2024 Vol. 41, No. 1
2024, 41(1): 1-11.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230388
Abstract:
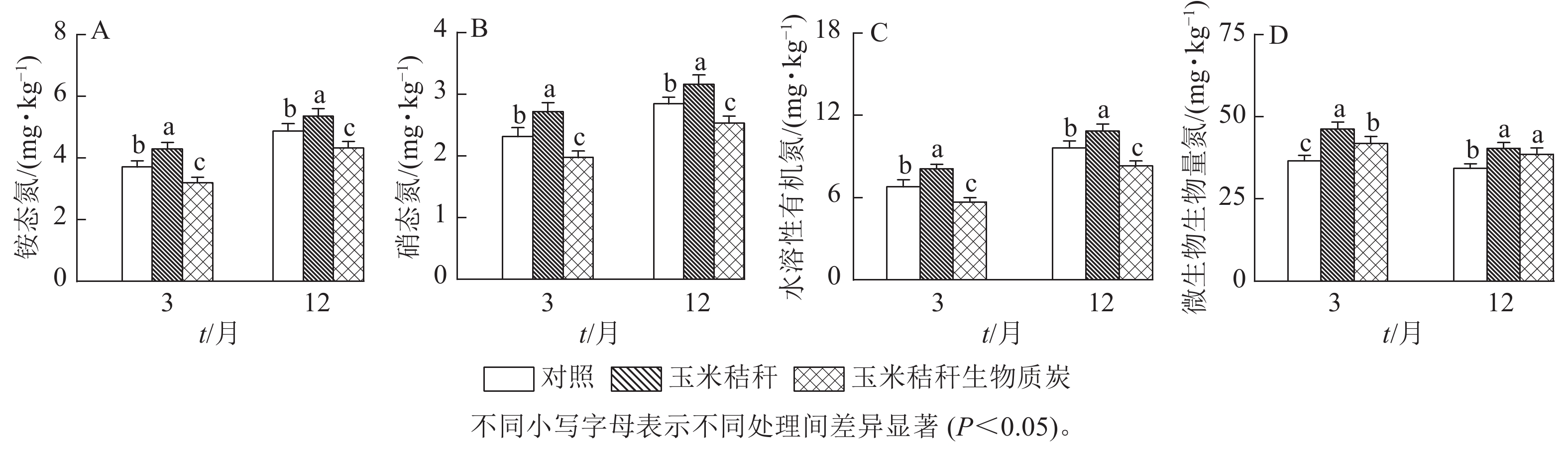
Objective The objective is to investigate the effects of different exogenous carbon application(Zea mays straw and its biochar) on soil ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms and N cycling related enzyme activities in a subtropical Phyllostachys edulis forest, so as to reveal the biological mechanism of soil nitrification. Method A 1-year field experiment was conducted in a typical subtropical Ph. edulis forest. Three treatments were set up: control (no application), straw (5 t·hm−2) and biochar (5 t·hm−2). Soil samples were collected at the 3rd and 12th month of the treatment. Quantitative PCR and high-throughput sequencing techniques were used to analyze the changes in soil ammonia-oxidizing microbial community structure characteristics, enzyme activities and gross nitrification rate under different treatments. Result Straw and its biochar treatment significantly changed the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in soil (P<0.05), but had no significant effect on the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizing archaea (AOA). Compared with the control, straw treatment significantly increased the abundance of AOB and the relative abundance of Nitrosospira, the activities of soil protease and urease, and the gross nitrification rate of soil (P<0.05), while biochar treatment had the opposite effect. Correlation analysis showed that AOB abundance and the relative abundance of its dominant genus Nitrosospira, protease and urease activity were positively correlated with the content of NH4 +-N, NO3 −-N and water-soluble organic nitrogen ( WSON ) , and the soil gross nitrification rate. Redundancy analysis revealed that the contents of NH4 +-N, NO3 −-N, microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) and WSON had a significant impact on the community structure of AOB (P<0.05). Conclusion The application of straw biochar reduces the contents of soil NH4 +-N, NO3 −-N and WSON, as well as soil AOB abundance and relative abundance of dominant genera, weakens N cycling related enzyme activity, and inhibits soil nitrification. Compared with direct application of straw, straw biochar is beneficial for reducing soil N2O emission and soil nitrogen loss in a Ph. edulis forest. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 57 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 12-21.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230408
Abstract:
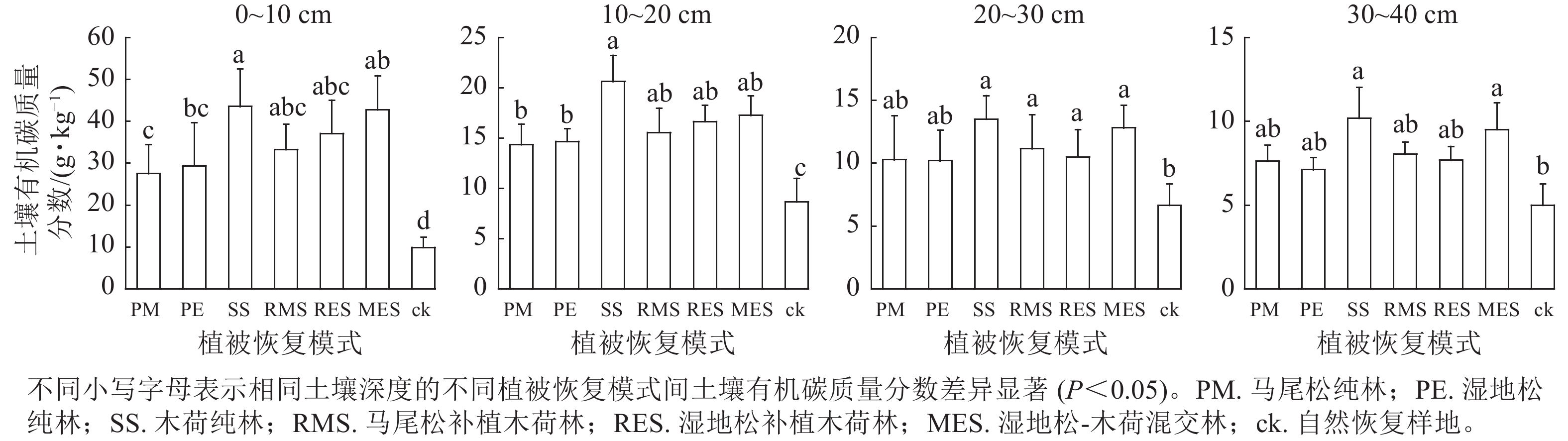
Objective This study is to explore the soil carbon stock characteristics of different vegetation restoration models in the process of vegetation restoration in red soil erosion areas of Jiangxi Province, so as to provide scientific support for revealing the impact mechanism of vegetation restoration on soil carbon sinks and ecological restoration and carbon pool management in red soil erosion areas of Jiangxi Province. Method The research objects included 6 types of forest stands after 27 years of vegetation restoration and reconstruction: Pinus massoniana pure forest (PM), P. elliottii pure forest (PE), Schima superba pure forest (SS), P. elliottii and S. superba mixed forest (MES), replanting S. superba with P. massoniana (RMS), and replanting S. superba with P. elliottii (RES). Natural restoration sites without artificial disturbance (ck) were used as controls to compare the changes in soil organic carbon (SOC) content and storage under different vegetation restoration models, and analyze their influencing factors. Result (1) Compared with ck, SOC mass fraction increased significantly (P<0.05) in the 0−20 cm soil layer in all 6 artificial vegetation restoration models. In the 20−30 cm soil layer, except for PM and PE, SOC mass fraction of the other 4 vegetation restoration models was significantly higher than that of ck (P<0.05). In the 30−40 cm soil layer, only SS and MES had significantly higher SOC mass fractions than ck (P<0.05). (2) SOC mass fractions of the 7 vegetation restoration models in the study area showed a strong surface aggregation effect, but the differences between soil layers of different vegetation restoration models were different, among which SS had the largest SOC mass fraction, with a difference of 33.26 g·kg−1 between 0−10 cm soil layer and 30−40 cm layer, and ck had the smallest difference, with only 4.90 g·kg−1. (3) The change rules of SOC density and SOC content were basically the same, both of which were the result of the joint action of vegetation factors and soil physicochemical properties. The correlation coefficient between litter nitrogen mass fraction (r=0.322, P<0.01) and SOC density was the largest among vegetation factors, and the correlation coefficient between SOC mass fractions (r=0.932, P<0.01) and SOC density was the largest among soil physicochemical traits. (4) From high to low, SOC storage increased by 50.12 Mg·hm−2 in SS, 42.73 Mg·hm−2 in MES, 38.20 Mg·hm−2 in RMS, 33.03 Mg·hm−2 in RES, 26.93 Mg·hm−2 in PE, and 20.85 Mg·hm−2 in PM, respectively, compared with ck, with a maximum enhancement of 2.46 times and a minimum enhancement of 1.02 times. Conclusion Artificial vegetation restoration and reconstruction have significant effects in red soil erosion areas and can be further promoted in future construction in the research area to promote plant community restoration and enhance and maintain the stability of soil carbon pool. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 40 ref.]
Effects of thinning on soil heterotrophic respiration of oak-pine mixed forests in Qinling Mountains
2024, 41(1): 22-29.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230193
Abstract:
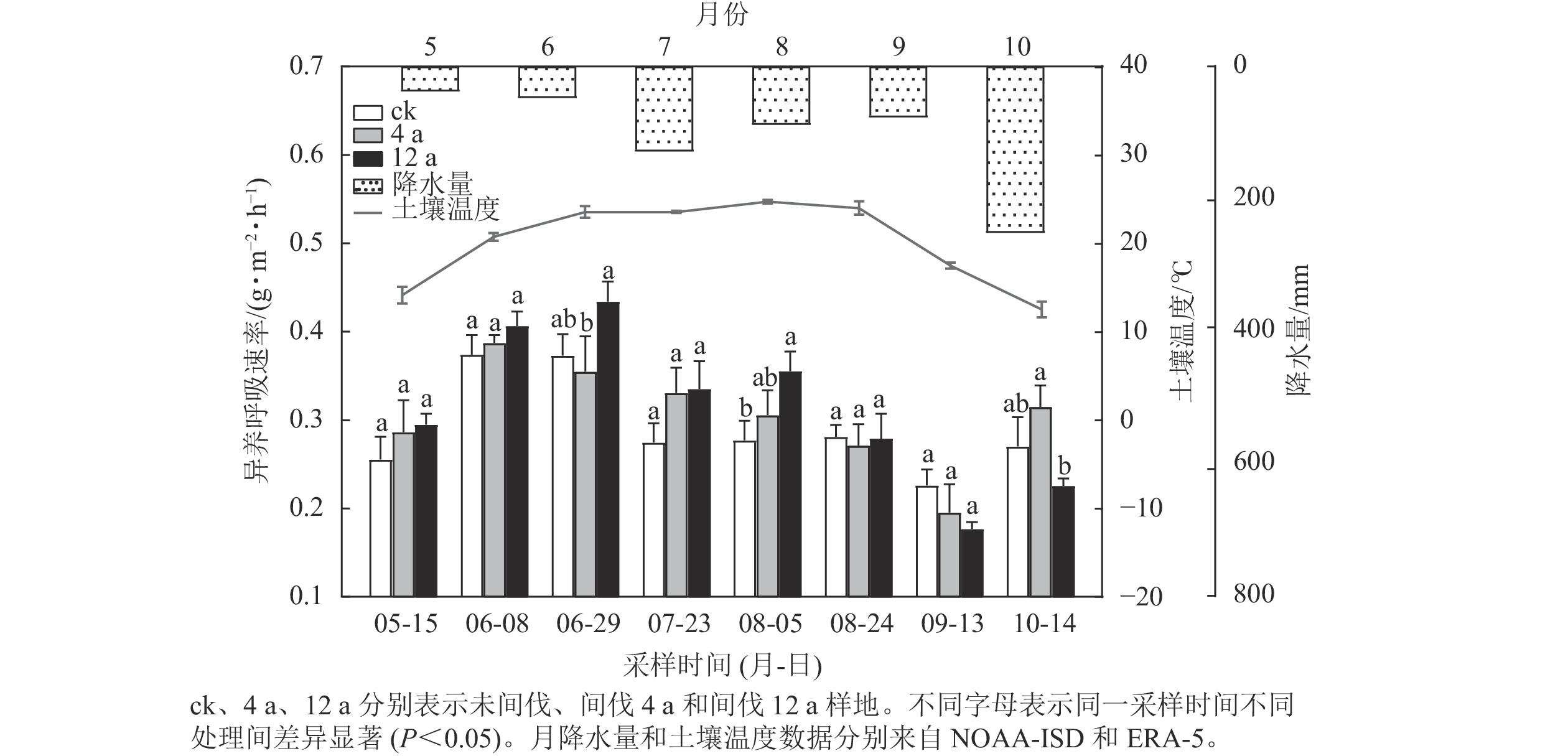
Objective This study, with an investigation of the effects of thinning on soil heterotrophic respiration in oak-pine mixed forests in the Qinling Mountains, is aimed to better understand the carbon loss caused by forest soil heterotrophic respiration under thinning treatments, providing a scientific basis for forest management decisions in the study area. Method The static chamber-gas chromatography technique was employed to monitor the variations of soil heterotrophic respiration flux in the growing season for the unthinned plots (4 replicates, ck) and the thinning plots (4 replicates) 4 and 12 years ago (4 a and 12 a), respectively. The temperature sensitivities (Q10) of heterotrophic respiration were also calculated. Result (1) There was a remarkable decrease in the soil microbial biomass carbon content (P<0.05), but a significant increase in the the soil pH (P<0.05) in both 4 a and 12 a compared to ck, while the decrease in the soil organic carbon content of 4 a after thinning was significant (P<0.05). Generally, the soil physical and chemical index in 12 a were closer to that in the ck than the 4 a treatment. (2) The soil heterotrophic respiration during the growing season showed a “bimodal” pattern, and the peaks appeared in June and October, respectively. However the cumulative heterotrophic respiration increased after thinning but not significantly, with the order from large to small being 12 a>4 a>ck. (3) The soil temperature was significantly and exponentially correlated with the soil heterotrophic respiration (P<0.05). The temperature sensitivities Q10 decreased after thinning, with the order from large to small being ck>12 a>4 a. Conclusion The soil temperature is a key factor affecting soil heterotrophic respiration in oak-pine mixed forests and the thinning treatment do not promote soil heterotrophic respiration of the oak-pine mixed forests in the growing season at the Qinling Mountains. [Ch, 3 fig. 2 tab. 34 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 30-40.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230205
Abstract:
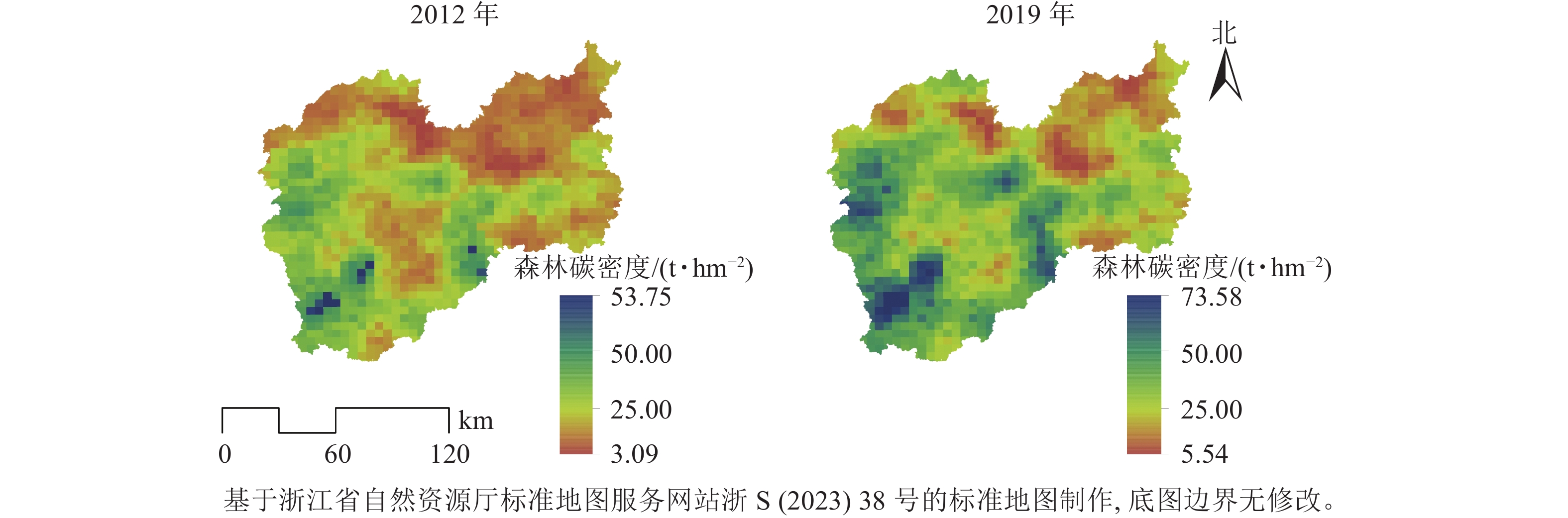
Objective This study, with an quantitative analysis of the effects of forest landscape pattern on forest carbon density in Lishui City, Zhejiang Province, is aimed to provide theoretical basis for forest management, ecological protection and restoration so as to improve forest carbon sink function. Method First, the forest carbon density of the continuous forest inventory plots was measured by using the biomass model and carbon coefficient. Then, the distribution map of regional forest carbon density was formed by ordinary Kriging interpolation before an analysis was conducted of the spatial autocorrelation characteristics of forest carbon density. Lastly, five landscape pattern indicators and three natural factors were selected, and multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR) models were used to investigate the effects of forest landscape pattern on forest carbon density, while the spatial non-stationarity affecting the results was analyzed. Result From 2012 to 2019, the average forest carbon density in Lishui increased from 23.19 t·hm−2 to 31.96 t·hm−2, and the spatial distribution showed a significant positive spatial autocorrelation. Forest landscape pattern significantly affected forest carbon density, showing different scale effects, and the degree of impact was also different in space. Landscape pattern indexes contagion (CONTAG) and patch density (PD) had a greater driving force on forest carbon density, while largest path index (LPI) had a smaller one. Conclusion The effects of forest landscape pattern on forest carbon density showed obvious spatial heterogeneity and the results of this paper can provide reference for making differentiated forest management policies and implementing targeted ecosystem protection and restoration projects. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 42 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 41-48.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230204
Abstract:
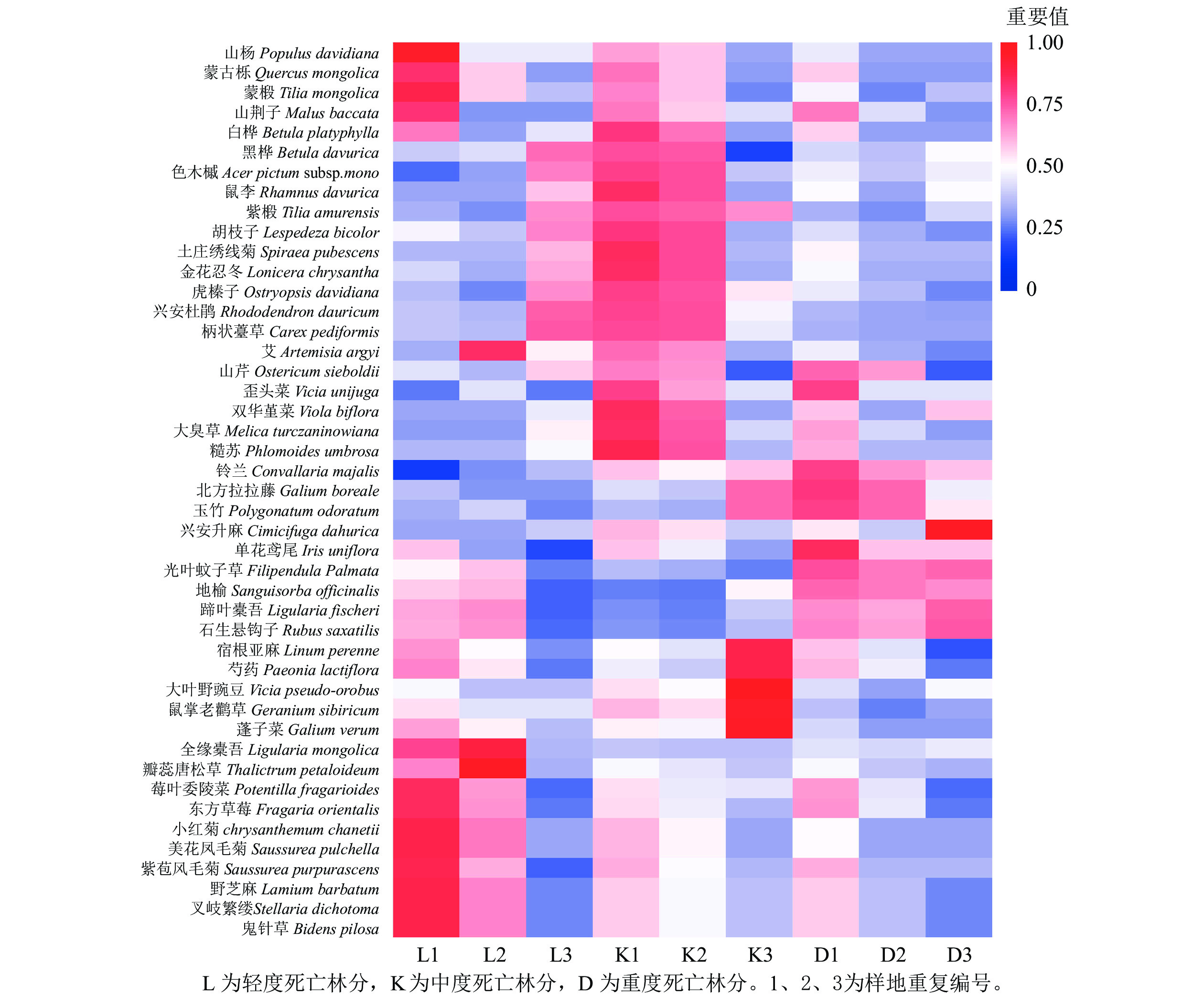
Objective Qingshan Reserve is a typical area in the northern section of the secondary forest in Hanshan, Inner Mongolia, in order to understand the characteristics of plant diversity under the forest death gradient in the northern section of the Hanshan secondary forest in Inner Mongolia, and to provide a basis for scientific protection and utilization of forest autogenous plant communities and explore plant communities more suitable for forest development. Method Taking the secondary forest of Populus davidiana in Qingshan Reserve as the research object, the plant composition of different dead gradients was investigated by sample survey method, and the differences in plant composition and diversity were analyzed by using biodiversity index and community similarity coefficient. Result There were 45 plant species in the northern section of Hanshan secondary forest area, Inner Mongolia, including 9 species of trees, 5 species of shrubs and 31 species of herbs, and the number of plant species in the sample plot was as follows: mild death plot>severe death plot>moderate death plot. The Simpson and Shannon-Wiener indices in the same field showed mildly dead stands>severely dead stands>moderately dead stands. Moderately dead plots had the highest richness and Pielou uniformity index. The greatest variation in communities within mildly fatal plots was found by PCoA analysis. The SI index was in the range of 55%−61%, there were 13 species in different death gradient forest stands, the difference between the relative coefficient of the tree layer and the shrub layer was not large, and the reduction benefit of herbaceous diversity was obvious, resulting in the difference of SI index of different death gradient forest stands became larger, and overall, with the increase of aspen mortality degree, the difference in vegetation composition also increased. Conclusion The mass forest mortality inhibits the development of herbaceous plant diversity, but promotes the renewal of trees and shrubs. The dominance of aspen in the study area declined, and whether the diversity of forest renewal could form mixed forests needed to be further studied. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 26 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 49-56.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230263
Abstract:
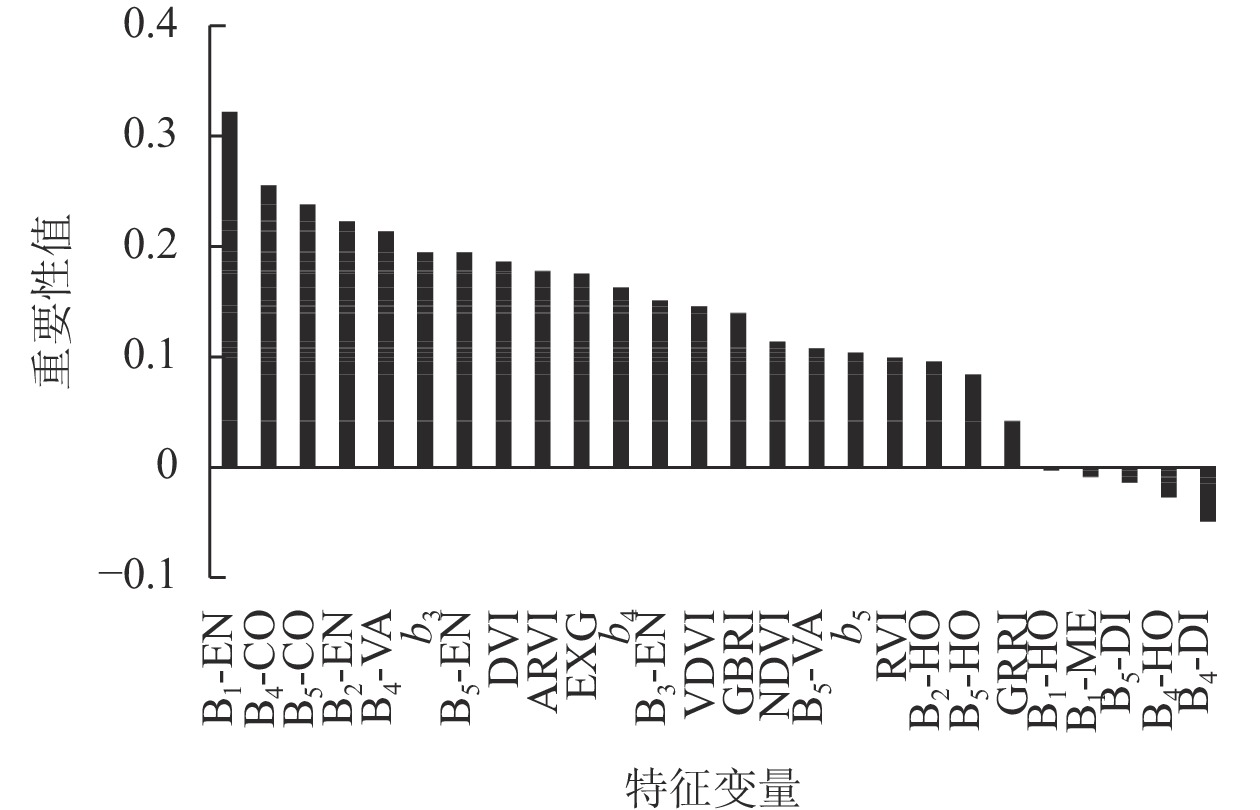
Objective Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) multispectral remote sensing images, with richer spectral information than visible light images, have great potential in forest volume estimation. Taking UAV-borne multispectral remote sensing images as the main data source, this study aims to explore the remote sensing estimation model of forest volume, so as to overcome the drawbacks of traditional ground survey, such as heavy workload, long time consumption and high cost. Method Taking the typical natural pure Pinus yunnanensis forest in Luomian Township, Fumin County, Kunming City as the research object, the single-band reflectance, vegetation index and texture feature were extracted according to the UAV multispectral image, and the standard ground mean of each characteristic variable was calculated. The characteristic variables significantly correlated with the forest volume were screened, and the forest volume estimation model was established using multiple linear regression, random forest and support vector machine. The model accuracy was evaluated by coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error (ERMS), mean absolute error (EMA) and mean relative error (EMR). Result (1) Among the three models, the random forest had the highest accuracy (R2=0.89, EMA=4.69 m3·hm−2, ERMS=5.45 m3·hm−2, EMR=14.5%), followed by the support vector machine (R2=0.74, EMA=5.27 m3·hm−2, ERMS=8.31 m3·hm−2, EMR=13.1%). The multiple linear regression model had the minimum accuracy (R2=0.35, EMA=10.12 m3·hm−2, ERMS=12.85 m3·hm−2, EMR=28.1%). The estimation accuracy of the three models in the test set decreased. The random forest had the best performance, followed by the support vector machine, and the multivariate linearity was the worst. (2) The three models had certain underestimation and overestimation in the estimation of P. yunnanensis forest volume. (3) Texture feature was still an important factor that could not be ignored in estimating the forest volume of P. yunnanensis based on UAV multispectral images. Conclusion Based on the multi-spectral images of UAV, the single-band reflectance, vegetation index, and texture factor mean values of the standard ground were extracted without individual tree segmentation, and the variables suitable for volume estimation were screened to construct an estimation model. Through the precision evaluation of the three models, the random forest is the best model for estimating P. yunnanensis volume. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 27 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 57-66.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220724
Abstract:
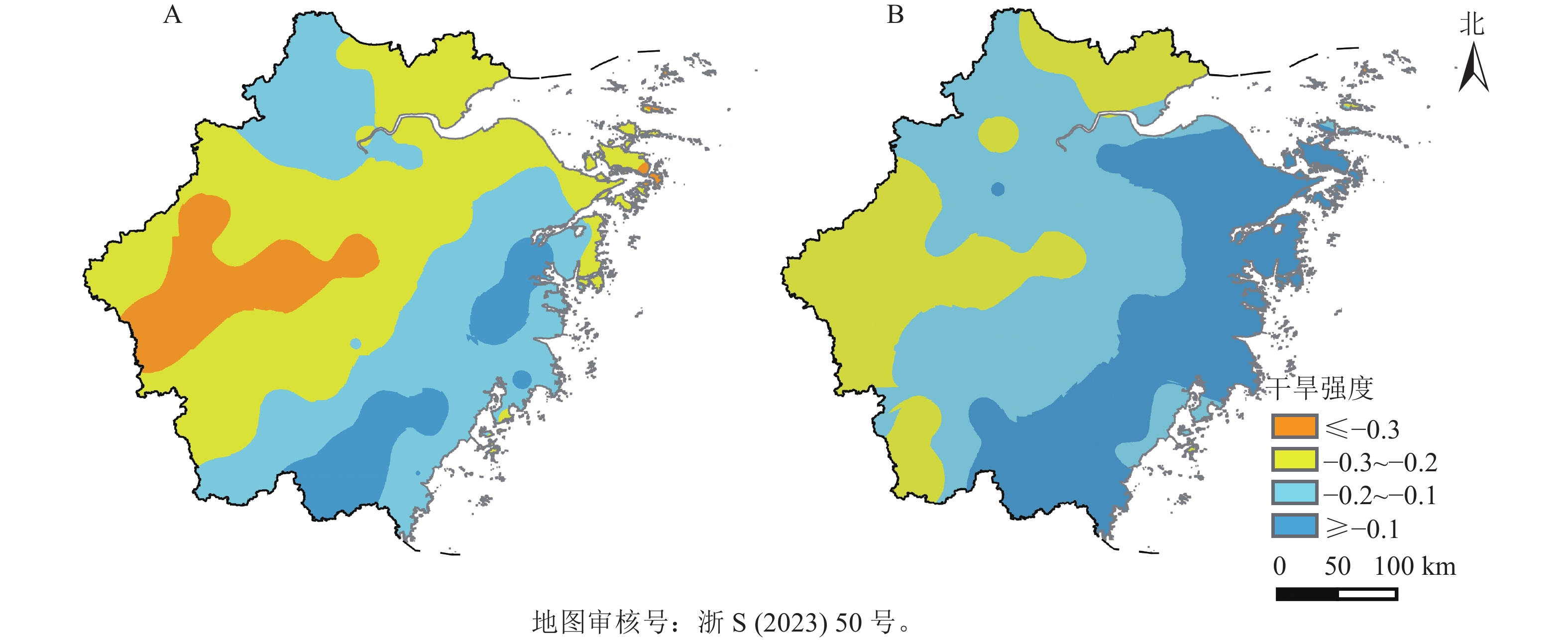
Objective The objective is to study the evolution law of tea meteorological drought in Zhejiang, which is important for safe production of tea. Method Based on the daily data (temperature, precipitation and sunshine duration) of 68 meteorological observation stations in Zhejiang Province for 50 years (1971−2020), the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of tea meteorological drought in Zhejiang were studied by relative humidity index, orthogonal empirical function (EOF), and wavelet analysis. Result The intensity and frequency of tea drought in summer were higher than those in autumn in Zhejiang, higher in the west and lower in the east. The drought intensity and frequency of drought were the strongest in the central and western parts of the province, especially in Jinqu Basin, followed by northern Zhejiang, and the least in coastal areas. The proportion of tea drought stations in summer decreased year by year, while in autumn it increased first and then decreased. After 2000, there was an increase in years of extreme large-scale tea drought in the summer and autumn seasons. The first modal of EOF of tea drought intensity in summer and autumn showed the consistency of changes in the whole province. In the second modal, local coastal areas and inland areas showed an inverse phase change. The main mode time series of drought intensity in summer and autumn had oscillation periods of 2−6, 2−4, and 6−10 years respectively. Conclusion The frequency of tea drought during summer and autumn in Zhejiang is decreasing, but the probability of extreme droughts has increased in recent years. Special attention should be paid to the improvement of drought monitoring and warning capability in the main tea producing regions. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 26 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 67-78.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230333
Abstract:
Objective This study, with analyses conducted of the genetic diversity and population structure of 114 germplasm resources of pinewood nematodiasis-resistant Pinus massoniana from Anhui Academy of Forestry and Forestry Technology Extension and Farm tourism Service Center of Linhai in Zhejiang Province, and the construction of a core collection of the germplasm resources, is aimed to provide a theoretical basis for the scientific management and efficient utilization of germplasm resources of P. massoniana. Method First, a total of 114 resistant P. massoniana germplasms were detected before their principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA), population structure and genetic diversity parameters were calculated by bioinformatics software. Then, the core collection was constructed by using M strategy and random sampling strategy so that a comparative analysis was conducted of the genetic diversity indicators of different core collection in order to determine the most suitable construction method. Result 115 alleles were detected in 114 resistant P. massoniana germplasms, with an average effective allele number (Ne) of 5.54, an average Shannon’s diversity index (I) of 1.51, and an average PIC value of 0.90 for polymorphic information content, which had a high genetic diversity. The population structure analysis based on Structure software showed that the 114 resistant P. massoniana germplasm resources were divided into four subgroups, and the result of principal coordinate analysis was basically consistent with the above. Based on the genetic diversity parameters and the sampling quantity, the core collection constructed by the M strategy could retain the maximum genetic diversity of the original germplasm with the minimum sampling quantity, which was the optimal sampling strategy. 72 core collections were obtained using this strategy, which retained 100% alleles of the original germplasm, with the ration rates of Ne, I, expected heterozygosity (He), PIC being 95.67%, 94.96%, 98.12%, 100.00%. No significant difference in genetic diversity was shown between the constructed core germplasm and the original germplasm according to the PCoA and UPGMA cluster analysis. Conclusion The level of genetic diversity of 114 resistant P. massoniana germplasm was high. The 72 core germplasm of resistant P. massoniana were constructed to remove genetic redundancy, which is conducive to the effective conservation and scientific utilization of resistant P. massoniana germplasm resources, and lays the foundation for excellent gene discovery and new cultivar selection. [Ch, 7 fig. 8 tab. 37 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 79-91.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230296
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to study the efficient utilization of nitrogen genes and the ammonium nitrogen transporter protein JrAMT2 gene, which is of great significance for variety improvement, rapid growth, and yield of Juglans regia. Method Using J. regia JrAMT2 overexpression (OE) seedlings as experimental materials, bioinformatics analysis was conducted on JrAMT2 gene. The growth and development, nitrogen absorption, chlorophyll content, and chlorophyll fluorescence of J. regia JrAMT2-OE plants were analyzed through gene expression level and phenotype determination. Result Fluorescence detection, polymerase chain reaction, and fluorescence quantitative PCR were performed on J. regia JrAMT2-OE plants to verify that the JrAMT2 gene is stably expressed in J. regia JrAMT2-OE plants. Compared with the wild type, the plant height, internode length, biomass and other growth parameters of JrAMT2-OE lines significantly increased, and the plant height and internode length of J. regia seedlings increased by 68.2% and 50.3%. The aboveground and underground biomass of JrAMT2-OE lines increased significantly, with a maximum increase of 56.26% (fresh weight) and 56.26% (dry weight) in the aboveground parts, and a maximum increase of 344.38% (fresh weight) and 354.33% (dry weight) in the underground parts. The uptake of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in the underground part of J. regia JrAMT2-OE significantly increased by 114.1% and 70.3% respectively. The JrAMT2 gene mediated the transport of ammonium nitrogen from the underground part to the aboveground part, and the content of ammonium nitrogen in the aboveground part increased significantly, up to 59.1%. The ratio of chloroplast surface area to monolayer cell surface area and chlorophyll content of JrAMT2-OE increased significantly, with the highest increase of 22.94% and 74.3%. The analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters showed that the activity, quantum yield and electron transfer efficiency of the oxygen-reactive body in the leaves of J. regia JrAMT2-OE plants significantly improved. Conclusion The JrAMT2 gene of J. regia plays a significant role in the growth and development, nitrogen absorption and photosynthesis of J. regia seedlings. [Ch, 9 fig. 2 tab. 41 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 92-103.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230169
Abstract:
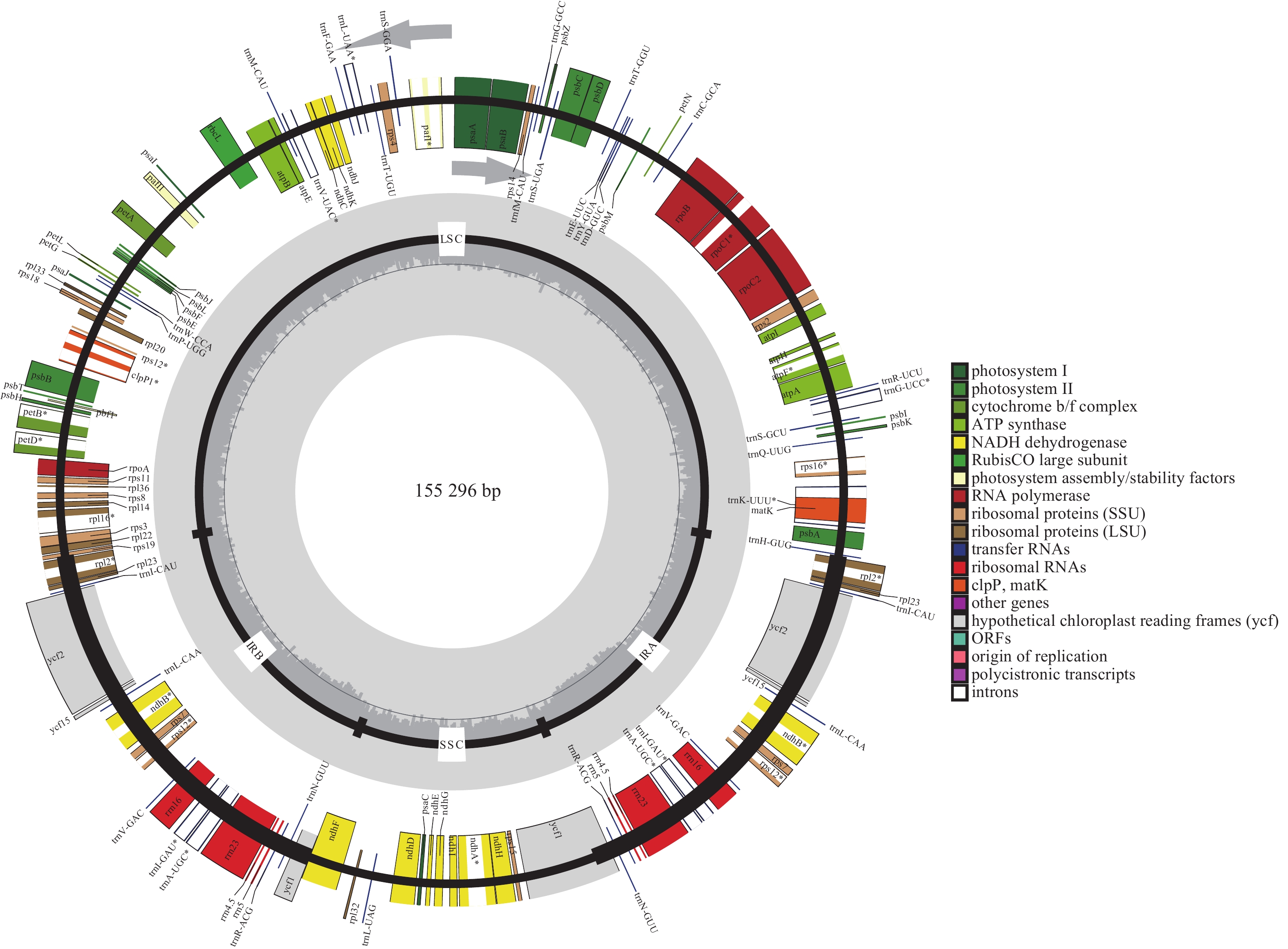
Objective This study aims to analyze the chloroplast genome characteristics and codon usage preference of Solanum tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’, so as to provide a reference and theoretical basis for future research on chloroplast genome codon optimization, chloroplast genome modification, exploration of species evolution, and increased expression of exogenous genes. Method The chloroplast genome of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’ was sequenced by high-throughput sequencing technology. The structure, gene composition and codon preference of the assembled and annotated chloroplast genome were analyzed using bioinformatics analysis software. Result The chloroplast genome size of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’ was 155 296 bp, which was a classical 4-segment structure. The length of large single copy region (LSC), small single copy region (SSC) and inverted repeat region (IR) was 85 737, 18 373 and 25 593 bp respectively, and the proportion of total guanine and cytosine (GC ratio) was 37.88%. A total of 133 genes were released, including 87 CDS genes, 37 tRNA genes, 8 rRNA genes and 1 pseudogene. A total of 38 simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci (36 single base repeats and 2 double base repeats) and 32 long repeat sequences (16 forward repeats and 16 palindrome repeats) were detected in the chloroplast genome of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’. The variation range of nucleotide diversity of chloroplast genome of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’ was 0 − 0.139 27. The hypervariable regions were mainly distributed in LSC and SSC regions. LSC region had the highest mutation rates of trnL-UAA-trnF-GAA, cemA, rps12-exon1-clpP1 and clpP1 genes, while SSC region had the highest mutation rates of rpl32-trnL-UAG and ycf1 genes. The average effective number of codon (ENC) value of 87 CDS genes in the chloroplast genome of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’ was 47.29, and there were 60 genes with ENC value larger than 45, indicating weak codon preference. The preference for codons ending with A and U in the chloroplast genome of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’ was largely affected by natural selection, and less affected by mutation pressure. CGU, AAA, CUU, GUU, GGA, GUA, GGU, UCA, GCU, and CCU were the 10 best codons in the chloroplast genome of S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’. Conclusion S. tuberosum var. cormosus ‘Huaiyushan’ has a close genetic relationship with S. tuberosum ‘Desiree’. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 41 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 104-112.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230355
Abstract:
Objective Phosphatidic acid (PA) serves as an important signal molecule involved in the regulation of plant growth and development and different responses to various stresses as well as a general precursor for glycerolipid biosynthesis. However, little is known thus far about the dynamic changes of PA in plant cells. This study attempted to construct a fluorescent probe that can effectively monitor the changes of PA in plant cells and use it to measure the changes of intracellular PA under saline-alkaline stresses. Method The corresponding nucleotide sequence for PA-specific binding domain within the Spo20p protein was fused to the green fluorescent protein gene. Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana lines bearing the fusion gene under the control of the constitutive promoter UBQ10 was then generated via genetic transformation. The resulting fusion protein constituted a fluorescent probe specifically binding to PA. Subsequently, this probe was employed to monitor the changes of cellular PA under saline-alkaline stresses. Result Seven transgenic A. thaliana lines homozygous for single insertion of the fusion gene was generated. Real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis showed that expression levels of the fusion gene varied among different lines. Experiments with various exogeneous PA concentrations revealed that as the expression level of the PA probe increased, it could effectively monitor the changes of cellular PA in the root tips treated with 2 μmol·L−1 exogenous PA for 10 min, whereas this was not the case when the expression level of the probe was low, indicating that the sensitivity of the probe for PA detection is, to a certain degree, associated with its expression level. Based on this fluorescent PA probe, PA accumulation at the plasma membrane or in the intracellular space was evident in the root tips under saline-alkaline stresses for 5 min, implying that PA may play important roles in early plant responses to saline-alkaline stresses. Conclusion A fluorescence probe for effective monitoring of cellular PA was developed in this study. This probe can monitor the alterations in cellular PA level during early plant responses to saline-alkaline stresses, thereby providing a new tool to study early responses to various stresses. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 36 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 113-123.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230213
Abstract:
Objective Prunus mume is an ornamental and fruit plant widely cultivated in China. The aim of this study is to select and evaluate P. mume cultivars with both flower and fruit functions, so as to provide basis for fruit processing and utilization. Method The 28 P. mume cultivars were selected as research object. Flower traits, fruiting capacity, fruit quality indexes were measured and evaluated by principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Result The flower diameter of 28 cultivars ranged from 19.14 to 31.38 mm, with 5−23 petals. White cultivars accounted for the largest proportion. There were significant differences in fruit setting among P. mume cultivars, with ‘Lijiang Zhaoshui’, ‘Yulong Hongfei’ and ‘Yulong Feixue’ being more prone to fruit setting. In addition, there were differences in fruit appearance and internal quality among different P. mume cultivars. Principal component analysis was conducted on 28 cultivars, and 16 indexes were simplified into 4 common factors, with a variance explanation percentage of 82.72%. The comprehensive scores showed that ‘Die Yuchong’, ‘Gu Lihong’, ‘Danfen Chuizhi’, ‘Hongyan Zhusha’, ‘ZAFU-CZ02’, ‘Jiangmei’ and ‘Lijiang Zhaoshui’ had higher scores. Cluster analysis showed that when the Euclidean distance was 24, P. mume cultivars could be divided into 6 groups. Based on the results of principal component and cluster analysis, 4 excellent varieties for both flower and fruit use were selected, including ‘Danfen Chuizhi’, ‘Lijiang Zhaoshui’, ‘Gu Lihong’, and ‘Hongyan Zhusha’. Conclusion There are differences in flower traits, fruit setting and fruit quality among different P. mume cultivars. According to the comprehensive characteristics of the flower, fruit yield, and fruit quality, it can be concluded that ‘Danfen Chuizhi’ and ‘Lijiang Zhaoshui’ are easy to bear fruit and have the best comprehensive fruit quality. They are excellent suitable for both flower and fruit. ‘Gu Lihong’ and ‘Hongyan Zhusha’ have bright flower color, with semi double petals and easy to bear fruit. They are suitable for flower and fruit production. [Ch, 6 fig. 6 tab. 30 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 124-131.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230308
Abstract:
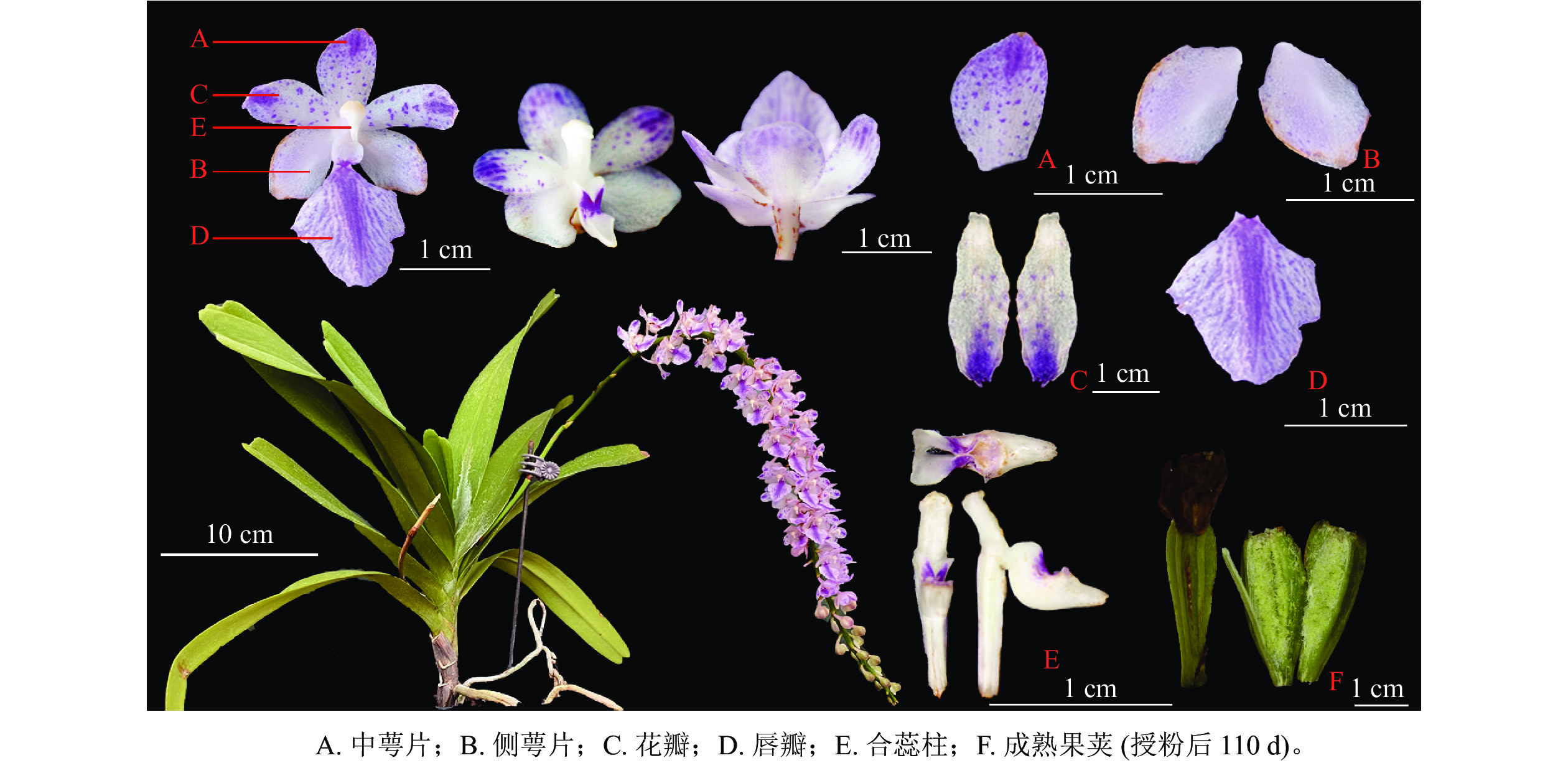
Objective This study, with an investigation of the breeding system of the Aerides rosea, is aimed to provide theoretical basis for the protection of its germplasm resources. Method The floral characteristics and flowering process of A. rosea under greenhouse cultivation conditions were carefully observed and recorded before the breeding characteristics were studied through the detection of pollen viability and stigma acceptability, and the estimation of hybridization index (OCI) and test of artificially pollination. Result (1) A. rosea blossomed from May to July with fragrance and the florescence of a single plant lasted about 15 d and that of a single flower lasted about 10 d, with the bud stage being 1−5 d before flowering, the initial flowering stage of 1−4 d after flowering, the full flowering stage of 5−6 d after flowering, the final flowering stage of 7−8 d after flowering, and the fade stage of 9−10 d after flowering. (2) A. rosea belonged with raceme with each plant having 1−4 inflorescences which were featured as long and densely packed with dozens of flowers, with a consistent flowering period throughout the entire plant. (3) During the bud stage before flowering, the pollen already displayed viability and stigma pollinability which reached the highest at 5−6 d of flowering and the OCI of A. rosea was 4. (4) The fruit set rate was 0 without artificial pollination, while the fruit set rate for those with artificial self-pollination, artificial cross-pollination of the same plant and artificial cross-pollination of the different plants was 85.71%, 88.00% and 84.00% respectively, higher than the ones without artificial pollination. Conclusion The flowering of A. rosea started in early May and ended at the end of July with a relatively short flowering period of about 2 d and the breeding system was a mixed mating system of self-pollination and cross-pollination that required pollinators to mix. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 22 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 132-144.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230301
Abstract:
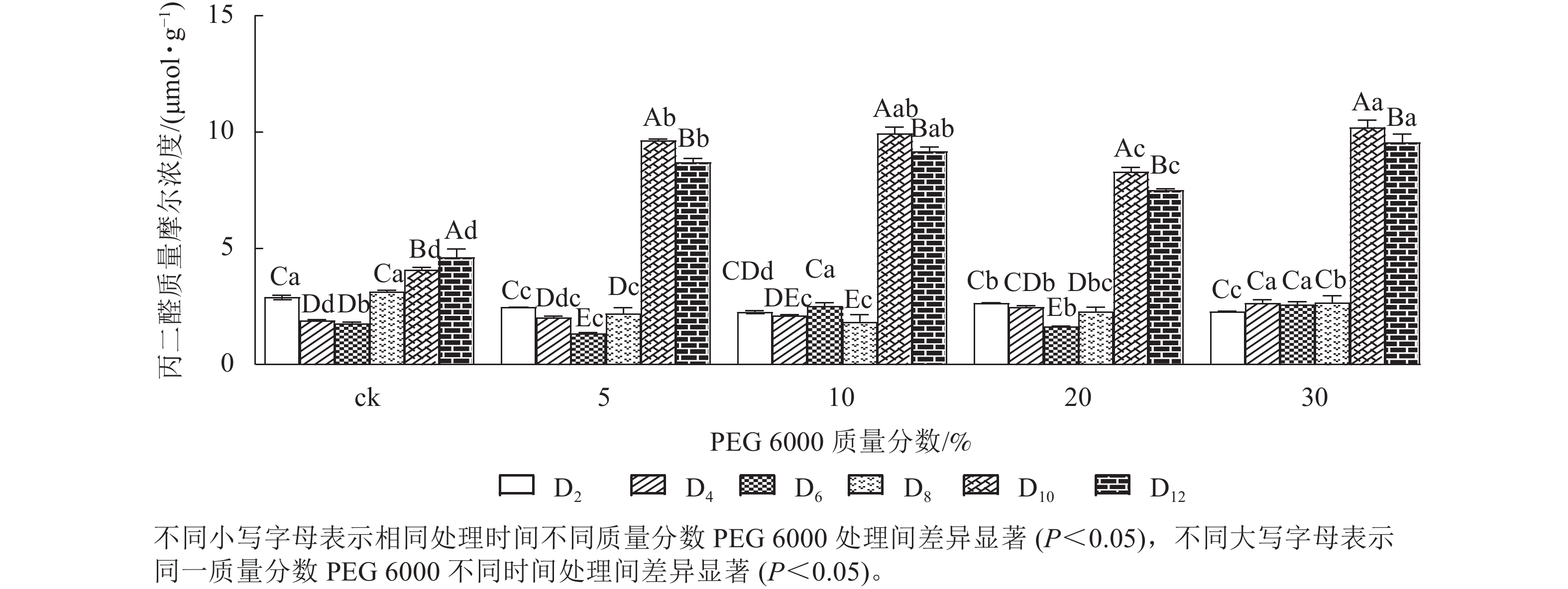
Objective The objective is to study the effects of PEG 6000 simulated drought on physiological and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Dendrobium candidum, so as to provide reference for variety selection, industrial cultivation, and near wild cultivation of D. candidum. Method The seedlings of D. candidum ‘Jingpin No. 1’ were used as experimental materials and treated with PEG 6000 at different concentrations to simulate drought stress. The stem segment and leaf cell structure of D. candidum seedlings were observed, and the dynamic changes of peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT) activity, malondialdehyde (MDA), soluble sugar, soluble protein, chlorophyll content and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in D. candidum leaves were detected. Result (1) The content of chlorophyll in the stem and leaf cells of D. candidum decreased after treatment with high concentration of PEG 6000 (20%−30%). (2) PEG 6000 simulated drought stress significantly affected the content of soluble sugar and protein, MDA, POD and CAT activity of D. candidum seedlings. The soluble sugar content increased with the increase of PEG 6000 concentration and the extension of treatment time, reaching its highest value on the 12th day, while the soluble protein showed a downward trend. MDA content, POD and CAT activity increased first and then decreased with the increase of PEG 6000 concentration, reaching the peak at a PEG 6000 concentration of 20%. (3) PEG 6000 simulated drought treatment of D. candidum seedlings significantly affected chlorophyll fluorescence parameters such as maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), photosynthetic efficiency (α), electron transfer rate (ETR), photochemical quenching coefficient (qP) and non-chemical quenching coefficient (qNP). With the extension of PEG 6000 stress treatment time and the increase of PEG 6000 concentration, α, ETR, Fv/Fm and qP showed a significant downward trend, while qNP showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. Conclusion 20% PEG 6000 treatment for 12 days can be used as a method for screening drought resistant varieties of D. candidum, which can resist and adapt to a certain degree of drought stress by increasing the content of soluble sugar, reducing the content of soluble protein and improving the activities of defense enzymes such as POD and CAT. The maximum light energy conversion efficiency of D. candidum seedlings decreases, and the photosystemⅡ (PSⅡ) is damaged by stress, which seriously affect the photosynthesis of D. candidum seedlings. At the same time, D. candidum seedlings consume the excess light energy absorbed by the PSⅡ reaction center by activating the qNP pathway to maintain normal photosynthesis. Therefore, soluble sugars and protein, POD and CAT, and chloroplast fluorescence parameters can all be used as indicators of drought resistance in D. candidum. [Ch, 6 fig. 44 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 145-153.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230227
Abstract:
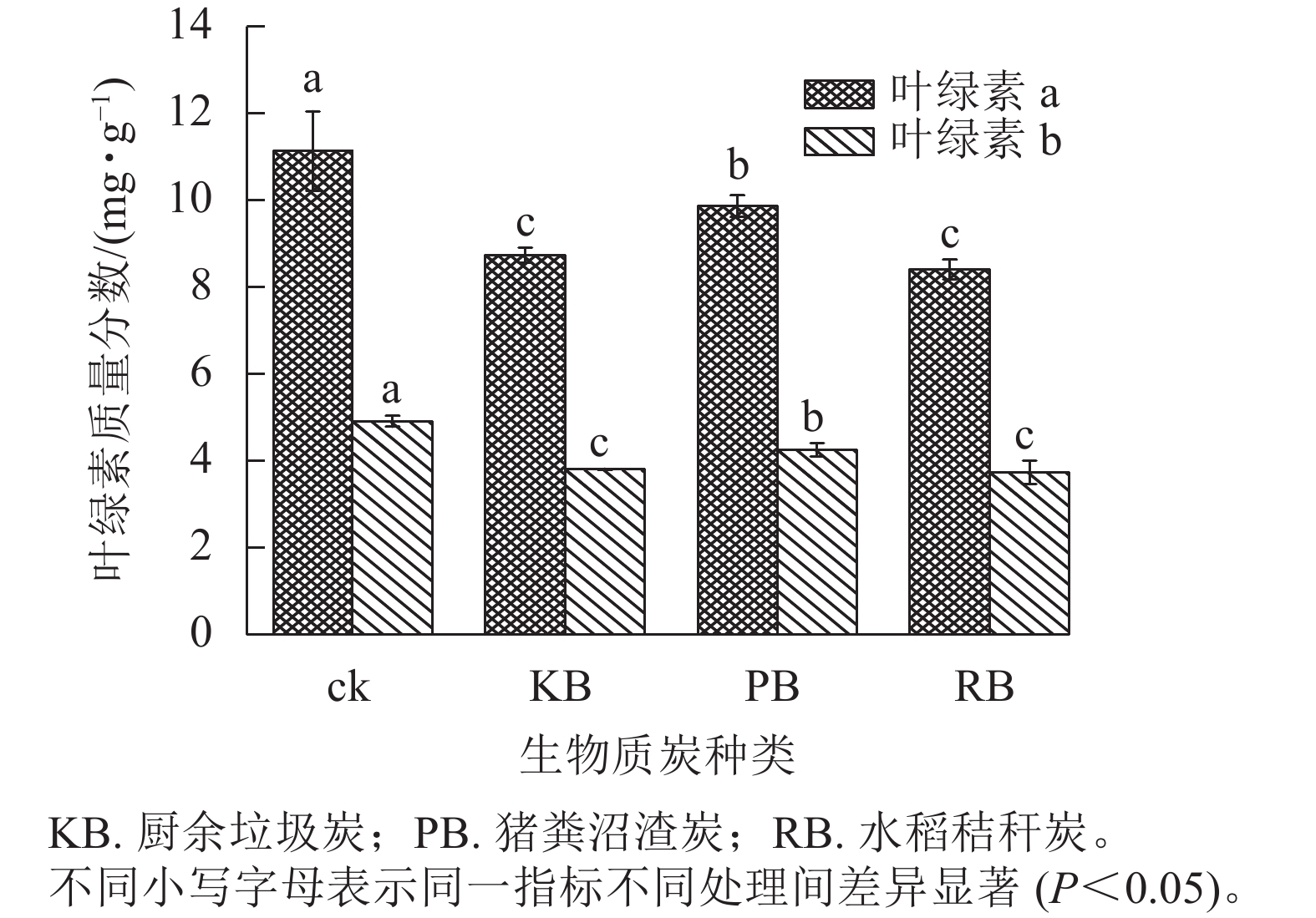
Objective This study, with an investigation of the toxic effects of biochar on seed germination and seedling growth, is aimed to provide a theoretical basis for the potential screening of typical organic waste carbonization in agriculture and the safe use of dosage, which is conducive to the safe application of biochar in agriculture. Method With kitchen waste biochar (KB), pig manure biogas digestion residues derived biochar (PB), and rice straw biochar (RB), chosen as the raw materials and the control group treated with deionized water, an assessment was conducted of the influence of biochar extracts with different solid-liquid ratios (1∶20, 1∶50, 1∶100, m/V) on seed germination and seedling growth of radish (Raphanus sativus). Result Compared with the control without biochar extracts, the biochar extracts with the solid-liquid ratio of 1∶100 have no significant effect on radish seed germination and seedling growth but those with the solid-liquid ratio of 1∶20 and 1∶50 inhibit the radish seed germination significantly (P<0.05). The seedling fresh weight, root length, and seedling length cultured by biochar extracts with a 1∶50 solid-liquid ratio were reduced by 29.55%−51.89%, 20.77%−76.04%, and 37.73%−56.01%, respectively, indicating a significant growth inhibition effect of biochar extracts (P<0.05). When cultured with 1∶20 biochar extract, the survival rate of radish seedlings was lower than 12%. The inhibitory effects of different kinds of biochar reduced in the following order: kitchen waste biochar>rice straw biochar>pig manure biogas digestion residues derived biochar. The pH, total concentration of inorganic salts, As, Na, and K concentration of the extract solution were negatively correlated with radish seed germination and seedling growth (P<0.05) and served as the main factors inhibiting radish growth. The root activity of radish seedlings cultured with the 1∶50 solid-to-liquid ratio decreased whereas the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) increased, indicating the destruction of seedling root cell membranes and the occurrence of resultant lipid peroxidation. Conclusion The biochar extracts with a high solid-liquid ratio (>1∶50, m/V) had toxic effects on radish seed germination and seedling growth. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 29 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 154-160.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230219
Abstract:
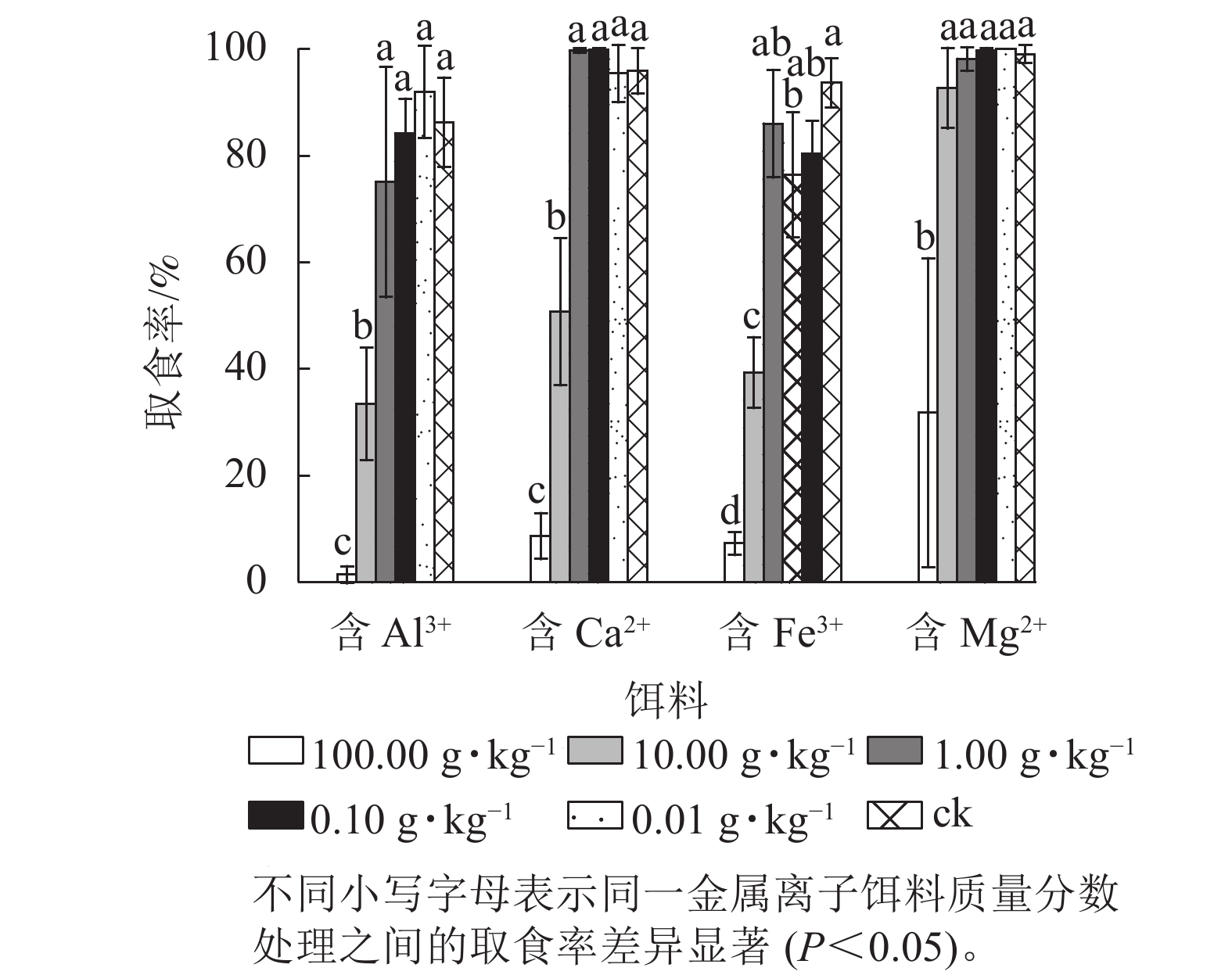
Objective This study aims to explore the role of metal ions in influencing the digestive generation process of Odontotermes formosanus, which is beneficial to explore the potential value of resource treatment of agricultural and forestry waste and kitchen waste containing metal ions by O. formosanus. Method According to the concentration gradient method, the bait containing different mass fraction of Al3+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Mg2+ was fed to O. formosanus to determine the maximum edible mass fraction of metal ions in bait for O. formosanus. ICP-OES was used to measure the corresponding metal elements in O. formosanus body and new-built fungus combs, and to obtain the effects of feeding baits containing Al3+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Mg2+ on the corresponding metal elements mass fraction in O. formosanus body and new-built fungus combs. The activities of laccase and cellulase in O. formosanus body and new-built fungus combs were determined by kit method, and the effects of feeding baits containing Al3+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Mg2+ on the activities of these enzymes were determined. Result The maximum edible mass fraction of Al3+, Ca2+ and Fe3+ in baits of O. formosanus was 1.00 g·kg−1, and Mg2+ in baits was 10.00 g·kg−1. Mg enrichment occurred both in O. formosanus body and new-built fungus combs after feeding baits containing 10.00 g·kg−1 Mg2+; Fe was only enriched in new-built fungus combs after feeding baits containing 1.00 g·kg−1 Fe3+. The laccase activity in O. formosanus body improved significantly after feeding baits containing 1.00 g·kg−1 Al3+. The laccase activity in O. formosanus body improved significantly, but the cellulase activity reduced significantly after feeding baits containing 1.00 g·kg−1 Ca2+. The laccase activity in O. formosanus body and cellulase activity in new-built fungus combs improved significantly, but the laccase activity in new-built fungus combs and cellulase activity in O. formosanus body reduced significantly after feeding baits containing 1.00 g·kg−1 Fe3+. The cellulase activity in O. formosanus body and the laccase activity in new-built fungus combs improved significantly, but the cellulase activity in new-built fungus combs reduced significantly after feeding foods containing 10.00 g·kg−1 Mg2+. Conclusion O. formosanus can feed on baits containing 1.00 g·kg−1 Al3+, Ca2+ or Fe3+ or 10.00 g·kg−1 Mg2+, and 1.00 g·kg−1 Al3+ can improve the combined degradation of lignin by O. formosanus and fungus-comb microbiome. O. formosanus have application potential for resource treatment of agricultural and forestry waste and kitchen waste. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 30 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 161-168.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220758
Abstract:
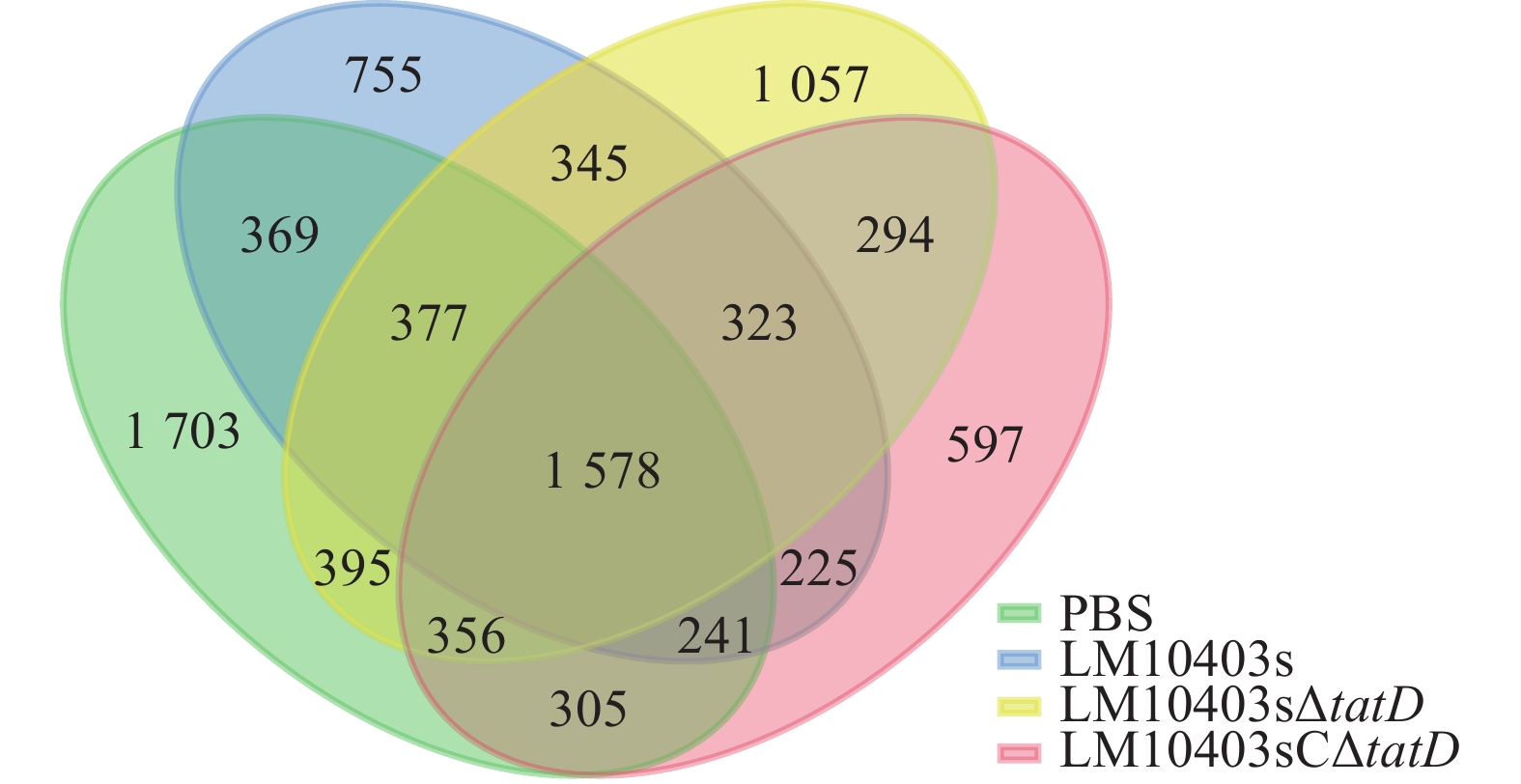
Objective This study, with an investigation of the effects of tatD gene deletion in Listeria monocytogenes on virulence and gut microbiota in mice (Mus musculus), is aimed to provide reference for the role of tatD in the interaction between L. monocytogenes and the host, as well as for the study of attenuated vaccines. Method First, mice were orally infected with LM10403s, LM10403sΔtatD and LM10403sCΔtatD strains using the Bliss method to determine the strain’s median lethal dose (LD50) for mice before immunoprotective effect of LM10403sΔtatD was observed in mice immunized with 1.00×105 CFU orally. Then, forty 6-week-old female mice were randomly and equally divided into PBS (ck), LM10403s, LM10403sΔtatD, and LM10403sCΔtatD groups, with those in the ck group gavaged with 200 μL of sterile PBS and the ones in the experimental group gavaged with 200 μL of bacterial solution containing 1.00 × 106 CFU, respectively. Next, after 24 h of gavage, the mice in each group were dissected and killed, with intestinal contents collected before Illumina Hiseq sequencing technology was used to determine the sequences of the microbial 16S rRNA V3−V4 regions of the cecum samples from each group so that a comparative analysis was conducted of the structure of microbial communities, diversity, and signaling pathway enrichment. Result The LD50 of LM10403sΔtatD was 8.11×107 CFU, which was less virulent than that of the parental strain. Oral immunization of mice with LM10403sΔtatD provided 80% protection against L. monocytogenes parental strain infection. Chao1 and Observed species indices showed that the difference between ck and LM10403sΔtatD group was not significant, but LM10403s and LM10403sCΔtatD group were significantly lower compared to ck group (P<0.05). At the phylum level, the relative abundance of the Firmicutes in LM10403sΔtatD group was higher than that in LM10403s and LM10403sCΔtatD group, and at the genus level, the relative abundance of the genus, Lactobacillus in LM10403sΔtatD group was higher than that in LM10403s and LM10403sCΔtatD group functional prediction analysis showed that LM10403s group in signaling pathways including cellular processes, environmental information processing, and metabolism was more enriched than the LM10403sΔtatD group. Conclusion The deletion of tatD gene reduced the virulence of L. monocytogenes and had animmuno protective effects while infection of the tatD gene deletion mutant strain in mice reduced the effect on intestinal flora dysbiosis and increased the beneficial bacteria. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 21 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 169-175.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230236
Abstract:
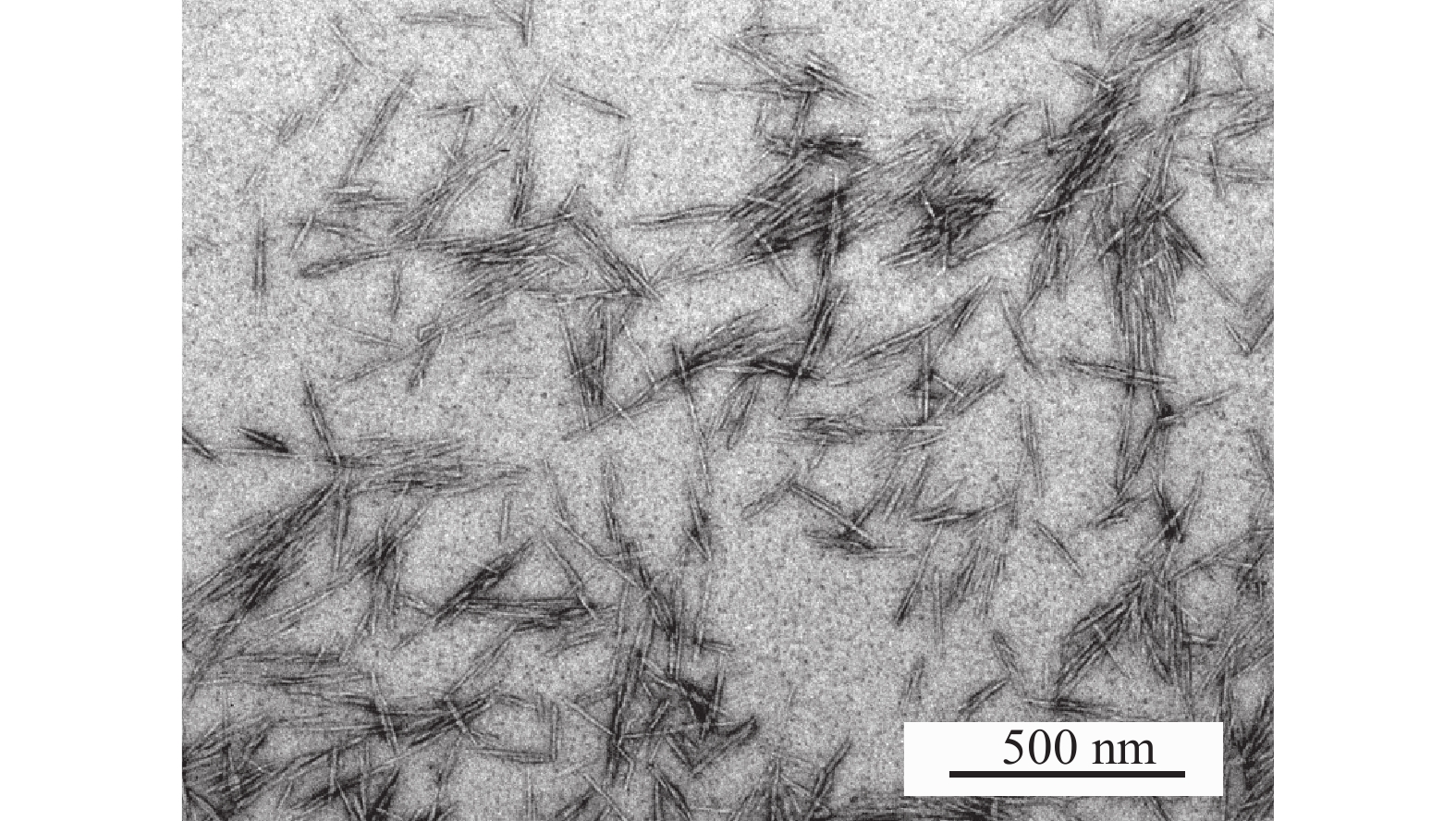
Objective Cellulose nanocrystalline (CNC) liquid crystal film, as a kind of photonic crystal with special optical properties, has a promising prospect in the fields of anti-counterfeiting technology, photoelectric functional materials and humidity responsive functional materials. This study, with an exploration of the influence of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the humidity response of CNC liquid crystal films, is aimed to explain its response mechanism to provide a theoretical basis for the development of low-cost, reusable and highly sensitive PEG/CNC composite film humidity sensors. Method The chiral nematic photonic liquid crystal films with humidity response were prepared by evaporation-induced self-assembly of PEG/CNC suspension, and the effects of PEG content on the microstructure, color evolution, mechanical properties and humidity response of the PEG/CNC films were investigated. Then, the cyclic properties of PEG/CNC liquid crystal films under different humidity conditions were studied. Result For pure CNC film system, with the increase of CNC content from 3% to 7%, the pitch of CNC liquid crystal film decreased, and the maximum wavelength of reflected light shifted from 596.5 nm to 511.0 nm. For PEG/CNC films, with the increase of PEG content, the pitch of PEG/CNC composite liquid crystal film decreased from 394.0 nm to 244.0 nm while the maximum wavelength of reflected light moved from 613.5 nm to 350.5 nm. The toughness increased first and then decreased, the optimal PEG addition amount was 5%, the breaking energy was 31.9 J·m−2 which was 138% higher than that of pure CNC film. After 5 hygroscopic and dehumidifying experiments, the PEG/CNC film showed good humidity response repeatability with the change rate of the equilibrium wavelength being lower than 0.6%. Conclusion An iridescent photonic PEG/CNC liquid crystal film for humidity sensing were prepared, and it was found that PEG can regulate the structural colour by modulate the pitch of the composite film. [Ch, 6 fig. 25 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 176-182.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230280
Abstract:
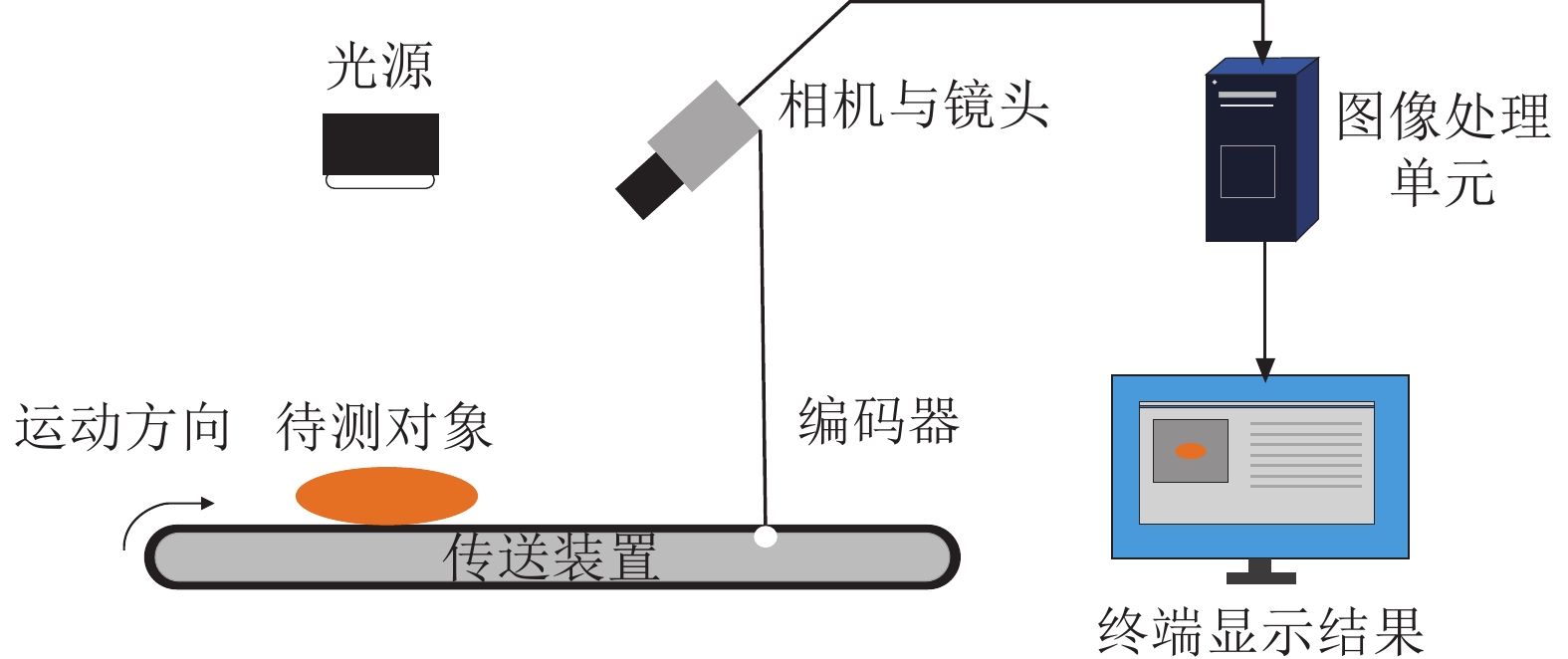
Objective Aiming at the problems of low detection efficiency, low accuracy and digital storage of detection results in the manual detection of surface defects of panel furniture parts, a surface defect detection method of veneer wood-based panel based on image segmentation and deep learning algorithm was proposed. Method The defect data set was constructed by the artificial panel images collected by industrial cameras. The global threshold and local dynamic threshold algorithms were used to segment surface defects and image interceptions. The ReLU6 nonlinear activation function was replaced by ReLU function, and the method of reciprocal residual structure was introduced to optimize the MobileNetv 2 deep learning network, and the defect identification and classification were carried out. Result The accuracy of the algorithm for the detection of edge breakage and scratch defects on the surface of the veneer panel is 93.1% and 97.5%, and the recall rate is 95.3% and 97.6%, respectively. The average detection time of a single sheet is 163 ms. Conclusion The method has high precision and stability, which can solve the problems of low accuracy and low efficiency of traditional manual detection methods, and provide a new idea for automatic detection of surface defects of furniture panels. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 21 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 183-191.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230248
Abstract:
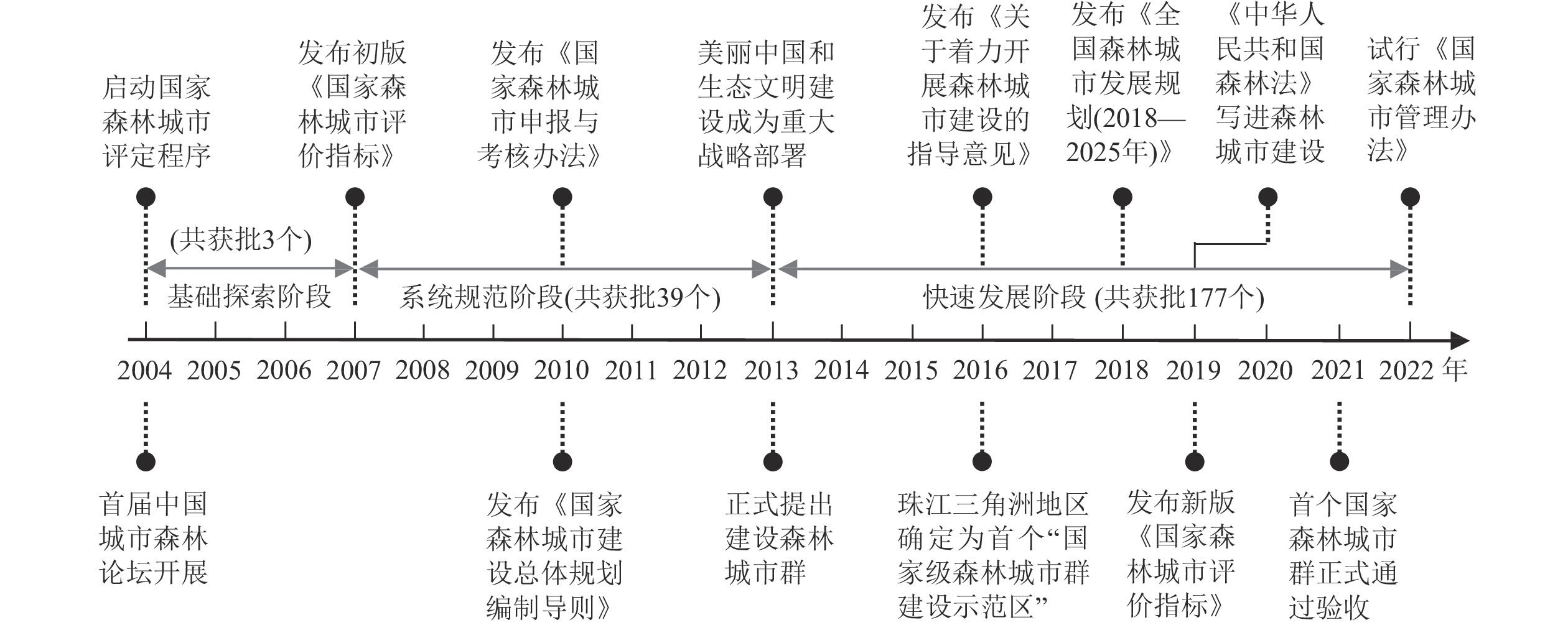
Objective This study, with an analysis of the courses, characteristics, and motivations of the spatiotemporal evolution of 219 national forest cities, is aimed to countermeasures and suggestions for the current imbalance in the spatial distribution of national forest cities so as to promote the coordinated development of China’s ecological, economic, and social systems. Method First, development stages and construction concepts of national forest cities were determined from the macro perspective of China’s social and economic development with an analysis of the literature and the survey of history. Then, kernel density estimation, Gini coefficient, and standard deviation ellipse were employed to analyze the spatial evolution characteristics of national forest cities. At last, an exploration was conducted of the factors affecting the space-time evolution of national forest cities with the employment of overlay analysis, matrix analysis and SPSS. Result (1) The macro development stage can be summarized into three stages, namely basic exploration, system standardization, and rapid development whereas the construction concepts were featured with three changes: from fragmentation to integration, from transition to natural wind and from green to live. (2) In terms of the evolution of spatial quantity, administrative regions covered five levels, the quantity distribution was highly consistent with the “Hu Huanyong Line”, and the number of gathering centers had increased. (3) The evolution of spatial situation was featured with agglomeration, directionality and linkage, displaying the linkage development mode of “breakthrough on the point, connection on the line and expansion on the whole”. Conclusion In terms of administrative power, the government provides support and guidance for the construction of national forest cities through policy regulation and concept upgrading; the natural binding force and social driving force determine whether the city has the necessary conditions to develop into a high-quality and low-cost national forest city, and determine the quantity distribution and spatial evolution trend of them whereas the urban transformation force provides a starting point for the upgrading of national forest cities in accordance with the needs of the masses. This study has also put forward the countermeasures and suggestions to promote the balanced development of national forest cities on the basis of motivation analysis. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 22 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 192-201.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230274
Abstract:
Objective This study, on the basis of landscape resource evaluation and multi-objective planning, is aimed to carry out the optimization of forest park functional zoning so as to provide technical support for future work. Method Taking Da’anding Forest Park as an example, an evaluation was conducted of the eco-resilience, visual sensitivity and landscape beauty of each landscape unit. The results were then, through linear transformation, translated into the suitability of four management countermeasures namely, key protection, maintaining the status quo, local regulation and construction and reconstruction. Finally, the multi-objective planning method (VMP) was used to investigate the optimal management countermeasures for each landscape unit. Result (1) The evaluation index system of ecological landscape quality of forest parks was established with eco-resilience, visual sensitivity and landscape beauty as the core suggesting that the overall level of ecological resilience and visual sensitivity of Da’anding Forest Park was high, but regional differences were large. The scenic beauty was high, but the regional differences were small. (2) A linear transformation model of attribute index management countermeasure suitability was proposed to realize the transformation from multi index evaluation results to the suitability of park functional zoning. (3) The multi-objective programming method was used to seek for the optimal solution for the management of 20 landscape units in the study area, with the optimization results highly coupled with the actual landscape situation. (4) Of the five multi-objective planning methods, the ideal point method, the objective planning method and the fuzzy planning method belonged to one group whereas the efficacy function method and the maximum minimum method belonged to the other group, with the fuzzy programming method showing the best balance and thus recommended in practice and the internal planning results of the two groups are basically the same, with slight differences in between. Conclusion The results obtained from the research on the evaluation of the ecological landscape quality of forest parks were converted into attribute index-countermeasure suitability, the optimal solution of management countermeasures was achieved at the global and landscape unit levels by using multi-objective planning, and the results were highly coupled with the actual situation. Besides, of five common multi-objective planning methods, ideal point method, objective planning method and fuzzy planning method performed well, with the performance of the fuzzy planning method being the best. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 202-210.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220741
Abstract:
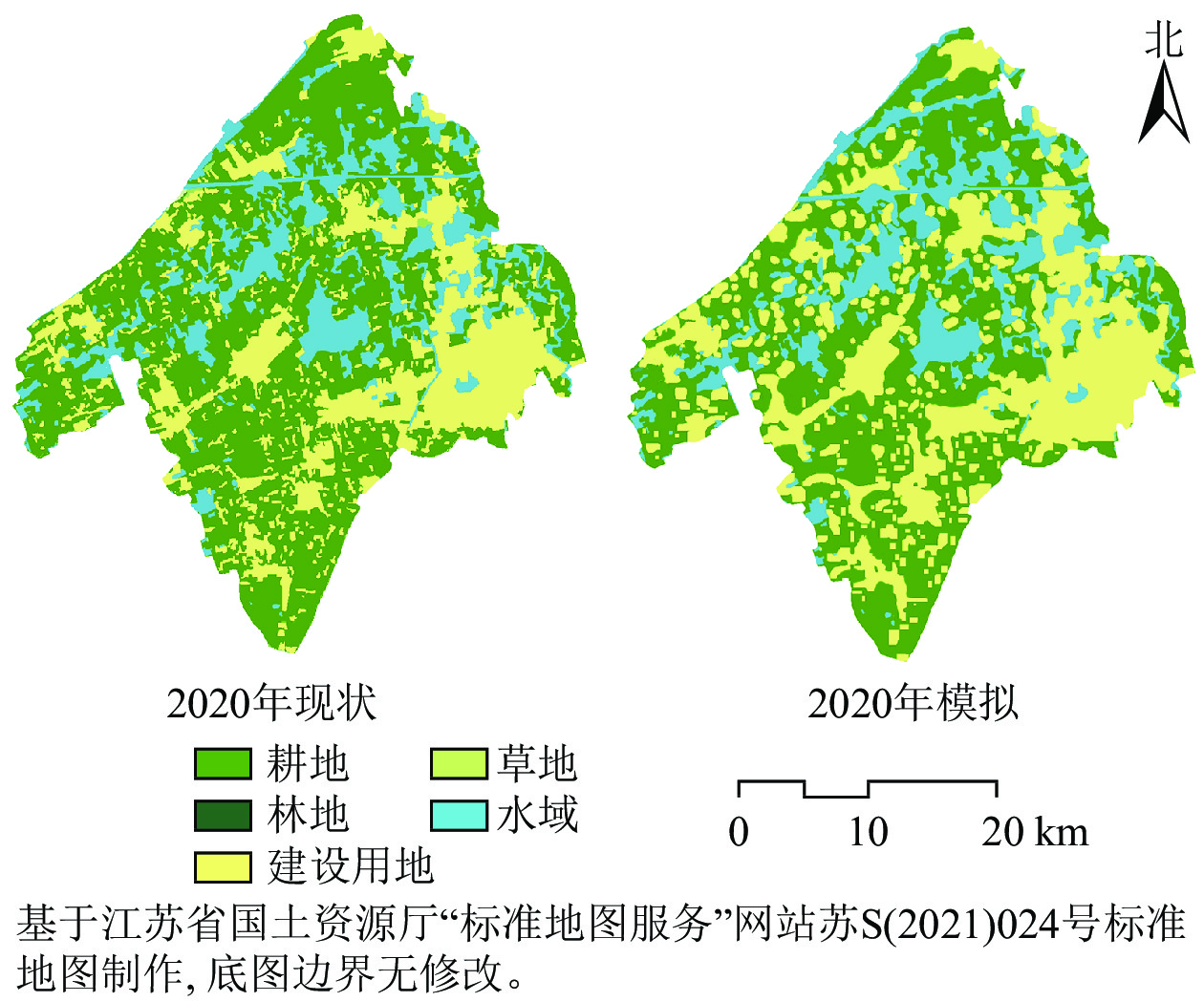
Objective The objective is to simulate and predict the multi-scenario development trend of the blue-green spatial pattern in the southern Jiangsu water network area, and explore scenario plans to promote sustainable development in the region. Method Taking the southern Wujiang District of Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province as sampling area, three scenarios were set up: natural development, ecological protection priority, and urban development priority. Based on CA-Markov model, a multi-scenario simulation analysis was conducted to simulate and analyze the changing trend of the blue-green spatial pattern in 2030. Morphological spatial pattern analysis (MSPA) and landscape connectivity evaluation were used to interpret the ecological structure and characteristics of the blue-green spatial landscape. Result There were significant differences in the scale and pattern of the blue-green space under different development scenarios. Under the priority scenario of natural development and urban development, the area of the blue-green space showed an accelerated reduction trend, with a reduction of 3 626.37 and 7 145.74 hm2 respectively. The shape types of the core area and pore of the blue-green space changed sharply in the negative direction, resulting in an increase in fragmentation and a decrease in connectivity in the blue-green space. Compared with the priority scenarios of natural development and urban development, the priority scenario of ecological protection increased the area of the blue-green space by 2 904.30 and 6 423.67 hm2, and the core area of the blue-green space and other morphological types increased significantly, with a significant reduction in porosity, a reduction in the fragmentation of the blue-green space, and an increase in connectivity. Conclusion The priority scenarios of natural development and urban development have a negative impact on the blue-green space in the water network area, and the priority scenario of ecological protection has a significant effect on maintaining the stability of the area and pattern of the blue-green space and improving its connectivity. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 23 ref.]
2024, 41(1): 211-222.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230380
Abstract:
Atmospheric nitrogen (N) deposition is a global threat to biodiversity and ecosystem function. Since emission controls, N deposition has decreased or stabilized in European and North America, and China began to be stabilized in 2010. The future trajectory of N deposition may differ by regions. In this study, literature retrieval and extensive analytic methods were used to analyze N deposition recovery. The reaction of the forest ecosystem’ s soil (acidification and solution chemistry), structure (vegetation-microbial diversity), and function (productivity and carbon sequestration) to decreasing N deposition was studied. Soil solution chemistry (e.g., nitrate and ammonium concentrations, etc.) may responded very rapidly to reducing N input, whereas plant species composition, soil microbial communities, and soil processes may be slow in recovery. When N deposition is controlled, soil acidification can be reduced, and tree growth can be promoted. It is also possible that the vitality of plant may still deteriorating and soil acidity persists due to high rate of atmospheric N deposition. Restoration of plant diversity may face potential barriers to recovery and maintain eutrophication in the short term, but it supports the rise of species in a nutrient-poor. The response of forest ecosystem restoration to emission reduction strategies is delayed. The legacy of earlier N deposition result in a slow recovery, but recovery is simply a matter of time. Therefore, recovery from high N loads is a long and sluggish process, and further emission reduction efforts is still needed in the future. [Ch, 94 ref.]
Atmospheric nitrogen (N) deposition is a global threat to biodiversity and ecosystem function. Since emission controls, N deposition has decreased or stabilized in European and North America, and China began to be stabilized in 2010. The future trajectory of N deposition may differ by regions. In this study, literature retrieval and extensive analytic methods were used to analyze N deposition recovery. The reaction of the forest ecosystem’ s soil (acidification and solution chemistry), structure (vegetation-microbial diversity), and function (productivity and carbon sequestration) to decreasing N deposition was studied. Soil solution chemistry (e.g., nitrate and ammonium concentrations, etc.) may responded very rapidly to reducing N input, whereas plant species composition, soil microbial communities, and soil processes may be slow in recovery. When N deposition is controlled, soil acidification can be reduced, and tree growth can be promoted. It is also possible that the vitality of plant may still deteriorating and soil acidity persists due to high rate of atmospheric N deposition. Restoration of plant diversity may face potential barriers to recovery and maintain eutrophication in the short term, but it supports the rise of species in a nutrient-poor. The response of forest ecosystem restoration to emission reduction strategies is delayed. The legacy of earlier N deposition result in a slow recovery, but recovery is simply a matter of time. Therefore, recovery from high N loads is a long and sluggish process, and further emission reduction efforts is still needed in the future. [Ch, 94 ref.]