate changes in soil carbon and nitrogen fractions, bacterial, fungal and archaeal abundances and enzyme activities involved in C, N and P cycling. Result Compared with CF, BF and OF treatments had no effects on soil pH, total C and N, available P and K and nitrate contents, but OF significantly increased soil ammonia and dissolved organic C contents. Compared with ck, OF treatment increased the content of soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) by 164%, bacterial 16S rRNA gene abundance by 35% and fungal 18S rRNA gene abundances by 98% and fungi/bacteria ratio by 50%, while BF and CF had no effects on them. The three fertilization treatments had no effects on the activities of β-glucosidase, β-xylosidase and Leucine aminopeptidase, whereas BF and OF treatments significantly increased the activities of α-glucosidase (AG) by 111%和136%, β-cellobiosidase (BG) by 77%和100%, β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) by 109%和177% and acid phosphatase (PHOS) by 97%和199%, respectively. Redundant analysis indicated that changes in soil enzyme activities were strongly dependent on the contents of soil ammonia, dissolved organic C and N, and fungal abundances. Conclusion The application of organic fertilizer and biochar-based fertilizer significantly increased soil enzyme activities involved in C, N and P cycling, with the OF treatment further increased soil microbial abundance, which was beneficial for soil nutrient cycling. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 33 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 869-875.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210647
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the influence of biological pretreatment on the properties of straw fiber and its composites prepared with urea formaldehyde resin, so as to provide theoretical basis for the preparation and development of straw based composites. Method Rice (Oryza sativa) straw was treated with microbial agent for aerobic fermentation. The changes of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin in rice straw under different treatment time were measured. The crystallinity and microscopic morphology of straw fiber without biological pretreatment (S0), straw fiber bio-pretreated for 5 days (S5) and 10 days (S10) were tested and compared. Straw fiber/urea formaldehyde resin composites (F0, F5, F10) were prepared. Then the surface properties and mechanical properties of straw based composites under different biological pretreatment time were compared. Result Substances such as silicon and wax on the surface of straw fiber were removed after biological pretreatment, but the longer biological pretreatment time (10 d) could destroy the structure of straw fiber itself. Compared with S0 and S10, S5 had the highest relative content of cellulose (37.99%) and best crystallinity (47.8%). In contrast, F5 had the best hydrophobicity, lowest surface energy, and highest impact toughness (7 665.64 J·m−2). F10 had the best flexural performance. The static flexural strength and flexural modulus were 27.73 and 20 354 MPa, respectively, which were 59.00% and 50.17% higher than the composites prepared by S0, respectively. Conclusion Biological pretreatment can improve the surface properties of straw fiber and the properties of straw fiber/urea formaldehyde resin composites. The straw fiber bio-pretreated for 5 days is better, and the properties of the composites are superior. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 876-883.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210672
Abstract:
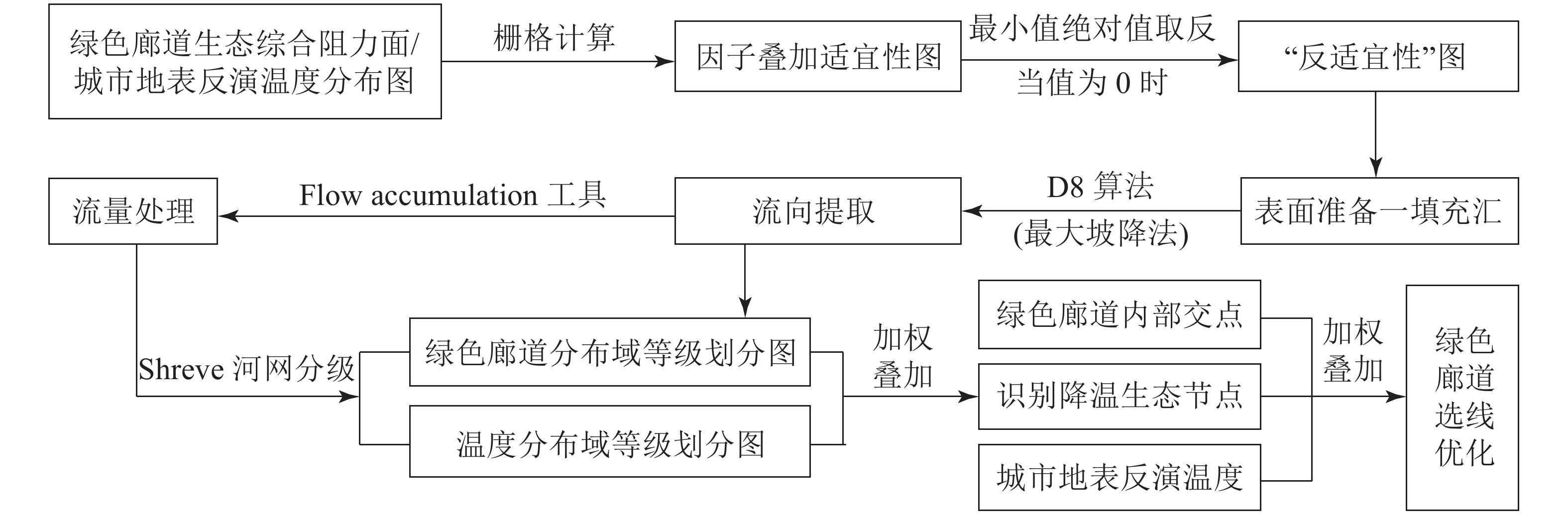
Objective The spatial distribution and structural characteristics of greenway have important ecological benefits for improving urban thermal environment. The route selection of greenway directly affects its attribute characteristics. Therefore, it is an effective ecological way and method to reduce the intensity of urban heat island by optimizing the landscape pattern of the greenway. Method Taking Fuzhou City, Fujian Province as the research object, aiming at alleviating the heat island effect, the landscape pattern of Fuzhou greenway was optimized based on the minimum cumulative model(MCR) and hydrological basin model. Result (1) Through the morphological spatial pattern analysis (MSPA), 30 ecological source patches were extracted to construct a comprehensive ecological resistance surface, and MCR model was used to generate 74 greenways with a total length of 918.11 km in Fuzhou, which, according to the importance evaluation of source patches, was divided into 4 levels: 9 pieces of 1st level totaling 132.88 km, 14 of 2nd level totaling 207.48 km, 14 of 3rd level totaling 153.57 km and 37 of 4th level totaling 424.18 km. (2) Through the hydrological basin model, 74 greenways were superimposed with the surface temperature of Fuzhou, and a total of 80 ecological ‘intersections’, 176 cooling ecological nodes and 35 cooling areas were extracted. Conclusion Accordingly, 14 new greenways are added in Fuzhou, including 8 road-based greenways and 6 waterfront greenways. The optimized greenways have a more comprehensive coverage of hot spots and a more obvious ecological regulation function for improving the urban heat island problem. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 25 ref.]
Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of forest villages in Zhejiang Province
2022, 39(4): 884-893.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210558
Abstract:
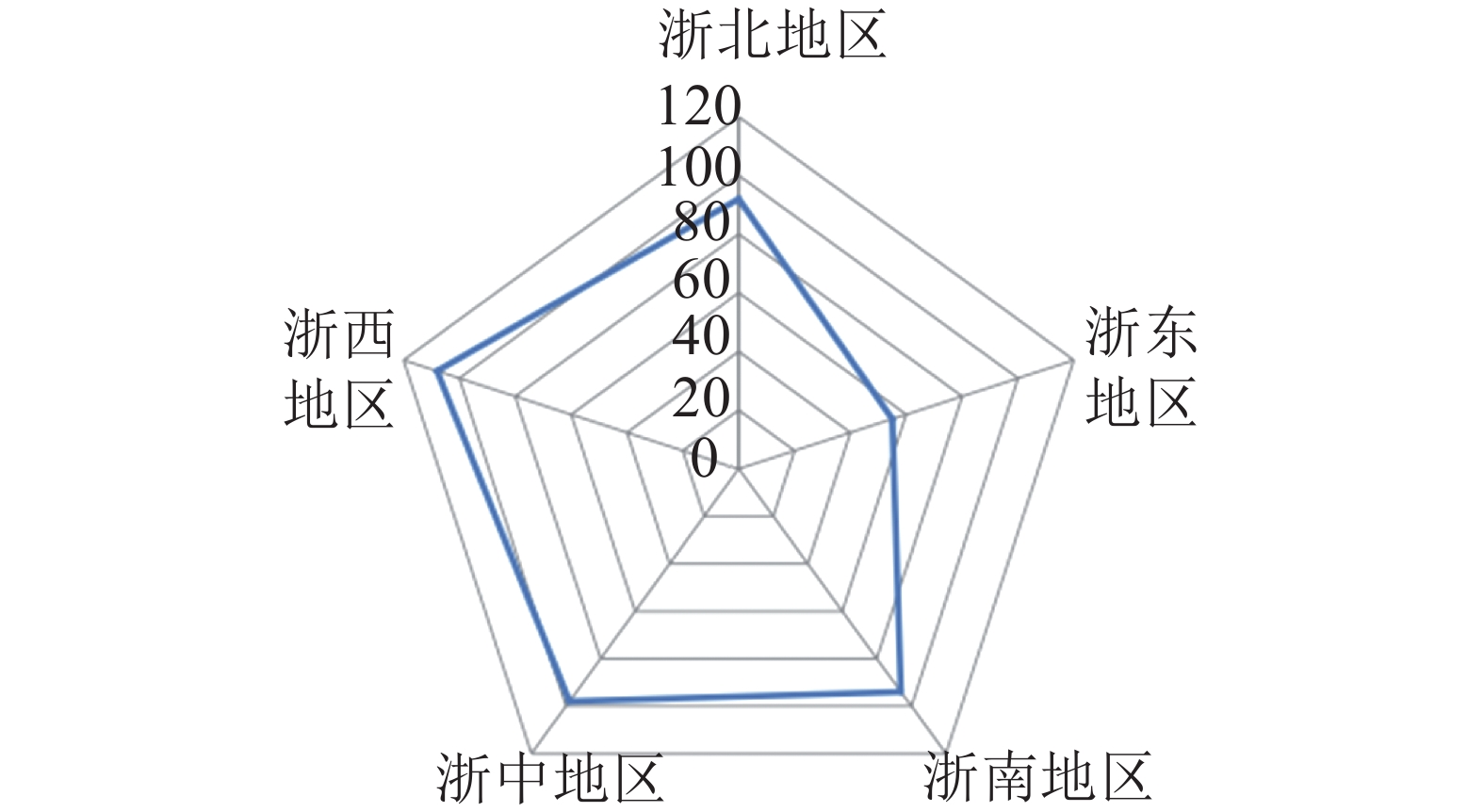
Objective This study is to explore the spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of forest villages, so as to optimize the spatial layout and understand the forming factors, so as to comprehensively promote the construction of ecological civilization and rural revitalization. Method The spatial distribution characteristics of 447 forest villages in Zhejiang Province were analyzed using spatial Gini coefficient, nuclear density analysis and spatial autocorrelation, and the natural and human factors affecting their spatial distribution were explored by Pearson correlation analysis and geographic detectors. Result (1) The overall spatial distribution of forest villages was in an agglomerated distribution state, with the characteristics of multi-center clusters of “small-scale aggregation and large-scale dispersion”. (2) The regional spatial distribution was uneven at the level of five major districts and cities, displaying a distribution pattern of “more in the west and less in the east”. (3) In terms of overall spatial density, a dual-core agglomeration area and a dual-core continuous area were formed. (4) In terms of spatial distribution correlation, it showed the spatial correlation characteristics of hot in the southwest and cold in the northeast. The change of sub-cold spot area was small, and the hot spot area changed from strip distribution to strip and sporadic distribution. (5) The spatial distribution of forest villages in Zhejiang Province was affected by topography, climate conditions, river systems, forest resources, cultural resources, socio-economic foundation and traffic accessibility. Conclusion Due to the comprehensive influence of nature and humanity, the spatial distribution of forest villages in Zhejiang Province is significantly different. Topography, climate and rivers nurture their ecological environment, while transportation, cultural resources and socio-economic foundations are related to basic conditions, resource advantages and economic support of their development. We should, according to resource advantages, basic conditions and local development policies, adhere to scientific planning, local conditions, coordinated layout and other measures so as to achieve global development, providing high-quality Zhejiang models for the construction of ecological civilization. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 32 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 894-901.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210644
Abstract:
Objective With an investigation of the characteristics of the the rural landscape, the study is aimed to research its construction model and propose a planning method for optimization. Method First, taking Pingyao Town of Hangzhou as an example, with the conduct of rural landscape character identification and comprehensive landscape evaluation and the collection of spatial data and survey information, spatial pictorial representation was carried out of the landscape features whereas the areas were divided using ArcGIS. Then a landscape function evaluation model related to landscape character was constructed to assess the rural landscape featured areas. Result (1) Pingyao Town enjoys four rural landscape featured areas, namely, the northern mountain forest ecological and cultural area, the central plain agricultural and cultural area, the eastern plain cultural area and the southern plain wetland ecological and cultural area; (2) Of the four rural landscape featured areas, the northern mountain forest ecological and cultural area (ecological landscape>living landscape>productive landscape) scored the highest, followed by the central plain agricultural and cultural area (productive landscape>living landscape>ecological landscape), the eastern plain area of historical sites (living landscape>productive landscape>ecological landscape) and the southern plain wetland ecological and cultural area (ecological landscape>productive landscape>living landscape). Conclusion In accordance with the regional and historical features of Pingyao Town in Hangzhou, four landscape construction models have been proposed: the mountain settlement landscape model, the plain agricultural landscape model, the historical site landscape model and the plain wetland landscape model, which provides a scientific basis for other and further rural landscape construction. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 25 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 902-912.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210652
Abstract:
The difficulty in the occurrence of adventitious roots which are produced by non-pericyclic tissues such as stems and leaves of plants, has been a bottleneck problem for the asexual reproduction and industrialized seedling raising of many woody species. However, there hasn’ t been a clear concept about the working mechanism of adventitious root occurrence, related mechanism is still unclear. At present, the research progress on the mainly includes the following three aspects: (1) With the formation time and position of root observed by paraffin section technology, it was found that the formation of root primordium is the key to adventitious roots and the process of adventitious root formation can be divided into three main periods according to the observation results of tissue morphology. (2) Adventitious root development is a complex physiological and biochemical process in which the dynamic changes of endogenous hormone content and rooting related enzyme activity play an important regulatory role with nutrients, phenols and polyamines as important influencing factors. (3) Efforts have been made to explore the key metabolic pathways in the process of adventitious root formation in some woody species, excavate the genes regulating adventitious root occurrence and identify the transcription factors and noncoding microRNAs involved in adventitious root occurrence. With a systematic summary of the research progress of histology, physiology and molecular regulation mechanism of adventitious root occurrence in woody species, this paper has provided an insight into future research direction in this field. [Ch, 1 tab. 80 ref.]
The difficulty in the occurrence of adventitious roots which are produced by non-pericyclic tissues such as stems and leaves of plants, has been a bottleneck problem for the asexual reproduction and industrialized seedling raising of many woody species. However, there hasn’ t been a clear concept about the working mechanism of adventitious root occurrence, related mechanism is still unclear. At present, the research progress on the mainly includes the following three aspects: (1) With the formation time and position of root observed by paraffin section technology, it was found that the formation of root primordium is the key to adventitious roots and the process of adventitious root formation can be divided into three main periods according to the observation results of tissue morphology. (2) Adventitious root development is a complex physiological and biochemical process in which the dynamic changes of endogenous hormone content and rooting related enzyme activity play an important regulatory role with nutrients, phenols and polyamines as important influencing factors. (3) Efforts have been made to explore the key metabolic pathways in the process of adventitious root formation in some woody species, excavate the genes regulating adventitious root occurrence and identify the transcription factors and noncoding microRNAs involved in adventitious root occurrence. With a systematic summary of the research progress of histology, physiology and molecular regulation mechanism of adventitious root occurrence in woody species, this paper has provided an insight into future research direction in this field. [Ch, 1 tab. 80 ref.]
2022, 39(4): 913-922.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210550
Abstract:
There is a long history of use of wild edible vegetables in China. They have abundant functional components, including mineral elements, amino acids, vitamins, polysaccharides, flavonoids and so on. It has important scientific significance and application value to study the basic components of wild edible vegetables for a comprehensive understanding of the nutrients and biological activities. We listed the main nutritional and functional components, summarized the current main research results in the biological activity, including: (1) the content of basic nutrients in wild edible vegetables; (2) the profiles of functional compounds in wild edible vegetables; (3) analysis of active components and efficacy of wild edible vegetables; (4) common methods and technologies to component analysis of wild edible vegetables. Wild edible vegetables are rich in basic nutrients and bioactive substances, including vitamins, phenols and terpenes, which have good activities in antibacterial, antioxidant, antitumor and anti-inflammatory. Future research should focus on functional components and biological activities, and serves as a reference for subsequent development and application. [Ch, 2 tab. 74 ref.]
There is a long history of use of wild edible vegetables in China. They have abundant functional components, including mineral elements, amino acids, vitamins, polysaccharides, flavonoids and so on. It has important scientific significance and application value to study the basic components of wild edible vegetables for a comprehensive understanding of the nutrients and biological activities. We listed the main nutritional and functional components, summarized the current main research results in the biological activity, including: (1) the content of basic nutrients in wild edible vegetables; (2) the profiles of functional compounds in wild edible vegetables; (3) analysis of active components and efficacy of wild edible vegetables; (4) common methods and technologies to component analysis of wild edible vegetables. Wild edible vegetables are rich in basic nutrients and bioactive substances, including vitamins, phenols and terpenes, which have good activities in antibacterial, antioxidant, antitumor and anti-inflammatory. Future research should focus on functional components and biological activities, and serves as a reference for subsequent development and application. [Ch, 2 tab. 74 ref.]