2023 Vol. 40, No. 6
2023, 40(6): 1149-1157.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230376
Abstract:
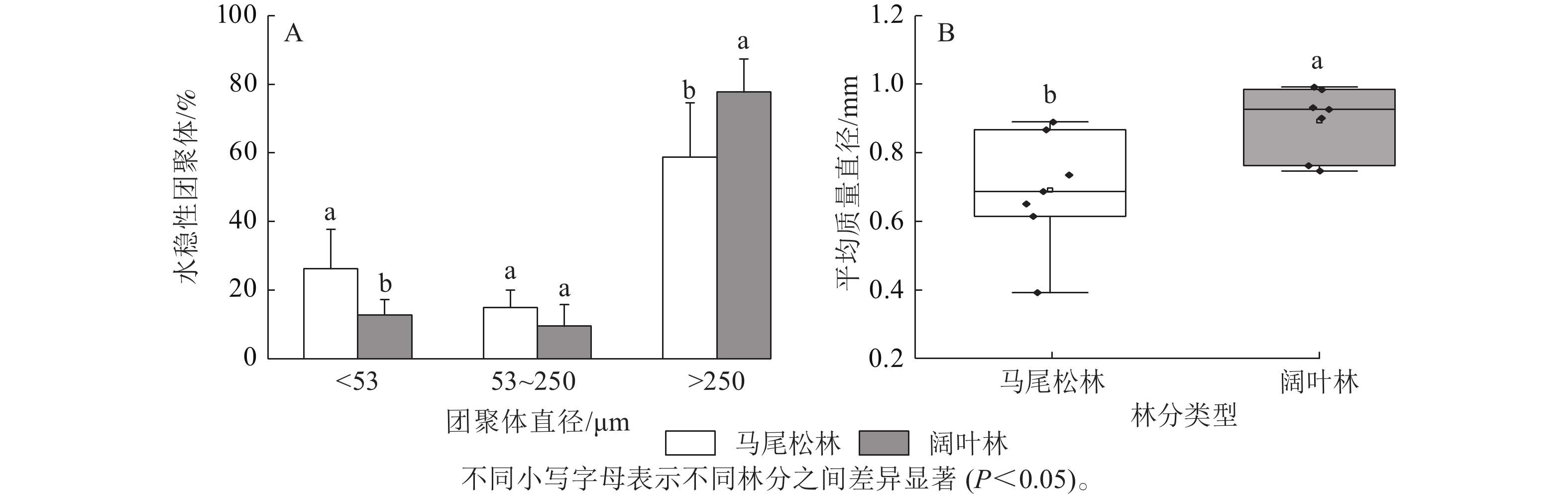
Objective It’s been observed that the transition of masson pine (Pinus massoniana) forest to broad-leaved forest generally contributes to the shift of the dominant mycorrhizal type from ectomycorrhiza (ECM) to arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM). Therefore, it’s of ecological significance to investigate the varying impact of different dominant mycorrhizal types on soil aggregate composition due to the changes in mycelial biomass and exudate, hence the current study. Method With data collected from a field experiment, analyses were conducted of soil aggregate composition as well as carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) content, mycelial biomass, and extracellular enzyme activities of three aggregate fractions. Result The conversion from masson pine forest (MF) to broad-leaved forest (BF) changed the composition and stability of soil aggregates and their carbon and nitrogen content. The proportion of macroaggregates (diameter d>250 μm) and the mean weight diameter (MWD) in BF were significantly higher than those in MF (P<0.05), while the proportion of clay (d<53 μm) and C∶N in macroaggregates showed an opposite result (P<0.05). β-glucosidase activity (BG) and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) activity were significantly higher in the MF aggregates than in the BF aggregates (P<0.05). The content of easily extractable glomalin-related soil proteins (EE-GRSP) and total glomalin-related soil proteins (T-GRSP) in macroaggregates were higher in the BF than in the MF, while in microaggregates and clay, the EE-GRSP and T-GRSP content was significantly lower in the BF (P<0.05), compared with that in MF. Soil organic carbon in aggregates was mainly related to EE-GRSP, T-GRSP, ECM biomass, and enzyme activities. Conclusion The transition of ECM-dominated masson pine forests to AM-dominated broad-leaved forests was accompanied with a significant increase in the stability of soil aggregates, and mycorrhizal biomass was associated with the content of organic C in soil aggregates. [Ch, 5 fig. 35 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1158-1166.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230179
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation into the diversity differences of rhizosphere soil fungi and root endophytic fungi in the wild population of Calanthe tsoongiana, is aimed to clarify the diversity characteristics of fungi in different growth and development stages so as to provide theoretical basis for population propagation. Method Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequencing technology was used to analyze the species composition and abundance changes of endophytic fungi communities in the rhizosphere soil and roots at the four stages of C. tsoongiana with the dominant fungi at each stage investigated. Result A total of 307 288 optimized sequences were obtained from the four periods, with an average length of 643 bp, belonging to 16 phyla, 68 classes, 176 orders, and 413 genera. At the germination stage, the dominant fungi in rhizosphere soil and root were Mortierella and Russula, respectively; Penicillium and Trechispora were the dominant fungi at the flowering stage; at the fruiting stage, the dominant fungi were Paraboeremia and Sebacina while Paraboeremia and Fusarium were the dominant fungi at the decay stage. The results of Alpha diversity index showed that the diversity and relative abundance of endophytic fungi increased from the germination stage to the fruiting stage, reaching the peak at the fruiting stage, and decreasing sharply at the declining stage. The diversity of rhizosphere soil fungi was the highest at the flowering stage, and the changes in the other three stages were relatively stable. Conclusion The diversity and richness of rhizosphere soil fungi and root endophytic fungi were significantly different during the whole growth and development period whereas flowering and fruiting fungal diversity was higher than in budding and dying. This study has provided an important reference for artificial breeding and conservation of wild resources in C. tsoongiana. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 34 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1167-1180.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220765
Abstract:
Phosphorus is an important element for biological growth and development. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are directly involved in the process of soil phosphorus activation and plant phosphorus acquisition, which is of great significance for the turnover of phosphorus nutrients in ecosystems and the formation of plant yield. In this paper, the mechanism of plant-microorganism collaboration in promoting the efficient absorption and utilization of phosphorus nutrients was summarized and analyzed from four aspects: the strategy of plant phosphorus acquisition and utilization, the coordination pathway of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for plant phosphorus absorption, the coordination pathway of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria for plant phosphorus absorption, and the synergy of plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. It was found in the analysis that the phosphorus acquisition process of plants required efficient root adaptability, which promoted soil phosphorus activation by regulating root morphological traits and changing the composition and secretion of root exudates. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi could promote the changes of soil biological activity and chemical properties in rhizosphere and hyphosphere by exchanging mutually beneficial symbiotic substances with plants, and promote plants to obtain phosphorus. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria had a positive interaction with plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at the soil interface, secreting a variety of organic acids, reducing soil pH, and increasing the activities of phosphorus activation-related enzymes to improve soil available phosphorus levels. On this basis, research prospect of plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-phosphate-solubilizing bacteria interaction to promote plant phosphorus uptake was prospected. Future research should focus on the following aspects: the role of mycorrhizal traits in the interaction system, analysis and identification of metabolite composition and potential functions of the member of the interaction system, and to explore the effects of biotic or abiotic factors on the construction and functional assembly of soil microbial community. [Ch, 141 ref.]
Phosphorus is an important element for biological growth and development. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are directly involved in the process of soil phosphorus activation and plant phosphorus acquisition, which is of great significance for the turnover of phosphorus nutrients in ecosystems and the formation of plant yield. In this paper, the mechanism of plant-microorganism collaboration in promoting the efficient absorption and utilization of phosphorus nutrients was summarized and analyzed from four aspects: the strategy of plant phosphorus acquisition and utilization, the coordination pathway of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for plant phosphorus absorption, the coordination pathway of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria for plant phosphorus absorption, and the synergy of plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. It was found in the analysis that the phosphorus acquisition process of plants required efficient root adaptability, which promoted soil phosphorus activation by regulating root morphological traits and changing the composition and secretion of root exudates. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi could promote the changes of soil biological activity and chemical properties in rhizosphere and hyphosphere by exchanging mutually beneficial symbiotic substances with plants, and promote plants to obtain phosphorus. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria had a positive interaction with plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at the soil interface, secreting a variety of organic acids, reducing soil pH, and increasing the activities of phosphorus activation-related enzymes to improve soil available phosphorus levels. On this basis, research prospect of plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-phosphate-solubilizing bacteria interaction to promote plant phosphorus uptake was prospected. Future research should focus on the following aspects: the role of mycorrhizal traits in the interaction system, analysis and identification of metabolite composition and potential functions of the member of the interaction system, and to explore the effects of biotic or abiotic factors on the construction and functional assembly of soil microbial community. [Ch, 141 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1181-1187.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220710
Abstract:
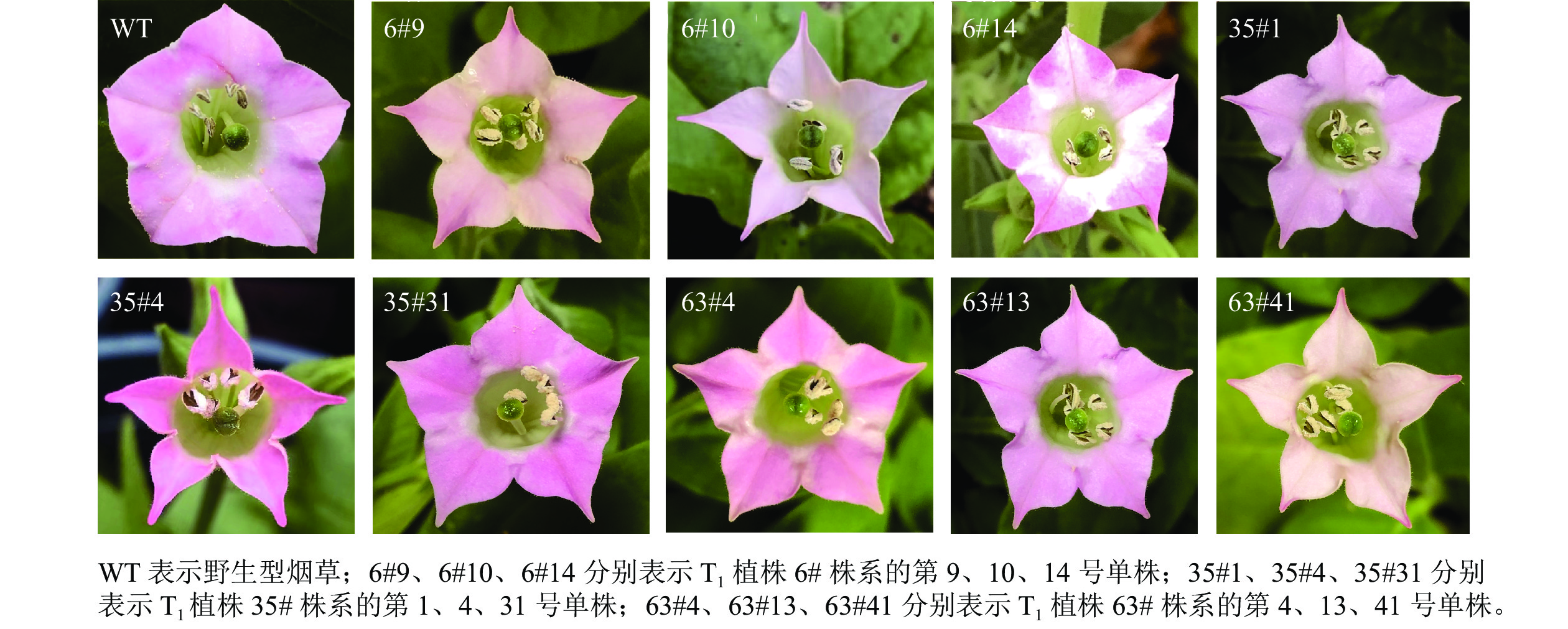
Objective This study, with an investigation into the transgenic plants of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) overexpressing CsRNF217, is aimed to verify the effect of the E3 ubiquitin ligase gene CsRNF217 of Citrus suavissima ‘Seedless’ on male sterility. Method First, an analysis was conducted of the pollen viability of wild type (WT) and the positive plants of the 1st generation of selfing of transgenic plants (T1) with the employment Alexander staining and pollen germination in vitro. Then, the seed setting rate was obtained via selfing and reciprocal crosses between transgenic plants and WT. Finally, semi-quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) was used to analyze the relative expression of CsRNF217 in T1 positive tobacco plants. Result CsRNF217 derived from C. suavissima ‘Seedless’ was efficiently expressed in T1 lines. The pollen dyeing viability and in vitro germination rate of T1 lines, selfing seed setting rate of T1 lines, and seed setting rate of T1 lines reciprocal crosses with WT were significantly lower than those of WT (P<0.05). Conclusion T1 plants overexpressing CsRNF217 had a severe decline in pollen fertility and partial aberrant of embryo sac, suggesting that an up-regulation of CsRNF217 could play a negative regulatory role on male and female fertility of C. suavissima ‘Seedless’. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 22 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1188-1196.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220768
Abstract:
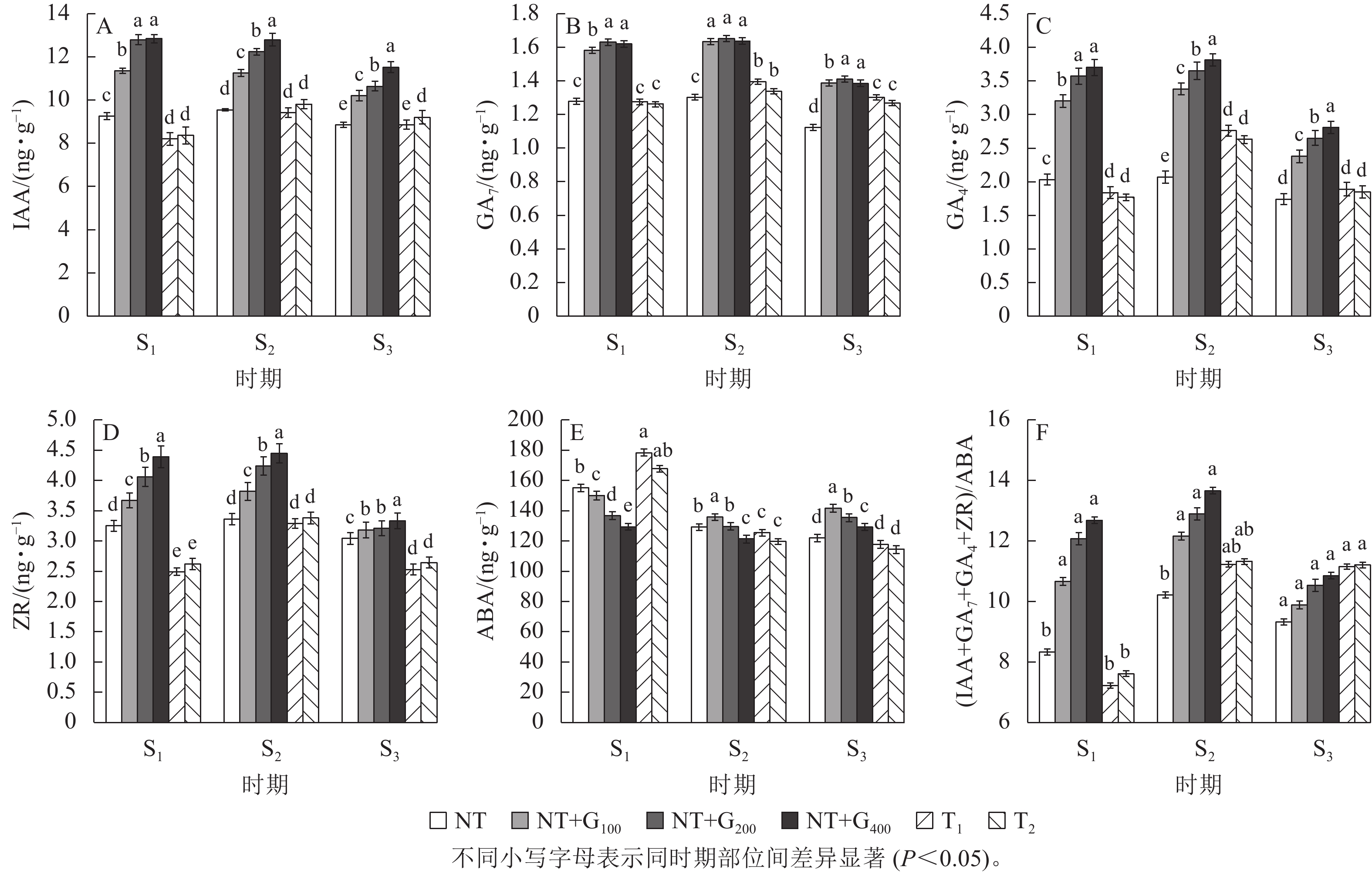
Objective This study is to investigate the effects of the change in endogenous hormone content on the growth of new branches and formation of female cones in Pinus massoniana after top pruning and hormone induction. Method A pot control experiment was conducted using a 3-year-old clone 209 of P. massoniana as the test material. Six treatments were set up, including retaining one layer of branches (T1), retaining two layers of branches (T2), no top pruning (NT), no top pruning + 100 mg·L−1 GA4/7 (NT+G100), no top pruning + 200 mg·L−1 GA4/7 (NT+G200) and no top pruning + 400 mg·L−1 GA4/7 (NT+G400) to measure the changes in the content and ratio of endogenous hormones in conifers at the early stage of flower primordium formation (S1), the stage of flower primordium formation (S2) and the late stage of flower primordium formation (S3). The effects on female cone density and branch growth were studied. Result Compared with NT, the female cone density, branch length and branch diameter of T1 treatment increased by 126.00%, 181.55% and 35.78%, respectively, while those of T2 treatment increased by 66.52%−82.67%, 119.31%−150.45% and 9.17%−111.49%, respectively. Compared with GA4/7 treatments, there was no significant difference in the growth of female cone density, branch length and branch diameter between T1 and T2 treatments and other treatments with GA4/7 after top pruning, except that the growth of branch length at the first layer was significantly lower than that of NT+G200 treatment. In S1 period, compared with NT, the content of indoleacetic acid (IAA) in the needles of T1 and T2 treatments decreased significantly by 11.24% and 9.62% (P<0.05), the content of abscisic acid (ABA) increased significantly by 15.09% and 8.15% (P<0.05), and the content of GA7, GA4 and zeatin nucleoside (ZR) in the needles decreased significantly, but the difference was not significant, with (IAA+GA7+GA4+ZR)/ABA ratios of 7.22 and 7.61 respectively. At S2 stage, the contents of IAA, GA7, GA4 and ZR in needles treated with T1 and T2 increased compared with that in S1 stage, while the content of ABA decreased, and the ratio of (IAA+GA7+GA4+ZR)/ABA increased. At S3 stage, the measured hormone content was lower than that in S2 stage. The change trend of the main hormone content after top pruning and GA4/7 induction was different. From S1 to S3, IAA content gradually decreased after GA4/7 induction, GA7, GA4 and ZR content first increased and then decreased, and ABA content first decreased and then increased. Within 20 days after top pruning, IAA, GA7, GA4 and ZR contents decreased first and then increased, while the ABA content decreased continuously. The intensity of top pruning affected the changes of IAA, GA4, ABA and ZR hormone contents in needles at different whorls. Conclusion Both top pruning and GA4/7 treatment at the early stage of flower primordium formation can promote the regeneration of fruiting mother branches and the formation of female cones in P. massoniana, which is closely related to the change of endogenous hormone content in needles. [Ch, 2 fig. 1 tab. 32 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1197-1204.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230146
Abstract:
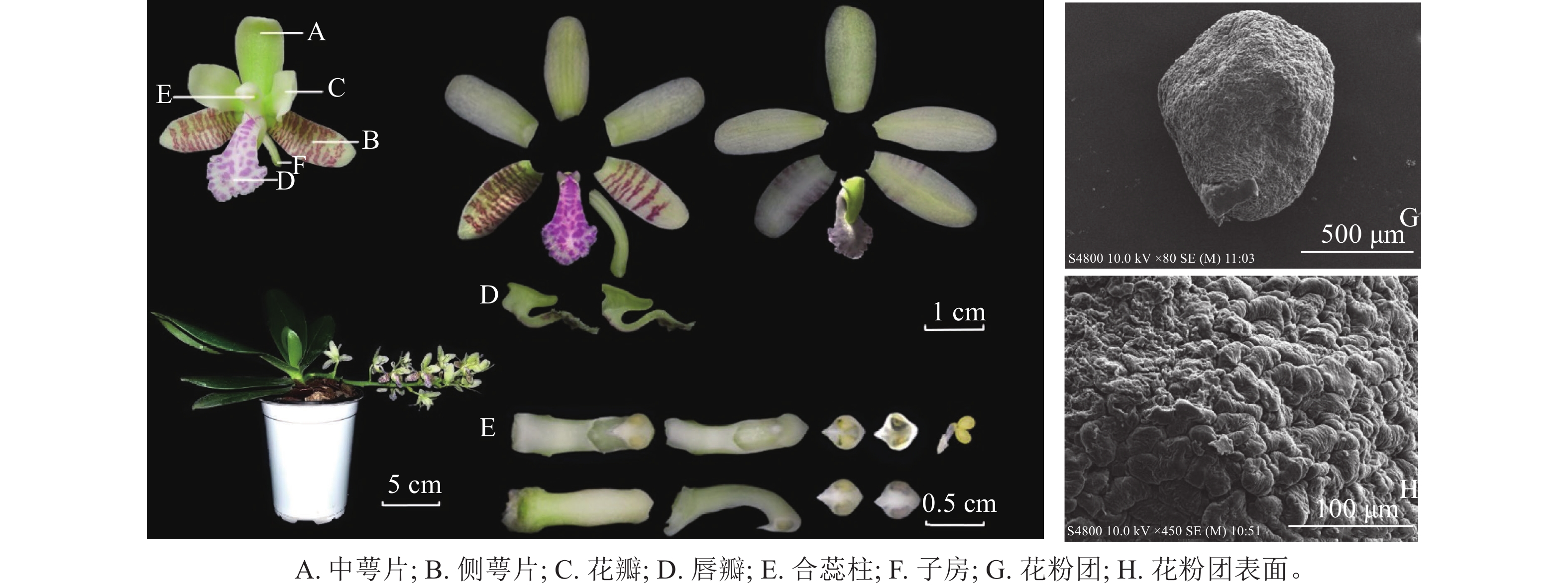
Objective This study, with an investigation of the breeding system of the Phalaenopsis japonica, is aimed to provide theoretical basis for P. japonica hybrid breeding and research basis for the preservation and protection of the plant germplasm resources of the endangered Phalaenopsis. Method With P. japonica in greenhouses taken as materials, their floral characteristics and flowering process were recorded for observation before the pollen viability and stigma acceptability were determined, the pollen histochemistry was analyzed, the hybridization index (OCI) was estimated and artificial pollination was tested. Result (1) The P. japonica blossomed from mid April to end of May, and was fragrant and the florescence of single plant lasted for 30 to 40 days and that of a single flower is about 30 days, with the bud stage being 1 to 7 days before flowering, the initial flowering stage being 1 to 5 days after flowering, the full flowering stage being 6 to 25 days after flowering, the final flowering stage being 26 to 30 days after flowering and the flower fading stage being 30 to 40 days. (2) The P. japonica was raceme with each plant having 1 to 2 inflorescences and each inflorescence having about 10 flowers. (3) The P. japonica pollen was nearly circular tetrad pollen which was mainly composed of lipids, suitable for insect pollination. (4) The P. japonica was monoecious and the pollen viability and stigma acceptability reached the highest in the blooming stage (flowering for 6 to 25 days) with the highest pollen viability being 84.98% and OCI of P. japonica being 4. (5) The fruit setting rate of natural pollination, natural self-pollination, and emasculation without pollination were 0 but the fruit setting rate of artificial self-pollination, artificial cross-pollination of the same plant, and artificial cross-pollination of different plant reached 60.00%, 80.00%, and 93.33% respectively. The fruits of artificial cross-pollination between different plants had the highest quality, with the largest seeds, highest viability (82.69%), and largest amount of seeds (about 43000 seeds). Conclusion The flowering of P. japonica starts in mid April and ends at the end of May with the full blooming period lasting for about 20 days and its breeding system is a mixed mating system of self-pollination and cross-pollination that required pollinators. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 26 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1205-1214.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230160
Abstract:
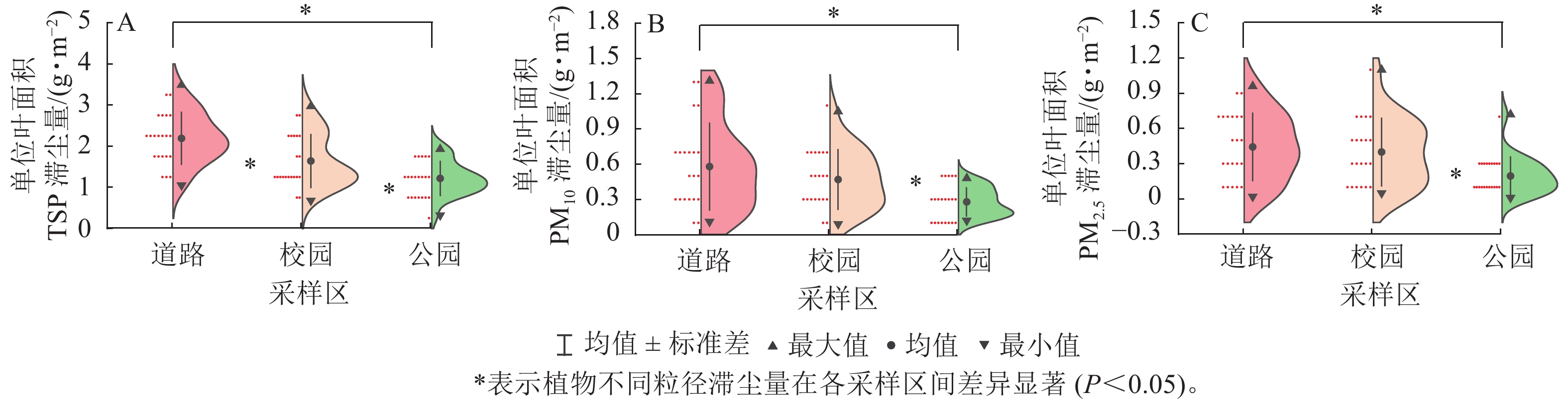
Objective The objective is to investigate the dust retention and comprehensive anti-pollution capacity of typical garden plants in Zhengzhou. Method 7 common garden plants (Ligustrum lucidum, Eriobotrya japonica, Photinia serrulata, Fatsia japonica, Euonymus japonicus, Pittosporum tobira, and Nandina domestica) were selected as the objects, and 3 sampling areas of streets, campuses and parks were set up. Atmospheric particulate matter with different particle sizes (total suspended particulate, inhalable particulate matter, fine particulate matter) retained by each plant leaf was collected. The dust retention per unit leaf area of each plant was determined by the method of graded membrane filtration. At the same time, the photosynthetic parameters and leaf physiological indicators of the plants under different pollution levels were compared. The correlation and principal component analysis of plant dust retention and physiological photosynthetic indexes were carried out, and garden plants with outstanding dust retention and comprehensive anti-pollution ability were screened. Result (1) The amount of dust retention per unit leaf area of plants was proportional to the mass concentration of atmospheric particulate matter in the environment. The increase in particulate matter retention by different plants was uneven with the aggravation of particulate matter pollution. (2) With the increase in atmospheric particulate matter concentration, the net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, chlorophyll a and b content of leaves decreased, while the malondialdehyde content and superoxide dismutase and peroxidase activities of leaves increased. (3) The results of principal component analysis showed that the comprehensive ability of dust retention and anti-pollution of P. tobira and F. japonica was more prominent. Conclusion In the future control of urban dust pollution and urban greening construction in Zhengzhou, P. tobira and F. japonica can be selected as priority plants. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 38 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1215-1223.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230150
Abstract:
Objective The aim is to study the secondary metabolites of Rhexocercosporidium panacis, so as to discover new active compounds and to provide a chemical basis for later research on the pathogenesis of R. panacis. Method The crude extracts of R. panacis were obtained through solid fermentation of rice, and purified by silica gel column chromatography, reversed silica gel column chromatography (ODS), Sephadex LH-20, and semi-preparative liquid chromatography to gain monomeric compounds. The structure of monomeric compounds was identified based on mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and literature data comparison. The antioxidant activities of 9 compounds were tested by DPPH radical scavenging method and the preliminary phytotoxic activity of compounds 4−9 was evaluated. Result 9 compounds were isolated from R. panacis, including three sterols: ergosterol (1), 5,8-epidioxy-5α,8α-ergosta-6,9,22E-tien-3β-ol (2), and 5,8-epidioxy-5α,8α-ergosta-6,22E-dien-3β-ol (3), and six polyketides: regiolone (4), 4,6,8-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one (5), 2,5-dimethyl-7-hydroxychromone(6), 2-methyl-5-carboxymenthyl-7-hydroxychromone (7), (+)-citreoisocoumarin (8), and de-O-methyldiaporthin (9). Compounds 1−9 exhibited no antioxidant activity and 4−9 did not display phytotoxic effects on ginseng roots. Conclusion Compounds 1−9 are isolated for the first time from R. panacis, enriching the database of secondary metabolites of this strain. Among them, compounds 4−9 exhibit various biological activities, but do not cause lesions in the isolated ginseng roots in the evaluation of phytotoxic activity. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 29 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1224-1231.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230140
Abstract:
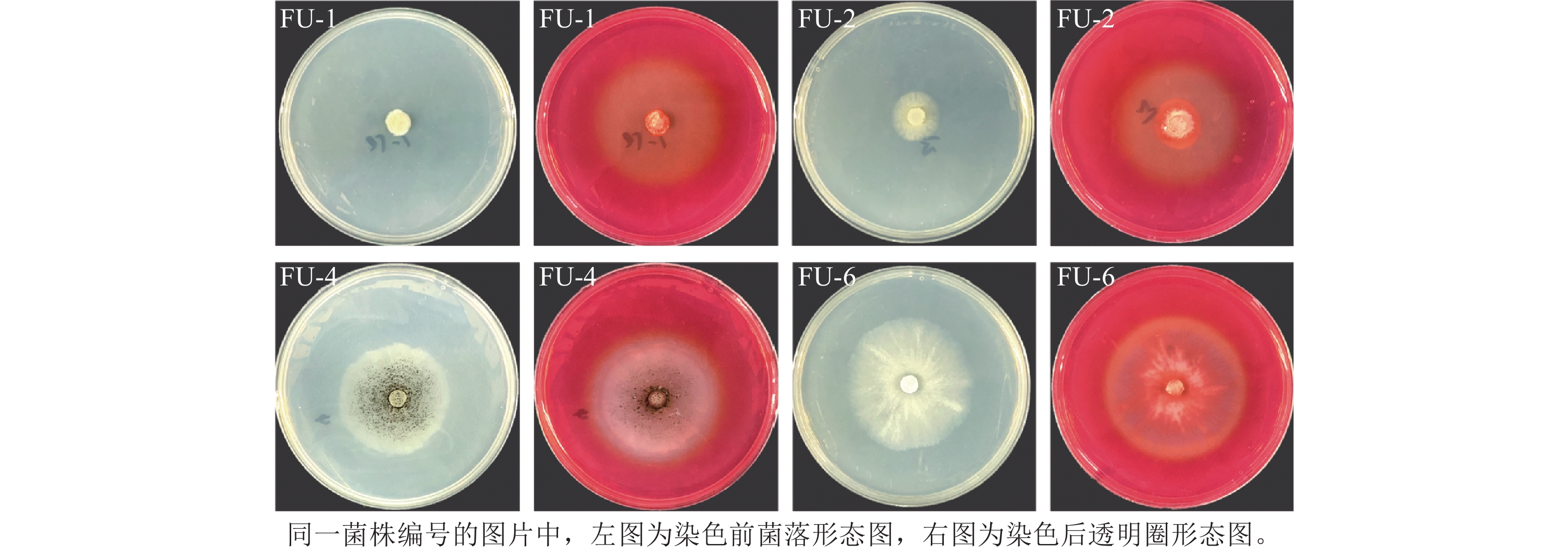
Objective This study aims to explore the application potential of symbiotic fungi of Odontotermes formosanus in the utilization of straw resources, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the industrialization of straw biodegradation and supplement strain resources. Method Using CMC-Na plate as isolation medium and Congo red staining method for screening, the fungi with lignocellulose degrading activity were isolated and screened from the gut of O. formosanus and cellulase activities were measured. The degradation effect of different fungi and fungal combinations on Oryza sativa (rice) straw was evaluated under liquid fermentation. The physicochemical properties of rice straw before and after degradation were analyzed using FTIR, XRD and SEM. Result 4 fungi with lignocellulose degrading activity were isolated from the gut of O. formosanus, identified as Talaromyces allahabadensis, T. aculeatus, Aspergillus niger and Perenniporia tephropora. Cellulase activity results showed that A. niger had the highest activity of endoglucanase and exoglucanase, while T. allahabadensis had the highest activity of β-glucosidase. The rice straw degradation test showed that the combination of A. niger and P. tephropora had the strongest straw degradation ability. Within 20 days, 38.27% of dry matter, 62.59% of cellulose and 51.75% of hemicellulose in rice straw could be degraded. After degradation, the internal chemical bonds and intermolecular forces in rice straw were destroyed, and crystallinity increased from 22.44% to 32.52%. The straw surface disintegrated and smashed, and the structure became fluffy. Conclusion A. niger and P. tephropora isolated from the gut of O. formosanus show strong degradation ability in the combined degradation of rice straw, and have potential development value in the industrialization of straw biodegradation. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 30 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1232-1240.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230161
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the effect of biochar-based fertilizer on root development, and yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) in Chongqing tobacco growing area, in order to provide theoretical basis and technical support for the rational application of biochar-based fertilizer in this area. Method N. tabacum ‘Yunyan 116’ was taken as the research object, and three treatments including conventional fertilization (T1), biochar-based organic fertilizer (T2) and biochar-based compound fertilizer (T3) were set up to analyze the effect of biochar-based fertilizer on the physiological activity of flue-cured tobacco root, chemical quality and economic traits of flue-cured tobacco. Result The application of biochar-based fertilizer could optimize the physiological and nutrient indexes of tobacco root. The root activity in T2 was the highest after transplantation, which increased by 4.2%−46.8% compared with T1. The number of lateral roots and adventitious roots in T3 was the most, which increased by 11.6%−41.1% and 19.0%−53.1% respectively compared with T1. The contents of nitrogen and potassium in root system decreased with the growth of tobacco plant, and the decrease was the slowest in T2. The nicotine contents in root system increased first and then decreased, and those in T2 and T3 were higher. The application of biochar-based fertilizer could increase the yield and output value of flue-cured tobacco and improve the chemical quality of flue-cured tobacco. Among them, T2 treatment had the highest yield and output value, which increased by 16.9% and 22.6% respectively compared with T1. In addition, biochar-based fertilizer could improve the nitrogen alkali ratio, sugar alkali ratio and potassium chloride ratio of flue-cured tobacco, improve the coordination of internal chemical components and improve the quality of flue-cured tobacco. Correlation analysis showed that the potassium contents (at 30, 60 and 120 d after transplanting) and the nitrogen contents (at 60, 90 and 120 d after transplanting) in root system were most closely related to the chemical quality of flue-cured tobacco. Conclusion Biochar-based fertilizer is beneficial to the growth and development of flue-cured tobacco roots, and can increase the output value as well as the chemical quality of flue-cured tobacco. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 31 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1241-1249.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230149
Abstract:
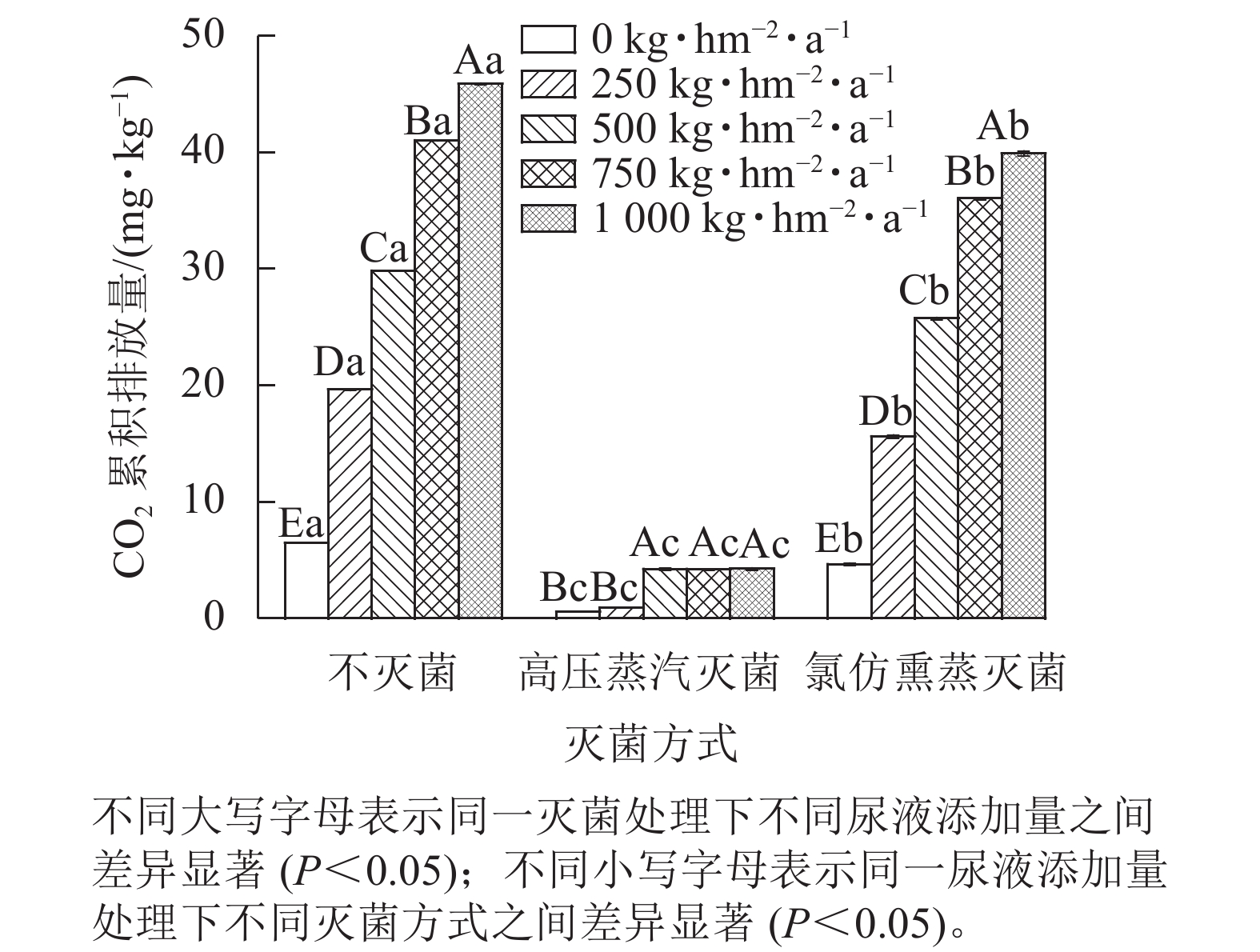
Objective This study, with an investigation of the variations of biotic and abiotic processes driving soil organic carbon (SOC) mineralization affected by livestock excreta deposition in grazing grassland ecosystems, is aimed to provide new insights into better understanding of the response and feedback of soil carbon pool changes induced by anthropogenic activities to global climate change. Method In this study, SOC mineralization rates (as indicated by CO2 emission rates) were measured of the soil of an alpine meadow added with different rates of urine (0, 250, 500, 750, 1 000 kg·hm−2·a−1) under different sterilization circumstances (no sterilization, autoclaving sterilization, chloroform fumigation sterilization), while the soil pH, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), total dissolved nitrogen (TDN), soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), ammonium nitrogen (NH4 +-N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3 −-N) concentration were simultaneously determined, so as to explore the differences in the response of biotic and abiotic SOC mineralization processes to urine addition. Result (1) The addition of urine promoted CO2 emissions, which increased with the increase in the amount of urine added under different sterilization methods, demonstrating a positive correlation between soil CO2 emissions and soil pH and NH4 +-N concentrations (P<0.05). (2) Soil CO2 emission was inhibited by sterilization, and the inhibition effect of autoclaving sterilization on soil CO2 emission was significantly higher than that of chloroform fumigation sterilization (P<0.05). (3) The CO2 emission from biotic and abiotic processes both increased with the increase of urine addition rate, with the contribution of biotic process to soil CO2 emission being greater than that of abiotic process. Conclusion Urine deposition can promote soil CO2 emission from biotic and abiotic processes, with more contribution from the biotic process, however, the contribution of abiotic SOC mineralization to soil CO2 emission should not be neglected. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 42 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1250-1260.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230185
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to investigate the effect of climate change from 1996 to 2017 on the community composition and structure, biodiversity, and flora of trees with diameter at breast height (DBH)≥10 cm in the deciduous broad-leaved forest layer of Mount Tianmu. Method A sample plot survey was conducted on 25 sample plots of 400 m2 of deciduous broad-leaved forest in the National Nature Reserve of Mount Tianmu, Zhejiang Province, China. Phase 2 (1996 and 2017) survey data and meteorological data of Mount Tianmu from 1996 to 2017 were used to analyze the dynamics of the tree layer in a deciduous broad-leaved forest. Result (1) The composition of life form of tree species in the tree layer changed significantly. The proportion of evergreen tree species increased from 17.5% to 35.5%, an increase of 102.9%, and the proportion of deciduous tree species decreased from 82.5% to 64.5%, which decreased by 21.8%. (2) The tree species in the tree layer changed drastically, with an exit of 8 species in 6 genera of 4 families, and entry of 4 species in 3 genera of 1 family. The exit and entry tree species reached 27.3%. The exit and entry of rare and occasional species were the keys to the change in species number in the tree layer. (3) The role of evergreen tree species in the tree layer was increasing. The variation range of the top 17 dominant tree species in the important value was 47.1%. Among them, the important value of Daphniphyllum macropodum, an evergreen tree species, increased from 1.88% in the 19th place to 10.36% in the 3rd place. The proportion of important values of evergreen tree species increased from 22.6% to 36.3%. (4) The α diversity of the tree layer decreased slightly, and the decline in various indices ranged from −9.1% to −3.1%. The α diversity index of evergreen tree species increased, ranging from −3.0% to 51.8%. (5) The flora tended to be tropical. The proportion of tropical components in the family increased from 55.6% to 58.3%. The proportion of tropical elements in the genus increased from 25.0% to 30.3%. (6) The diameter class structure showed an inverted J type, and the community was stable. The number of small-diameter evergreen tree species increased by 165.3%, while the number of medium-diameter evergreen tree species increased by 45.5%. There was no significant change in the large-diameter species. In 1996, there were 11 growth-type tree species, 1 stable-type tree species, and 4 declining-type tree species. In 2017, there were 7 growth-type tree species, and 5 stable-type tree species, and declining-type tree species did not change. Tilia chingiana, Cyclocarya paliurus, Cladrastis wilsonii, and Acer pictum changed from growth-type to stable-type. The growth potential of Pinus taiwanensis, Cyclobalanopsis shennongii, Cornus kousa ssp. chinensis, Daphniphyllum macropodum and Acer sinopurpurascens increased. Conclusion Under climate warming and humidification, the dynamic change of the tree layer in the deciduous broad-leaved forest in Mount Tianmu is very significant. The appearance of the tree layer in the deciduous broad-leaved forest has transitioned from the dominance of deciduous tree species to the balanced state between evergreen and deciduous trees, with a slight decrease in biodiversity and a trend towards tropical elements in the flora. [Ch, 7 tab. 39 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1261-1272.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220766
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to clarify the distribution and evolution of wild Cymbidium faberi and explore the succession law of its natural population in China, so as to provide scientific basis for the conservation of its natural population. Method Based on the ArcGIS platform, a historical geographic information database of wild C. faberi was constructed to analyze its spatiotemporal distribution and influencing factors since 1368. Result (1) Since 1368, wild C. faberi has been mainly distributed in the south of Qinling Mountains-Huaihe River in China, with the distribution center gradually migrating from 28.585°N and 113.503°E to 29.365°N and 112.675°E. From 1368 to 1644, it was mainly concentrated in Jiangnan, Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Sichuan and Yunnan regions. From 1644 to 1912, the degree of aggregation in Sichuan and Yunnan weakened. From 1949 to 1978, the degree of aggregation in Sichuan and Chongqing regions increased. Since 1978, wild C. faberi has gathered at multiple sites, with Hubei and Shaanxi becoming new gathering areas. (2) Natural factors such as temperature, precipitation, soil type, topography and distance from water sources directly affected the distribution of wild C. faberi. It was mainly distributed in the warm bauxite areas with an annual average temperature of 15−25 ℃ and pH 5.3−6.2, as well as on the southern or southeastern slopes with an altitude of 620−980 m and a slope of 19.9°−25.0°, and within a distance of 1 000−2 000 m from water sources. (3) The distribution and migration of wild C. faberi was indirectly affected by activities such as agricultural cultivation and industrial development. Conclusion Wild C. faberi mainly gathers in southern China and tends to migrate to higher latitude areas. Its distribution is significantly affected by temperature and precipitation, and human activities indirectly lead to a decrease in its distribution. Therefore, it is necessary to build or expand suitable areas of wild C. faberi in typical areas such as Jiangnan, Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Yunnan, Guizhou, Shaanxi and Hubei to strengthen the protection. [Ch, 3 fig. 5 tab. 44 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1273-1281.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230026
Abstract:
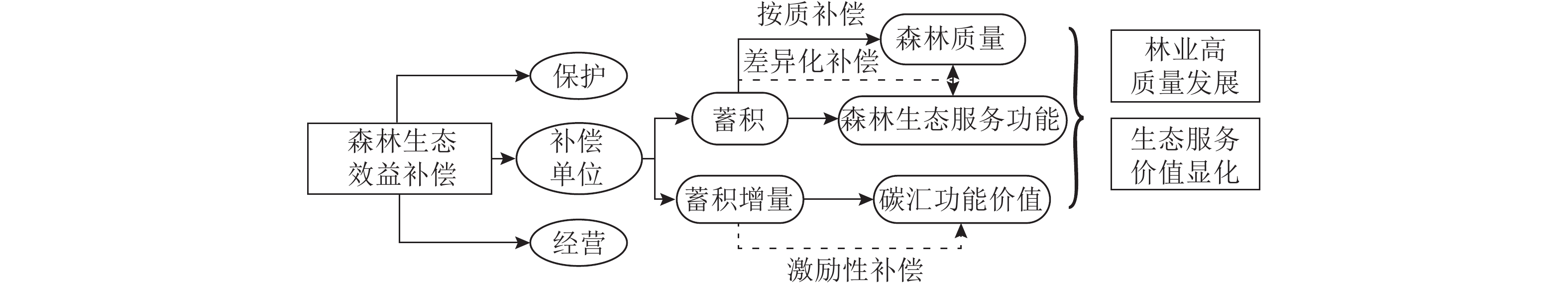
Objective Transforming the unit of forest payments for ecosystem services is the requirement for promoting the quality of ecological public forests and stimulating the enhancement of forest ecological services. There is an urgent demand for the theory and academic aspects to improve the method of payments funds allocation scientifically through diversified units of forest payments for ecosystem services, which can evaluate the different ecological service value of ecological public forests reasonably. Method Based on the scope and characteristic of forest ecosystems accumulation and increment, we explored diversified units of payments for forest ecosystem services, and propose the idea that forest ecosystems accumulation compensation in terms of volume unit which can promote “compensation by quality” for forest ecological benefits, and “incentive” compensation in terms of volume increment unit which can promote the enhancement of forest carbon sink capacity. Taking the ecological public forest in Linqi Town, Chun’an County, Zhejiang Province as a case, this paper analyzed and evaluated the feasibility of ecological public forest payments funds allocation using volume unit and volume increment unit based on the smallest forest division unit - small class. Result Using volume as unit of ecological public forest payments is more effective than that of area, which could highlight the differentiation of forest water-holding function and forest quality. Payments using volume increment as unit could promote improvement of carbon sink function, which met the requirements of multi-functional management of forest ecological services. Conclusion Implementing payments of ecological public forests using volume unit combined with volume increment unit could effectively maintain the existing forest ecosystem stock and stimulate the of forest ecosystem increment, which can make up for the inability of area unit on value incentive and dynamics in the current payments for public forest ecosystem services, and point out the direction of improvement for forest management to effectively promote ecological services. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 28 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1282-1291.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220716
Abstract:
Objective With an investigation of the site stand of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in southwest Zhejiang Province, this study is aimed to explore the main factors affecting the site quality of the plantation so as to provide a theoretical basis for C. lanceolata plantation management. Method First, with C. lanceolata plantation in Qingyuan District of Zhejiang Province taken as the research object, the parse tree data and generalized algebraic difference approach was employed to establish the site index (SI) model of C. lanceolata plantation. Then, with SI chosen as the dependent variable, random forest algorithm was used to screen out the dominant factors affecting the forest position index from the data of ClassⅡ C. lanceolata sub class data, on the basis of which, the site quality level was determined by the score value of SI, and the site classification and site quality evaluation were carried out for C. lanceolata sub classes in Qingyuan District. Result The generalized algebraic difference approach based on Richards equation was the most consistent with the growth process of C. lanceolata in Qingyuan District with the coefficient of determination (R2), root mean squared error (ERMS) and mean absolute deviation (EMA) being 0.969, 1.778 and 0.400 respectively and the multishape curve of the model was in accordance with the physiological significance. The main site factors affecting the SI of C. lanceolata plantation are landform, humus thickness and soil layer thickness, as was shown in the factor selection of random forest, which had a greater contribution and more reasonable interpretation of the nonlinear relationship between factors when compared with the traditional partial correlation coefficient method. With landform, humus thickness and soil layer thickness selected as the site factors, the sub class was divided into 17 site types, among which the sub classes under investigation were of medium site quality or above. Conclusion The site index based on generalized algebraic difference method is suitable for C. lanceolata plantation in southwest Zhejiang Province, and when combined with the dominant factors selected by permutation importance method, it can effectively evaluate the site quality. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 27 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1292-1299.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230148
Abstract:
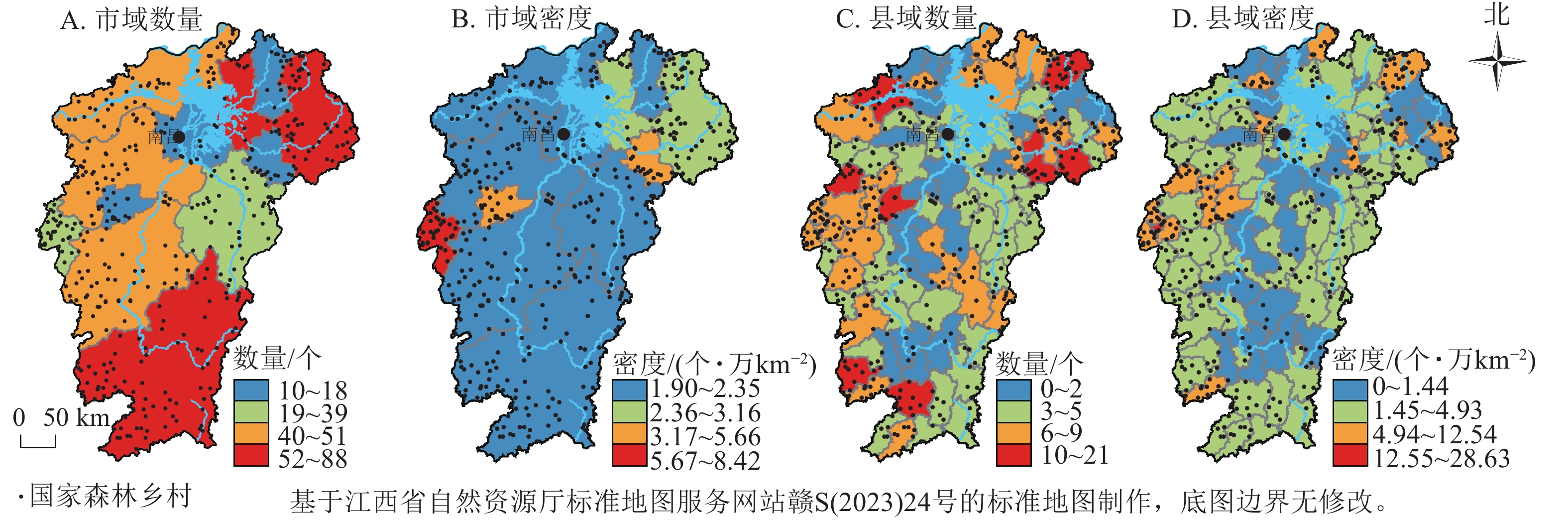
Objective Explore the spatial pattern and impact mechanism of national forest villiages is helpful for rural greening, beautification, and optimization. Method Taking 430 national forest villages in Jiangxi as the research object, a four-dimensional structure system of “evaluation-analysis-index-data” was constructed, and the spatial pattern and its formation mechanism were discussed by comprehensively using GIS spatial analysis, geographical detectors and geographical weighted regression. Result (1) The national forest villages in Jiangxi exhibit a low land oriented terrain pattern, a geopolitical pattern at the edge of the provincial boundary, an administrative pattern that emphasizes minority administrative regions, and an economic pattern that deviates from the economic center. (2) The explanatory power of forest vegetation and ecological environment in natural environmental factors on the formation of national forest villages spatial pattern is significantly better than that of geographical environmental indicators. The tourism resources in social environmental factors have a stronger explanatory power on the formation of the national forest villages spatial pattern. (3) From the perspective of spatial pattern, the dominant areas of the main influencing factors are mainly distributed in the marginal areas of the provincial boundary, especially in the northern-northeastern Jiangxi or southern-southwestern Jiangxi regions. From the perspective of regression coefficients, the main influencing factors have a positive and negative relationship with the formation of the national forest rural spatial pattern, showing a comprehensive impact effect. Conclusion There is spatial coupling between environmental factors such as biological abundance, vegetation index, and the distribution of national forests villiages, but the impact varies significantly, reflecting the coexistence of commonality and individuality at different spatial scales, and possessing a certain value of “correction”. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 19 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1300-1310.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230188
Abstract:
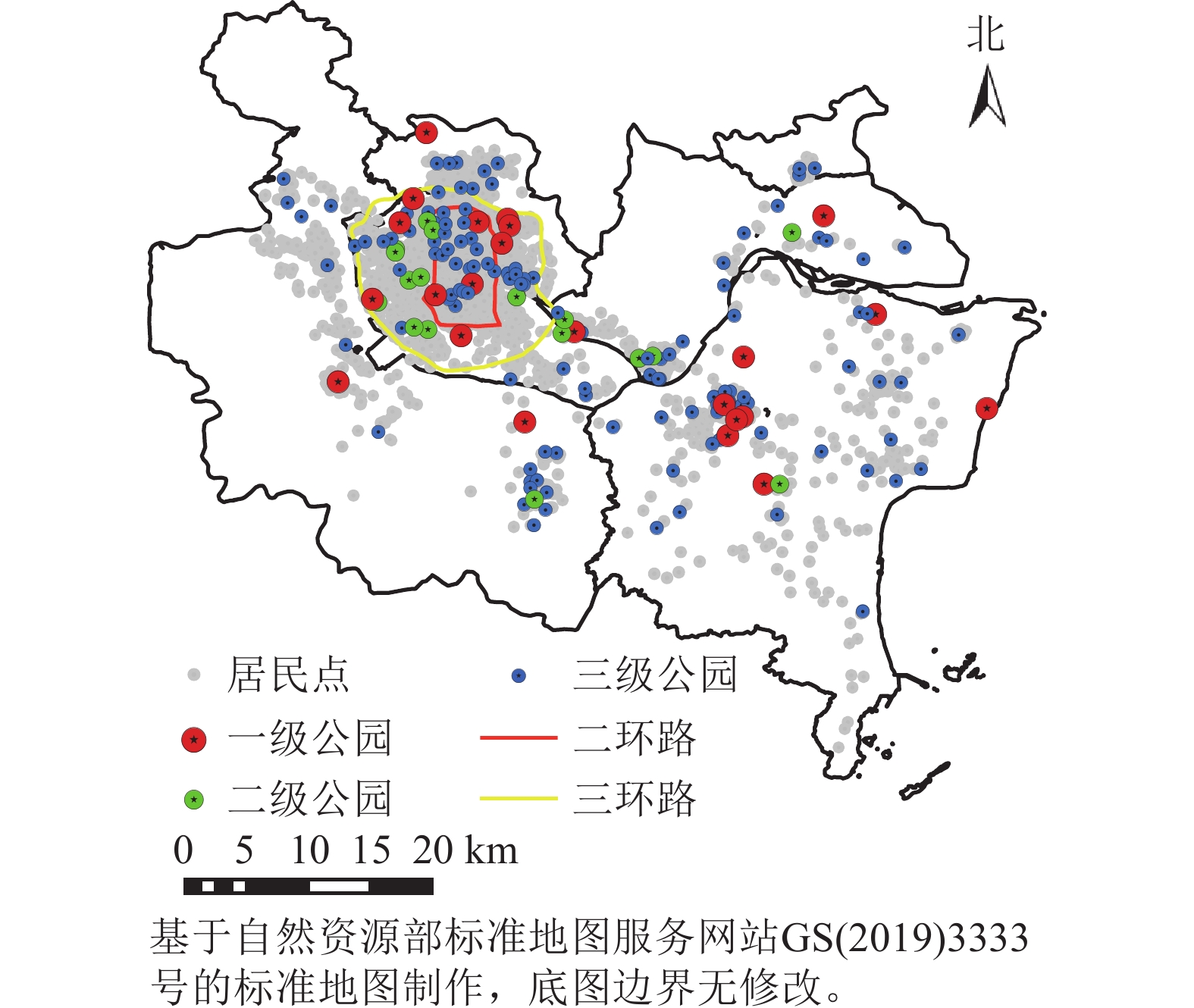
Objective This study, with an investigation of the supply and demand relationship and layout rationality of park green space, is aimed to provide reference for the optimization of park green space layout and the formulation of construction planning schemes in Fuzhou City. Method With the downtown area of Fuzhou taken as an example, the two-step floating catchment area method was employed to analyze the accessibility so as to quantify the supply of park green space while the needs of vulnerable groups are considered when exploring the supply-demand relationship and layout fairness of park green space from the perspective of vulnerable groups. Result (1) Approximately 51.0% of the township streets had good accessibility, and the overall layout of accessibility displays a spatial pattern of low accessibility−high accessibility−low accessibility from the second ring to the surrounding areas. (2) The number of streets with relatively unfair supply was the largest, accounting for 46.4%, the proportion of township streets with very unfair supply shortage reached 1.5% and the supply of park green space for 47.9% of township streets has failed to meet the demand of various groups. (3) The fair performance index of women was slightly lower than the average level of the total permanent population in the study area, the overall equity performance index of children and the elderly was above the average, but the equity index in each administrative unit was featured with great fluctuation. Conclusion The lack of supply is manifested by the highest number of unfair streets, indicating that the overall supply of park green space for various groups is not sufficient. Most streets’ park green space cannot meet the demand of the group and fails to achieve true regional fairness. In the future planning, focus should be laid on the improvement of the areas with insufficient supply, so as to realize the general regional fairness in the use of the park. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 40 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1311-1321.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230163
Abstract:
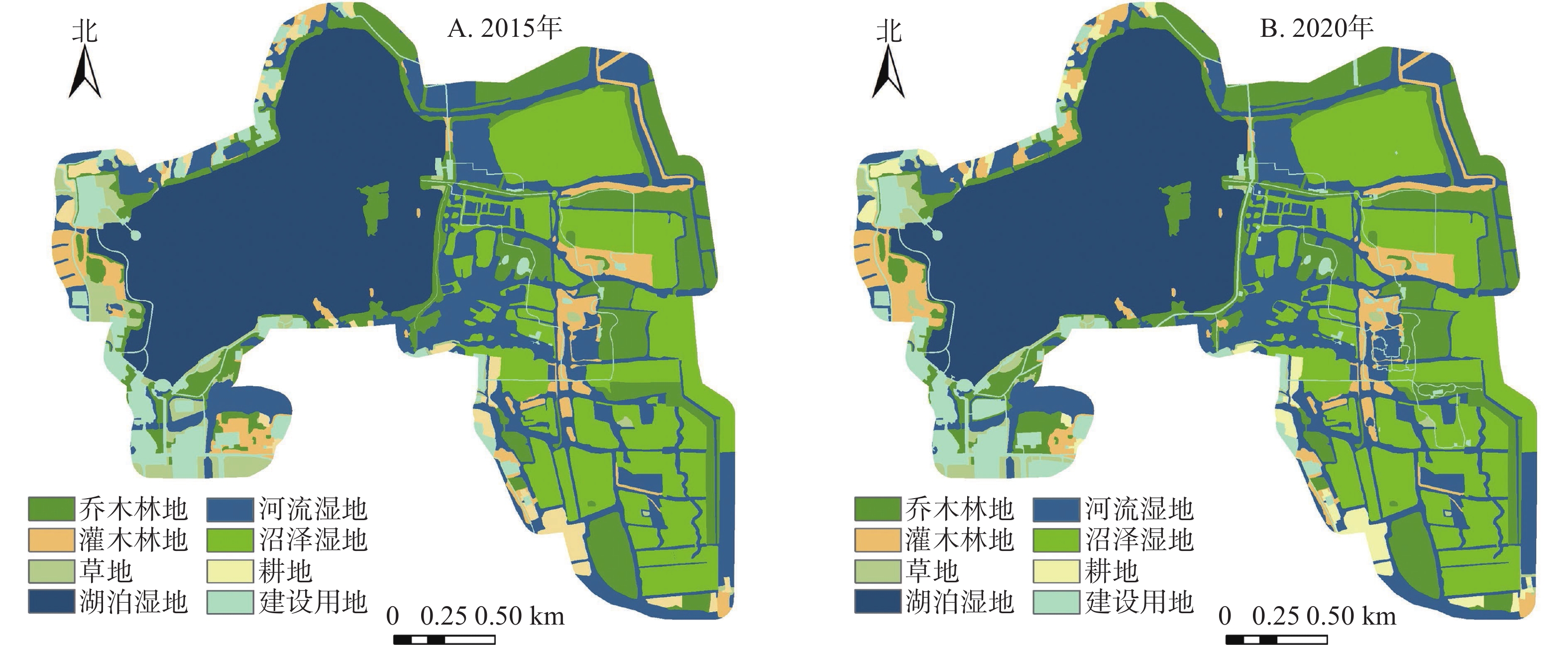
Objective This study aims to explore the scenario plan for promoting the sustainable development of Qinhu National Wetland Park in Jiangsu Province. Method Taking Qinhu National Wetland Park as an example, according to the construction goal and upper level planning of the research area, three scenarios were constructed: natural development, ecological protection and tourism development. Based on the simulation results of PLUS model, an optimization scenario was constructed. Result (1) From 2015 to 2020, the conversion of shrub land and construction land in the study area increased the most, which was 14.88% and 8.77% respectively, while the conversion of grassland decreased the most, which was −33.25%. The area of arbor forest land, lake wetland, river wetland, marsh wetland and cultivated land was relatively stable. (2) The land use changes under the three scenarios showed different trends. Under the scenarios of natural development and tourism development, the construction land expanded greatly in the east, middle and southwest of the study area, while the shrub land increased more significantly under the natural development scenario. Under the ecological protection scenario, the central lake wetland and the eastern river wetland showed an expanding trend, and the construction land and cultivated land were the main sources. (3) Under the optimization scenario, various wetlands showed an expanding trend, totaling 69.05%. Arbor forest and shrub land accounted for 16.19% and 5.57% respectively, and the construction land area accounted for 5.90%. Conclusion Construction land under natural development and tourism development scenarios encroaches on all kinds of wetlands and forestland, while the area of all kinds of wetlands and forestland under ecological protection scenario increases effectively, and construction land is not fully utilized. Under the optimization scenario, all land use types are reasonably regulated, which helps to coordinate the dual goals of ecological protection and rational development in the study area. [Ch, 6 fig. 5 tab. 30 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1322-1332.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220731
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the process of land desertification changes in the Xiaoluanhe River Basin in Weichang Manchu and Mongolian Autonomous County (Weichang County) of Hebei Province, a typical agricultural-pastoral interlacing zone suffering from a serious problem of land desertification, is aimed to understand the influence of land use changes and elevation on land desertification so as to provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of land desertification in the basin and the comprehensive management of mountains, water, forests, lakes, grasses and sands. Method First, Google Earth Engine and ArcGIS platform was utilized to analyse the Landsat series remote sensing data in 2000, 2010 and 2020. Then, the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and surface albedo feature space were constructed to establish the desertification difference index (DDI) model and classify the sandy land in the degree of desertification. Result The past 20 years has witnessed an overall improvement trend in the land of Xiaoluanhe River Basin with the land area of extremely severe and severe desertification decreased by nearly 80% and 56% respectively and light desertification and non-desertification land accounting for about 65% of the basin area. The improvement rate of desertification land decreased in the later stage, and the improved area was concentrated in Saihanba Forest Farm and the lower reaches of Xiaoluanhe River. The desertification landscape in the river basin tended to be concentrated with the degree of landscape fragmentation continuing to decrease. There was an obvious improvement on the desertification for woodland and grassland and the desertification tended to decrease with the increase of altitude. Conclusion Since 2000, the land in the Xiaoluanhe River Basin has improved as a whole in terms of desertification whereas there is a trend of deterioration of land in areas such as the town of Yudaokou and the pastures. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen measures in the conduct of precision sand control so as to deal with the desertification in the river basin and eventually realize the sustainable development of the Xiaoluanhe River Basin. [Ch, 6 fig. 4 tab. 34 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1333-1340.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220718
Abstract:
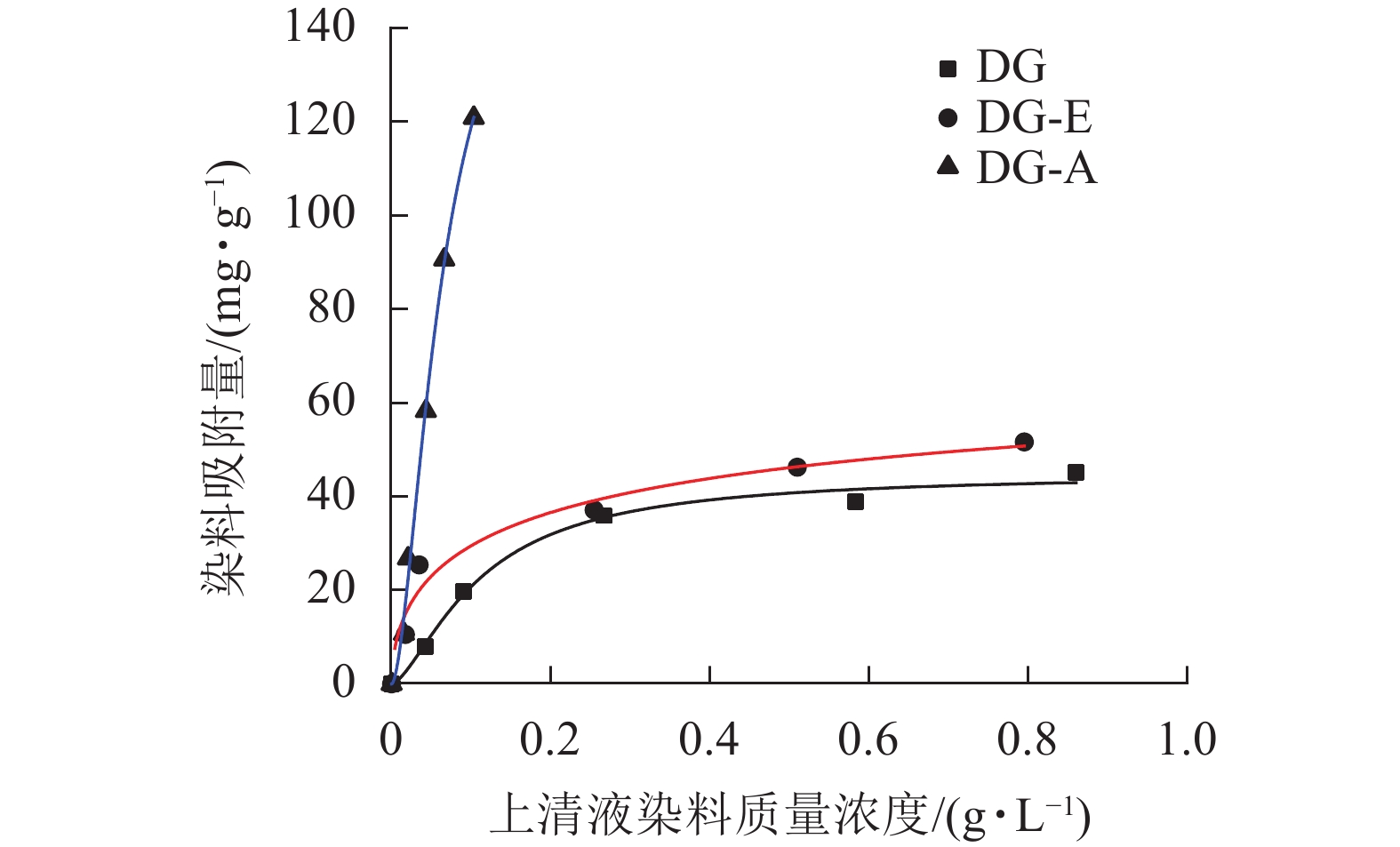
Objective This study, with gallic acid modified Dendrocalamus giganteus (DG) prepared by esterification reaction, is aimed to investigate the effect of gallic acid (GA) on antibacterial performance of DG. Method The modified products (DG-GA) were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, X-ray diffractometer, scanning electron microscope and thermogravimetric analysis before the antibacterial tests were performed by shaking method after modification. Result Gallic acid formed graft copolymer with bamboo powder successfully with a layer of coating formed on the surface of bamboo fiber bundle, making the surface become smoother. After gallic acid modification, the thermal stability of bamboo powder increased by about 40 ℃, the inhibition rate against Escherichia coli increased from 30.70% to 93.24%, and the inhibition rate against Staphylococcus aureus increased from 32.18% to 75.29%. Conclusion The modification of gallic acid can obviously improve the inhibition ability of bamboo powder against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, making it an effective method to improve the antibacterial property of bamboo. [Ch, 8 fig. 26 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1341-1347.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230207
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to investigate the testing method for determining the compressive strength of small-diameter bamboo culms as well as the impact of fiber sheath volume fraction and distribution density of vascular bundles on it. Method Four species of small-diameter bamboo, namely Pleioblastus amarus, Phyllostachys nidularia, Phyllostachys heteroclada, and Phyllostachys propinqua, with a diameter at breast height of less than 50 mm, were selected as research subjects before bamboo culm samples were utilized to investigate the compressive strength testing method for small-diameter bamboo and to examine the impact of varying length-to-diameter ratios on compressive strength. At the same time, a bamboo vascular bundle detection model based on the YOLO deep learning algorithm was employed to determine the number of vascular bundles and fiber sheath area so as to investigate their influence on compressive strength. Result There were no significant differences in the test results among specimens with different length-to-diameter ratios and the test results for the specimen with a length-to-diameter ratio of 2.0 were more reasonable. Of specimens at the length-to-diameter ratio of 2.0, Phyllostachys propinqua exhibited the highest compressive strength at 82.91 MPa while Phyllostachys heteroclada demonstrated the lowest strength at 67.01 MPa. The volume fraction of fiber sheath was highest in Phyllostachys nidularia at 35.64% and lowest in Phyllostachys heteroclada at 33.05%. The density of vascular bundles in Pleioblastus amarus was highest at 7.94 pieces·mm−2, while that of Phyllostachys propinqua was the lowest at 5.77 pieces·mm−2. Studies that treated various species of bamboo as a unified entity have shown that the positive effect of the volume fraction of fiber sheath on compressive strength was significant while the influence of vascular bundle distribution density on compressive strength was relatively minor. Conclusion A specimen with a length-to-diameter ratio of 2.0 is an ideal choice for testing the compressive strength of small-diameter bamboo and the specimen should be controlled for a period of (90±30) seconds before it collapses. Furthermore, the small-diameter bamboo selected for this experiment exhibited excellent compressive performance while there was a direct correlation between the volume fraction of fiber sheath (y) and compressive strength (x), as shown in the equation y=260.44x−18.26. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 33 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1348-1356.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230141
Abstract:
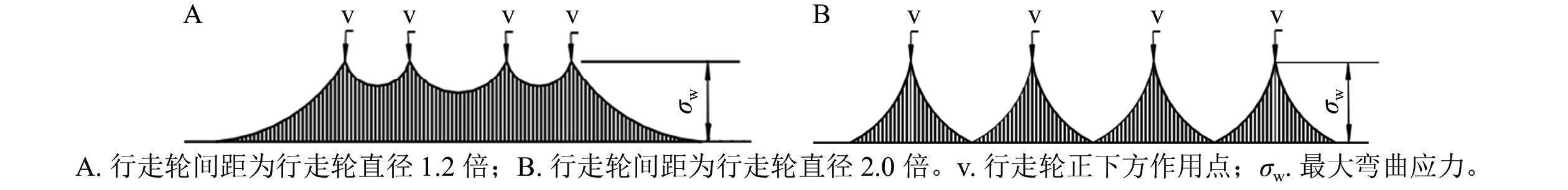
Objective In response to the difficulties in transporting bamboo down the mountain after logging, the unstable effect of current simple cable type mechanical equipment, the insufficient endurance of transportation sports cars, and the lack of safety assurance, this study aims to design a bamboo cableway skidding sports car transportation system, so as to achieve safe and efficient transportation of bamboo down the mountain. Method Through research on bamboo forest farms in Fujian, Hunan Provinces with abundant bamboo resources, the basic design parameters of the bamboo cableway skidding and sports car transportation system were determined. The overall functions, dimensions, and key components of the suspension cable and sports car were designed. The main load-bearing components of the sports car were analyzed by finite element analysis, and the strength and stiffness of the sports car were verified. The coupling vibration of cableway sports car system was analyzed by ADAMS software, and the main influencing factors in transporting bamboo by cableway were determined. Taking transportation speed, the total weight of sports cars and bamboo, and the inclination angle of the cableway as evaluation factors, and comprehensive evaluation of the safety and efficiency of sports car transportation of bamboo as indicators, Box-Behnken simulation experiments were conducted to optimize parameter combination. Result The results of the quadratic regression orthogonal rotation combination experiment indicated that the three factors which had significant impact on the safety and efficiency of sports car transportation in descending order were cableway inclination angle, transportation speed, and total weight of sports car and bamboo. When the transportation speed was 3.95 m·s−1, the total weight of the sports car and bamboo was 576.67 kg, and the inclination angle of the cableway was 17.09°, the comprehensive transportation safety and efficiency reached the best. Conclusion The transportation safety and efficiency are good when the inclination angle of the carrying cable is 16.50° − 20.40°, the transportation speed is 3.00 − 4.00 m·s−1, and the total weight of the sports car and bamboo is 420.00 − 580.00 kg. It can achieve charging and energy storage during the bamboo cableway skidding transportation operation, and ensure the safe and efficient transportation of bamboo down the mountain. [Ch, 6 fig. 5 tab. 13 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1357-1365.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220742
Abstract:
Carbon peak and carbon neutrality (dual carbon) is a broad and profound systemic change that requires the participation of various industry sectors. Unlike other industries, crop industry is not only an important source of greenhouse gas emissions, but also has enormous potential for carbon sequestration. Promoting emission reduction and carbon sequestration in crop industry is an indispensable part of achieving national dual carbon. In this paper, the main emission sources of nitrous oxide (N2O) and methane (CH4) in the field of planting were sorted out, including N2O emissions caused by excessive nitrogen application, water-saving irrigation of rice fields, and livestock and poultry waste, as well as CH4 emissions from flooded rice fields and ruminant animals. In addition to the direct emissions mentioned above, there existed a significant amount of indirect carbon emissions during agricultural production processes. The greenhouse gas emission reduction and carbon sequestration potential of crop industry were analyzed and the main emission reduction and sequestration pathways were summarized, including N2O emission reduction in dryland, CH4 emission reduction in rice fields. The potential of carbon sequestration and sink enhancement in crop industry could be increased through the application of organic fertilizer, straw return to the field, conservation tillage and return of farming waste to the field through pyrolysis and charring. This paper also discusses the feasibility and importance of carbon labeling and carbon trading in promoting green and low carbon development in China’s crop industry. It is clarified that emission reduction and soil carbon sink increase in crop industry must be based on the premise of safeguarding food security, avoiding blind emission reduction and excessive emission reduction, and must be coordinated with green development of crop industry. A sound guarantee and innovation system should be established to provide assistance for China’s carbon peak and carbon neutrality. [Ch, 49 ref.]
Carbon peak and carbon neutrality (dual carbon) is a broad and profound systemic change that requires the participation of various industry sectors. Unlike other industries, crop industry is not only an important source of greenhouse gas emissions, but also has enormous potential for carbon sequestration. Promoting emission reduction and carbon sequestration in crop industry is an indispensable part of achieving national dual carbon. In this paper, the main emission sources of nitrous oxide (N2O) and methane (CH4) in the field of planting were sorted out, including N2O emissions caused by excessive nitrogen application, water-saving irrigation of rice fields, and livestock and poultry waste, as well as CH4 emissions from flooded rice fields and ruminant animals. In addition to the direct emissions mentioned above, there existed a significant amount of indirect carbon emissions during agricultural production processes. The greenhouse gas emission reduction and carbon sequestration potential of crop industry were analyzed and the main emission reduction and sequestration pathways were summarized, including N2O emission reduction in dryland, CH4 emission reduction in rice fields. The potential of carbon sequestration and sink enhancement in crop industry could be increased through the application of organic fertilizer, straw return to the field, conservation tillage and return of farming waste to the field through pyrolysis and charring. This paper also discusses the feasibility and importance of carbon labeling and carbon trading in promoting green and low carbon development in China’s crop industry. It is clarified that emission reduction and soil carbon sink increase in crop industry must be based on the premise of safeguarding food security, avoiding blind emission reduction and excessive emission reduction, and must be coordinated with green development of crop industry. A sound guarantee and innovation system should be established to provide assistance for China’s carbon peak and carbon neutrality. [Ch, 49 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1366-1375.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230495
Abstract:
As one of the precious afforestation trees in China and the source of raw materials for the industrial production of the first-line anticancer drug paclitaxel, Taxus spp. are now widely distributed. However, the ability to develop efficient cultivation technology of Taxus spp. is compromised for lack of systematic analysis of factors affecting the growth characteristics. This study has explored the growth characteristics, including morphological/structural parameters and physiological and biochemical parameters the measurement methods of each parameter. The influencing factors of the growth characteristics is mainly focused on the growth characteristic parameters, the genetic factors, the cultivation conditions and the environmental factors. The growth characteristics are evaluated by morphological structure and physiological and biochemical indicators. Genetics is the main factor that determines the shape of the cultivated trees, and Taxus species with large crown widths are suitable for artificial afforestation. Environmental factors, such as site conditions, moisture, fertilizers, soil, light, and temperature, have significant impacts on the growth of Taxus trees. The future research, involving genomics, metabolomics, multi-feature correlation studies, protection of genetic resources, stress resistance studies and ecosystem service functions, will further promote the protection and utilization of Taxus. [Ch, 72 ref.]
As one of the precious afforestation trees in China and the source of raw materials for the industrial production of the first-line anticancer drug paclitaxel, Taxus spp. are now widely distributed. However, the ability to develop efficient cultivation technology of Taxus spp. is compromised for lack of systematic analysis of factors affecting the growth characteristics. This study has explored the growth characteristics, including morphological/structural parameters and physiological and biochemical parameters the measurement methods of each parameter. The influencing factors of the growth characteristics is mainly focused on the growth characteristic parameters, the genetic factors, the cultivation conditions and the environmental factors. The growth characteristics are evaluated by morphological structure and physiological and biochemical indicators. Genetics is the main factor that determines the shape of the cultivated trees, and Taxus species with large crown widths are suitable for artificial afforestation. Environmental factors, such as site conditions, moisture, fertilizers, soil, light, and temperature, have significant impacts on the growth of Taxus trees. The future research, involving genomics, metabolomics, multi-feature correlation studies, protection of genetic resources, stress resistance studies and ecosystem service functions, will further promote the protection and utilization of Taxus. [Ch, 72 ref.]
2023, 40(6): 1376-1376.
Abstract: