2024 Vol. 41, No. 6
column
2024, 41(6): 1105-1113.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240574
Abstract:
Objective The radial growth dynamics of xylem is considered one of the indicators of sensitivity to environmental change. Investigating the xylem formation is crucial to elucidate the relationship between trees growth and the climate. Method Microcore sampling and paraffin sections technology were used to monitor the intra-annual growth dynamics of xylem formation. We collected the microcores of Catalpa bungei, Cinnamomum camphora, Fraxinus chinensis and Koelreuteria paniculata every 7−10 d, and Gompertz model was used to fit the modeled value of cumulative radial growth. Result (1) Cambial activity began in early March and ended in mid-October. The duration of cambial activity was shortest for C. bungei [(189.0±14.6) d], and longest for C. camphora [(216.0±17.4) d]. (2) Four species finished the xylem differentiation in early November, and their maximum growth rate occurred in the middle of May. However, the widths of cumulative radial growth showed great variations among four ring-porous species which were from (5 807.0±2 192.9) μm for F. chinensis to (8 276.0±1 744.2) μm for C. bungei. (3) Additionally, temperature may be the main climatic factor influence the radial growth in study area. Both air temperature and surface ground temperature had a significantly positive correlation on the xylem growth increment for four ring-porous wood species (P<0.01). The positive correlation between precipitation and xylem growth was only in C. camphora (P<0.05). It may explained by the smallest diameter and area of vessel of C. camphora, which led to the trees were more sensitive to precipitation. Conclusion The radial growth of the four tree species in the local area is highly significantly positively correlated with air temperature. The response of the C. camphora plants to climatic factors is stronger than the other three ring-porous porous tree species. [Ch, 5 fig. 4 tab. 52 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1114-1123.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240253
Abstract:
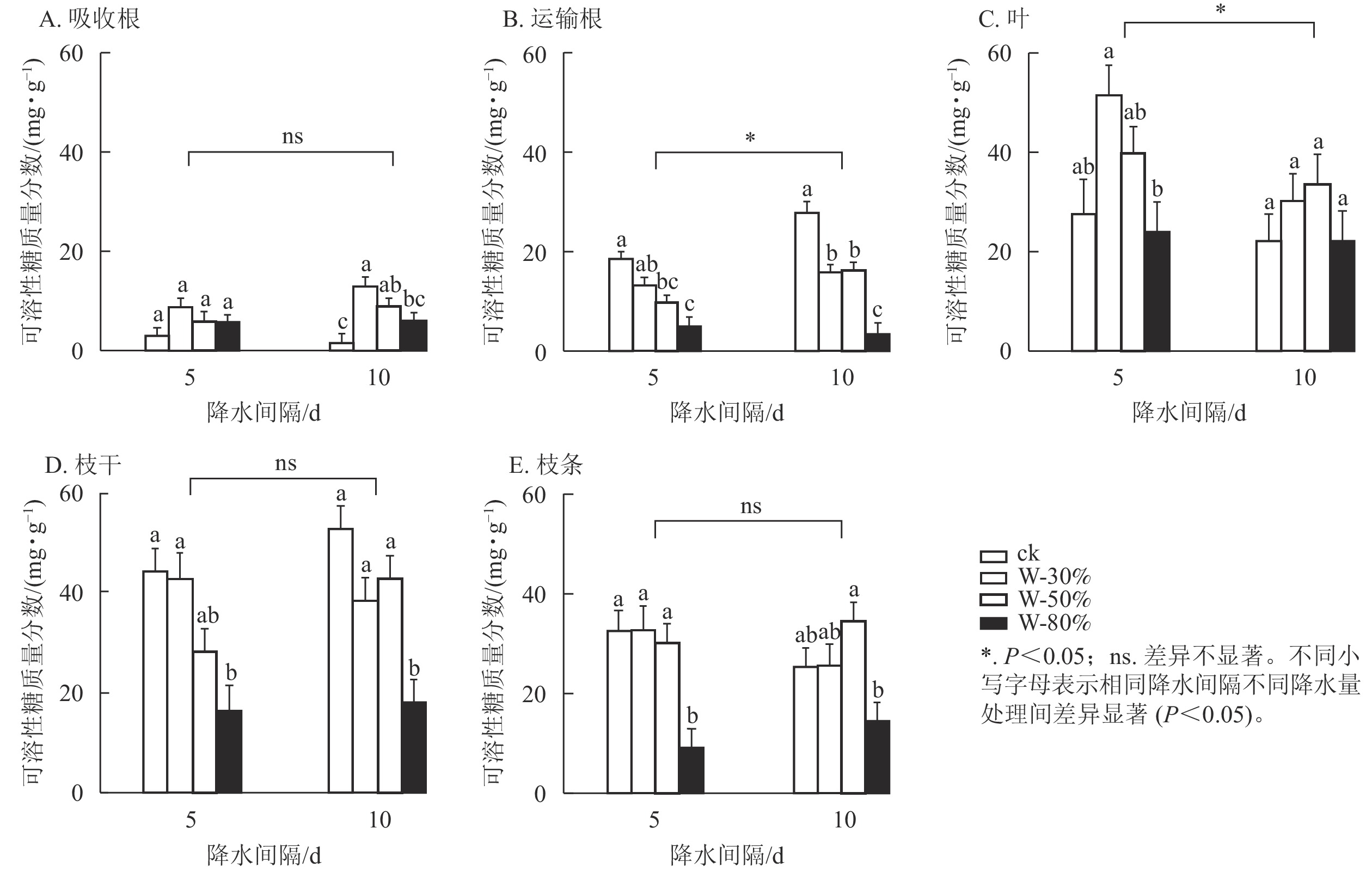
Objective Frequent droughts caused by global temperature rise and precipitation pattern change have significant impacts on forest ecosystems, so information of plant water utilization and adaptation during and after droughts is crucial. Method The seedlings of Cunninghamia lanceolata were used as test material. A two-factor controlled experiment with 4 precipitation amount and 2 precipitation intervals gradients was set to investigate the response of non-structural carbohydrates (NSC) and related fractions content in different organs that suffer different precipitation amount and intervals. Result With the decrease of precipitation, NSC content of the seedlings showed an overall trend of firstly increasing and then decreasing in absorbing roots, transport roots, branches and leaves, and continuous decreasing in branches and trunks. C. lanceolata seedlings increased NSC content in transport roots, absorbing roots, leaves and branches, while hydrolyzed and converted the starch from the absorbing roots to soluble sugars to regulate intracellular water potentials; soluble sugars content showed an overall trend of continuous decreasing in transport roots and trunks, and an overall trend of firstly increasing and then decreasing in absorbing roots, leaves and branches; starch content of all organs showed an overall trend of firstly increasing and then decreasing. When precipitation was too low, C. lanceolata seedlings would consume NSC to preferentially meet the survival needs of absorbing roots, which led to a significant decrease of NSC content in transport roots, branches and twigs (P<0.05). When precipitation intervals increased, NSC content in leaves and transport roots of the seedlings increased significantly (P<0.05); soluble sugar content of leaves decreased significantly (P<0.05), and soluble sugar content of transported roots increased significantly (P<0.05). Conclusion To improve the survival of C. lanceolata plantation forests under changes in precipitation patterns, soil water content should be maintained at more than 50% of the average monthly precipitation in the local multi-year dry season, and watering intervals can be extended in areas with higher precipitation. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 51 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1124-1133.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240180
Abstract:
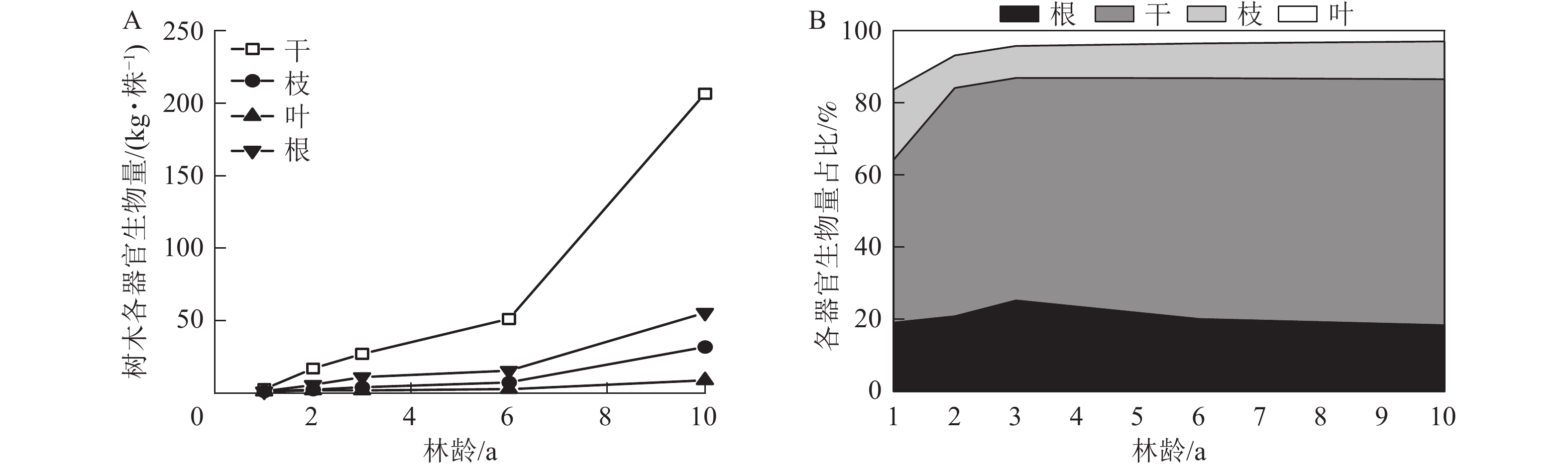
Objective This study aims to analyze the biomass distribution pattern of Eucalyptus plantations at different ages, so as to provide theoretical basis and data support for accurate assessment of carbon storage and carbon sink in China’s Eucalyptus industry. Method Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation in Leizhou Peninsula was taken as the research object. The whole-plant harvesting method was used to measure the biomass of various organs in 57 trees aged 1, 2, 3, 6 and 10. Using diameter at breast height (DBH), height (H), and diameter at breast height-tree height (DBH 2 H and DBHH) as independent variables, allometric growth models for organ biomass, aboveground biomass, and total biomass without and with age variables were established, respectively, to screen for the optimal model. Result The biomass of different parts of E. urophylla×E. grandis increased with age, but the proportion of each organ to the total biomass varied with age. The proportion of stem biomass increased with age, from 45.21% at 1 year old to 68.25% at 10 years old, whereas the proportion of branch and leaf biomass decreased with forest age, from 19.43% and 16.31% at 1 year old to 10.51% and 2.91% at 10 years old , respectively. The proportion of root biomass first increased from 19.05% at 1 year old to 25.21% at 3 years old, and then gradually decreased to 18.33% at 10 years old. The root to shoot ratio of E. urophylla×E. grandis ranged from 0.16 to 0.39. In selecting the optimal model for biomass of various organs, the model with DBH as the independent variable (without age variable) had better predictions for root biomass and total biomass than other models. The model with DBH 2 H plus age as independent variables had the best predictions for leaf biomass and aboveground biomass. The model with DBH, H, and age as independent variables had the best predictions for branch biomass. Regarding the prediction accuracy for stem biomass, there was no significant difference between the prediction models with DBHH and DBH 2 H plus age as independent variables, and both models could predict stem biomass well. Conclusion Forest age has significant impacts on the biomass allocation ratio of various organs in E. urophylla×E. grandis plantations. The prediction accuracy of branch, leaf, and aboveground biomass in E. urophylla×E. grandis plantations significantly improves if forest age is included in the allometric growth model. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 45 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1134-1141.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240148
Abstract:
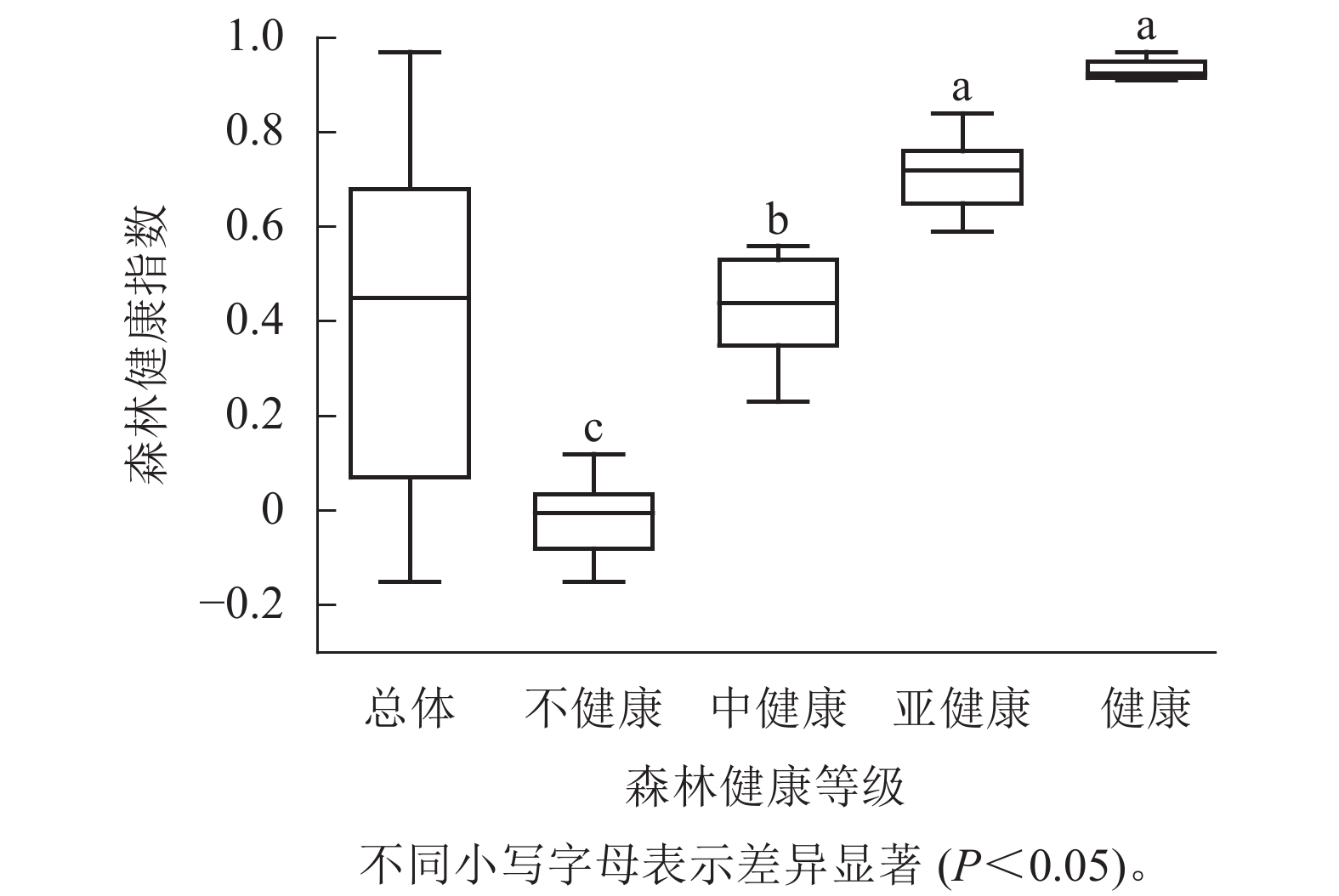
Objective The widespread degradation of Populous euphratica forests seriously threatens the ecological security of oases in arid zones. Therefore, mapping the health of P. euphratica forests is important for their sustainable management. Method The P. euphratica forests in Dali Yabuyi Oasis in the desert hinterland were taken as the object, and based on the field survey of 68 typical sample plots in the region, 17 indexes were selected from the aspects of forest productivity, forest community structure and habitat factors, and the health evaluation index system and health evaluation model applicable to the P. euphratica forests in the region were constructed by using the principal component analysis and the cluster analysis method, the forest health indexes were calculated, and the health of the P. euphratica forests in the region was comprehensively evaluated. Result (1) The overall forest health of oasis P. euphratica forests was poor, with 29.4% in an unhealthy state, 33.8% in a medium-healthy state, 30.9% in a sub-healthy state, and 5.9% in a healthy state. Groundwater burial depth, total nitrogen, depression, Simpson index, and Shannon-Wiener index were the main factors affecting forest health. (2) In the P. euphratica forests of Dali Yabuyi Oasis, the forest health index of deep groundwater burial depth is significantly lower than that of shallow and medium groundwater burial depth (P<0.05), and the forest health level is relatively low. Shallow groundwater burial depths have relatively high levels of forest health. Overall, the forest health indices of different groundwater depths: shallow groundwater depth (0.65)>medium groundwater depth (0.45)>deep groundwater depth (0). (3) Among the P. euphratica forests in different regions of the oasis, the forest health index of the P. euphratica forests in the north is significantly lower than that in the center and south, and the forest health level is relatively low. Forest health is relatively high in the south. Overall, the forest health index showed an increasing trend from the north, center to the south, and the forest health index in different regions: south (0.61)>center (0.58)>north (−0.01). Conclusion The overall health level of P. euphratica forests in the oasis is poor, the shallower the water table is, the higher the health index of P. euphratica forests is, and the health index shows a decreasing trend from the south, the center to the north in different regions. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 29 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1142-1149.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240170
Abstract:
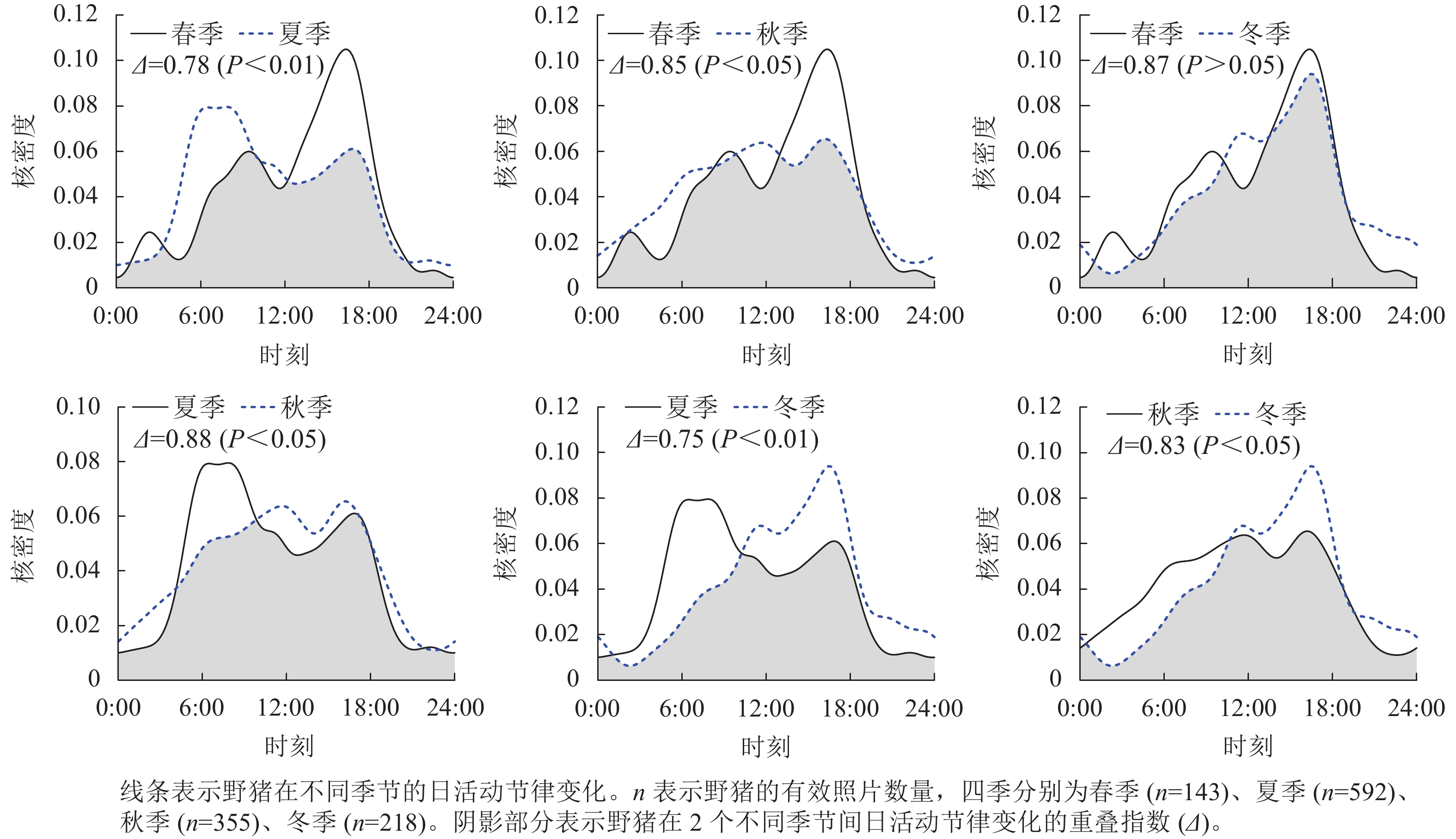
Objective By investigating the population density and activity rhythm of wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Longyou County of Zhejiang Province, this study is aimed to research the accurate countermeasures for wild boar prevention and control, and to provide exemplary monitoring and evaluation work from theory and practice to methodological application at the county level. Method Firstly, with the employment of infrared camera technology, a total of 1 308 independent and valid photographs were obtained from January 2021 to August 2023. Then the population density was estimated using a random encounter model, and the activity rhythm of the wild boar in the studied area was also investigated using the kernel density estimation method. Result The population density of wild boar in Longyou County ranged from 0.957 to 1.291 per square kilometer, with the total estimated population size of 417 to 563. The number of wild boar decreased from the southern mountainous areas, the northern mountainous areas to the central regions. In terms of habitat selection, the wild boar population preferred coniferous forests (relative abundance index IRA=38.45%), mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests (IRA=24.39%), and the elevation range of 1 100 to 1 300 m (IRA=57.25%). High population density was observed at 17:00 in all four seasons. The daily activity rhythms were similar in spring and winter, exhibiting an unimodal pattern. When come to summer, the daily activity rhythm was bimodal, with the main peaks occurring around sunrise and sunset. There was no significant fluctuation of daily activity rhythm in autumn and the population exhibited a highly significant seasonal migration along the altitudinal gradient (P<0.01). Conclusion The distribution of wild boars in Longyou County exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity, and their activity rhythms are deeply influenced by the factors of altitude and season. This study provides direct scientific evidence for the formulation of wild boar control policies in Longyou County and will serve as a reference for estimating population density as well as studying the activity rhythms of wild boar at the county level. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 29 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1150-1159.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240282
Abstract:
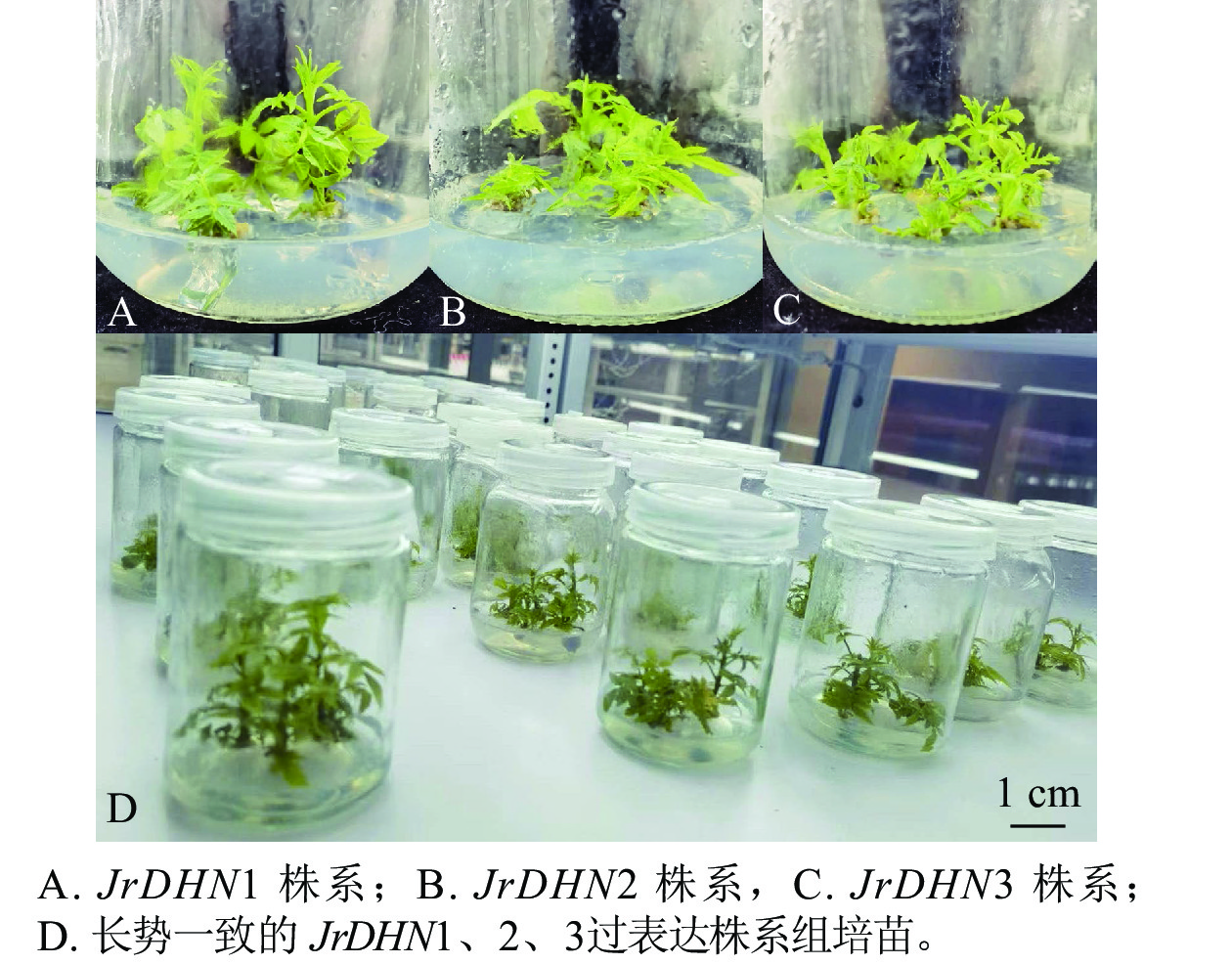
Objective This purpose was to investigate the physiological and molecular responses, as well as the molecular mechanisms, of Juglans hindsii×J. regia overexpressing line JrDHN during drought stress, to provide theoretical basis for breeding drought-resistant J. regia (walnut) cultivars. Method Healthy overexpressing walnut JrDHN were subjected to drought stress at different time points. The response of the overexpressing JrDHN line to drought stress was observed from various aspects including phenotype, antioxidant enzyme activity, and reactive oxygen species content. Quantitative PCR was conducted to analyze the expression levels of drought-related genes MYB, ADH, and CAM in plant tissues, exploring the molecular mechanism by which overexpression of JrDHN gene affects plant drought resistance. Result The results confirmed the overexpression of JrDHN gene in walnut seedlings, with expression levels in JrDHN1, 2, 3 being 2.55, 1.72, and 1.49 times higher than the WT respectively. Phenotypic traits of the overexpressing JrDHN line were superior to WT after 1−4 weeks of drought treatment, with significantly lower stomatal aperture in the overexpressing JrDHN line compared to WT after 2 weeks of drought treatment. The activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, POD, CAT) showed an initial increase followed by a decrease trend, reaching maximum values at 2 weeks, with SOD and POD activities in JrDHN1 significantly higher than WT (P<0.01), and CAT activity showing significant difference (P<0.05). Chlorophyll content reached its minimum after 4 weeks of drought treatment, with significantly higher levels in the overexpressing JrDHN line compared to WT. Levels of MDA, H2O2, and O2·− increased gradually with prolonged drought stress, reaching maximum values at 4 weeks, with significantly lower levels in JrDHN1 compared to WT. Expression levels of drought-related genes MYB, ADH, CAM showed an initial increase followed by a decrease trend, with significantly higher levels in the overexpressing JrDHN line compared to WT after 2 weeks. Conclusion The overexpressing JrDHN transgenic walnut seedlings exhibited superior phenotype, photosynthetic capacity, and antioxidant capacity under PEG-simulated drought stress compared to WT. Overexpression of JrDHN gene in walnut seedlings effectively enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzyme system, scavenged reactive oxygen species, reduced cell damage, thereby improving plant drought resistance. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 34 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1160-1169.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240195
Abstract:
Objective Transposable elements (TE), an essential component of eukaryotic genomes are prone to activation under stress when they account for over 63% of the Phyllostachys edulis genome. This study, with an analysis of the expression patterns of transcripts of uncertain coding potential (TUCP) from transposable elements under abiotic stress, is aimed to provide insights into the molecular mechanisms of TEs in stress resistance in Ph. edulis. Method First, bioinformatics techniques were employed to investigate the transcriptional characteristics and patterns of TE-TUCPs, and neighboring genes in Ph. edulis under 4 stress treatments: low temperature, high temperature, high salinity, and UV irradiation. Then the reliability of the differentially expressed TE-TUCPs, data derived from the transcriptome was validated using RT-qPCR. Result A total of 57 627 TE-TUCPs were identified from the transcripts of Ph. edulis under 4 stress treatments. These TE-TUCPs exhibited specific expression patterns in response to different abiotic stresses. High temperature, high salinity, and UV irradiation promoted differential expression of genes neighboring TE-TUCPs with transcriptional activity, whereas low temperature suppressed such differential expression. Conclusion TE-TUCPs were primarily derived from the Ty1/Copia and Ty3/Gypsy superfamilies. The expression potential of genes and that of nearby TE-TUCPs were mutually inhibitory and the transcription of TE-TUCPs was regulated by abiotic stress to modulate the expression of neighboring genes in response to stress. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 44 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1170-1179.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230603
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to study the genetic variation patterns of oil-related traits in complete diallel progenies of Camellia oleifera, and to provide basis for parental selection in cross breeding. Method 5×5 complete diallel hybridization (no self-crossbreeding) was carried out with 5 excellent clones of C. oleifera as parents, and the oil content, lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose contents of 20 hybrid families were determined. The correlation among traits was analyzed, the general combining ability of parents and the specific combining ability of hybrid combinations were determined, and the genetic variation rules among traits were analyzed. Result The kernel oil content of 20 families ranged from 252.30 to 537.08 mg·g−1, the lignin content was from 49.64 to 222.20 mg·g−1, the cellulose content was from 42.11 to 130.43 mg·g−1, and the hemicellulose content was from 3.72 to 111.96 mg·g−1. There were significant differences in oil, lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose contents of kernels among 20 families (P<0.01), and there were significant correlations (P<0.01) among the 4 traits. The correlation coefficient between oil content and lignin content was the highest (−0.47). Except for the specific combining ability of lignin content and reciprocal cross effect of oil content, the general combining ability, specific combining ability and reciprocal cross effect of the parents were significantly different (P<0.01) in the 4 traits. Oil and hemicellulose contents of kernels were jointly controlled by additive and dominant effect, and dominant variance was greater than additive variance. The lignin content was mainly affected by additive effect and the cellulose content was mainly controlled by dominant effect. The broad-sense heritability of the 4 traits ranged from 7.86% to 14.03%, and the narrow-sense heritability was 0 to 14.03%, all of which were strongly influenced by environmental factors. Conclusion Based on the analysis of combining ability, 2 excellent parents ‘Changlin No. 4’ and ‘Changlin No. 40’, as well as 2 excellent combinations ‘Changlin No. 40’× ‘Changlin No. 95’ and ‘Changlin No. 4’בChanglin No. 53’ are selected. [Ch, 8 tab. 35 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1180-1188.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240326
Abstract:
Objective Flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H) is a key enzyme in the synthesis of plant flavonoids. This study aims to investigate the relationship between RcF3H gene and flavonoid metabolism in Rubus chingii and analyze its biological function, so as to provide reference for further exploring the mechanism of RcF3H in the process of flavonoid accumulation in R. chingii. Method RcF3H gene was cloned from R. chingii, and bioinformatics analysis was performed, including physicochemical properties, homology comparison, phylogenetic tree and promoter cis-acting elements. At the same time, this study detected the expression level of RcF3H gene in different tissues, fruit growth period and exogenous methyl jasmonate (MeJA) induction. Result RcF3H gene, belonging to the 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase superfamily, was located on the first chromosome, and its fragment length was 1098 bp. RcF3H gene consisted of 1 exon and encoded 365 amino acids. RcF3H belonged to the hydrophilic stable protein. Subcellular localization predicted that the protein was located in the cytoplasm. The secondary and tertiary structure of RcF3H was mainly composed of α-helix and irregular curl, which had the closest genetic relationship with dicotyledons such as Rubus coreanus and Arabidopsis thaliana. Analysis of promoter cis-acting elements showed that the promoter region of RcF3H gene contained multiple cis-acting elements, and its function mainly focused on responding to hormones and stress. RcF3H gene was highly expressed in fruits, and had obvious tissue specificity. In addition, the expression of RcF3H gene in different ripening stages of fruits was consistent with the accumulation of flavonoids, and the expression increased under the treatment of 100 μmol·L−1 MeJA. These results suggested that RcF3H gene is the key enzyme to promoting flavonoid synthesis. Conclusion RcF3H gene responds to MeJA stimulation and may act as a positive regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in R. chingii, affecting flavonoid accumulation. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1189-1200.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240264
Abstract:
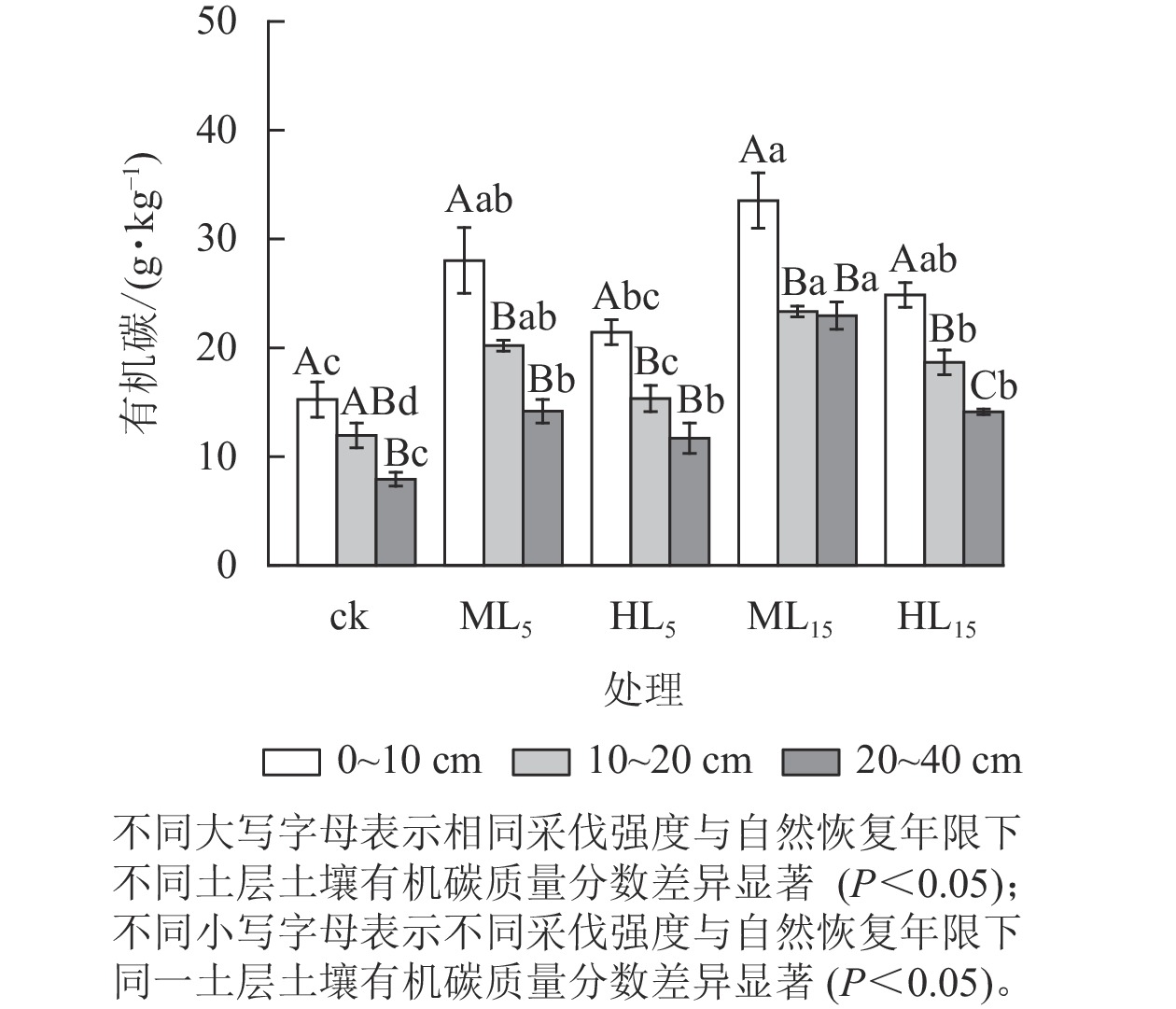
Objective The objective is to study the distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon (SOC) and its active components in Pinus massoniana forest affected by pine wilt disease, so as to reveal the influence mechanism of natural vegetation restoration after logging on soil carbon sink in P. massoniana secondary forest and provide scientific support for organic carbon pool management. Method From March to June 2023, in Yuhang District and Lin’an District of Hangzhou City, the undamaged P. massoniana forest was used as the control (ck), four vegetation restoration types were set up by using the space substitution time survey method: moderate logging restoration for 5 a (ML5), moderate logging restoration for 15 a (ML15), heavy logging restoration for 5 a (HL5) and heavy logging restoration for 15 a (HL15) to compare the variation characteristics of SOC, readily oxidizable carbon (ROC), particulate organic carbon (POC), microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC) in different soil layers ( 0−10, 10−20, 20−40 cm ) of P. massoniana secondary forest under natural recovery after different logging intensities, and their relationship with soil physicochemical properties was analyzed to explore their mechanisms. Result (1) The content of SOC and its active components in each soil layer ranking from high to low were SOC, ROC, POC, MBC and WSOC, and the content decreased accordingly with the deepening of soil layer. The highest SOC content was 33.53 g·kg−1 in 0−10 cm soil layer of ML15, and the lowest WSOC content was 136.55 mg·kg−1 in 20−40 cm soil layer of ck. (2) Under the same logging intensity, the content of active organic carbon in soil of P. massoniana secondary forest increased with the increase of natural recovery years, among which the content of POC in each soil layer changed the most, and the content of POC in each soil layer of 15 a was over 2.6 times higher than that in each soil layer of 5 a. (3) The content of active organic carbon component in 0−10 cm soil layer of ML15 was the highest, and was significantly higher than that in ck (P<0.05 ). (4) The results of correlation analysis showed that there were significant positive correlations among active organic carbon components in soil and between active organic carbon components and \begin{document}${\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $\end{document} Conclusion Moderate logging has a significant promoting effect on SOC and its active components in P. massoniana secondary forest. The longer the natural recovery time of vegetation, the more favorable it is to increase the content of soil active organic carbon components. Moderate logging of P. massoniana pure forests and their natural recovery can promote soil carbon pool accumulation. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 46 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1201-1210.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240185
Abstract:
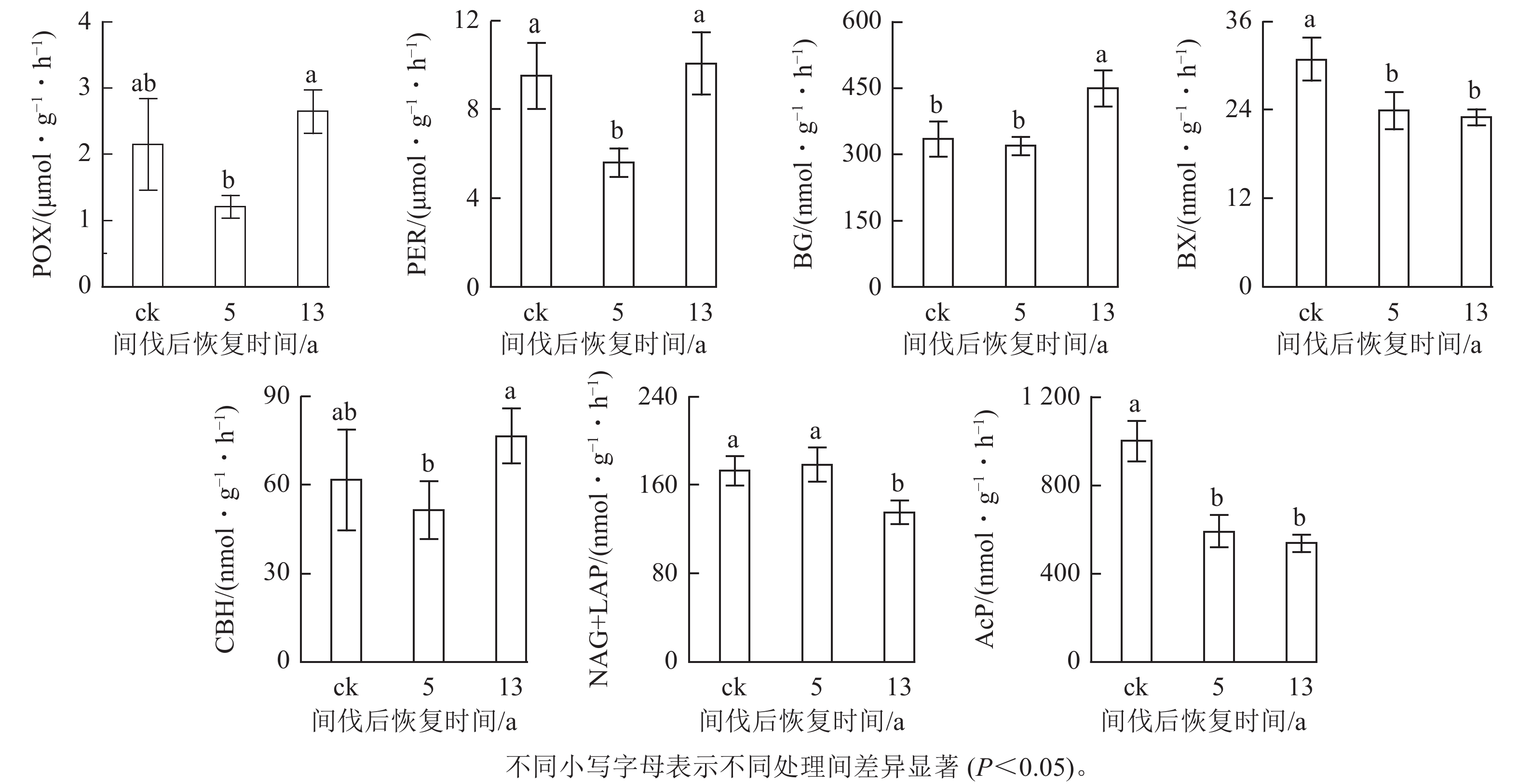
Objective This study, with an investigation of the effects of different recovery periods after thinning on soil physical-chemical proprieties and extracellular enzyme activities in oak-pine mixed forests in the Qinling Mountains, is aimed to better understand the nutrient cycling processes under thinning treatments, providing basis for developing programs of sustainable forest management and exploring better ecological restoration measures. Method First, pace-for-time substitution was employed to explore the effects of thinning restoration process (5 and 13 years, no thinning as the control) on soil physical-chemical proprieties and enzyme activity changes in the surface layer at 0−10 cm depth. Then the enzyme stoichiometric ratios and enzyme vectors were calculated for each treatment. Result (1) The total phosphorus, microbial biomass carbon, and microbial biomass nitrogen contents in the soil increased significantly, whereas the inorganic nitrogen content decreased in the 13-year restoration (P<0.05) and the soil pH increased in the 5-year and 13-year restorations; following a 13-year restoration, the soil organic carbon content progressively recovered to pre-thinning levels after declining dramatically in the 5-year restoration (P<0.05). (2) Thinning significantly increased the activity of β-glucosidase (BG), while decreasing the activities of β-xylosidase (BX), nitrogen acquiring enzyme (NAG+LAP), and acid phosphatase (AcP) (P<0.05); after the 13-year restoration, the activities of phenol oxidase (POX) and peroxidase (PER) showed a decreasing tendency during the initial stage of thinning (5 years treatment) and then reverted to pre-thinning values. (3) In the 13-year restoration, thinning significantly increased the soil enzyme carbon-nitrogen ratio (EC/N), soil enzyme carbon-phosphorus ratio (EC/P) and vector length value (P<0.05) whereas the EC/P and soil enzyme nitrogen-phosphorus ratio (EN/P) increased significantly and the vector angle value decreased in the 5-year restoration (P<0.05). Conclusion Soil nutrients, organic carbon, and oxidase activities showed a recovery trend with the thinning recovery stage with the soil pH being a key factor affecting soil enzyme activity and the change of enzyme vectors. Thinning decreases the phosphorus limitations of soil microorganisms during the initial stage of recovery, but it has little effect on the phosphorus and carbon limitation in the later stage of recovery. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 41 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1211-1221.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240571
Abstract:
Objective This study is in order to explore the effects of stand density on biomass and soil physicochemical properties in Pinus tabuliformis forests, for high-quality development and performance of the ecological service function. Method A 30-year-old P. tabuliformis forest in Caijiachuan watershed, Jixian County, Shanxi Province, was used as the research object, and the standard wood method was used to measure the biomass of individual plants and the overall biomass of the sample plots under the conditions of different densities, and the soil physicochemical properties were determined, so as to analyze the effects of stand density on the biomass of P. tabuliformis forest and soil physicochemical properties, and to determine their relationship by redundancy analysis (RDA) and Spearman’s correlation analysis. Result (1) The differences in stand biomass and total tree biomass between different densities were significant (P<0.05), and with the increase of stand density, stand biomass gradually decreased, and the total tree biomass had a peak at a density of 1 750 plants·hm−2; (2) The physicochemical properties of soil in forests of different densities differed significantly (P<0.05), with soil porosity being the highest at 1 750 plants·hm−2, reaching 52.38%, soil moisture content being the highest at 2 750 plants·hm−2, reaching 13.84%, and soil fertility being the best at a density of 1 750 plants·hm−2; (3) RDA and Spearman’s correlation analyses revealed that total soil porosity, organic carbon and quick-acting phosphorus were all highly significantly correlated with arbor biomass in the sample plots (P<0.01), and below-ground biomass was significantly affected by soil water content (P<0.05). Conclusion The stand density should be maintained at 1750 plants·hm−2 for the purpose of sequestering carbon and releasing oxygen and maintaining maximum productivity, and for the purpose of increasing the carbon sink capacity of the soil and improving fertility, and at 1 750−2 750 plants·hm−2 for the purpose of retaining soil and water and improving soil water retention properties. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 40 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1222-1232.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240171
Abstract:
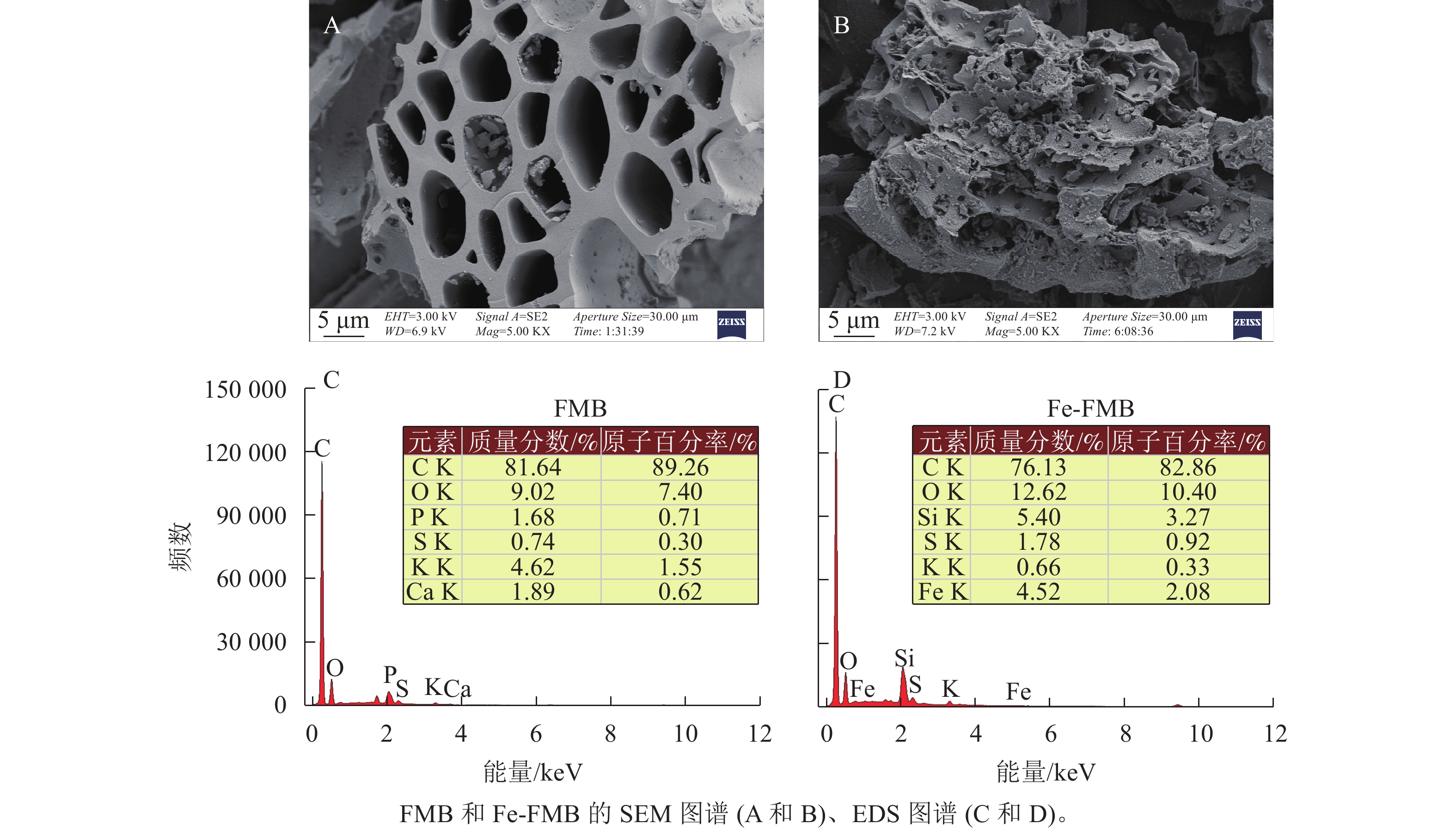
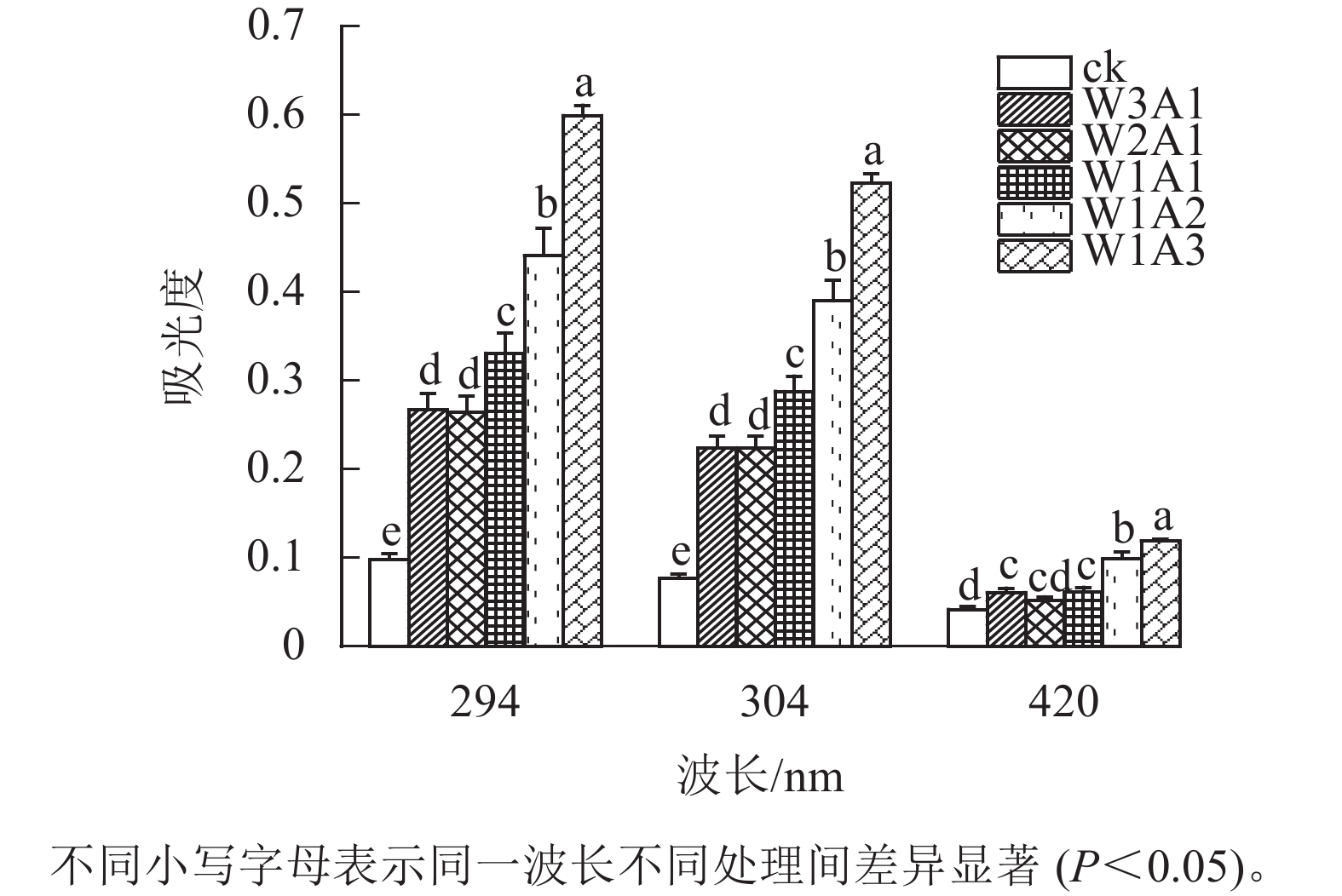
Objective To investigate the effects of raw and iron-modified biochar on the nutrient content and bioavailability of arsenic (As) and lead (Pb) in con-contaminated agricultural soil. Method An experiment using rice potted in soil mixed with 2% raw Ficus microcarpa biochar (FMB) and Polyferric Sulfate (iron)-modified biochar (Fe-FMB) was conducted, no biochar soil as control. Soil nutrient availability, soil enzyme activity, rice biomass and As and Pb concentrations in various plant organs at different growth stages were measured. The bioavailable As and Pb in the soil were determined using the NH4H2PO4 and DTPA extraction methods, respectively. Result The results indicated that, compared to the control, Fe-FMB significantly enhanced the availability of nutrients such as phosphorus (P) and silicon (Si) in the soil and significantly altered the distribution of Si forms in the soil (P<0.05), primarily increasing the content of amorphous silicon (by 25.2%) and iron-manganese oxidized silicon (by 11.1%). Fe-FMB was more effective in immobilizing soil As (P<0.05), reducing it by 37.9% compared to the control, while original biochar (FMB) was more effective for soil Pb immobilization, reducing it by 24.9%. Application of Fe-FMB led to a 67.2% reduction in As content in rice grains as compared to the control. Furthermore, Fe-FMB significantly increased the activities of leucine aminopeptidase, acid phosphatase, and catalase (P<0.05), with maximum increases of 121.1%, 99.1%, and 33.2%, respectively. Pearson correlation analysis showed that soil enzyme activity was significantly related to pH and As availability (P<0.05), indicating that biochar application can regulate soil enzyme activity by influencing soil pH and As bioavailability. Conclusion While F. microcarpa biochar is effective in remediating soils contaminated with Pb only, it is not suitable for the treatment of soils co-contaminated with As and Pb. On the other hand, iron-modified biochar shows a better prospect for remediating soils co-contaminated with As and Pb. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 36 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1233-1241.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240212
Abstract:
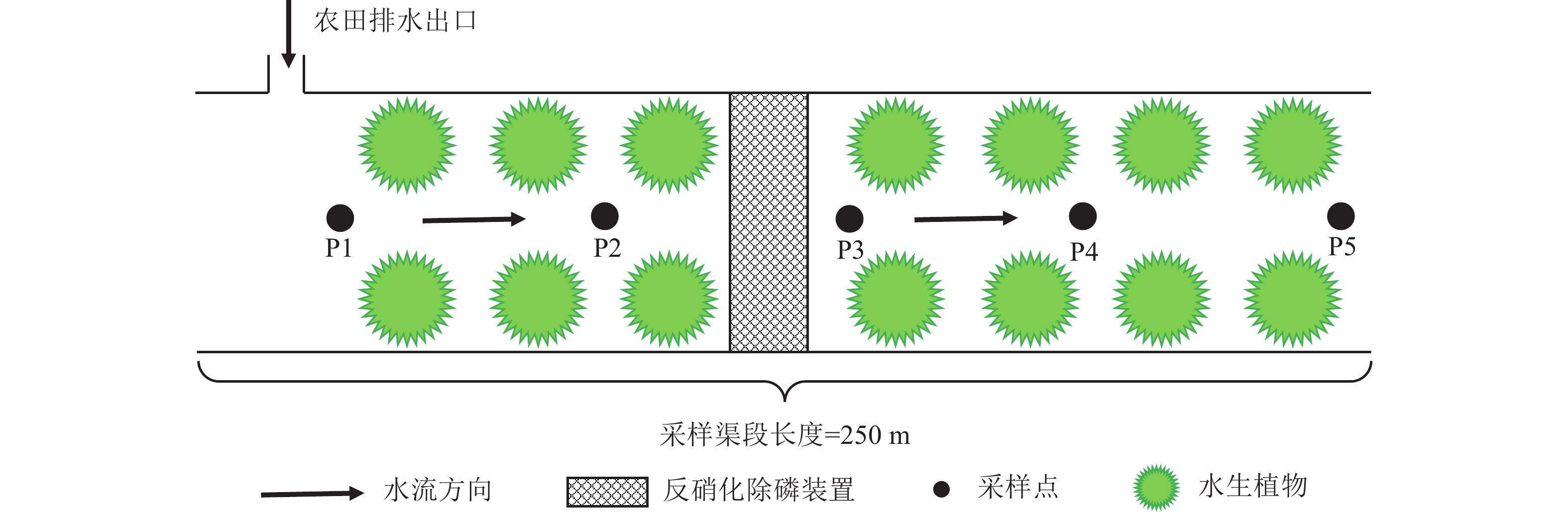
Objective This study is to comprehensively evaluate the role of ecological ditches in the blocking process of agricultural non-point source pollution and scientifically assess the effect of ecological ditches on pollutant removal. Method 6 ecological ditches in Tonglu, Lin’an, Jiande, Dongyang, Yiwu, and Zhuji in Zhejiang Province were selected for water quality monitoring. The removal rates of major agricultural non-point source pollution by ecological ditches were calculated, including total nitrogen (TN), ammonium nitrogen (\begin{document}${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $\end{document} Result The average removal rates of TN, \begin{document}${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $\end{document} \begin{document}${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $\end{document} \begin{document}${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $\end{document} \begin{document}${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $\end{document} Conclusion The water purification function of ecological ditches in Zhejiang Province can be strengthened by constructing ecological slopes, installing denitrification phosphorus removal devices, and increasing plant density. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 34 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1242-1251.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240217
Abstract:
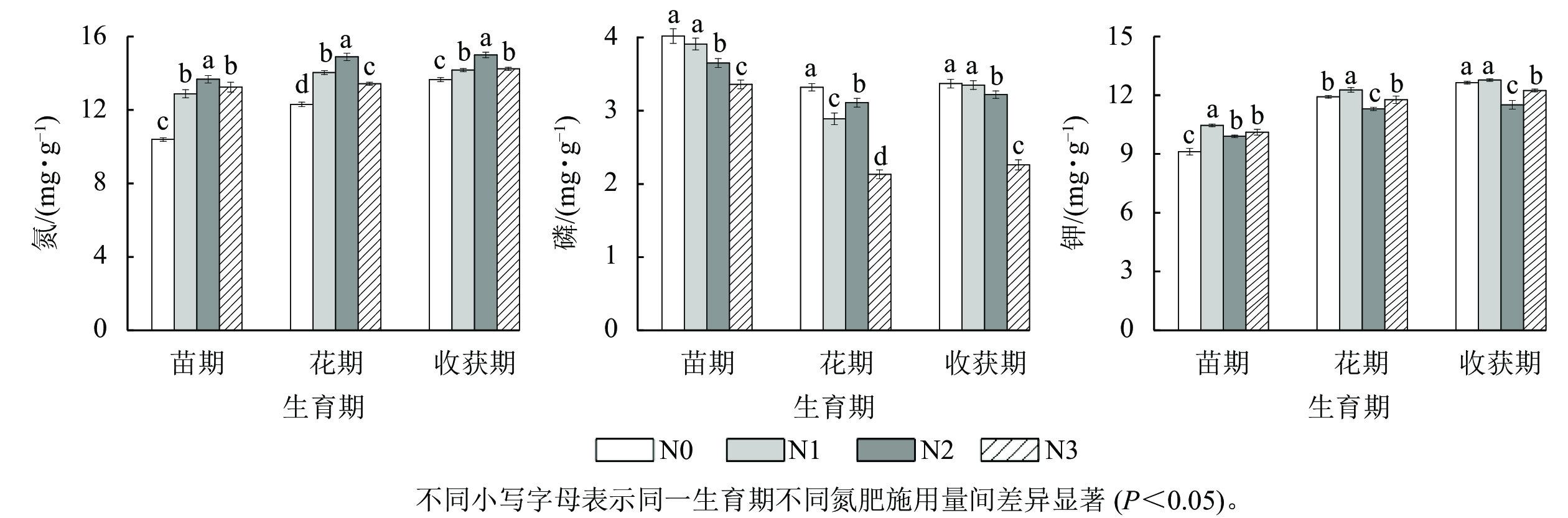
Objective This study aims to analyze the annual variation of the concentration and accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in Fritillaria hupehensis bulbs, and explore the impacts of different nitrogen dosages on the accumulation of dry matter and alkaloids of F. hupehensis, so as to provide scientific basis for rational fertilization of F. hupehensis. Method F. hupehensis obtained from Xintang township, Enshi City, Hubei Province was used as the material. Under the conditions of 102.4 kg·hm−2 phosphorus pentoxide and 86.4 kg·hm−2 potassium oxide for both phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, 4 nitrogen fertilizer treatments were set up: no nitrogen fertilizer (N0), 58.0 kg·hm−2 nitrogen fertilizer (N1), 116.0 kg·hm−2 nitrogen fertilizer (N2), and 174.0 kg·hm−2 nitrogen fertilizer (N3). Samples were collected at seedling, flowering and harvest stages to determine the concentration of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and various alkaloids in the bulbs of F. hupehensis at different growth stages. Result The accumulation of dry matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, total alkaloid, verticine, verticinone, peimissine and hupehenine in F. hupehensis bulbs significantly increased with increasing nitrogen application (P<0.05), and all reached their peak at a nitrogen fertilizer application of 116.0 kg·hm−2. With the increase of nitrogen application, potassium to phosphorus ratio in F. hupehensis bulbs was less than 3.4 at seedling stage, while that during the flowering and harvesting periods was more than 3.4. Throughout the entire growth period, nitrogen to phosphorus ratio in F. hupehensis bulbs was less than 14.0, and nitrogen to potassium ratio was less than 2.1. During the seedling and harvest stages, the concentration of total alkaloid, verticine, verticinone, and hupehenine in F. hupehensis bulbs all decreased with increasing nitrogen application. During the flowering period, the concentration of verticine, verticinone and peimissine in F. hupehensis bulbs showed an increasing trend with the increase in nitrogen application. When the nitrogen fertilizer application amount was 116.0 kg·hm−2, the peak accumulation of total alkaloid, verticine, verticinone, hupehenine and peimissine in F. hupehensis bulbs were 56.50, 4.20, 12.73, 1.66, and 3.68 mg·plant−1, respectively. When the same amount of nitrogen fertilizer was applied, with the extension of growth period, except for peimissine, the concentration of all other alkaloids was the highest during the harvest period and the lowest during the flowering period. When the nitrogen fertilizer application amount was 116.0 kg·hm−2, the accumulation rate of verticine, verticinone and peimissine in bulbs decreased from flowering to harvest stage. The dry matter accumulation rate was relatively fast from seedling to flowering stage, and the accumulation ability of total alkaloids in the bulb during the flowering to harvest period was strong. Conclusion The amount of nitrogen fertilizer significantly affects the yield and quality of F. hupehensis. Excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer is not conducive to the accumulation of dry matter and alkaloids in bulbs. The accumulation of dry matter and alkaloids in bulbs of F. hupehensis at different growth stages is a dynamic process. Yield increase is predominant at vegetative growth stage, while alkaloids accumulation is dominant at productive growth stage. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1252-1260.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240193
Abstract:
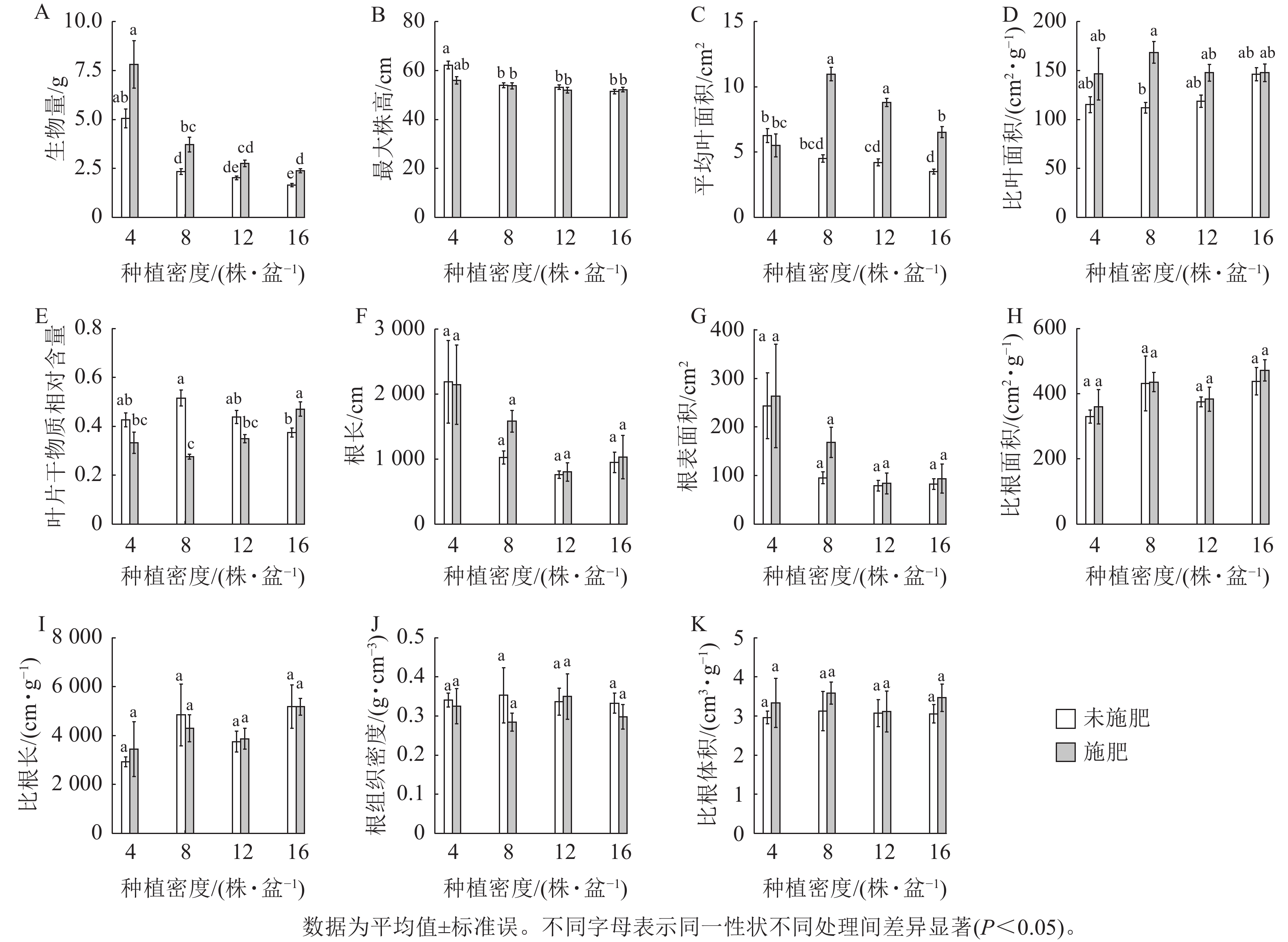
Objective This study, with an investigation of the effects of planting density, fertilization, and neighboring weed species identity on wheat growth, is aimed to provide scientific guidance for wheat cultivation. Method With wheat (Triticum aestivum) and two dominant weed species [wild oat (Avena fatua) and barnyard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli)] selected as target species, a competition experiment was conducted between pairs of wheat and weeds, by setting four planting densities (4, 8, 12 and 16 plants·pot−1), four wheat-weed planting ratios (25%∶75%, 50%∶50%, 75%∶25% and 100%∶0), as well as with or without nitrogen addition. After growing for about six months, the total biomass, plant height, leaf and root functional traits of wheat were measured. Result (1) In monoculture or mixtures with weed species, individual wheat’s biomass decreased with the increase of planting density and the proportion of wheat (P<0.05) (i.e., the occurrence of negative density dependence). (2) For individual wheat plants grown in monoculture, fertilization significantly increased their biomass and leaf area (P<0.05) while for those grown in mixture with wild oats or barnyard grass, fertilization had the trend to increase the biomass, root length and root surface area, which did not depend on weed species identity. (3) The interaction effects of planting density, proportion, and fertilization significantly affected wheat root length and area, but demonstrated no effects on other traits. Conclusion Fertilization enhanced wheat’s aboveground traits in monoculture and belowground traits in mixed cropping, with consistent negative density dependence in both systems. This indicates that agricultural management outcomes are influenced by weed interactions. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 38 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1261-1273.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240256
Abstract:
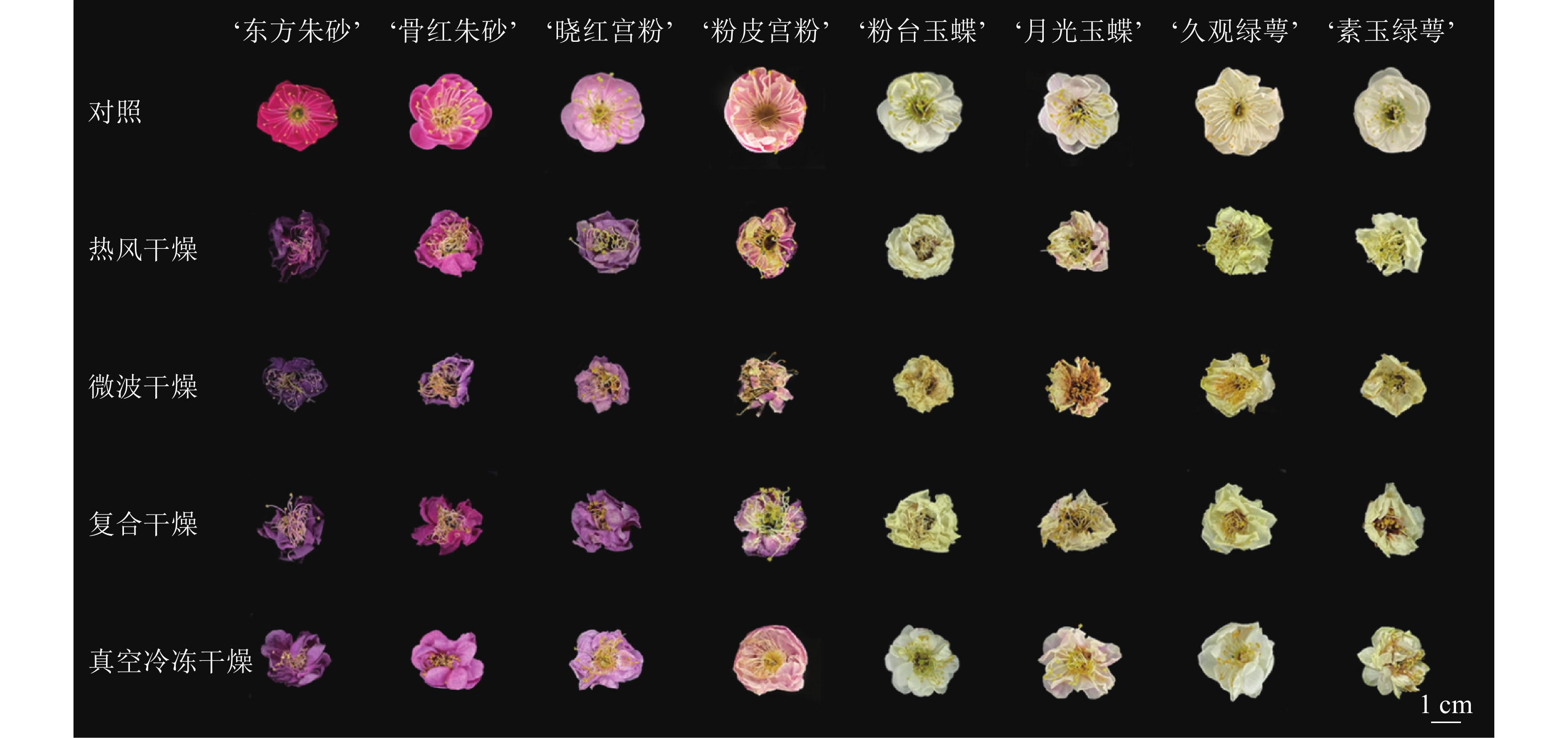
Objective The impact of different drying methods on the quality of dried Prunus mume flowers is to be studied and evaluated, so as to provide reference for maintaining the quality of dried P. mume flowers in drying process. Method 4 different drying methods (hot air drying, microwave drying, compound drying and vacuum freeze-drying) were used to treat 8 P. mume flower cultivars (‘Dongfang Zhusha’ ‘Guhong Zhusha’ ‘Xiaohong Gongfen’ ‘Fenpi Gongfen’ ‘Fentai Yudie’ ‘Yueguang Yudie’ ‘Jiuguang Lve’ and ‘Suyu Lv’). Color difference, antioxidant capacity, and total flavonoid content were used as evaluation indicators to compare the impact of different drying methods on the quality of P. mume flowers. The entropy weight-coefficient of variation method was used for combined weighting to calculate the comprehensive score. The evaluation model was verified by the weighted proximation ideal solution sorting method and the optimal drying method was obtained. Result The color difference and shrinkage rate treated with vacuum freeze-drying were the smallest, less than 33.09 and 28.7%, respectively, and the total flavonoids, anthocyanins, and total chlorogenic acid mass fractions of the samples were the highest. The soluble protein mass fraction and antioxidant capacity of the materials treated with vacuum freezing and composite drying methods were the highest. The retention rate of volatile substances was the highest after composite drying, exceeding 50%. The comprehensive scores ranking from high to low was vacuum freeze-drying group, composite drying group, hot air drying group, and microwave drying group. Conclusion The mass fraction of active ingredients is the highest after vacuum freeze-drying, followed by composite drying. The quality of P. mume flowers is the best after vacuum freeze-drying and composite drying, which can be used for high-quality processing and mass production. [Ch, 8 fig. 6 tab. 29 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1274-1282.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240243
Abstract:
Objective This study used whey protein (WPI) and alginate dialdehyde (ADA) to prepare WPI-ADA copolymer microcapsules, and the interactions between WPI and ADA and their effects on the controlled release of curcumin in the microcapsules were investigated to provide a theoretical basis for the development of the encapsulation system of curcumin. Method WPI-ADA copolymers were prepared using a wet-heat method, and the interaction between WPI and ADA was explored through analysis of grafting degree, browning intensity, and infrared spectroscopy. The effects of different proportions of copolymers on the emulsion were studied in terms of particle size, zeta potential, and rheological properties. The influence of copolymers on microcapsules was investigated using X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, and the release characteristics of curcumin. Result The results indicated that the optimum mass ratio of WPI and ADA for preparing microcapsules was 1∶3. Grafting degree, browning intensity and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses confirmed the formation of conjugates. Driven by covalent binding, the particle size of WPI-ADA emulsion decreased from 415.4 nm to 325.9 nm, and the microcapsule encapsulation efficiency increased from 83.9% to 95.4%. Additionally, WPI-ADA copolymer microcapsules exhibited good thermal stability. In vitro simulated digestion experiments demonstrated that WPI-ADA copolymer microcapsules exhibited certain controlled release capabilities, extending the time for maximum curcumin release from 12 hours to 24 hours in simulated gastric fluid and intestinal fluid. Conclusion Under covalent interaction, WPI-ADA copolymers can improve the physicochemical properties and curcumin release properties of microcapsules, and can be used to modify the microcapsule system and the delivery of hydrophobic active substances. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 27 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1283-1292.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240169
Abstract:
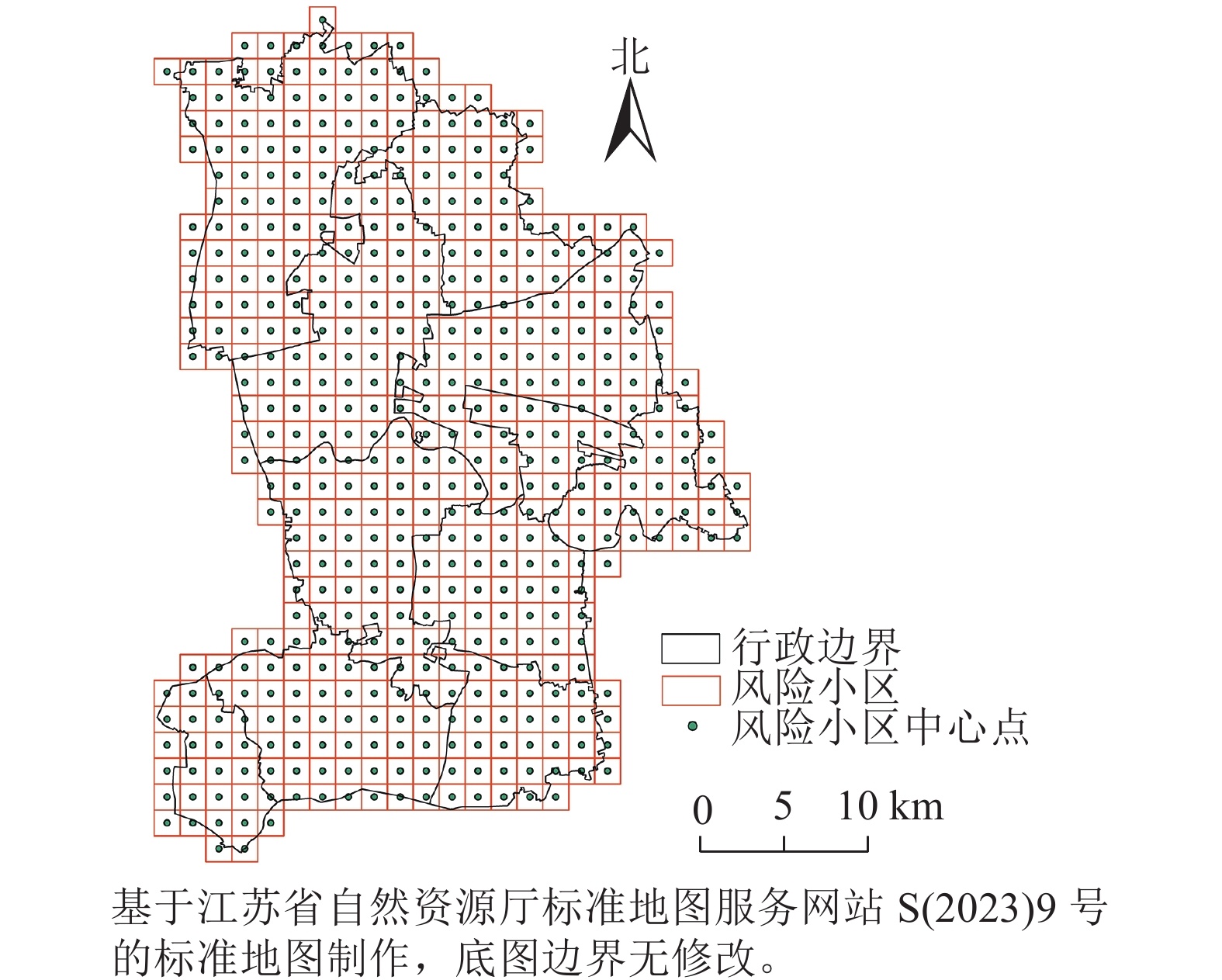
Objective This study aims to discuss the ecological risks caused by landscape fragmentation and habitat quality decline in green space in the water network area of southern Jiangsu Province under the background of rapid urbanization. Method Taking Kunshan City as an example, the land use data from 2000, 2010 and 2020 were selected, and the landscape pattern index was used to construct a landscape ecological risk assessment model. The spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of landscape ecological risks in green space of Kunshan City from 2000 to 2020 were analyzed, and green space control zones were defined based on the characteristics of landscape ecological risk level transfer and change. Result (1) From 2000 to 2020, the total area of green space in Kunshan City showed a continuous reduction trend, with a significant decrease in cultivated land, a total reduction of 20 203.11 hm2, accounting for 21.70%. The water area first slightly increased and then continued to decrease, with an overall decrease of 3813.66 hm2. The proportion of forest land and grassland was relatively small and stable. The area transfer matrix between land types of green space mainly showed a shift from arable land to construction land, reflecting the increasing interference degree of green space by artificial construction. (2) There were certain changes in the distribution of landscape ecological risks, mainly manifested as a shift from low risk level to higher risk level. The proportion of the highest and high risk areas increased by 8.10% and 6.61%, respectively, while the area of low and the lowest risk areas decreased by 8.25% and 9.73%, respectively. (3) Based on the characteristics of landscape ecological risk level transfer and change, the study area was divided into three types of control zones: key restoration zone, coordinated buffer zone and optimal utilization zone. Conclusion The landscape ecological risk of green space in Kunshan City shows an upward trend. There is a correlation between the transformation of green space land use type and landscape ecological risk, reflecting the increasing ecological pressure of green space under human construction activities. Green space zoning regulation strategies based on the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of risks are proposed in this study. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 28 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1293-1302.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230610
Abstract:
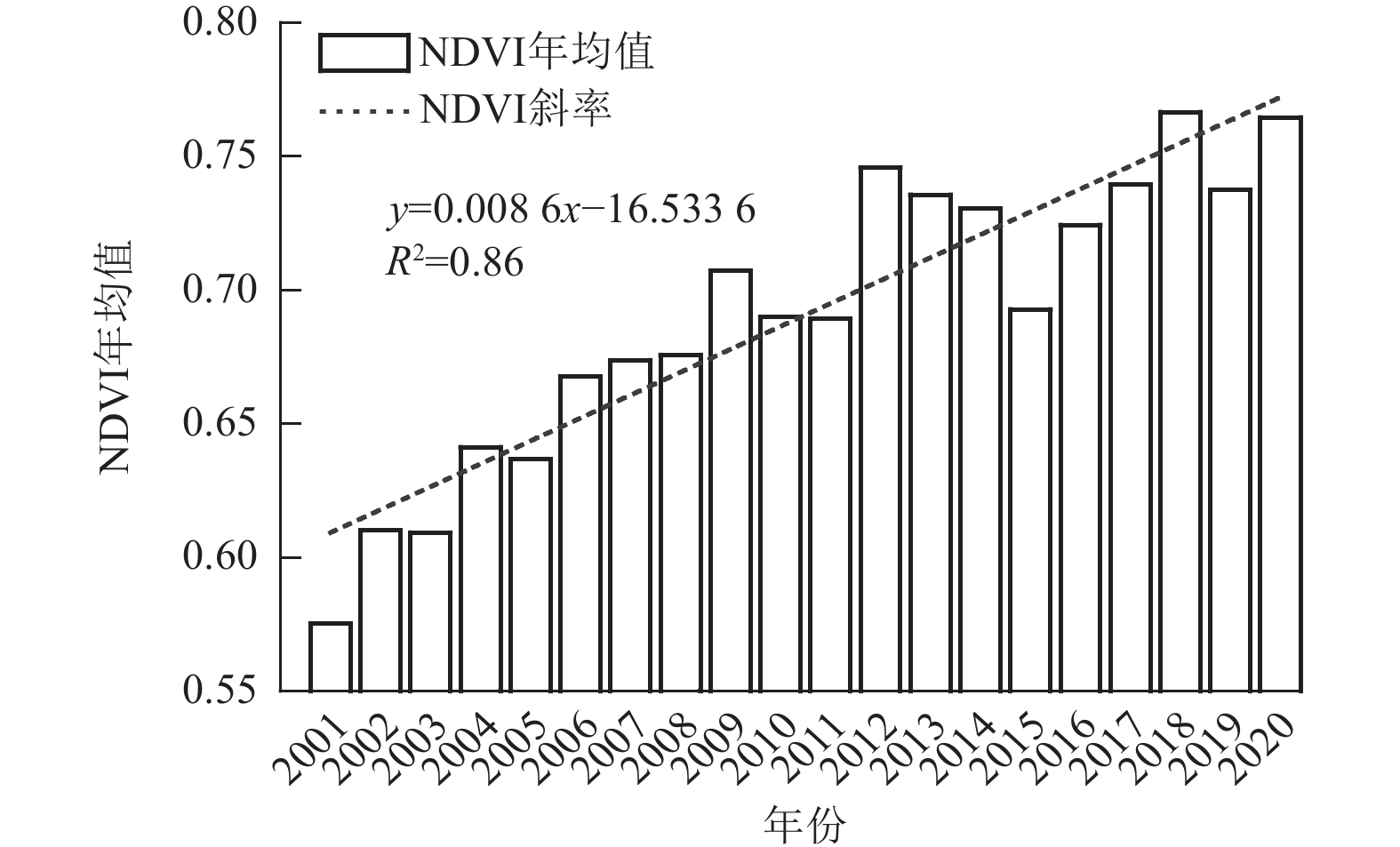
Objective Vegetation is a principal component of terrestrial ecosystems. This study intends to investigate the spatiotemporal variation in regional vegetation coverage, and quantify the relative contributions of climate change and human activities, which can provide scientific support for future ecological environment construction and sustainable development of the region. Method Based on the MODIS-normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) dataset and meteorological data of Yan’an City from 2001 to 2020, Mann-Kendall trend analysis, partial correlation analysis and residual analysis were employed to investigate the response of NDVI to climate change and human activities. Result (1) From 2001 to 2020, the annual mean NDVI value in Yan’an City was 0.69, indicating a significant upward trend, with a spatial distribution pattern of high in the south and low in the north. (2) The impact of temperature and precipitation on NDVI varied significantly at different temporal scales. At the annual scale, NDVI was influenced more by precipitation than temperature. At the seasonal scale, NDVI in spring was influenced by both temperature and precipitation, while precipitation in summer had a greater impact on NDVI. In autumn and winter, the correlation between NDVI and temperature and precipitation was not significant in most regions. (3) The overall NDVI exhibited a trend of improvement, with 83.27% of the area showing significant improvement. (4) The impact of climate change and human activities on vegetation had a dual effect, with 91.26% of the area affected by both factors. The relative contributions of the two to vegetation change were 17.81% and 82.19%, respectively. Conclusion The overall vegetation in Yan’an City demonstrates a positive trend, and compared to climatic factors, human activities have a stronger driving effect on NDVI changes. [Ch, 7 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1303-1312.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240297
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the impact of various industrial organization models on the value realization of non-timber forest products and their mechanism of action, and to clarify effective pathways for the value realization of material-based ecological products. Method Based on the survey data of 811 farming households from 7 counties (cities) in Zhejiang Province in 2022, this study empirically analyzed the impact of different industrial organization models on the value realization of non-timber forest products, as well as the role of regional public brands in this process. Result Both horizontal cooperation (cooperative + farmer) and vertical collaboration (company + farmer) models had significant positive effects on the value realization of non-timber forest products. Mechanism verification showed that regional public brands played a mediating role in the value realization process of non-timber forest products by industrial organizations. Heterogeneity tests revealed that the premium effect of non-timber forest products sold by farmers with small operation scale and through the Internet was more significant. Conclusion Industrial organizations can facilitate the value realization of non-timber forest products by promoting farmers’ participation in regional public brands. Therefore, it is suggested that while improving the organization degree of farmers, it is necessary to strengthen the construction of regional public brand and optimize sales channels. [Ch, 6 tab. 35 ref.]
2024, 41(6): 1313-1322.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240187
Abstract:
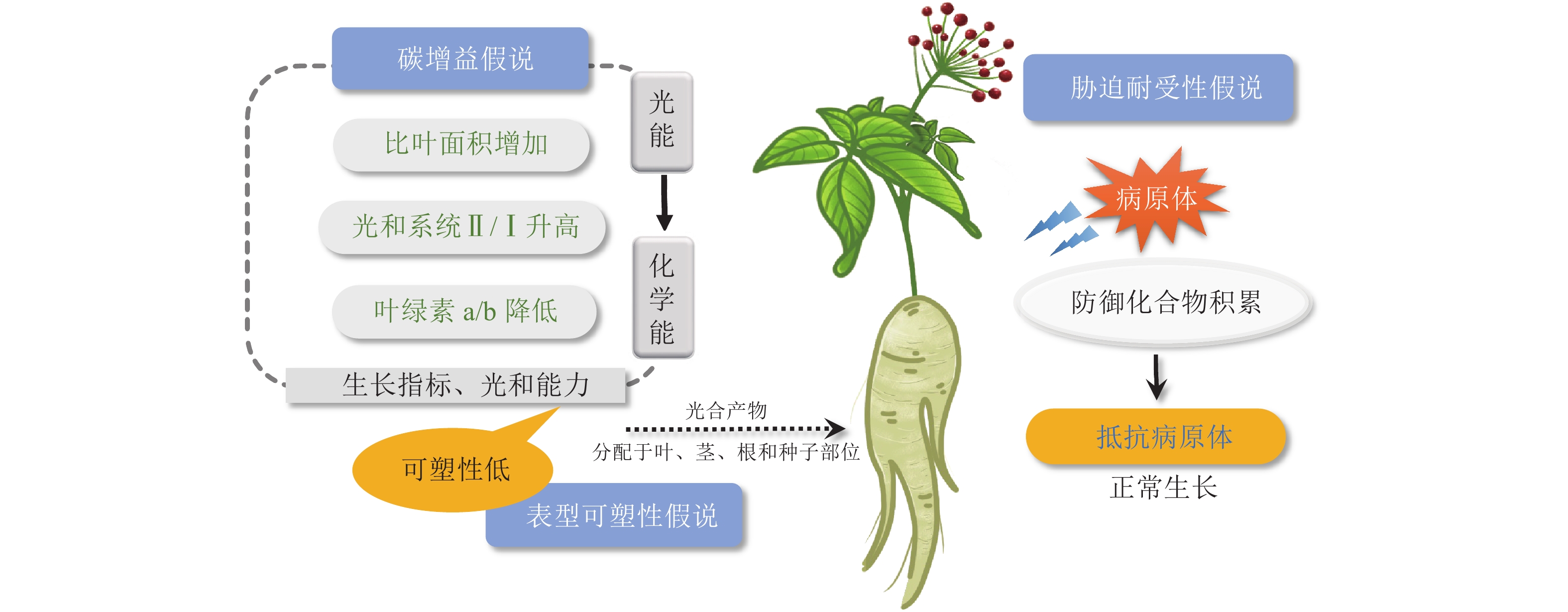
Light is a crucial environmental factor affecting plant growth and development. It is of great scientific significance and application value to enhance plant yield and quality in agricultural production by improving its photosynthetic efficiency. In dense plant communities, lower plants receive less light energy due to the coverage of upper vegetation, so lower plants need to compete for more light energy to maintain growth. Plants have two strategies to obtain more light energy: shade avoidance syndrome (SAS) and shade tolerance response (STR). Research on SAS is relatively thorough, but there is a lack of in-depth research on STR. This paper provides an overview of how sunny plants adapt to lower light level by extending hypocotyl, petioles, stems and other physiological morphological changes in shaded environments. At the same time, shade tolerant plants respond to limited light conditions by exhibiting shade resistance characteristics such as promoting carbon acquisition, low phenotypic plasticity ability and improving stress resistance. Combined with the mechanism of shade avoidance response of sunny plants in response to low light environment through the interaction between hormones and light signaling pathways, the shade tolerance response mechanism of shade tolerant plants in shaded environments is studied, which involves both activating antagonistic factors to inhibit shade avoidance syndrome and improving the transcription activity of shade tolerance response genes to enhance low light adaptability. This review provides reference for research on the mechanism of different plants responding to low light environments, and proposes effective ways to improve the efficiency of plant light energy utilization, cultivate crop varieties with high light efficiency, and construct efficient forest ecosystems. [Ch, 3 fig. 61 ref.]
Light is a crucial environmental factor affecting plant growth and development. It is of great scientific significance and application value to enhance plant yield and quality in agricultural production by improving its photosynthetic efficiency. In dense plant communities, lower plants receive less light energy due to the coverage of upper vegetation, so lower plants need to compete for more light energy to maintain growth. Plants have two strategies to obtain more light energy: shade avoidance syndrome (SAS) and shade tolerance response (STR). Research on SAS is relatively thorough, but there is a lack of in-depth research on STR. This paper provides an overview of how sunny plants adapt to lower light level by extending hypocotyl, petioles, stems and other physiological morphological changes in shaded environments. At the same time, shade tolerant plants respond to limited light conditions by exhibiting shade resistance characteristics such as promoting carbon acquisition, low phenotypic plasticity ability and improving stress resistance. Combined with the mechanism of shade avoidance response of sunny plants in response to low light environment through the interaction between hormones and light signaling pathways, the shade tolerance response mechanism of shade tolerant plants in shaded environments is studied, which involves both activating antagonistic factors to inhibit shade avoidance syndrome and improving the transcription activity of shade tolerance response genes to enhance low light adaptability. This review provides reference for research on the mechanism of different plants responding to low light environments, and proposes effective ways to improve the efficiency of plant light energy utilization, cultivate crop varieties with high light efficiency, and construct efficient forest ecosystems. [Ch, 3 fig. 61 ref.]