2023 Vol. 40, No. 5
2023, 40(5): 921-929.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230177
Abstract:
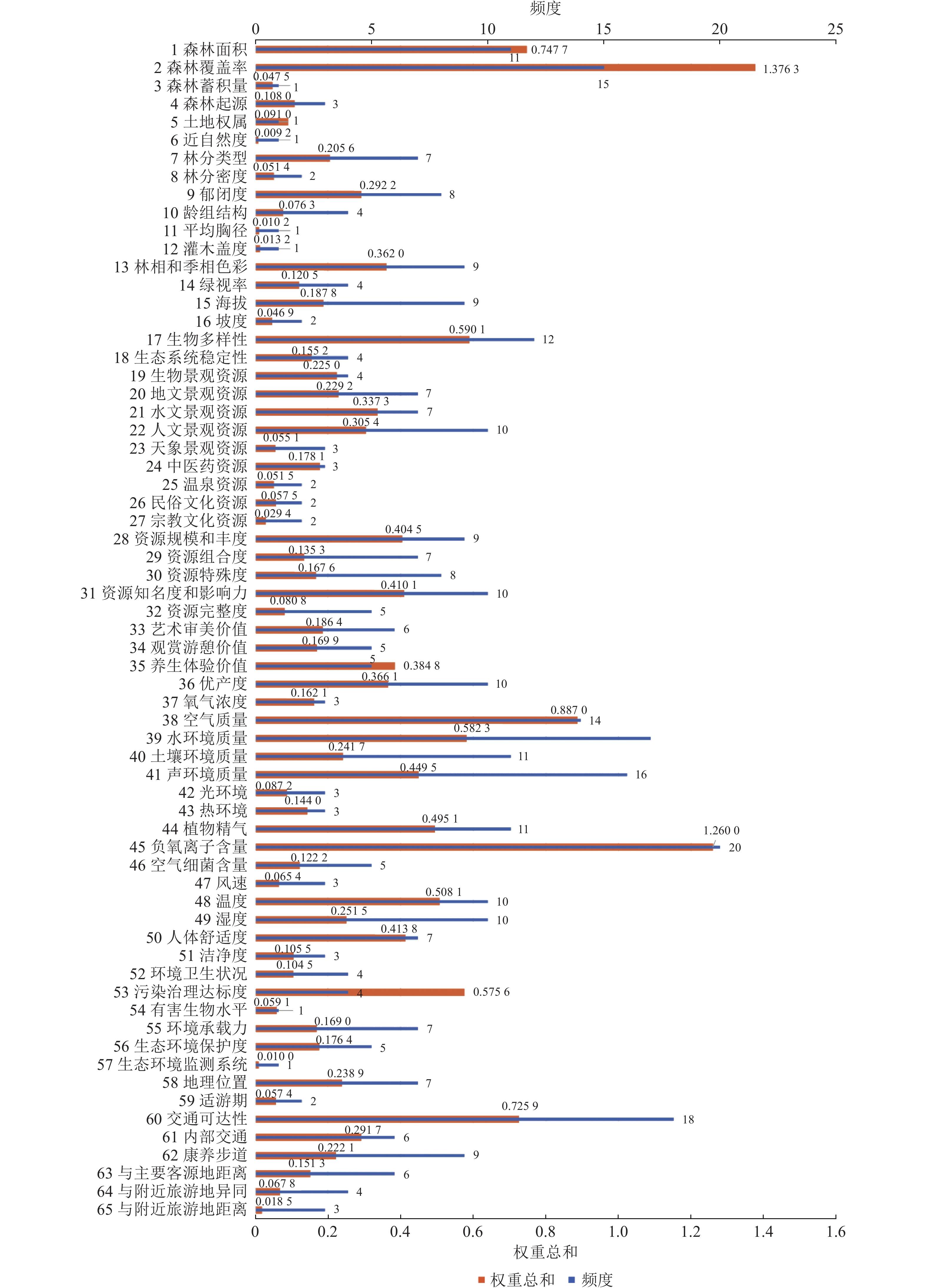
Objective This study, with a Meta integrated review using the existing index system related to forest therapy, is aimed to construct a more objective and scientific index system and further optimize the forest therapy indicator system so as to provide reference for the further promotion of the empirical research of related indicators. Method First, a summary was made of the evaluation results of the existing forest therapy related index system using the Meta integration method. Then, with foreign indicator systems and domestic published standards integrated, a new and more comprehensive indicator system was constructed before the evaluation and analysis were carried out through the membership theory of fuzzy mathematics and the principle of fuzzy relation composition. Result (1) The three-level indicator system with 32 basic indicators regarding resources, environment and location has offset the negative impact of the existing indicator systems that featured with unclear classification, duplication of reference and anaphora overlapping due to their excessive focus on tourism resources, landscape planning and geography forestry. (2) As indicated in the comprehensive evaluation results, the weight of environmental conditions was 0.497 5, and of the sub indicators comfort index and negative oxygen ion content were considered as the most favorable indicators for forest therapy; the resource condition weight was 0.368 8, and of the sub indicators the forest area and coverage index had a significantly higher weight than the others, which may attribute to the current insufficient research on the impact of specific forest structure on the health efficacy whereas the location condition index is 0.133 7. Conclusion It is feasible to introduce the method of Meta integration into the construction of forest therapy index system. The comprehensive evaluation results have reflected the public’ s recognition of the current forest therapy indicators, and it is necessary to further study the effects of stand density and human comfort in the forest therapy base, and strengthen the empirical exploration of the base medicine. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 37 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 930-939.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220676
Abstract:
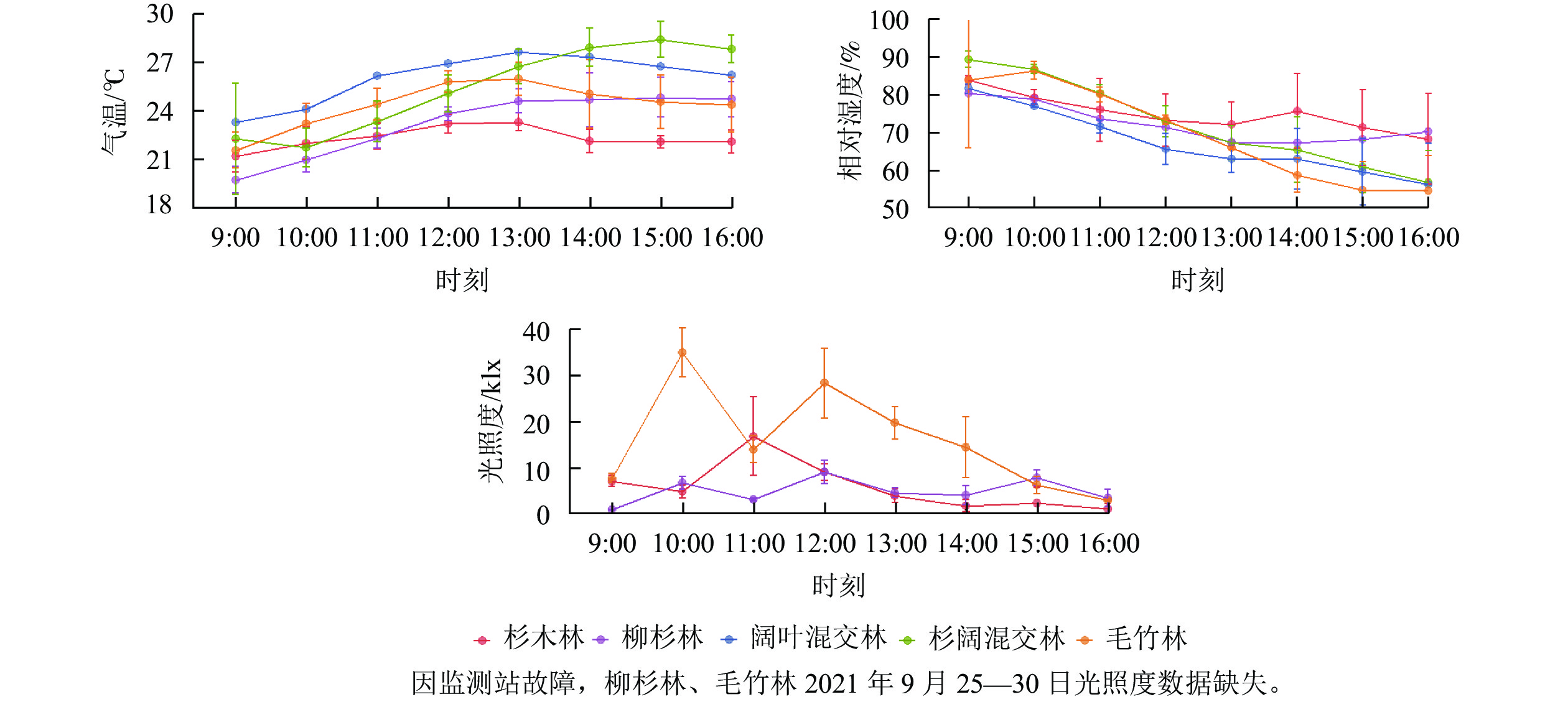
Objective This study aims to explore the release characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from different forest stands, so as to provide a scientific basis for the development of forest therapy activities. Method A combination of sorbent tube enrichment sampling and real-time online sampling was used to analyze VOCs composition and mole fractions of 5 typical forest stands: Cunninghamia lanceolata forest (SM), Cryptomeria fortunei forest (LS), Cyclobalanopsis glauca-Quercus fabri mixed forest (KY), C. lanceolata and Cinnamomum camphora mixed forest (SK), Phyllosachys edulis forest (MZ) in Baiyun National Forest Park in Zhejiang Province from September 25 to 29, 2021. Result (1) Monoterpenes were mainly released from the other 4 stands except for MZ. The monoterpene release from SM, LS, KY and SK accounted for 47.5%, 60.0%, 50.4% and 39.9% of the total VOCs, respectively. (2) The monoterpene concentrations in different stands ranging from large to small were LS (3.15 nmol·mol−1), KY (1.89 nmol·mol−1), SM (1.69 nmol·mol−1), SK (1.47 nmol·mol−1) , and MZ (1.24 nmol·mol−1); in which the monoterpene concentration of LS was significantly higher than that of other stands (P<0.05). (3) The daily variation trend of monoterpene mole fractions in the human respiratory layer of different stands was different, among which SM and KY showed a gradual downward trend, SK and LS showed a gradual upward trend, and MZ showed first an increasing trend and then a decreasing trend. (4) The correlations between monoterpene mole fraction and environmental factors varied in different stands. LS and SK both had a significant negative correlations with relative humidity, PM2.5 and PM10 (P< 0.001). There was a significant positive correlation between the monoterpene mole fraction and humidity in SM and KY (P<0.001). The correlation between MZ and various environmental factors did not reach a significant level. Conclusion LS have a higher mole fraction and proportion of monoterpene than other forests, and are highly recommended for forest therapy sites. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 46 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 940-950.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230249
Abstract:
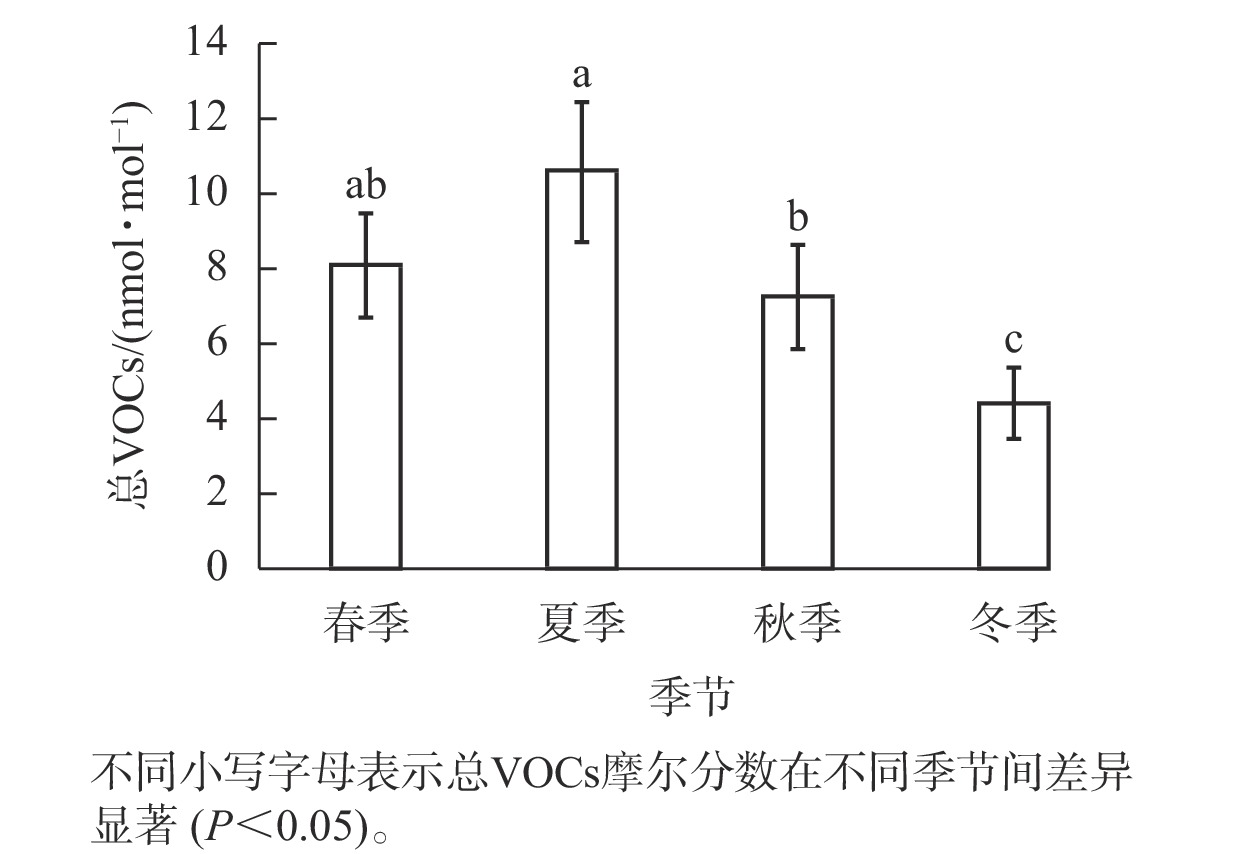
Objective The aim is to understand the seasonal dynamics and daily variation patterns of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in Phyllostachys edulis forest, and analyze the influence of environmental factors on their concentration changes. Method The VOCs in Ph. edulis forest in Zhuji Wuxie scenic area, Shaoxing City of Zhejiang Province were determined by sorbent tube enrichment sampling and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Its variation pattern was analyzed and the correlation between VOCs concentration and various environmental factors was also analyzed based on the data from environmental meteorological monitoring stations. Result (1) A variety of substances were detected in Ph. edulis forest, mainly including alkanes, terpenes, aromatic hydrocarbons, esters, alcohols and ketones. The largest concentration of terpenes was released, with a maximum of 7.249 nmol·mol−1, of which the dominant component was isoprene, accounting for about 80% of terpene. (2) From the perspective of seasonal variation, the concentration of total VOCs was the largest in summer (10.600 nmol·mol−1), followed by spring and autumn (8.068 and 7.254 nmol·mol−1, respectively). The smallest was in winter, only 4.432 nmol·mol−1, and the seasonal variation trend of various major VOCs was the same as that of total VOCs. (3) From the perspective of daily variation, the total VOCs concentration was maximum in the morning in spring (9.074 nmol·mol−1), followed by 8.621 nmol·mol−1 at noon and a minimum of 6.509 nmol·mol−1 in the afternoon. In summer, autumn and winter, the maximum VOCs concentration at noon was 11.710, 8.038 and 5.298 nmol·mol−1, and the lowest values in the afternoon were 8.455, 5.702 and 3.418 nmol·mol−1. The daily variation trend of various major VOCs were the same as that of total VOCs, with higher concentrations in the morning and at noon. (4) VOCs were correlated with various environmental factors, among which terpenes, alkanes, esters and total VOCs were significantly positively correlated with temperature, and significantly negatively correlated with PM2.5, PM10 and ozone (P<0.05). Conclusion The types and contents of VOCs in Ph. edulis forest are different in different seasons and time periods, and isoprene is the main substance that determines the dynamics of VOCs. [Ch, 3 fig. 2 tab. 42 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 951-960.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220734
Abstract:
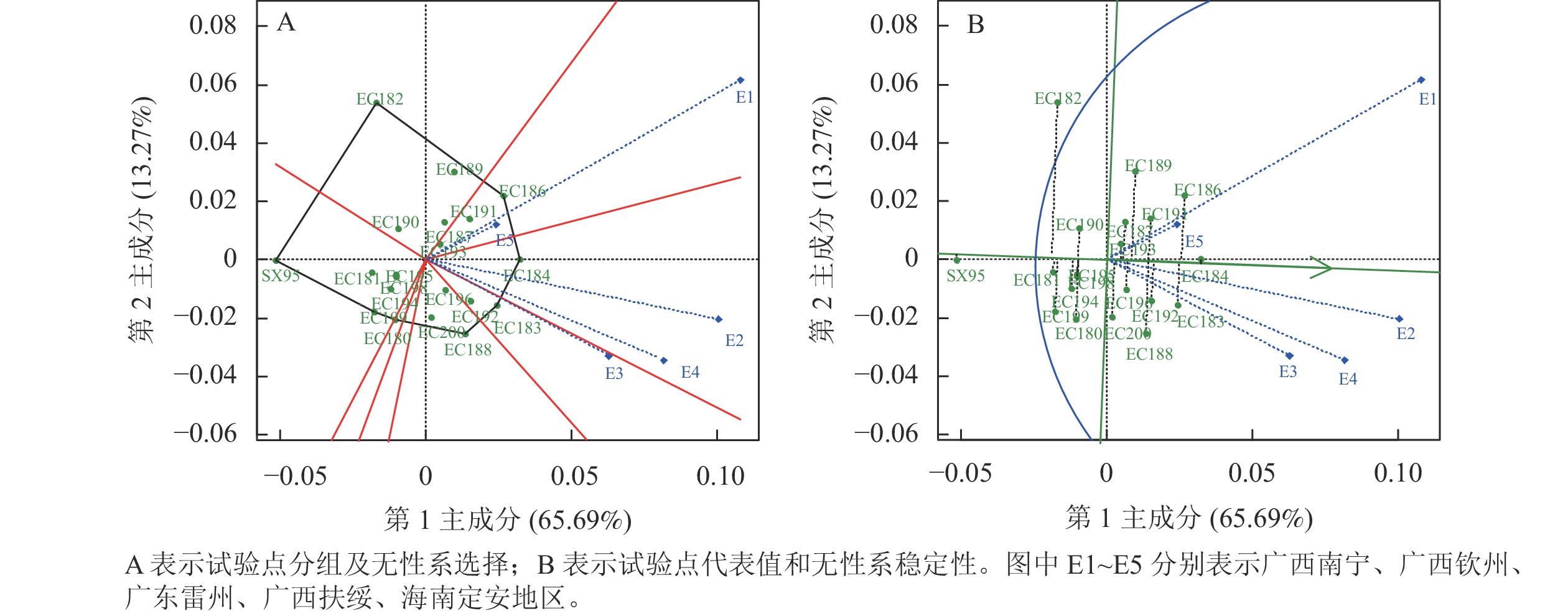
Objective 20 Eucalyptus clones, including 1 Eucalyptus camaldulensis and 19 Eucalyptus hybrid clones, are tested at Nanning, Qinzhou, Fusui in Guangxi, Leizhou in Guangdong and Dingan in Hainan, respectively. And, the influence of genotype and environment interaction on Eucalyptus clones were mainly discussed. The results can provide a basement for screening suitable environment to the tested clones and reference for the promotion of excellent clones of Eucalyptus. Method The 4.5-year-old Eucalyptus clones tested at different sites were selected as the research objects. Based on the survey data of tree height, diameter at breast height (DBH), individual volume and survival rate of each clone, the growth performance of each clone at different sites was compared. A linear mixing model was established for single site and multi-site to calculate the variance components and clonal repeatability of each trait. The best linear unbiased predictive (BLUP) value of single site and the variance effect size of each trait at multi-site were also calculated. Finally, the average volume and BLUP values were used for genotype main effects (G) and genotype × environment interaction (G×E) analysis model (GGE). Result In single site analysis, the order of optimal clones in each site were different, and the traits in different sites were also affected by different environments. In the multi-site analysis, there were significant differences in genotype, environment and G×E interaction among Eucalyptus clones. The clone repeatability of each trait ranged from 0.781 6 to 0.868 5, among which the DBH trait had the highest and most stable repeatability, the tree height trait was most easily affected by environment. Based on the individual volume trait, EC186, EC188 and EC184 were selected as superior clones. Based on the average volume and BLUP value, the GGE model analysis showed that EC183 and EC184 were clones with high volume and high stability. Conclusion Among the 20 clones, EC183 and EC184 are clone with high individual volume and high stability. Compared with the five regions, Nanning in Guangxi is suitable for the rapid growth of these clones, Qinzhou in Guangxi is the ideal environment for the material selection of these clones. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 38 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 961-969.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230021
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to investigate the compatibility of Michelia foveolata with M. figo and M. crassipes. Method On the one hand, fluorescence microscope was used to observe the pollen tube growth after 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 10 h, 12 h, 1 d, 2 d, 4 d, 6 d and 8 d. On the other hand, the reciprocal cross test was carried out of M. foveolata with M. figo and M. crassipes respectively to calculate the fruit and seed setting status. Result (1) The fruit setting rates of the reciprocal cross of M. foveolata and M. figo were 75.0% and 78.8% respectively. (2) The fruit setting rate of M. foveolata × M. crassipes (80.0%) was significantly higher than that of M. crassipes × M. foveolata (6.7%). (3) The pollen germination of M. figo × M. foveolata was 2 h later than that of M. crasspies × M. foveolata and pollen tubes entered ovule on 8 d with no significant difference in growth rate. (4) There was no obvious hybridization barriers in the combination of M. foveolata as mother, and the pollen tube entered the ovule successively within 2 to 6 days with well developed fruit and seeds. (5) There were some pre-fertilization barriers, such as disarranged growth of pollen tube on stigma surface, callose accumulation in pollen tube, and callose accumulation in style channel cells and interstitial space and it was speculated that callose accumulation in style channel as the main cause of pre-fertilization barriers does not affect fruit setting, but has an effect on seed setting. (6) There were pre-fertilization and post-fertilization barriers in M. crassipes×M. foveolata. Pre-fertilization barriers include the failure of pollen to germinate on the stigma surface, the growth of pollen tubes in circles on the stigma surface, without entering the stigma, the expansion of pollen tubes due to the accumulation of callose inside and at the apex and the pollen tube becoming twisted and entangled within the ovule. However, post-fertilization barriers may be an important factor affecting fruit fall. Conclusion The reciprocal cross of M. foveolata and M. figo shows good compatibility with the compatibility degree of M. foveolata × M. crassipes being high, while the compatibility degree of M. crassipes×M. foveolata being low. [Ch. 5 fig. 1 tab. 23 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 970-981.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220737
Abstract:
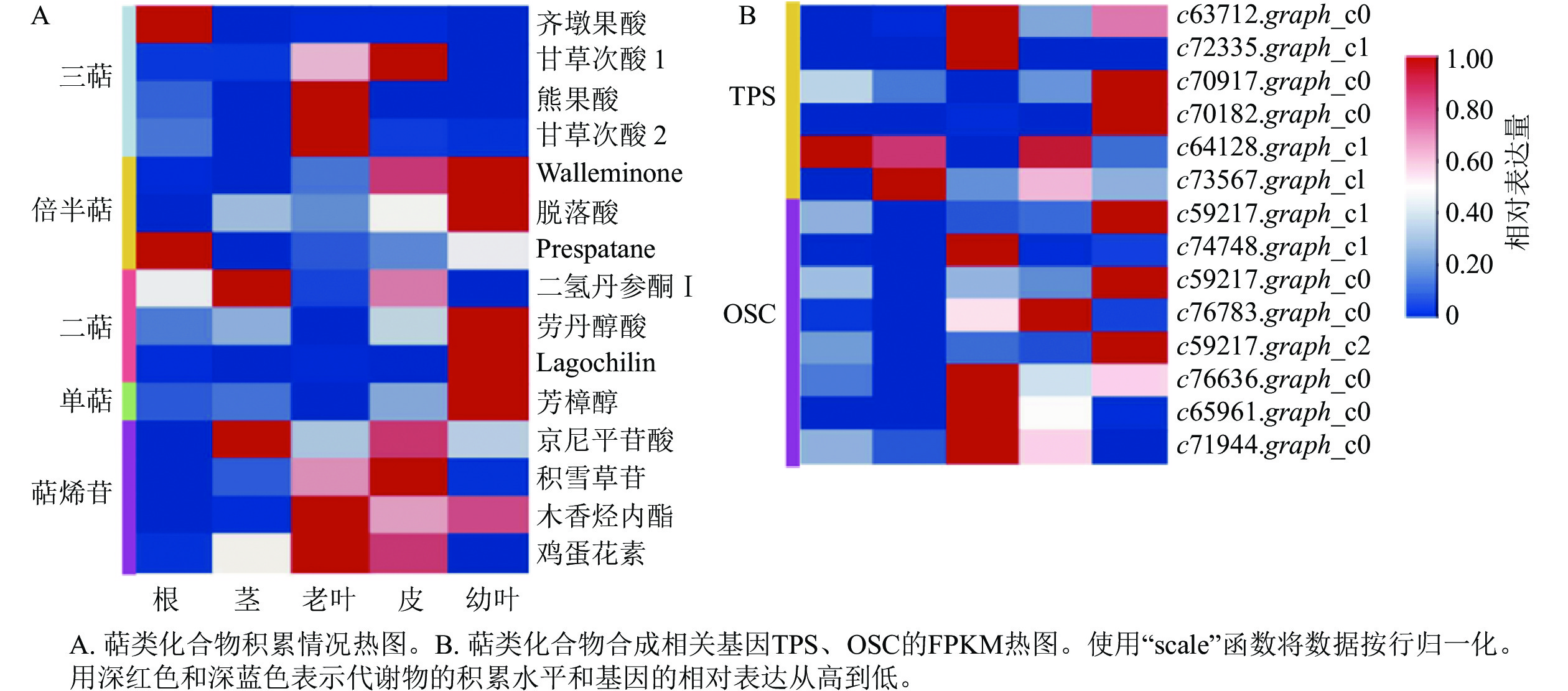
Objective Ormosia henryi is an important woody medicinal plant. This study aims to explore the accumulation pattern of terpene secondary metabolites and analyze the terpene biosynthesis pathway and related key enzyme genes, which is of great significance to the development of medicinal value in O. henryi. Method Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and high-throughput transcriptomic sequencing were used to find the associated enzyme genes of terpene biosynthesis from differentially expressed genes based on bioinformatics analysis. Result A total of 15 terpene compounds were detected in the metabolomic data and they contained enoxolone, oleanolic acid, linalool and other substances with medicinal activity, most of which were relatively higher in leaves than in other tissue parts. Transcriptome data screened 49 candidate genes related to terpene synthesis, and after analysis it was found that differential genes in the MVA pathway were highly expressed in young leaves while differential genes in the MEP pathway were highly expressed in old leaves. Based on WGCNA analysis, it was found that transcription factor families such as MYB, WRKY, bHLH and HB-HD-ZIP played an important role in terpene synthesis of O. henryi, and 6 transcription factors that might be related to terpene biosynthesis content were predicted, namely HB-HD-ZIP (c64527.graph_c1), GRF (c76195.graph_c0), DBB (c66970.graph_c2), DBB (c75593.graph_c0), HB-HD-ZIP (c63393.graph_c0) and C3H (c70385.graph_c1). Conclusion Important terpenes and candidate key enzyme genes that may participate in the biosynthesis pathway of these terpenes have been preliminarily obtained from the database of metabolomics and transcriptome of O. henryi . [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 36 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 982-990.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220761
Abstract:
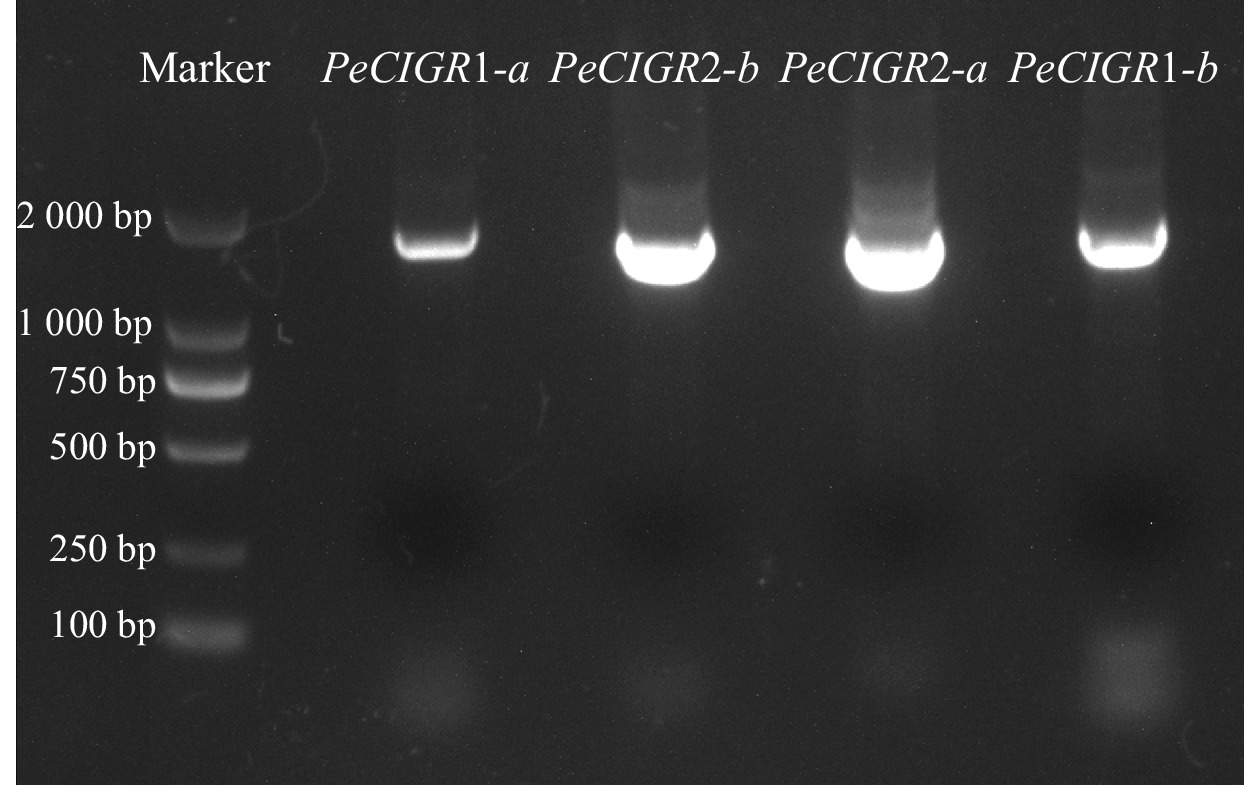
Objective The aim is to explore the role of PeCIGRs in the development of Phyllostachys edulis stem and abiotic stresss, as to provide reference for the study of high growth and stress resistance mechanism. Method The PeCIGRs gene was cloned from the internodes located in the middle of a 3-m young Ph. edulis. The physical and chemical properties and phylogenetic relationship of PeCIGRs protein were explored by bioinformatics analysis. The expression pattern of PeCIGRs gene in different tissues and under abiotic stresses and hormone treatment were analyzed based on transcriptome data. Result Four CIGR genes were cloned from Ph. edulis, named PeCIGR1-a, PeCIGR1-b, PeCIGR2-a and PeCIGR2-b. The nucleotide sequence length of the four CIGR genes was 1 635−1 716 bp, and the amino acid sequence length was 544−571 bp. Multiple sequence alignment revealed that all four CIGR genes had conserved GRAS domains, which belonged to GRAS family. Tissue-specific expression analysis revealed that PeCIGRs was mainly expressed in Ph. edulis stem and reached its peak at the top of 3-m young Ph. edulis. In addition, the expression analysis under different stresses and hormone treatments found that PeCIGRs showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing under drought, salt stress and salicylic acid treatment. Under abscisic acid treatment, PeCIGR1-a and PeCIGR1-b genes increased first and then decreased, while PeCIGR2-a and PeCIGR2-b showed a downward trend after 24 h of treatment. Conclusion PeCIGRs gene is involved in the regulation of the growth and development of Ph. edulis stem, and response to abiotic stress (drought and salt) and hormone (abscisic acid and salicylic acid) as well. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 38 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 991-998.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220677
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an exploration of the salt tolerance of delayed aging wheat (Triticum aestivum) and premature aging wheat, is aimed to determine the optimal concentration and mechanism of calcium to alleviate salt stress in wheat. Method First, with the premature senescence strain DH70 and delayed senescence strain DH106 in the wheat doubled haploid (DH) population selected as materials, the wheat was subjected to stress with a 300 mmol·L−1 salt solution selected from the preliminary experiment before a comparison was made of the salt tolerance between the two materials. Then, different concentrations (5, 10, 20, 40, 60 mmol·L−1) of calcium chloride solution were used to treat wheat under salt stress before the optimal concentration of calcium chloride solution to alleviate salt stress was determined. Result (1) The stress of 300 mmol·L−1 salt solution significantly inhibited the germination of wheat seeds and the growth of seedlings, and the delayed aging type of wheat DH106 showed better salt tolerance (P<0.05). (2)The application of different concentrations of CaCl2 solution alleviated the salt injury to a certain extent, so that the germination rate, seedling length, root length and fresh weight of the two materials of wheat were significantly increased compared with those with 300 mmol·L−1 salt stress treatment (P<0.05) and the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT) were significantly increased compared with those after salt treatment (P<0.05), while the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) was significantly decreased compared with that after salt treatment (P<0.05), with the best relief effect achieved with 40 mmol·L−1 CaCl2 treatment. (3)Under the treatment of 40 mmol·L−1 CaCl2, the SOD and POD activities of the premature aging strain DH70 increased by 58.0% and 43.5%, respectively, while the MDA content decreased by 33.0% and the SOD and POD activities of the delayed aging strain DH106 increased by 52.9% and 42.3%, respectively, whereas the MDA content decreased by 21.1%. Conclusion Salt stress significantly inhibited the normal growth and development of wheat, and delayed senescence type wheat showed good salt tolerance exogenous application of CaCl2 can increase wheat antioxidant enzyme activity, reduce MDA content, and enhance wheat salt tolerance. And the best treatment effect is achieved with a concentration of 40 mmol·L−1 CaCl2. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 24 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 999-1007.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220705
Abstract:
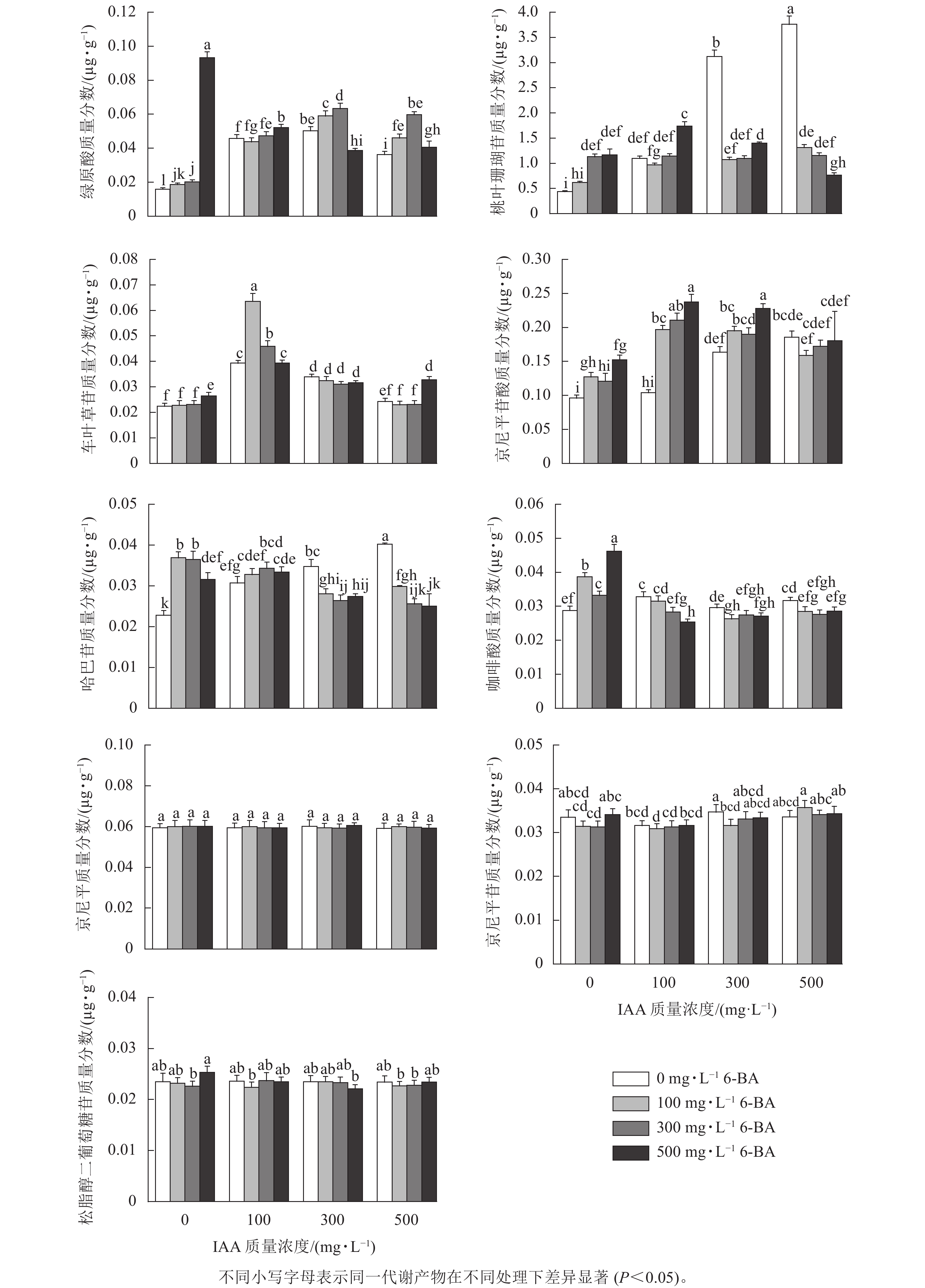
Objective The objective is to explore the effects of different concentrations of plant growth regulators on the accumulation of secondary metabolites in Eucommia ulmoides leaves and screen the optimal ratio conditions of plant growth regulator to promote the generation of secondary metabolites, so as to provide reference for the regulation of secondary metabolites in E. ulmoides. Method The 2-year-old E. ulmoides seedlings with different concentrations of 3-indole acetic acid (IAA) and 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA) (15 groups) were used as materials, and growth morphological characteristics and dry and fresh weight of E. ulmoides leaves were measured. The contents of 9 secondary metabolites were determined by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). The optimal growth ratio conditions for high-yield secondary metabolites were selected by principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis combined with biomass. Result Compared with the control, the leaf area, leaf circumference, leaf width, dry and fresh weight significantly increased (P<0.05) when the conditions of plant growth regulators was 500 mg·L−1 IAA + 500 mg·L−1 6-BA. Correlation analysis showed that the IAA concentration was significantly positively correlated with leaf area, aucubin, geniposide and geniposidic acid (P<0.05). The concentration of 6-BA was significantly positively correlated with the content of chlorogenic acid and geniposidic acid (P<0.05). The comprehensive indicator analysis showed that when 500 mg·L−1 6-BA was applied alone, the accumulation of chlorogenic acid, aucubin and pinoresinol diglucoside were the highest , which were 0.036, 0.046 and 0.031 μg·g−1 respectively. Conclusion The concentration of IAA has significant effects on the accumulation of aucubin and asperulosidic acid, while the concentration of 6-BA has significant effects on the accumulation of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid (P<0.05). When 100 mg·L−1 IAA + 300 mg·L−1 6-BA is applied in combination, it is beneficial for plant growth. When 100 mg·L−1 IAA + 100 mg·L−1 6-BA is applied, it is beneficial both for the biomass and the accumulation of secondary metabolites in E. ulmoides. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 26 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1008-1017.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220753
Abstract:
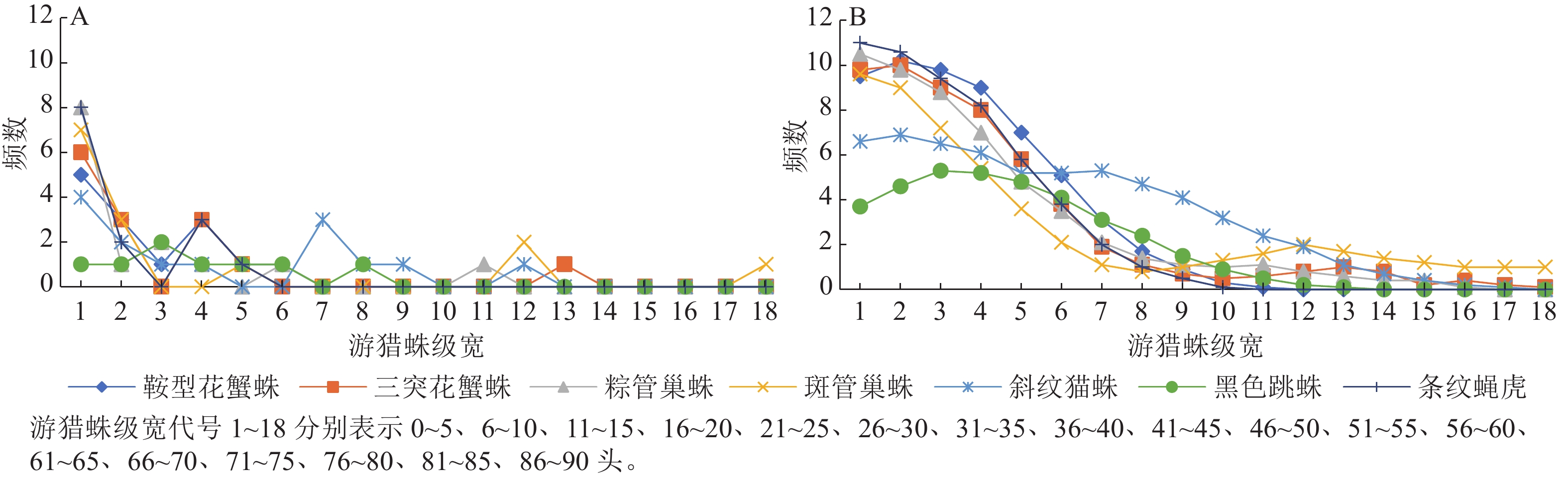
Objective The objective is to explore the interspecific competition of wandering spiders feeding on Empoasca onukii in tea plantations, so as to provide scientific basis for the rational conservation and control of wandering spiders against E. onukii. Method The population dynamics of E. onukii and wander spiders in ‘Nongkangzao’ and ‘Pingyangtezao’ tea plantations in Science and Technology Demonstration Garden of Anhui Agricultural University in 2021 were analyzed using grey correlation method, Fuzzy classification method and competition coefficient method. The competitive relationship between different wandering spiders was studied and the most competitive wandering spiders were identified. By combining grey correlation degree with competition coefficient, the concept of competition intensity index was derived to verify the accuracy of the obtained results. Result According to the grey correlation results, it could be seen that the wandering spiders most correlated with the number of E. onukii were Clubiona reichlini (0.896 7) and Clubiona japonicola (0.890 2) in ‘Nongkangzao’ tea plantation, and ‘Pingyangtezao’ tea plantation was also dominated by C. reichlini(0.860 3)and C. japonicola (0.857 1). Based on the variance analysis results of competition coefficient and competition intensity index, it was found that C. japonicola differed significantly from other spiders, followed by C. reichlini. Oxyopes sertatus differed very significantly from the two in feeding on E. onukii, regardless of the type of wandering spider in the competition. Conclusion When feeding on E. onukii in tea plantations, C. japonicola and C. reichlini are the most competitive, while O. sertatus is the least competitive. Effective control of E. onukii can be achieved by reasonably protecting and utilizing highly competitive spiders such as C. japonicola and C. reichlini. [Ch. 2 fig. 6 tab. 33 ref ]
2023, 40(5): 1018-1025.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230029
Abstract:
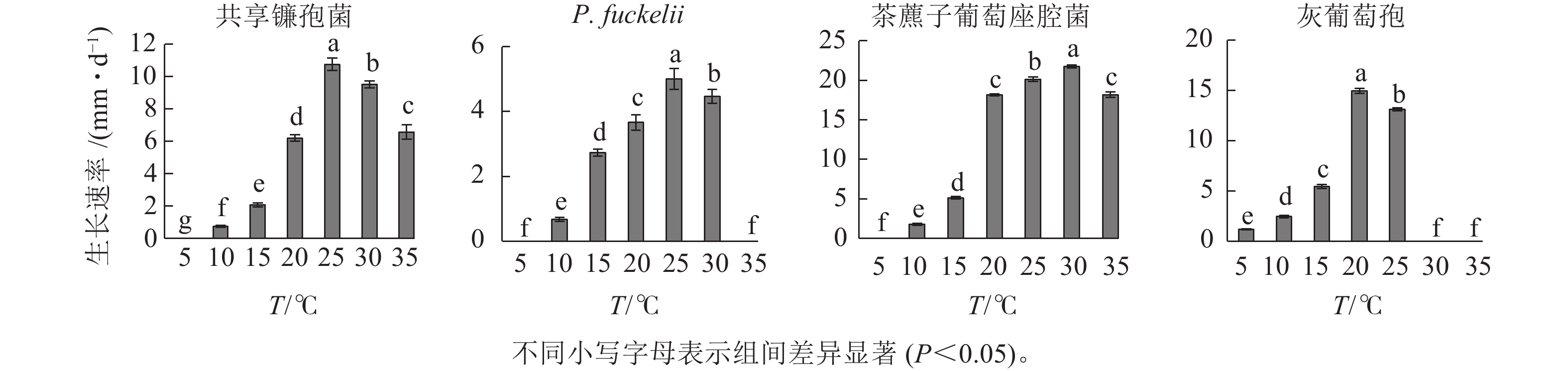
Objective This study aimed to determine the biological characteristics and toxicity of four pathogens, namely Fusarium commune, Phaeosphaeria fuckelii, Botryosphaeria dothidea, and Botrytis cinerea, that cause leaf spot in Carya illinoinensis and explore the optimal growth conditions for these pathogens and effective control agents. Method The mycelium growth rate method was utilized to measure the growth rates of the pathogens under different culture conditions and the inhibition rates of 5 chemical fungicides on the pathogens. The EC50 was calculated using DPS. Result F. commune and P. fuckelii grew optimally at 25 ℃, while Botryosphaeria dothidea and Botrytis cinerea grew optimally at 30 ℃ and 20 ℃, respectively. The optimal pH for growth were 8.0, 7.0, 7.0, and 6.0 for F. commune, P. fuckelii, Botryosphaeria dothidea and Botrytis cinerea, respectively. Glucose, soluble starch, sucrose, and soluble starch were the optimal carbon sources, respectively. Similarly, potassium nitrate, tryptone, urea, and tryptone were the optimal nitrogen sources for these four fungal species, respectively. Of the five fungicides tested, 450 g·L−1 prochloraz exhibited the highest level of toxicity to F. commune, Botryosphaeria dothidea, and Botrytis cinerea, with EC50 of 0.010 8, 0.091 5, and 0.021 0 mg·L−1, respectively. Additionally, the 250 g·L−1 pyrazolyl ester demonstrated the strongest toxicity to P. fuckelii, with EC50 of 0.004 1 mg·L−1. Conclusion The four types of pathogenic fungi growed well in carbon sources with elevated levels of glucose and soluble starch, as well as nitrogen sources that contain urea, potassium nitrate, and tryptone. Prochloraz and pyrazolyl ester can effectively controll the disease. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 31 ref. ]
2023, 40(5): 1026-1034.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220552
Abstract:
Objective Soil lead (Pb) pollution has serious ecological and health risks. This study tries to explore the source of Pb pollution to prevent and control soil pollution and ensure the healthy and sustainable development of soil resources. Method Taking Xinsheng Basin in Zhejiang Province as the research object, soil and parent rock samples were collected from rural areas with less anthropogenic activities. The content of trace elements in the study area was measured, and the changes in Pb content and its migration patterns in soil were analyzed. Pb isotope tracer method was used to qualitatively analyze the Pb pollution sources in the study area, and quantitatively analyze the contribution of Pb to the pollution sources in the study area. Result The Pb content was significantly enriched in the topsoil layer, up to 1.5 times the soil background value, and gradually decreased with the increase of the profile depth, indicating a significant impact of the exogenous input near the surface layer. When the Pb content in the site was high, its 206Pb/207Pb value was relatively low. The variation ranges of 206Pb/207Pb and 208Pb/206Pb values in the soil samples were 1.176 3−1.186 7 and 2.090 6−2.103 9, respectively. The larger the variation range of 206Pb/207Pb value, the greater the impact of human activities on soil Pb content. Pb isotope tracers indicated that the 206Pb/207Pb end member value of the parent rock was 1.196 0, and the 206Pb/207Pb endmember value of anthropogenic source was 1.172 0. Coal burning was the main anthropogenic source of Pb pollution in the study area, with a contribution rate of 38.8%−82.9% from anthropogenic sources. Conclusion The low 206Pb/207Pb value indicates the input of Pb from coal burning to the study area, and particulate pollutants enter the soil surface through continuous deposition process. Therefore, reducing the emission of particulate pollutants is an important way to reduce local Pb pollution. [Ch, 3 fig. 2 tab. 51 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1035-1044.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220727
Abstract:
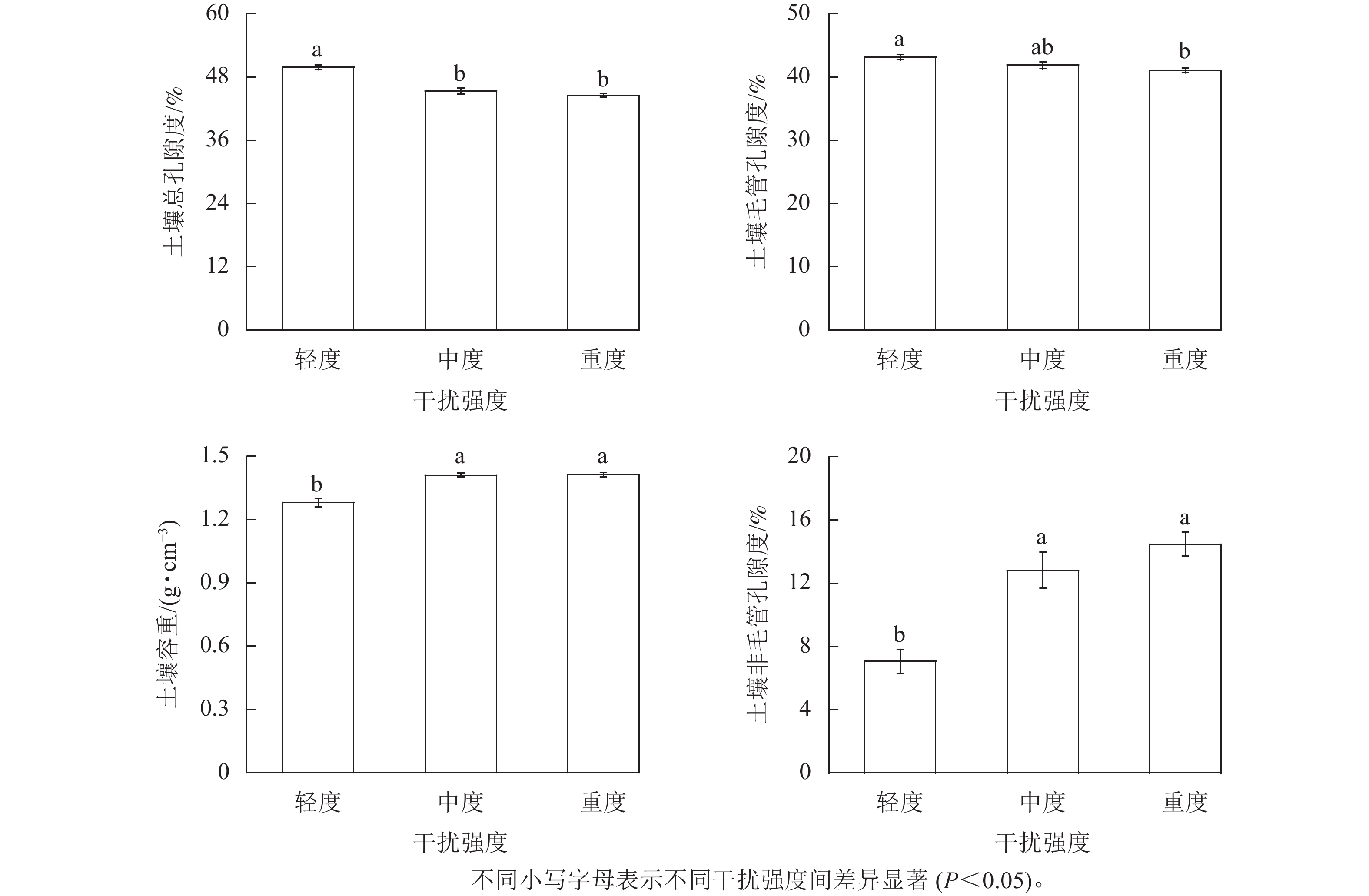
Objective This study aims to explore the impact of human disturbance on soil physical properties in the riparian zone, in order to provide a scientific basis for ecological restoration and regulation of the Yellow River riparian ecosystem. Method In October 2021, three types of sample sites with different degrees of disturbance were selected in the Luoyang-Zhengzhou section of the Yellow River based on the degree of human trampling, where the topography and surface vegetation coverage were relatively consistent. The near riparian zone was divided into 200 m×200 m sample plots according to a 5×3 grid, and a total of 15 sample points were set up. Differences in soil physical properties such as bulk density, moisture content, capillary water capacity, maximum water capacity, minimum water capacity, total porosity, capillary porosity, and non-capillary porosity in the Yellow River riparian zone with different levels of human disturbance intensity (mild, moderate and severe) were systematically compared and analyzed. Result (1) With the increase of human disturbance intensity, soil bulk density and non-capillary porosity increased gradually. Soil moisture content first increased and then decreased. Soil capillary water capacity, maximum water capacity, minimum water capacity, total porosity and capillary porosity decreased gradually. (2) Soil bulk density was negatively correlated with soil moisture content and capillary porosity, but it did not reach a significant level. There was a significant negative correlation between soil bulk density and soil capillary water capacity, maximum water capacity, minimum water capacity and total porosity (P<0.01), and a significant positive correlation with non-capillary porosity (P<0.01). Conclusion Excessive human disturbance such as trampling increases the soil compaction in the riparian zone, leading to the degradation of soil physical properties, and a decrease in soil water retention and holding capacity. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 41 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1045-1053.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220620
Abstract:
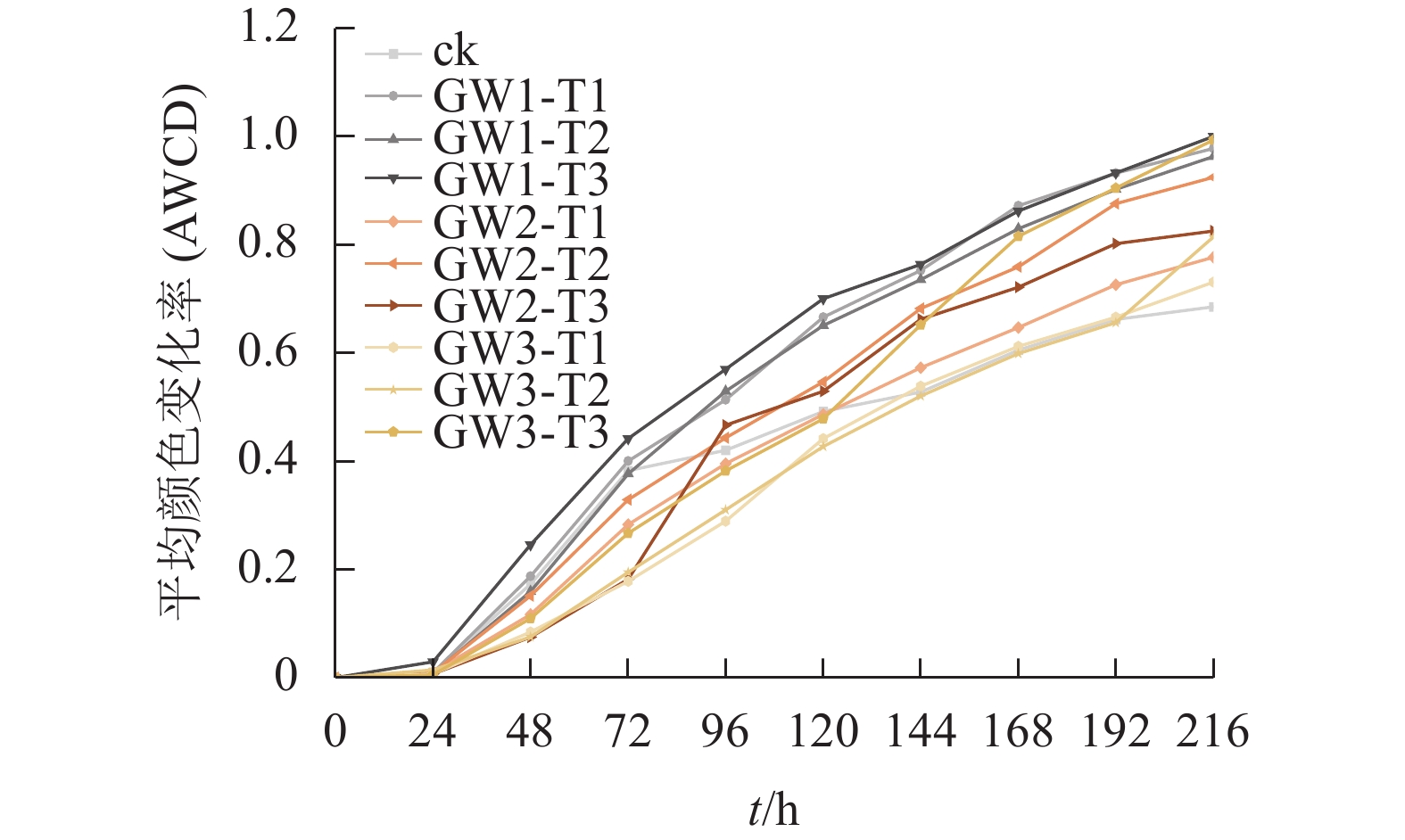
Objective Resource utilization of garden waste is an effective way to improve soil fertility and enhance carbon sink function of plantations. Study on the effects of different reuse treatments of garden waste on soil chemical properties and microbial community in the plantation soil can provide scientific basis for efficient utilization of garden waste. Method Experiments were carried out in an Ulmus pumila ‘Jinye’ plantation, in Fangshan District, Beijing City. Experimentation including three types of garden wastes products, crushed material, compost and biochar, and 1, 2 and 4 kg·m−2 carbon-based amounts were set up. Biolog-ECO microplate method combined with conventional soil chemical properties measurement were conducted in order to analyze the effects of different materials of garden waste and their application amounts on soil pH, nutrient content, microbial carbon source utilization and functional diversity indices of soil microbial community. Result (1) All three types of organic materials increased the content of soil organic carbon and nitrate nitrogen while crushed material and compost significantly reduced the pH value of weakly alkaline soil, with little impact on the content of ammonium nitrogen and available phosphorus. Meanwhile, biochar increased the soil pH value and decreased the content of ammonium nitrogen and available phosphorus; (2) The microbial utilization of carbon sources and the functional diversity of microbial community are as follows: crushed material>compost>biochar. (3) Among the six types of carbon sources, carbohydrate, carboxylic acids and amino acid carbon source were the main carbon sources used by microorganisms, which could distinguish the three treatments of garden waste. The three organic materials all promoted the microbial utilization of phenolic acid carbon source and reduced the utilization of amino acid carbon source. The utilization of amino acid, polymer and other carbon sources by carbon-oriented microorganisms in treatment of crushed materials and compost were stronger than that of biochar while the microbial utilization of carbohydrate carbon source in biochar is the strongest among the three treatments; (4) The effect of application amounts on soil microbial carbon source utilization was not significant, and functional diversity of microbial community increased with the increase of application amounts. Conclusion Garden waste could be used to improve the soil quality of plantation by three types of treatments. Compared to biochar, crushed material and compost were more effective in reducing the pH of weakly alkaline soil, increasing soil fertility, and improving the functional diversity of soil microbial community. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 33 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1054-1062.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220704
Abstract:
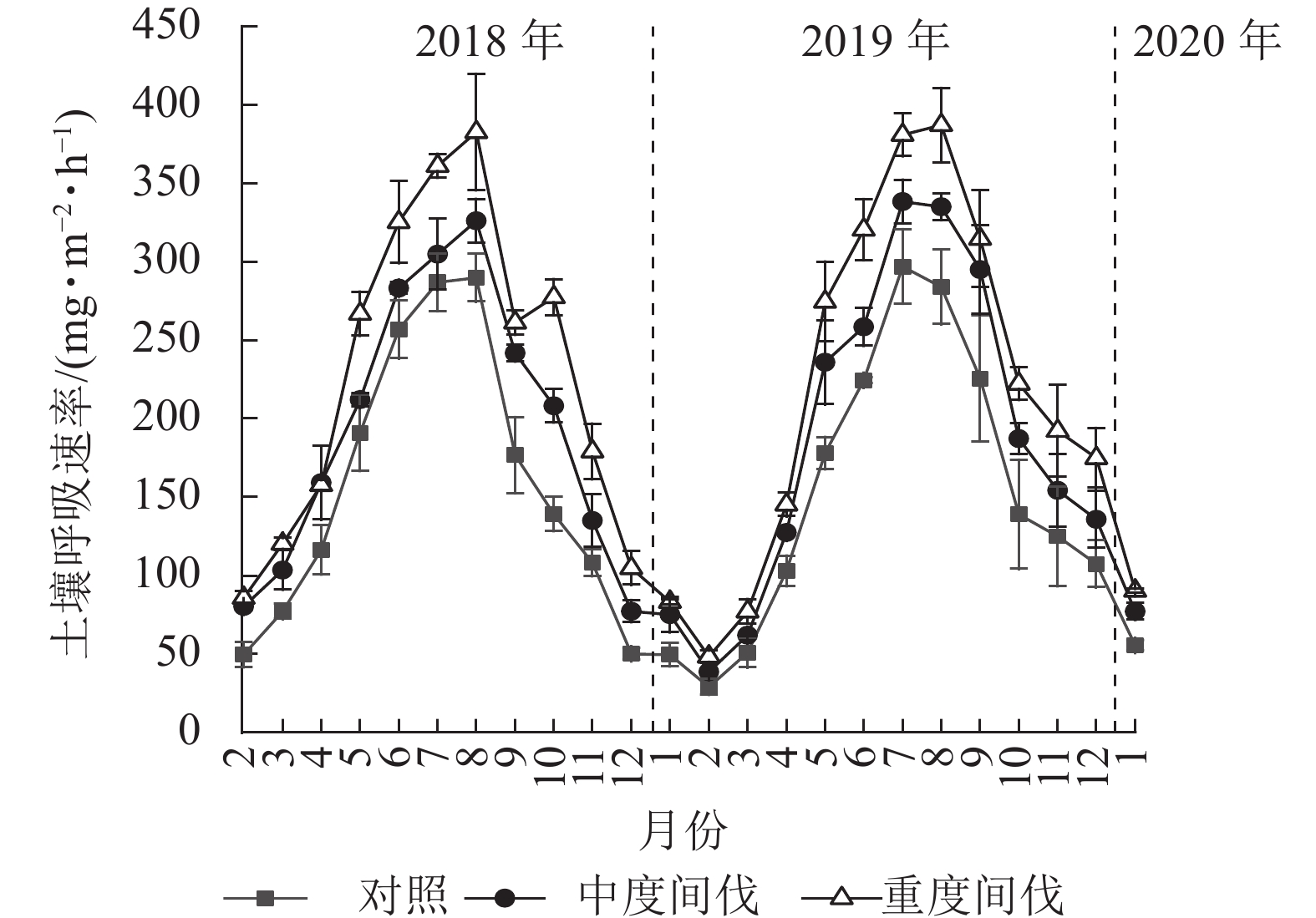
Objective This study, with a comparison of the differences in soil respiration rates of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations under different thinning intensities, is aimed to investigate the main factors affecting soil respiration rates, so as to provide a scientific basis for forest management and carbon sink management. Method With a randomized block design, three thinning treatments, namely control (thinning 0%), moderate thinning (thinning 45%) and heavy thinning (thinning 70%) were arranged before short-term in-situ monitoring was conducted of soil respiration rates in C. lanceolata plantations using static box-meteorological chromatography. Result Thinning significantly increased the soil respiration rate in C. lanceolata forest, with an increase of 23.30% and 44.94% for the ones treated with moderate and heavy thinning respectively. Soil respiration rate was exponentially correlated with soil temperature at 5 cm depth, but not with soil water content. The temperature sensitivity coefficient (Q10) of soil respiration ranged from 1.77 to 2.16 under different thinning treatments, with the Q10 being the highest under the control treatment, and thinning decreased the temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in C. lanceolata stands. Soil respiration rate of C. lanceolata plantation was positively correlated with soil water-soluble organic carbon, microbial biomass carbon and permanganate-oxidizable carbon (P<0.01). Conclusion Thinning promoted the soil respiration rate of C. lanceolata forest which increased with the increase of thinning intensity. Soil temperature is the main factor affecting the change in soil respiration rate, with soil active organic carbon being an important factor. [Ch, 3 fig. 5 tab. 44 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1063-1072.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220651
Abstract:
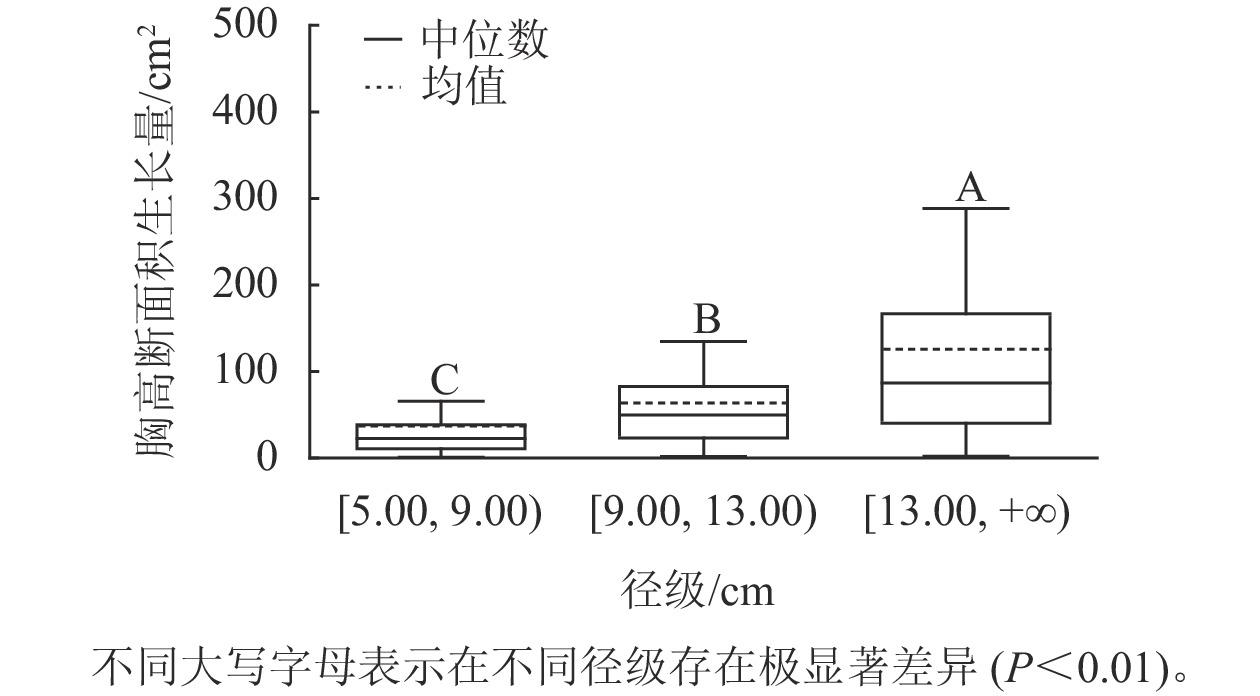
Objective The objective is to study the growth model of breast-height basal area of evergreen broad-leaved forest and to explore the factors affecting breast-height basal area increment (BAI) of evergreen broad-leaved forest, so as to provide a theoretical basis for evergreen broad-leaved forest management. Method Taking the evergreen broad-leaved forest in Mount Tianmu as the research object. Firstly, the correlation between BAI and diameter at breast height (DBH), competition and terrain factors were analyzed. Secondly, the differences of BAI among different diameter classes, crown diameter classes and competition classes were discussed. And finally, based on the ridge regression analysis, the individual tree growth model with logarithm of BAI as the dependent variable was established to quantitatively describe the relationship between BAI and DBH, competition and terrain factors. Result The Spearman’s correlation coefficients between BAI and DBH, crown diameter, and competition were 0.531, 0.427 and −0.34 respectively. BAI was extremely significant different among trees of different diameter classes (P<0.01), and increased with increase of DBH. There was a significant difference (P<0.01) in BAI among trees with different competition classes, and trees with low competition level had the largest BAI. Individual tree growth models based on average diameter grade were superior to those based on individual tree, and the regression parameters of DBH in both types of models were extremely significant (P<0.01). Conclusion In the evergreen broad-leaved forest of Mount Tianmu, the main factors affecting BAI are DBH, crown diameter and competition index. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 45 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1073-1081.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220784
Abstract:
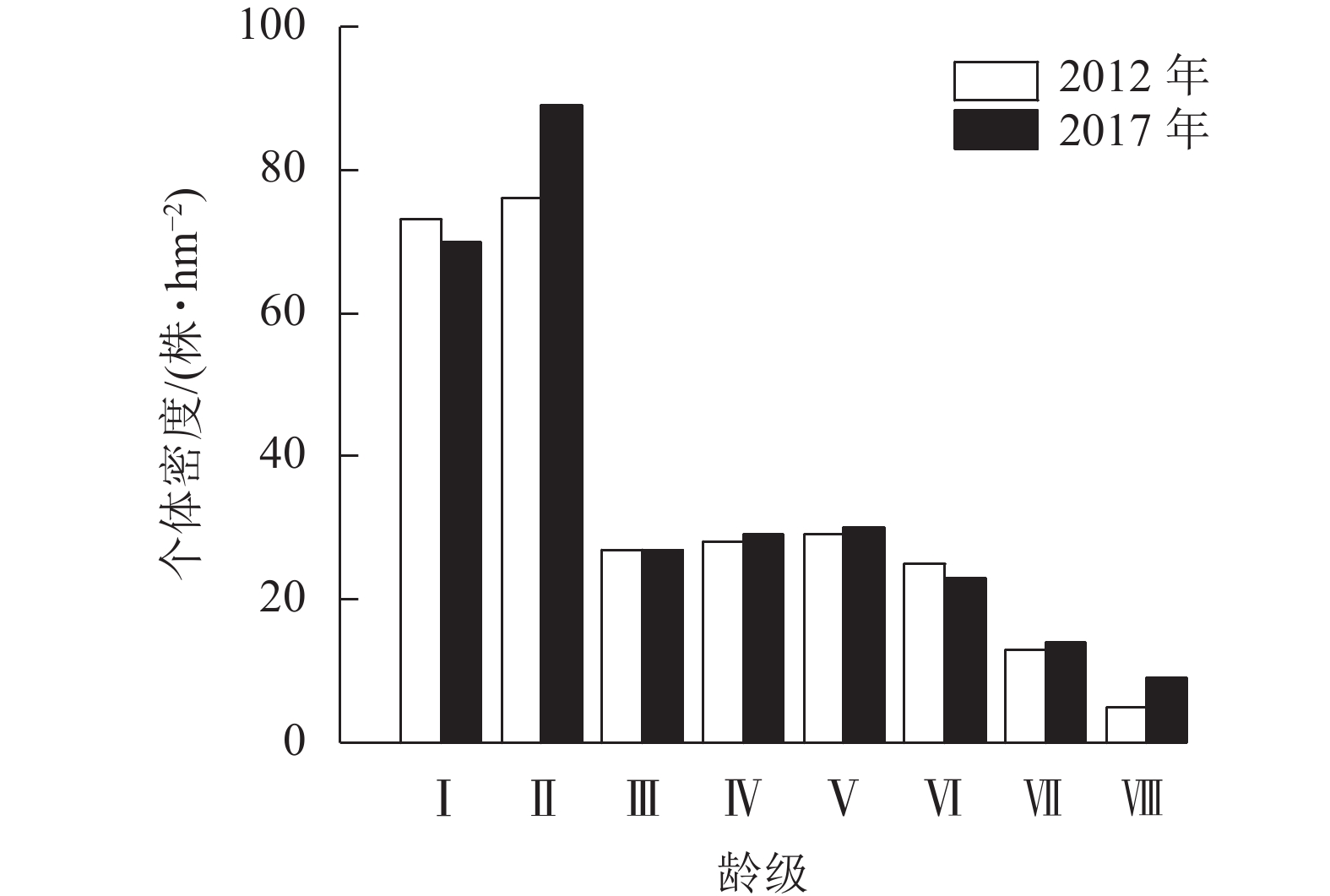
Objective Cyclobalanopsis gracilis is the main tree species in central subtropical forests and one of the dominant tree species in the evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest in National Nature Reserve of Mount Tianmu. The purpose is to investigate the population structure and spatial distribution pattern of C. gracilis in forest communities under natural conditions, as well as its dynamic law and impact mechanism, which is of great significance for forest ecological restoration, development of C. gracilis population, and conservation and management of the evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest in the study area. Method Based on the survey data in the fixed monitoring sample plots of 1 hm2(100 m×100 m) of the evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest in Mount Tianmu in 2012 and 2017, the dynamic variation characteristics of population structure and distribution pattern of C. gracilis were analyzed from the aspects of population quantity characteristics, age class structure and spatial distribution. Result (1) From 2012 to 2017, the individual population of C. gracilis increased from 276 to 291, with 25 dead individuals and 40 new individuals. The annual population growth rate was 1.06%. The average diameter at breast height (DBH) of the population increased from 10.65 cm to 10.82 cm, and the basal area increased from 4.71 m2·hm−2 to 5.15 m2·hm−2. (2) The age structure of C. gracilis population showed an inverted “J”shape, with a good natural regeneration and stable population structure. (3) The new and dead individuals of C. gracilis population were concentrated in the seedling and young stage (Ⅰ−Ⅱ age classes ), and showed a downward trend with the increase of age class. (4) The distribution of C. gracilis population was aggregated as a whole, and changed to random distribution with the increase of age class. The aggregation intensity of seedlings in 2017 decreased compared with 2012, while the aggregation intensity of young and middle trees was slightly enhanced. (5) The spatial correlation between each growth stage was positively correlated at a small scale, and transitioned to no correlation or negative correlation with the increase of scale. In 2017, the spatial positive correlation between the other growth stages was slightly enhanced except for seedlings and middle trees, young and big trees. Conclusion The population of C. gracilis in the evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest of Mount Tianmu belongs to the stable growth type, and is clustered as a whole. The spatial correlation between different growth stages is positively correlated in small-scale space, reflecting a survival strategy and adaptive mechanism in the development of C. gracilis population. There is no significant change in population structure and spatial distribution pattern during the five years. The aggregation distribution of young individuals is restricted by density and the competition among young individuals is intense. To maintain long-term stability of the population, artificial control can be carried out in stages if necessary. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 25 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1082-1092.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220682
Abstract:
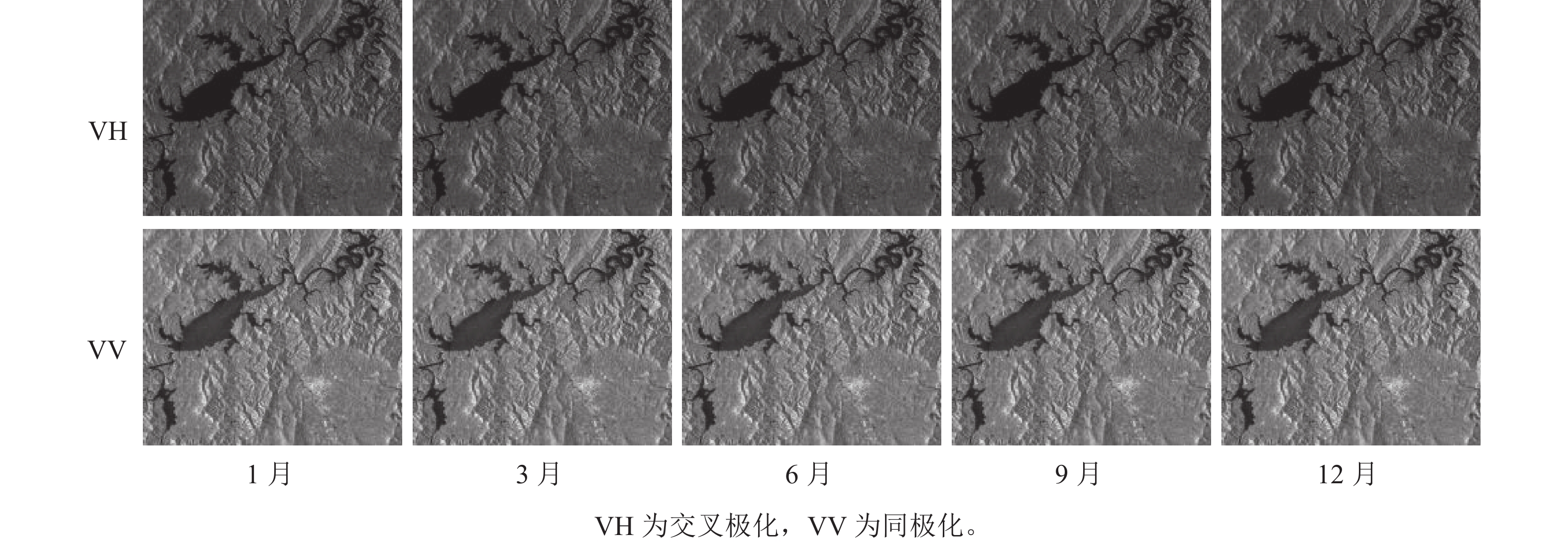
Objective This study, with the inversion of the above-ground biomass (AGB) of forests in Taiping Lake Ecological Reserve using the Senitinel-1 (SAR) and Sentinel-2 (optical) data with different seasonal time series, is aimed to investigate the inversion potential of optical and radar satellite remote sensing on subtropical forest biomass. Method First, based on backscatter coefficients, spectral bands, vegetation indices and biophysical parameters, the regression random forest algorithm was used to explore the accuracy of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 in AGB mapping. Then, an exploration was conducted of the optimal image acquisition period for AGB mapping of subtropical forests which was followed by an evaluation of the contribution of optical and SAR remote sensing feature parameters to the improvement of AGB estimation accuracy. Result The accuracy of AGB estimation for forests in the study area using Sentinel-2 data [coefficient of determination (R2)=0.68, root mean square error (ERMS)=37.69 Mg·hm−2] was better than that of Sentinel-1 (R2=0.47, ERMS=49.11 Mg·hm−2), but the combination of the two produced the best results (R2=0.78, ERMS=31.56 Mg·hm−2). The combination of optical data based on the growing season (June and September) and SAR obtained in the dry season (December) was beneficial to improving the accuracy of AGB estimation. The leaf area index (LAI), photosynthetically active radiation absorption ratio (fapar) and cover (fcover) extracted by Sentinel-2 and the VH polarization and VH+VV indices extracted by Sentinel-1 had important contributions to the AGB estimation. Conclusion By combining optical and SAR in different seasons, it was clarified that June, September and December are the best temporal phases for AGB inversion while its best predictors are LAI, fapar, VH polarization and VH+VV index. [Ch, 8 fig. 3 tab. 29 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1093-1101.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220702
Abstract:
Objective This study, with a quantitative portrait of the relationship between the dynamic characteristics of urban park green space system and urban spatial layout, is aimed to provide reference for the rational configuration of urban green space pattern, urban landscape ecological planning and high-quality greening mode in Haikou in the future. Method Based on the four periods of remote sensing data and point of interest (POI) data from 2008 to 2020 in Haikou, this study studied the evolution characteristics of green landscape pattern in the park and established State-and-Evolution Detection Models (SEDMs) to explore the spatial configuration relationship between urban environment and park green space through the spatial evaluation of park green space (park availability and accessibility). Result The landscape pattern of community parks and historical gardens changed significantly from 2013 to 2017, while other types of parks demonstrated no obvious evolutionary features. The area of urban parks in Haikou continued to grow from 2008 to 2020, with unbalanced development of various types of green spaces and stable growth of parks for residents in the built-up area. Large parks in the eastern and northern parts of the built-up area of Haikou had higher accessibility and wider radiation range. Parks in the western and southern parts were smaller in numbers and radiation range with poor accessibility. Conclusion The park green space has evolved from complexity to landscape fragmentation and local regularity, and the landscape spatial structure has developed from discrete discontinuous layout to local centralized layout whereas the general trend of green land vegetation has been featured with a high concentration space and high-quality green pattern. [Ch, 5 fig. 5 tab. 26 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1102-1110.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220596
Abstract:
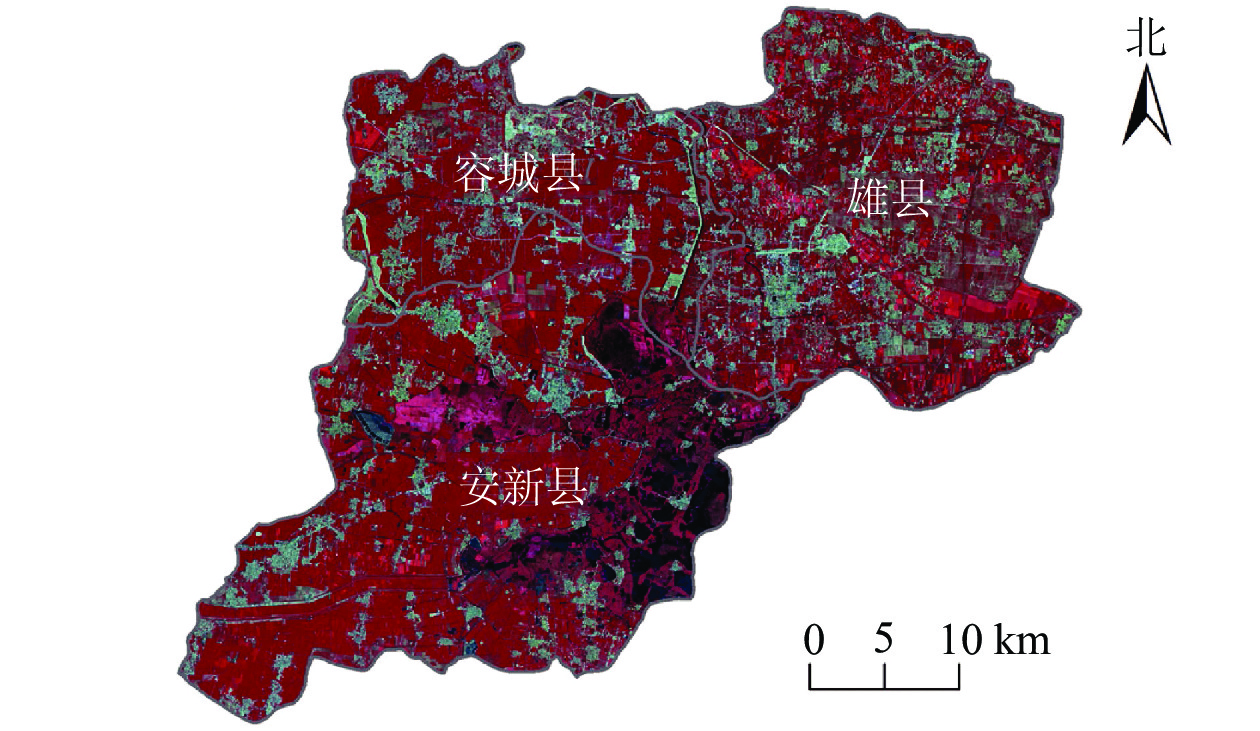
Objective This study, with an investigation into the dynamics of land use change and ecological quality of Xiong’an New Area, is aimed to provide a theoretical basis and data support for the policy making in this area. Method With all the three counties of Xiong’an New Area included as the study area, on the basis of three intervals of land use data in 2000, 2017 and 2020, the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) model was employed in the evaluation of the spatial and temporal changes of ecological quality and the exploration of the potential effects of land use changes on ecological quality. Result (1) In the traditional urbanization stage (2000−2017), land use types mainly changed from arable land to construction land or unutilized land whereas in the new area construction stage (2017−2020), the change was mainly from arable land and unutilized land to woodland. (2) From 2000 to 2017, the average value of RSEI in Xiong’an New Area decreased from 0.62 to 0.57, with the overall ecological quality degraded while the average value of RSEI increased to 0.59 in 2020, with the ecological quality improved slightly. (3) With the distribution and changes of land use consistent with ecological quality in space, significant impact was detected of the area changes in woodland and arable land on ecological quality. (4) At the current construction level and 1 km spatial scale, the ecological quality of 13% area ratio was improved with 10% increased area ratio of unutilized land converted to arable land while the ecological quality of 7% area ratio was improved with 10% increased area ratio of unutilized land converted to woodland. Conclusion The optimization of quality and quantity of woodland and arable land can not only help maintain the ecological quality of Xiong’an New Area but also contribute to the sustainable and healthy development of this area. [Ch, 4 fig. 6 tab. 29 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1111-1120.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220666
Abstract:
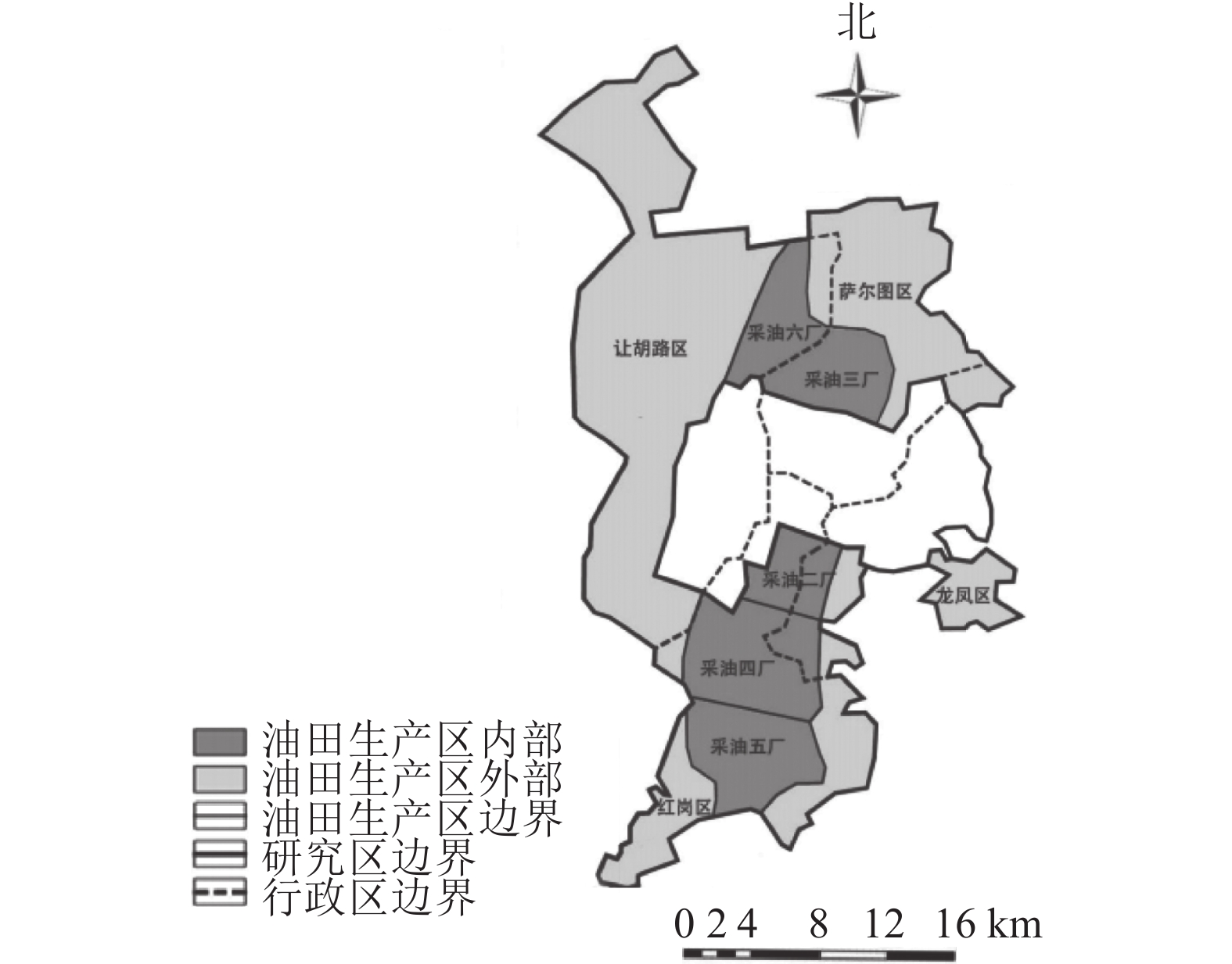
Objective This study aims to explore the spatio-temporal characteristics of land use and risk-value changes in resource-based cities from the perspective of “production-living-ecological space”, taking Daqing urban fringe as an example, so as to provide guarantee for maintaining regional ecological security. Method Based on the multi-source data of five periods in 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020, the distribution and transfer characteristics of land use, spatio-temporal heterogeneity spatial correlation of risk−value are analyzed by using geo-information atlas, spatio-temporal cube model, local spatial auto-correlation analysis and other methods. The factor analysis method and coupling degree coordination model are used to further explore the impact of human activities on the spatial changes of land use, the development trend of “production-living-ecological space” coupling coordination, and the future development path of the city. Result The area of “production-living-ecological space” in the study area: ecological space>production space>living space. Among them, the transfer between production space and ecological space is the most active, with an area of 418.44 km2 during 1980−2020. The landscape ecological risk and ecosystem service value index in the study area showed an upward trend. The oilfield area is characterized by high risk and low value. Outside the oilfield area is characterized by low risk and high value. Conclusion Affected by factors such as population, oilfield exploitation, and industrial output, the “production-living-ecological space” inside the oilfield is imbalanced, while the “production-living-ecological space” outside the oilfield is coordinated. In the process of ecological environment construction in the urban fringe of Daqing, the primary task should be to narrow the differences between the inside and outside of the oilfield area, strengthen the cooperation mechanism between the regional governments and the oilfield administration, so as to achieve the coordinated development between the inside and outside of the oilfield area. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 35 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1121-1129.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220688
Abstract:
Objective This study, with the employment of MATLAB 2019a software, is aimed to complete the time-temperature equivalence in bending creep of white oak in steam pretreatment on the basis of digital characterization of earlywood vessel belt characteristics. Method First, an investigation was carried out of the creep behavior of specimens pretreated by steam at 100, 110, 120 ℃ using a dynamic thermo-mechanical analyzer (DMA-Q800) at the test temperature ranging from 20 to 80 ℃. Then, time-temperature equivalence was applied to predict the long-term creep behavior of white oak on the basis of 45 min creep curves of tested specimens. At last, a further analysis was conducted of the relationship between horizontal shift factor and temperature in accordance with Williams-Landel-Ferry (WLF) equation. Result (1) Instantaneous strain and 45 min strain under the permanent load of 5 MPa for tested specimens increased with the rise of test temperature yet the strain of specimens decreased with the increase of steam treatment temperature. (2) The 45 min creep curves of specimens can be processed to obtained the long-term creep curves at the referenced test temperature of 20 ℃ according to time-temperature equivalent. (3) The curves between horizontal shift factor and temperature of specimens met the requirements of WLF equation with R2 greater than 0.93. (4) The WLF equation can effectively describe the relationship of creep characteristics between test time and temperature. Conclusion Steam pretreatment, test temperature and earlywood vessel belt affected the creep behavior of white oak wood significantly and it is feasible to predict the long-term creep behavior of white oak wood by WLF equation in test temperature of 20−80 ℃ and steam pretreatment temperature ranging from 100 to 120 ℃. [Ch, 9 fig. 2 tab. 25 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1130-1138.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220693
Abstract:
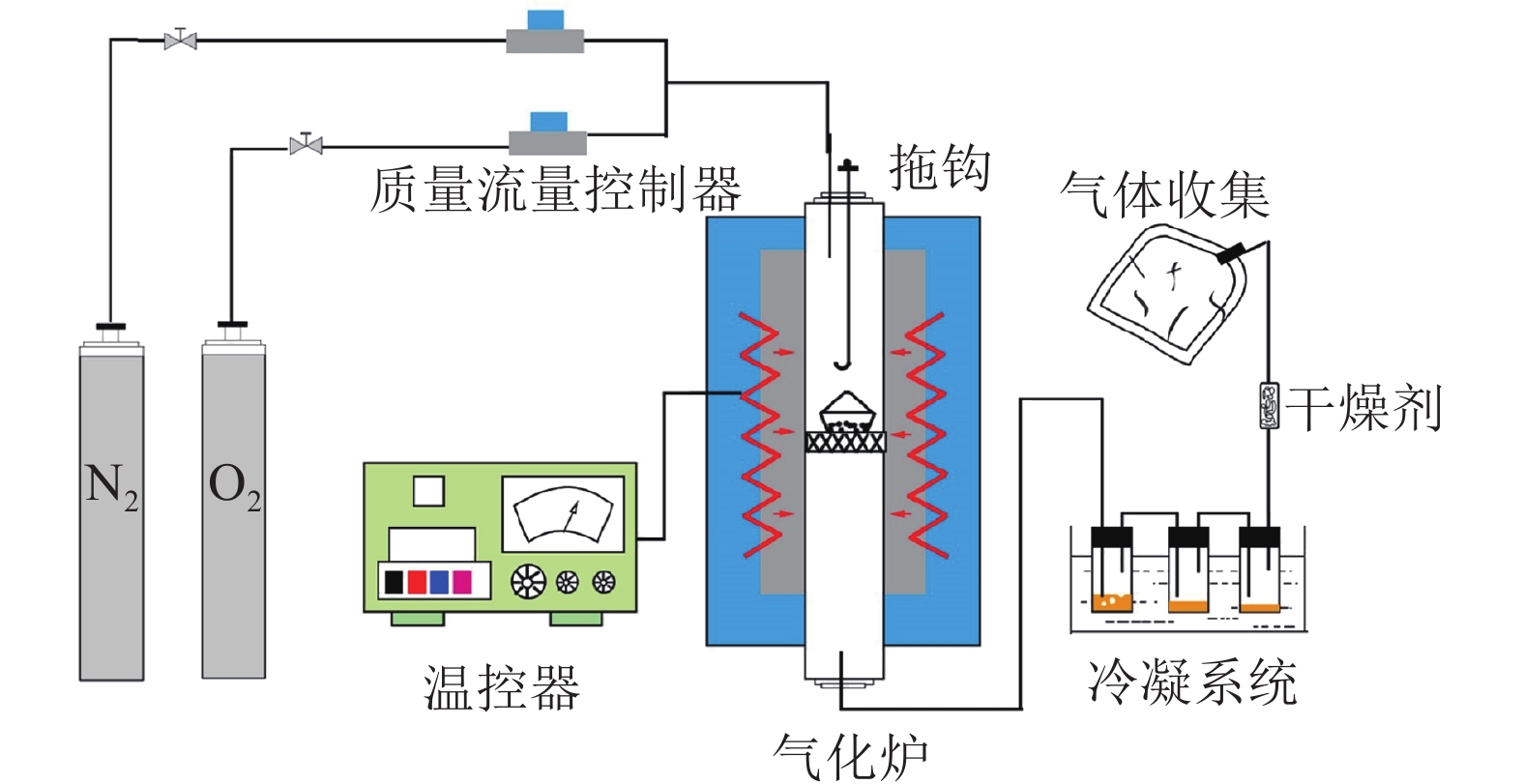
Objective Biomass gasification technology is a clean and renewable energy utilization approach. The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence mechanism of gasification temperature on the properties of gasification products, and to build the evolution law of the characteristics of gasification products, which is of great significance for China to achieve the goal of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. Method Three types of lignocellulosic biomass, namely Zea mays, Trachycarpus fortunei, and Pinus massoniana, were gasified in a home-made fixed bed gasification reactor. The effect of different gasification temperatures (GT) (700, 800, 900 ℃) on gasification performance were systematically studied, as well as the mechanism of their effects on the characteristics of gasification products (bio-gas, bio-char, and tar). Result With the increase of GT from 700 ℃ to 900 ℃, the yield of bio-gas gradually increased, while the yields of bio-char and tar gradually decreased. Higher GT resulted in better quality of bio-gas. Among the three types of biomass, bio-gas from P. massoniana had the highest calorific value. The contents of CO, H2, and CH4 were 40.03%, 18.27%, and 18.29%, respectively, and the lower calorific value was 13.58 MJ·m−3. With the increase of GT, the contents of C and ash increased, while the contents of H decreased. The calorific value of bio-char from P. massoniana was the highest, reaching 29.70 MJ·kg−1. With the increase of GT, the content of acids, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and furans in the liquid products of biomass gasification gradually decreased, while the content of aromatics increased significantly, with the highest aromatic content in P. massoniana, reaching 61.12%. Conclusion GT has a significant influence on the yield and properties of gasified products. Optimizing the gasification temperature is crucial for improving the calorific value and gasification efficiency. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 25 ref.]
2023, 40(5): 1139-1148.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230139
Abstract:
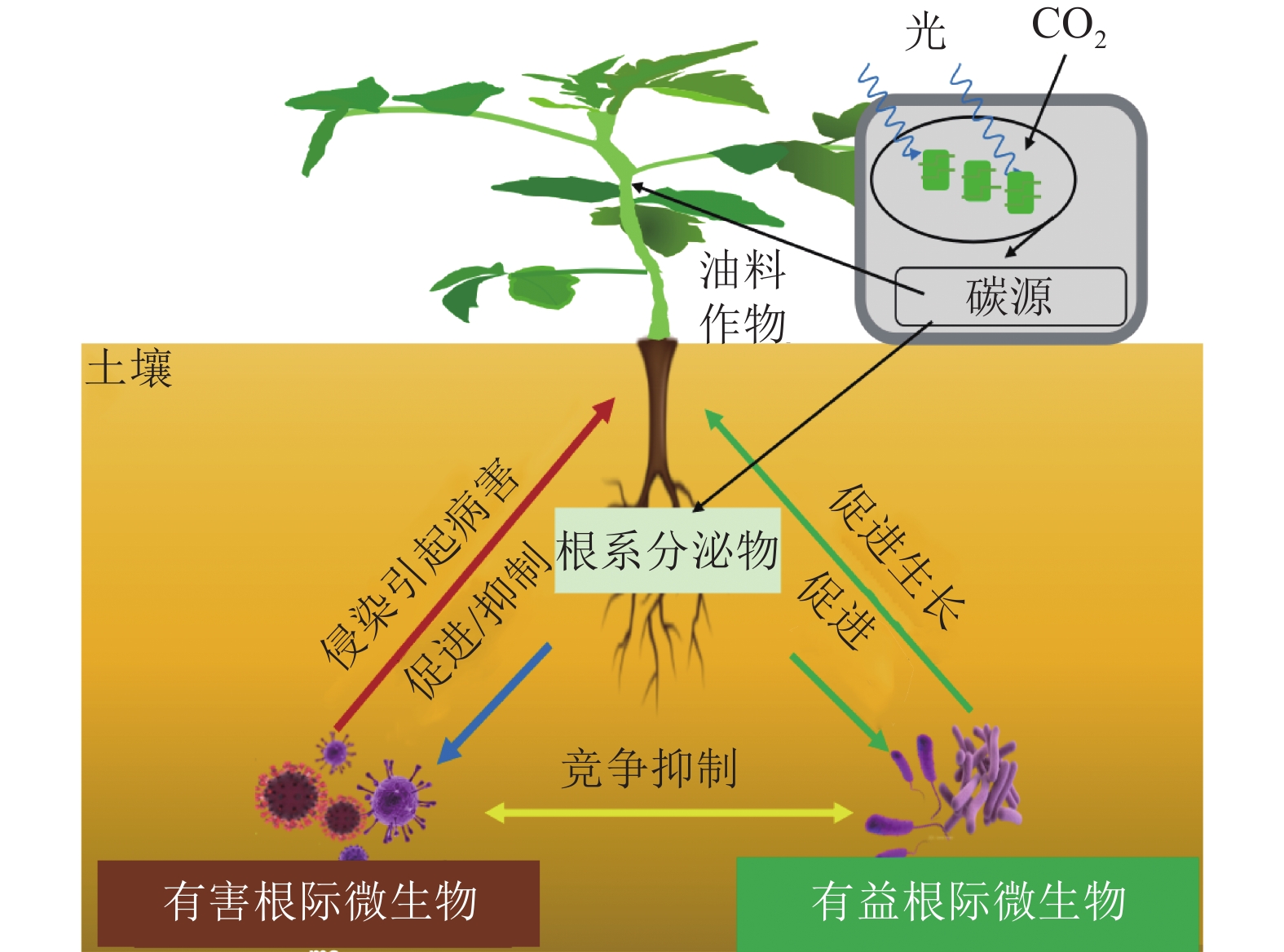
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea), rape (Brassica napus) and soybean (Glycine max) are important sources for edible and industrial oil in China. The yield and quality of oil could be affected by the activities of the rhizospheric microbes and the interactions between them. In recent years, the rhizospheric microbes of oil crops are receiving more and more attentions around the world. The research progress in microbes community composition and influencing factors, interaction mechanisms and the agricultural applications of the root microbes in oil crops were summarized. Results show: (1) The main factors affecting the composition of rhizosphere microorganisms in oil crops include: cultivar, growth period, soil environment, and cultivation methods of oil crops; (2) The research on the interaction between oil crops and rhizosphere microorganisms mainly focuses on utilizing beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms to improve the stress resistance, yield, and quality of oil crops; (3) At present, in agricultural production, the growth of oil crops is mainly promoted by regulating rhizosphere microorganisms, regulating host oil crops, and regulating cultivation methods. By studying the interaction between oil crops and rhizosphere microorganisms, scientific references are provided for exploring the interaction relationship between oil crops and rhizosphere microorganisms in the future, as well as expanding the application of microbial agents in oil crops. [Ch, 1 fig. 1 tab. 75 ref.]
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea), rape (Brassica napus) and soybean (Glycine max) are important sources for edible and industrial oil in China. The yield and quality of oil could be affected by the activities of the rhizospheric microbes and the interactions between them. In recent years, the rhizospheric microbes of oil crops are receiving more and more attentions around the world. The research progress in microbes community composition and influencing factors, interaction mechanisms and the agricultural applications of the root microbes in oil crops were summarized. Results show: (1) The main factors affecting the composition of rhizosphere microorganisms in oil crops include: cultivar, growth period, soil environment, and cultivation methods of oil crops; (2) The research on the interaction between oil crops and rhizosphere microorganisms mainly focuses on utilizing beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms to improve the stress resistance, yield, and quality of oil crops; (3) At present, in agricultural production, the growth of oil crops is mainly promoted by regulating rhizosphere microorganisms, regulating host oil crops, and regulating cultivation methods. By studying the interaction between oil crops and rhizosphere microorganisms, scientific references are provided for exploring the interaction relationship between oil crops and rhizosphere microorganisms in the future, as well as expanding the application of microbial agents in oil crops. [Ch, 1 fig. 1 tab. 75 ref.]