2023 Vol. 40, No. 4
2023, 40(4): 695-706.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220764
Abstract:
Objective Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT) catalyzes the first acylation reaction in the triacylglycerol (TAG) biosynthetic pathway. Understanding the structure-function relationship of GPAT is important for genetic or chemogenetic manipulation of the TAG biosynthetic capacity as a key trait in oilseed crops but associated with human obesity disease. This study aimed to identify key amino acid residues controlling the activity of GPAT9 in plants. Method Site-directed mutagenesis was employed to construct 58 GPAT9 mutant genes, and yeast genetic complementation specific for GPAT enzyme was utilized to dissect the effects of alterations of single and multiple amino acid residues on the activities of GPAT9 from Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus. Result By analyzing 19 amino acid residues of AtGPAT9 and BnGPAT9, it was found that single mutations (T10A, S11A, S13A, S28A, S30A, S31A) at the N-terminus of AtGPAT9 could not enhance its activity when the respective variants were expressed heterologously. In contrast, the alteration of the other six amino acid residues at positions 85, 114, 119, 230, 237, and 322, respectively, which are located outside the conserved domains of acyltransferases significantly affected GPAT9 enzymatic activity. Additionally, mutual interactions were evident between these amino acids. For instance, the simultaneous mutation of the three residues (Y85W, N119H, S237N) greatly increased the activity of AtGPAT9, as exemplified by the findings that the expression of the corresponding mutant enzyme could accelerate the growth of yeast cells and enhanced the synthesis of TAG by 45.7%, compared with that of yeast cells expressing BnGPAT9. Noticeably, the presence of potentially phosphorylated amino acids at positions 114 and 237 was detrimental to acyltransferase activity, implying that plant GPAT9 activity may be regulated through protein phosphorylation and non-phosphorylation. Conclusion This study describes six previously unreported amino acid residues key to the regulation of GPAT enzymatic activity. Among them, W85 and H119 are prerequisite for the proper functioning of GPAT9, and L114, D230, N237, and A322 are beneficial to maintaining the activity of GPAT9. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 37 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 707-713.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220738
Abstract:
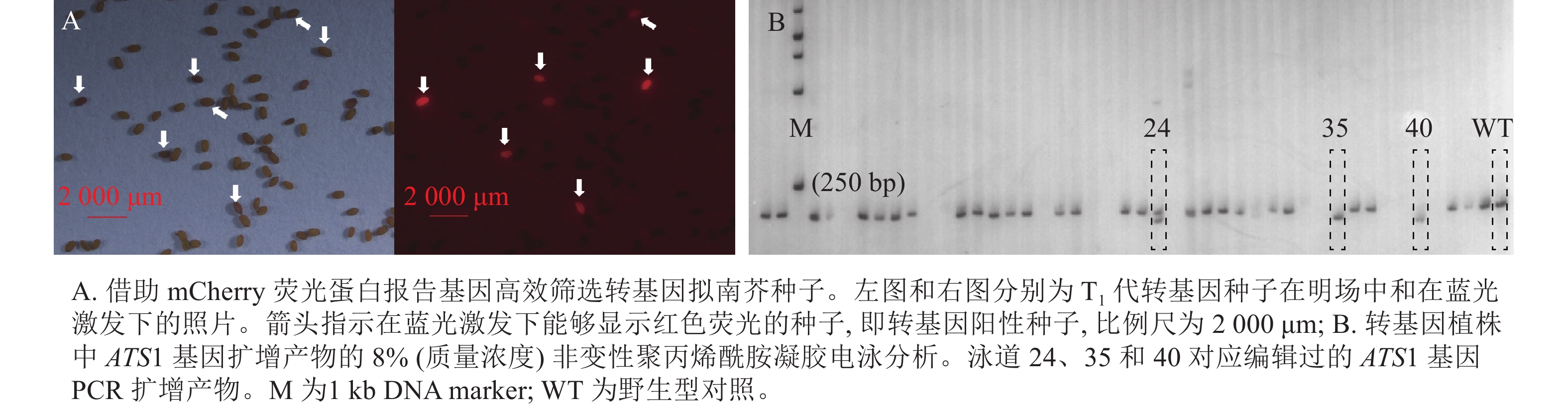
Objective Glycerolipids are the main constituents of biological membranes. ATS1 catalyzes the first acylation reaction in the prokaryotic pathway of glycerolipid synthesis. However, the function of ATS1 in normal plant growth and development is not completely understood. The present study was intended to dissect the effect of loss of function of ATS1 on plant growth and development by taking a reverse genetic approach. Method Loss-of-function mutants of the ATS1 gene were constructed by using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology. Then, comparative analysis was conducted on phenotypic difference between the mutants and wild type Arabidopsis thaliana during the entire growth phase. Result Molecular characterization of multiple mutants revealed that the number of base pairs inserted or deleted in the first exon of the ATS1 gene is not a multiple of three, resulting in frameshift mutations or premature translation termination. Consistent with this, the content of polyunsaturated fatty acid C16:3 in the leaves of these mutants decreased sharply, concomitant with significant increases in the content of C18:3. Meanwhile, phenotypic analysis showed that loss of ATS1 gene function sometimes made the leaves turn slightly yellow, while having no visible effect on seed development. Conclusion The above results strongly indicate that ATS1 is dispensable for A. thaliana seed development under normal growth conditions. [Ch, 3 fig. 2 tab. 25 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 714-722.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230224
Abstract:
Torreya grandis‘Merrillii’is one of the precious economic tree species with high nutritional and medicinal value. T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernels are rich in nutrients such as oil, protein, and vitamins. The main components on T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel oil are fatty acids and their derivatives, which play an important role in reducing blood lipids, antioxidant and preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. In the past, studies on T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel oil mainly focused on the composition, extraction methods and functional characteristics. With the development of forest molecular biology, more and more studies have been conducted on T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel oil synthesis and regulation mechanism, including the excavation of anabolic pathway for oil synthesis, identification of key genes for oil accumulation and special fatty acid synthesis, and construction of regulatory networks. This study is to review the current research status of T. grandis‘Merrillii’kernel oil, including studies on fatty acid composition, oil quality, oil extraction methods, and oil synthesis regulation mechanism of T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernels, so as to provide ideas and methods for the later development and utilization of T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel resources. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 58 ref.]
Torreya grandis‘Merrillii’is one of the precious economic tree species with high nutritional and medicinal value. T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernels are rich in nutrients such as oil, protein, and vitamins. The main components on T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel oil are fatty acids and their derivatives, which play an important role in reducing blood lipids, antioxidant and preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. In the past, studies on T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel oil mainly focused on the composition, extraction methods and functional characteristics. With the development of forest molecular biology, more and more studies have been conducted on T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel oil synthesis and regulation mechanism, including the excavation of anabolic pathway for oil synthesis, identification of key genes for oil accumulation and special fatty acid synthesis, and construction of regulatory networks. This study is to review the current research status of T. grandis‘Merrillii’kernel oil, including studies on fatty acid composition, oil quality, oil extraction methods, and oil synthesis regulation mechanism of T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernels, so as to provide ideas and methods for the later development and utilization of T. grandis‘Merrillii’ kernel resources. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 58 ref.]
Cloning and expression analysis of low phosphorus stress response gene GhGDPD1 in Gossypium hirsutum
2023, 40(4): 723-730.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220624
Abstract:
Objective Based on the analysis of differential expression sequence data of genome-wide expression profile of Gossypium hirsutum‘Xinluzao 19’ seedlings under low phosphorus stress in our previous research, this study aims to explore the related genes, and to clone and analyze their expression, so as to provide a scientific reference for further research on the biological functions of GhGDPD1 gene and the cultivation of new cotton germplasm with the efficient utilization of phosphorus. Method GhGDPD1 gene was cloned from ‘Xinluzao 19’. Genomic DNA and cDNA sequence of the gene were performed, and the genetic structure and evolutionary relationship of GhGDPD1 were analyzed by bioinformatics method. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR and fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) were used to detect the changes of gene expression in root, stem, leaf and flower tissues, as well as the expression pattern under low phosphorus stress. Result The GhGDPD1 gene was cloned, with an open reading frame sequence length of 1 149 bp, encoding 382 amino acids. This gene sequence belonged to the GDPD family, with a conservative structure domain named GDPD_GDE5_like_1_plant. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR and RT-qPCR showed that GhGDPD1 gene was mainly expressed in roots, moderately expressed in flowers and stems, and slightly expressed in leaves. After being stimulated by low phosphorus stress, the gene would immediately respond to low phosphorus stress and its expression level reached the highest value after 4 hours of stress. Conclusion The GhGDPD1 gene of ‘Xinluzao 19’ is successfully cloned for the first time. The tissue expression of GhGDPD1 and its expression pattern under low phosphorus stress are obtained. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 18 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 731-737.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220553
Abstract:
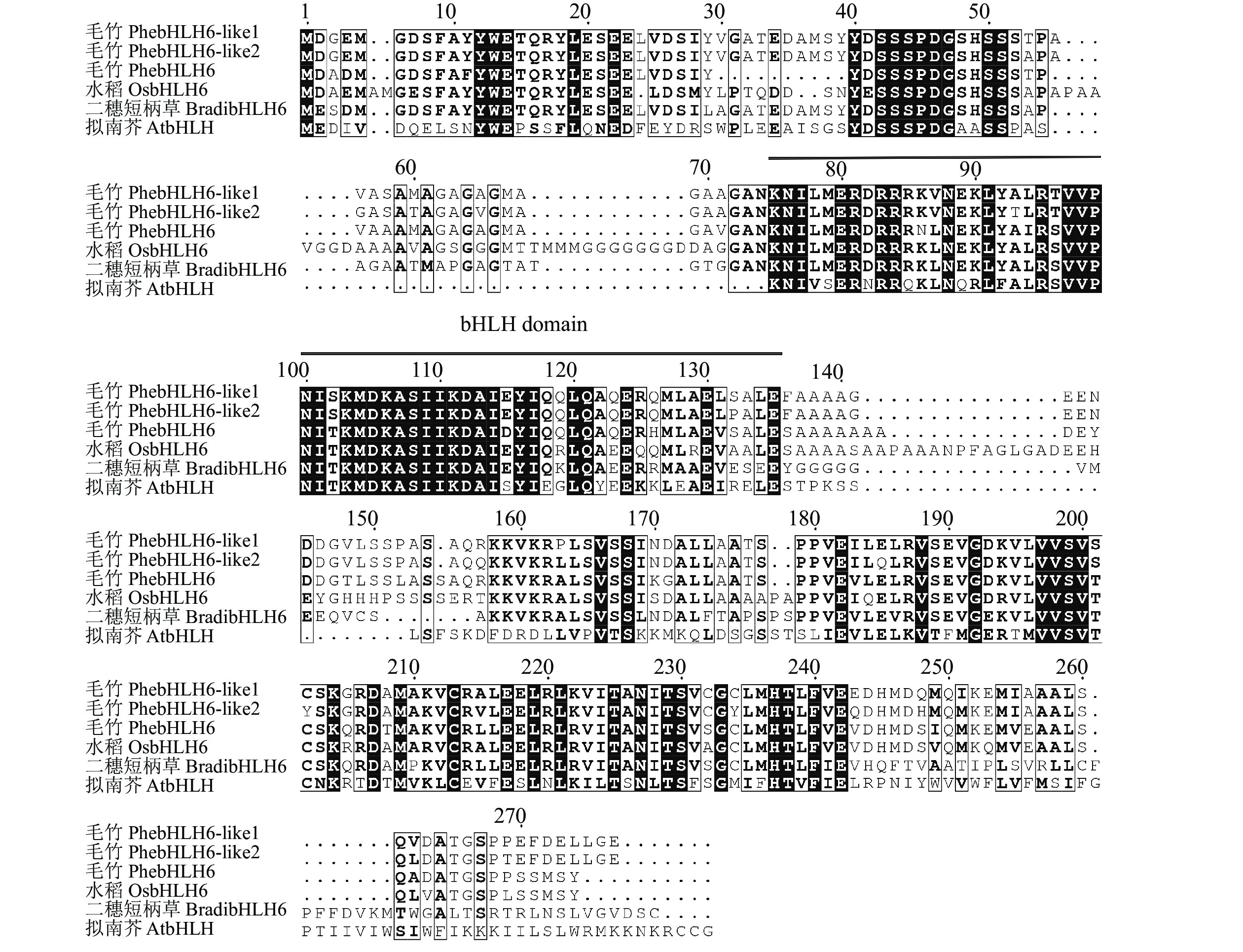
Objective The objective is to study the role of PhebHLH6 transcription factor in stress response of Phyllostachys edulis; so as to explore the molecular mechanism of resistance to stress in Ph. edulis. Methods Seedlings of Ph. edulis were treated with abiotic stress, including treatments of drought stress, salt stress, salicylic acid (SA) and abscisic acid (ABA). A differentially expressed gene named PhebHLH6 was screened using transcriptome data, and its gene cloning and bioinformatic analysis were performed. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to analyze the expression patterns of PhebHLH6 under drought, salt stress and SA and ABA treatments. Result The coding region of PhebHLH6 gene had a base of 801 bp, encoding 266 amino acids, including bHLH domain, which was a typical bHLH transcription factor. Tissue-specific expression analysis showed that PhebHLH6 was expressed in nearly all the tissues of Ph. edulis, with the highest abundance at the top of 1.5 m and 3.0 m shoots. Under drought and high salt stress, the expression levels of PhebHLH6 were strongly induced after 3 h of treatment but significantly down-regulated after 24 h of treatment. Under SA and ABA hormone treatment, the expression levels of PhebHLH6 increased first and then decreased when induced by SA and ABA, with strong SA induction and weak ABA induction. Conclusion PhebHLH6 may be involved in the early response pathway to drought and salt stress of Ph. edulis and may play a regulatory role in SA and ABA hormone signaling pathways. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 32 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 738-746.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220634
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to reveal the heredity and variation of the growth and branching traits of the full-sib families of Schima superba and provide reference for scientific breeding. Method Taking a 4 × 4 half diallel mating design that was conducted in Longquan of Zhejiang Province in 2015 as the research object, the genetic variation parameters, general combining ability (GCA), and special combining ability (SCA) of the growth and branching characters were analyzed. Result The growth and branching traits differed significantly across the 6-year-old full-sib families (P<0.01). The coefficient of variation for the growth and branching traits ranged from 20% to 53%. The growth and branching traits were under strong genetic control, and the heritability of full-sib families was 0.86−0.93. The paternal heritability of the growth traits was higher, which was jointly controlled by gene additive and dominant effects. The maternal heritability of branching traits was higher, which was controlled by gene additive effect. The correlation analysis showed that there was a significant phenotypic correlation between the growth and branching traits (r=0.20−0.87, P<0.01), and there was a significant genetic correlation between DBH growth and bole height and primary branch number (r=0.67−0.70, P<0.01). The GCA and SCA effects of the growth and branching traits reached significant (P<0.05) and extremely significant (P<0.01) levels. According to the results of GCA and SCA, SY42 in Shangyou of Jiangxi and LC31 in Liancheng of Fujian were considered as excellent parents, and SY42 × LC31 combination had special combining ability with fast-growing characters. In addition, the six super-crossing progenies could be used as parent materials for the second-generation breeding. Conclusion The growth and branching traits of full-sib families of S. superba are under strong genetic control, with stronger paternal control over growth traits and stronger maternal control over branching traits. Parents can be selected according to the growth and branching traits, and the super parent combination with fast growth and high quality can be obtained. [Ch, 1 fig. 7 tab. 27 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 747-755.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220543
Abstract:
Objective This paper, with a comparative analysis conducted of the changes of flower color of the Sinicalycanthus chinensis, the Calycanthus floridus var. glaucus and their hybrid progenies, is aimed to analyze the different metabolite basis of the flower color. Method Targeted metabolomics methods were adopted to determine the content of related metabolites in the petals of S. chinensis, C. floridus var. glaucus, and their hybrid progenies, screen the differential metabolites and decide the metabolic pathways involved in the differential metabolites before identification and analysis were performed to analyze the metabolite basis of petals showing different colors. Result (1) In terms of the flower color phenotype, the lightness (L*) values, yellowness (b*) values and hue angles (h) of the inner and outer petals of S. chinensis were significantly higher than those of C. floridus var. glaucus (P<0.05). The redness (a*) values of outer petals of S. chinensis were significantly lower than those of C. floridus var. glaucus; the chroma (C*) values of inner petals of S. chinensis were significantly higher than those of C. floridus var. glaucus (P<0.05). L* values of the hybrid offsprings were significantly lower than those of the inner and outer petals of S. chinensis, but significantly higher than those of C. floridus var. glaucus; a* values of the hybrid progenies were significantly higher than those of the parents, b* values were significantly lower than those of the inner and outer petals of S. chinensis while C* values were significantly lower than those of the inner and outer petals of S. chinensis; C* values of the hybrid progenies were significantly lower than those of the inner petals of S. chinensis, and significantly higher than those of the outer petals of S. chinensis and C. floridus var. glaucus. whereas h were significantly lower than those of the parents (P<0.05). (2) A total of 1 059 metabolites were detected by widely targeted metabolomics with the relative content of flavonoids being the highest among the three different metabolites of the petals. (3) With KEGG metabolic pathway enrichment analysis performed on the differential metabolites, it was shown that among the 3 groups, the number of metabolites annotated in metabolic pathways, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, and flavonoid biosynthesis was the largest. (4) The comparison of the relative contents of the main coloring substances in the three plants showed that the relative contents of anthocyanins and flavonoids dropped from high to low in the descending order of hybrid progenies, C. floridus var. glaucus and S. chinensis while the relative contents of flavonols dropped from high to low in the descending order of C. floridus var. glaucus, hybrid progenies and S. chinensis. (5) The analysis of the correlation between pigment components and flower color phenotypes showed that flavones were negatively correlated with L* value, but negatively correlated with h (P<0.05) whereas there was a very significant negative correlation between flavonols and L* value (P<0.01); Anthocyanins were negatively correlated with h (P<0.05) while chalcones and L* value showed an extremely significant negative correlation (P<0.01). Conclusion There were significant differences in petal flower color phenotype and metabolites among S. chinensis, C. floridus var. glaucus, and hybrid progenies. The significant differences in metabolites, mainly flavonoids, and their main annotation pathways among the three were clarified, laying a foundation for further study in mechanism of the flower colors of these three plants. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 20 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 756-764.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220613
Abstract:
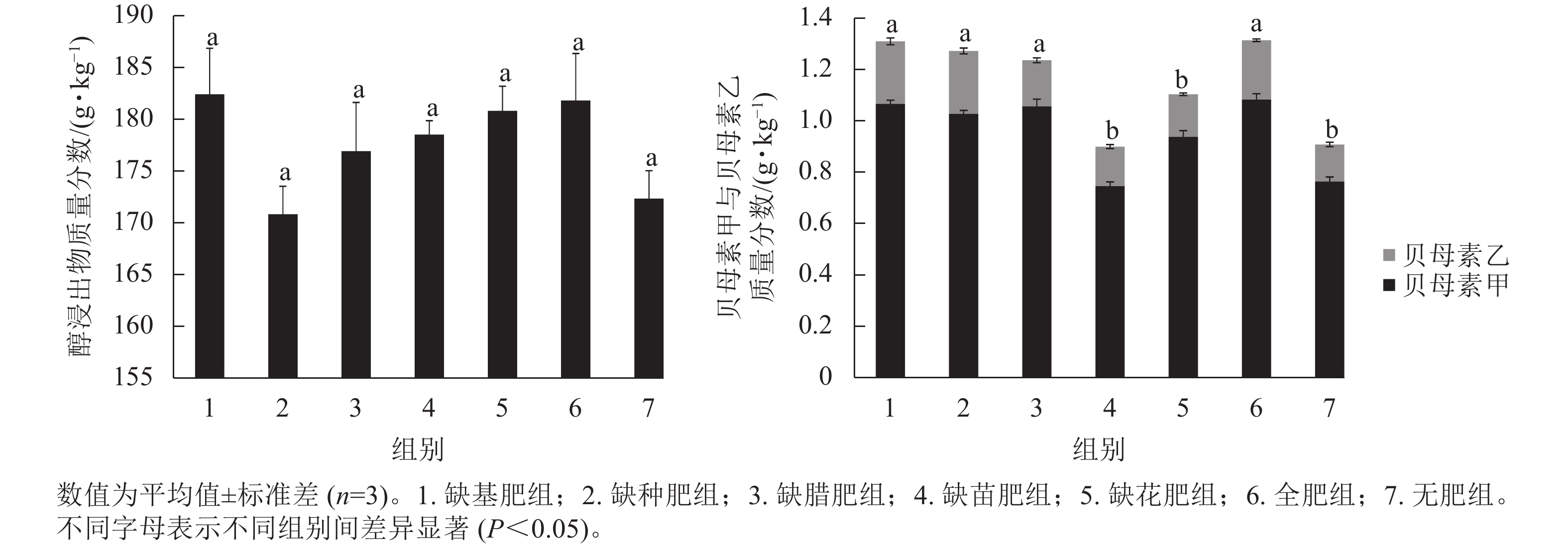
Objective This study explores the impact of fertilization at different growth stages on yield and quality of Fritillaria thunbergii, a traditional herb from Zhejiang Province, in order to provide scientific guidance in fertilizer application. Method The cultivar ‘Zhebei 3’ was used as the material in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province in October 2021. Experimental groups were set up, including full fertilizer control group, no fertilizer control group and treatment groups without basal fertilizer, seed fertilizer, winter fertilizer, seedling fertilizer or flower fertilizer. The morphological and physiological indexes of ‘Zhebei 3’ at different growth stages were measured, such as plant height, fresh weight, leaf size, soluble sugar, malondialdehyde and antioxidant enzymes. In harvesting period in May 2022, the yield of bulbs was counted and the quality indexes were measured. The changes of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in bulbs before and after cultivation were measured. Result There were no significant differences in yield and quality indexes among treatment groups without basal fertilizer, seed fertilizer or winter fertilizer. The yield of ‘Zhebei 3’ in the groups without seedling fertilizer or flower fertilizer decreased by 19.15% and 21.58% (P<0.05), and the total content of Peimine and Peiminine decreased by 30.76% and 15.38% (P<0.05). Compared with seed bulbs, the content of nitrogen and potassium in the new bulbs of the treatment groups without basal fertilizer, seed fertilizer or winter fertilizer significantly increased (P<0.05) and phosphorus content significantly decreased (P<0.05). The lack of seed fertilizer or winter fertilizer significantly reduced the phosphorus content of new bulbs (P<0.05), but did not affect the content of nitrogen and potassium. The lack of seedling fertilizer or flower fertilizer significantly reduced the contents of nitrogen and phosphorus in the new bulb (P<0.05), but did not affect the content of potassium. Conclusion The deficiency of basal fertilizer, seed fertilizer or winter fertilizer has no significant effect on yield and quality of ‘Zhebei 3’. Under the condition of sufficient basal fertilizer, fertilization before seedling emergence can be appropriately reduced. The lack of seedling fertilizer or flower fertilizer will significantly decrease yield and quality of ‘Zhebei 3’, so the supply of appropriate types of fertilizer should be timely and sufficient at the seedling and flowering stages. [Ch, 1 fig. 6 tab. 24 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 765-772.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220568
Abstract:
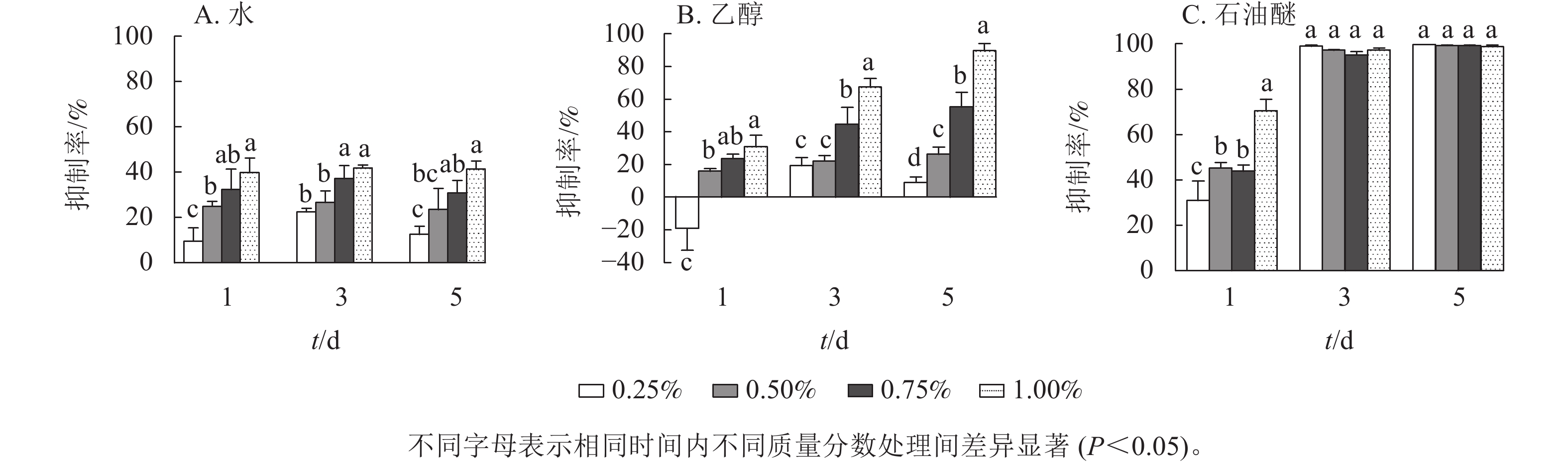
Objective This study aims to investigate the allelopathic and potential algal inhibition mechanism of submerged Rotala rotundifolia, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the application of R. rotundifolia in algal bloom control engineering. Method Taking Microcystis aeruginosa as the representative algal species, the algal inhibition ability of water, ethanol and petroleum ether extracts of the plant was investigated using ultrasound-assisted solvent extraction technique. The inhibition effects of R. rotundifolia and six common submerged plants on M. aeruginosa were compared from the perspectives of chlorophyll a (Chl a) content, maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Result The algae inhibition ability of the three solvent extracts of R. rotundifolia in descending order was petroleum ether, ethanol, and water. The petroleum ether extract exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on M. aeruginosa (P<0.05) with an inhibition rate up to 99.9%. Quantitative analysis showed that the petroleum ether extract of R. rotundifolia presented low concentration promotion and high concentration inhibition, with a minimum median effect concentration (EC50) of 11.56 g·L−1 (day 5). The contents of Chl a in R. rotundifolia and Myriophyllum spicatum treatments were significantly lower than those in other treatments (P<0.05, day 1). The Fv/Fm of all plant treatments were significantly lower than that of the control (P<0.05). The SOD activities of R. rotundifolia and Cabomba caroliniana were 1.48 and 1.53 times higher than those of the control, respectively, while the SOD activity of Myriophyllum spicatum decreased significantly (P<0.05). The treatments of Vallisneria natans, Ceratophyllum demersum, Elodea nuttallii, and Hydrilla verticillata showed no significant difference from the control. Conclusion The petroleum ether extract of R. rotundifolia has a strong inhibitory effect on algal. It can reduce the Chl a content in Microcystis aeruginosa cells, decrease photosynthetic efficiency, and intensify the oxidative damage. It has strong application potential in the prevention and control of Microcystis algal blooms. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 35 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 773-782.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220507
Abstract:
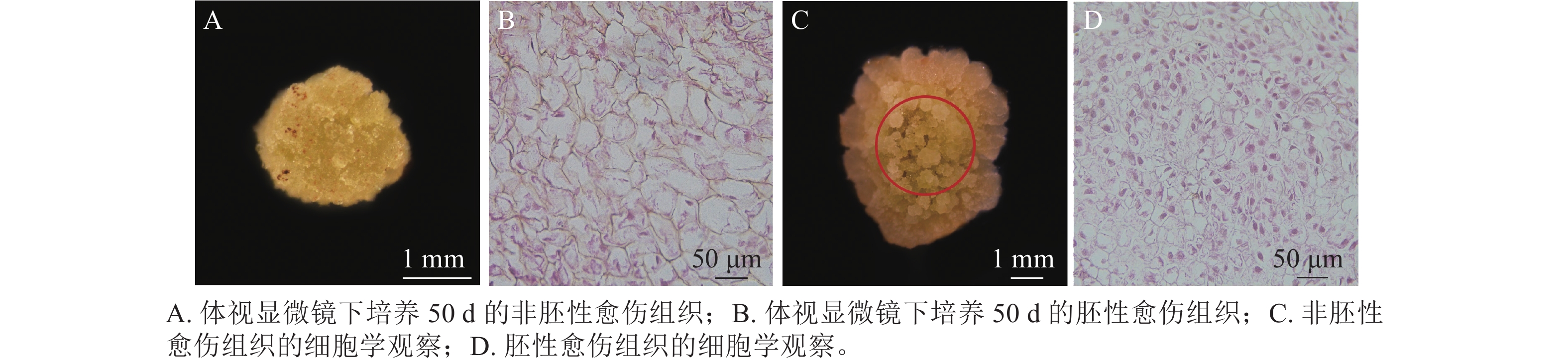
Objective The objective is to screen the optimal medium suitable for callus induction from unpollinated ovules of Camellia oleifera, and explore the origin and developmental process of callus by cytological observation, so as to provide data reference for haploid breeding of C. oleifera. Method C. oleifera ‘huajin’ was used as the test material to screen the optimal medium formula for inducing callus from unpollinated ovule, and to study the basic medium types MS, WPM, MT, 1/2MS, and B5, as well as effects of plant growth regulator concentration such as auxins NAA, IAA, IBA, and 2,4-D, and cytokinins 6-BA, KT, and TDZ on callus induction. Calluses with different external morphology were selected for paraffin section, and their origin and development process were studied according to the ploidy identification results of flow cytometry. Result MS was used as the basic medium, and the highest induction rate was 92.97% when 1.0 mg·L−1NAA+2.0 mg·L−1 TDZ+40 g·L−1 sucrose was added. NAA and TDZ had significant effects on the induction rate(P<0.05), and the impact of TDZ was greater than that of NAA. The embryogenic callus was light green granular, with cytological characteristics of close arrangement, large nucleus, and ploidy identification of hexaploid. Conclusion The optimal medium for inducing embrygenic callus from unpollinated ovules of C. oleifera is MS+40 g·L−1sucrose +7 g·L−1 AGAR +1.0 mg·L−1 NAA+2.0 mg·L−1 TDZ. The callus is formed by dedifferentiation of outer integument cells. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 33 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 783-791.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220578
Abstract:
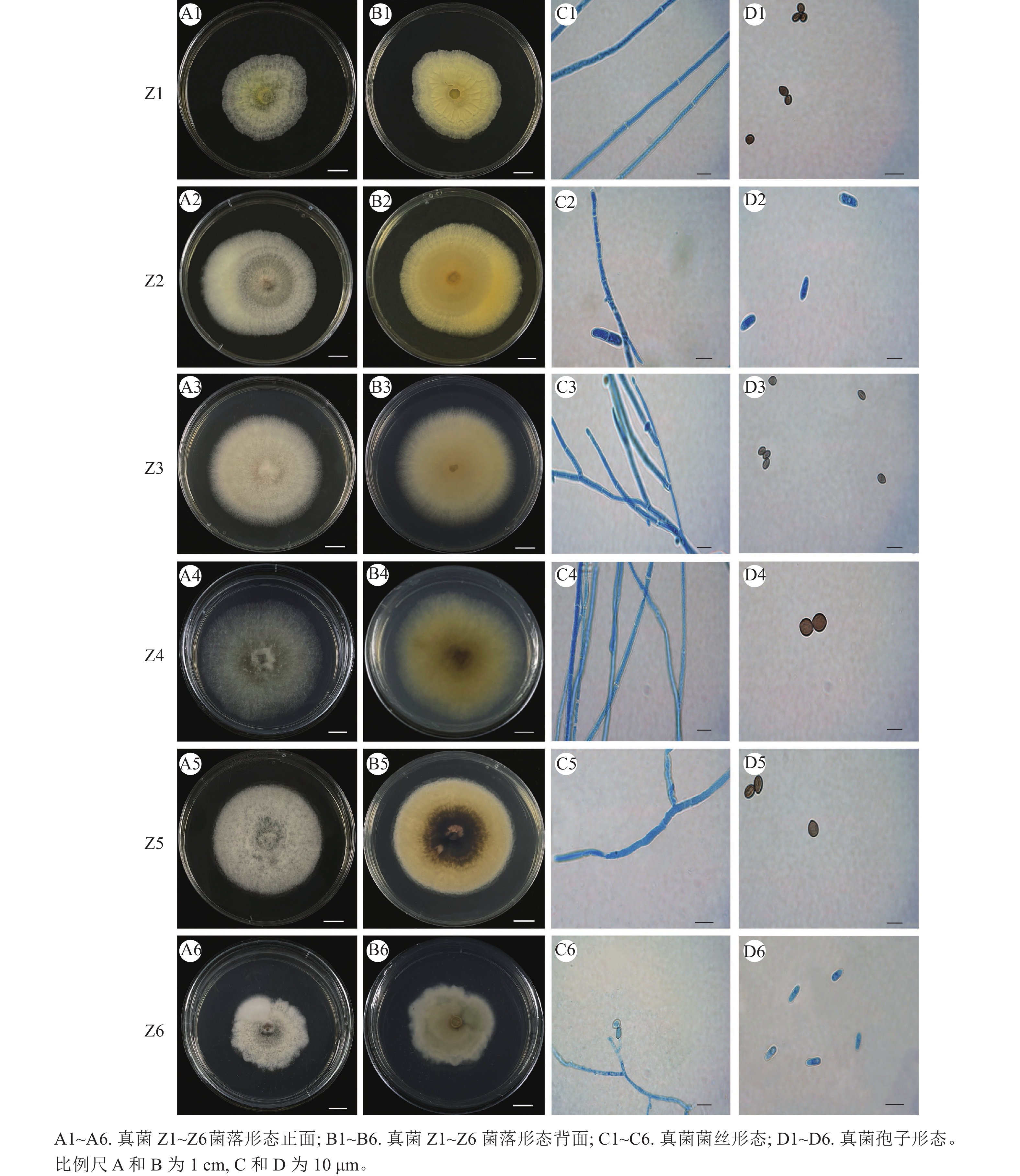
Objective The objective is to screen and obtain the biocontrol fungi against orchid plant diseases from Cymbidium faberi ‘Hongxiangfei’ , so as to provide scientific basis for mycorrhizal cultivation and green biological control of C. faberi. Method The endophytic fungi were isolated, purified and identified from the healthy root segments of C. faberi ‘Hongxiangfei’ . With 5 common plant pathogens as indicator fungi, the endophytic fungi with the best biocontrol effect were screened by plate confrontation culture method, and their bacteriostatic effect was verified by in vivo inoculation. Result 6 endophytic fungi were isolated from the root segment culture of healthy plants of C. faberi ‘Hongxiangfei’ , and 4 strains belonged to Chaetomium spp., 1 strain belonged to Fusarium spp. and 1 belonged to Scedosporium spp. It was found in the plate confrontation culture that all 6 endophytic fungi had certain inhibitory effect on 5 pathogenic strains, among which Z2 strain (Fusarium solani) had an obvious inhibitory effect on F. oxysporum (the causative agent of orchid stem rot), with an inhibition rate of 67.51%. The inhibition rate of Z3 strain (Dichotomopilus funicola) against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (the pathogen of orchid anthracnose) was 68.56%. The in vivo inoculation test of Cymbidium goeringii ‘Green Cloud’ showed that the rate of diseased leaves and disease index of the experimental group treated with Z3 strain were significantly lower than those of the control group (P<0.01). Conclusion Z3 is selected as the dominant antagonistic biocontrol strains against orchid diseases. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 792-800.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220640
Abstract:
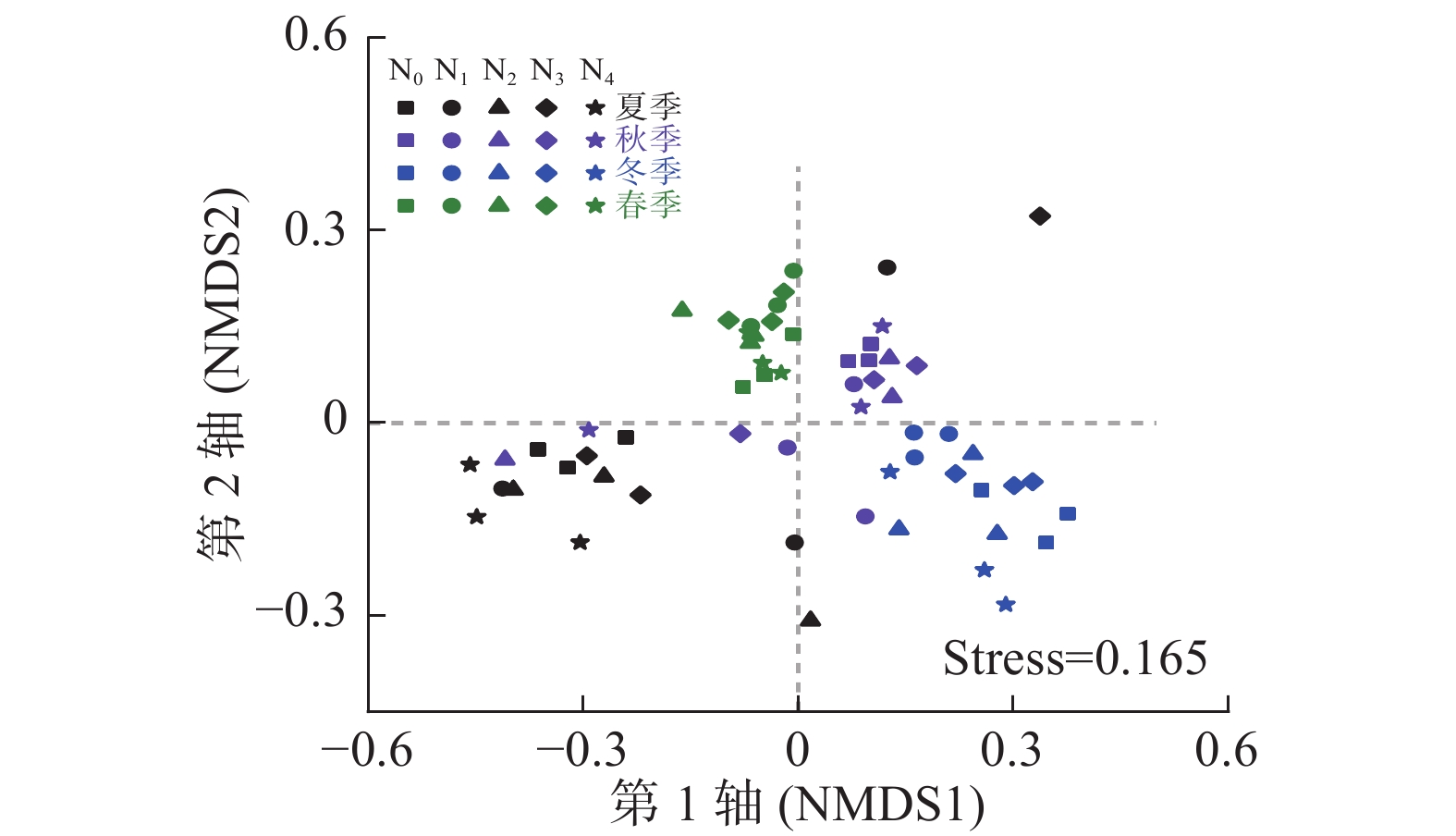
Objective The study aimed to investigate the effects of nitrogen addition and sampling season on soil arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungal community structure and diversity in a poplar plantation, and clarify the driving factors. Method A field simulating experiment with five nitrogen addition levels (0, 5, 10, 15 and 30 g·m−2·a−1) was conducted in a poplar plantation in Dongtai Forest Farm, Jiangsu. After six years of continuous nitrogen additions, the dynamic changes of soil physicochemical properties, AM fungal community diversity and composition in four seasons (spring, summer, autumn and winter) were examined, and the relationships between the characteristics of AM fungal community and soil environmental factors were also analyzed. Result (1) A total of 1 307 513 high-quality AM fungal sequences were identified by high-throughput sequencing, and they were assigned to 196 OTUs, 4 orders, 8 families, and 10 genera. The dominated genera were Glomus and Diversispora, and the total average relative abundances of them reached to 99.3%. (2) Nitrogen addition had no significant effect on the AM fungal community structure and diversity. However, the relative abundance of Diversispora decreased significantly with the increase of nitrogen addition level, and the relative abundances of Glomus under high nitrogen addition (30 g·m−2·a−1) was significantly higher than under low nitrogen additions (5 and 10 g·m−2·a−1) (P<0.05). (3) Season had significant effects on the AM fungal community Chao index, Simpson index and community structure (based on OTUs, r=0.695), and the AM fungal community diversity indexes in autumn and spring were significantly higher than that in summer (P<0.01). (4) Redundancy analysis showed that nine environmental factors measured in this study explained 57.6% variance in the AM fungal community composition, passing the Monte Carlo test with 999 permutations (P=0.001). Among these factors, temperature had the greatest correlation with the AM fungal community composition (r=0.766). Moreover, pH, total P, total C and NH4 +-N were significantly correlated with the AM fungal community composition and diversity (P<0.05). Conclusion Nitrogen addition and sampling season had effects on the AM fungal community. Temperature, pH, total P, total C and NH4 +-N of soil were important drivers for the AM fungal community dynamic changes in this poplar plantation. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 34 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 801-810.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220498
Abstract:
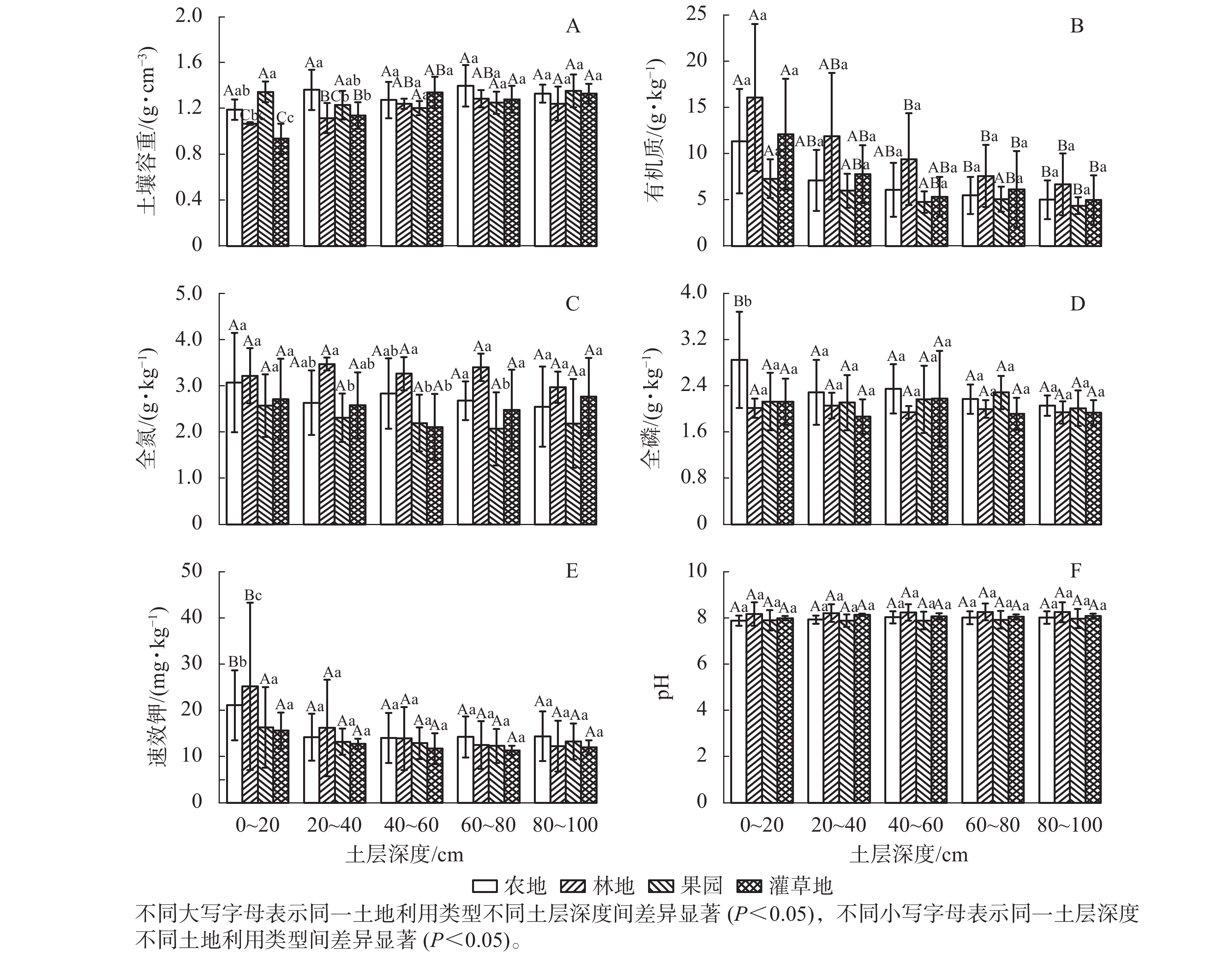
Objective This study aims to explore and evaluate the soil quality under different land use types in Qingshui River Basin in gully regions of the Loess Plateau, and quantify its relationship with environmental factors. Method Taking 4 typical site types (agricultural land, forest land, orchard, and irrigated grassland) in the basin as the study site, and based on 9 soil physical and chemical property indicators including soil bulk density, soil mechanical composition, soil nutrient content (organic matter, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, total potassium, and available potassium), principal component analysis and correlation were used to establish a minimum data set (MDS), and the soil quality of different land use types was calculated according to the weighted summation index method. Result (1) The contents of organic matter and total nitrogen of each soil layer in the forest land were the highest among the 4 site types. In 0−20 cm soil layer, the bulk density and total phosphorus content of agricultural land were significantly higher than those of other land types (P<0.05). In 0−20 cm soil layer, the available potassium content in forest land was significantly higher than that in other 3 land use types (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in pH among different land use types. The content of organic matter decreased gradually with the increase of soil depth and showed a significant positive correlation with total nitrogen (P<0.05). (2) MDS for soil quality index evaluation included bulk density, sand percentage and available potassium content. The soil quality of the 4 land use types from high to low was forest land, irrigated grassland, agricultural land, and orchard. The soil quality index increased with the increase of altitude. Conclusion The overall soil quality of Qingshui River Basin is good, and the soil quality of forest land and irrigated grassland is high, while the soil quality of agricultural land and orchard is relatively low. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 34 ref.]
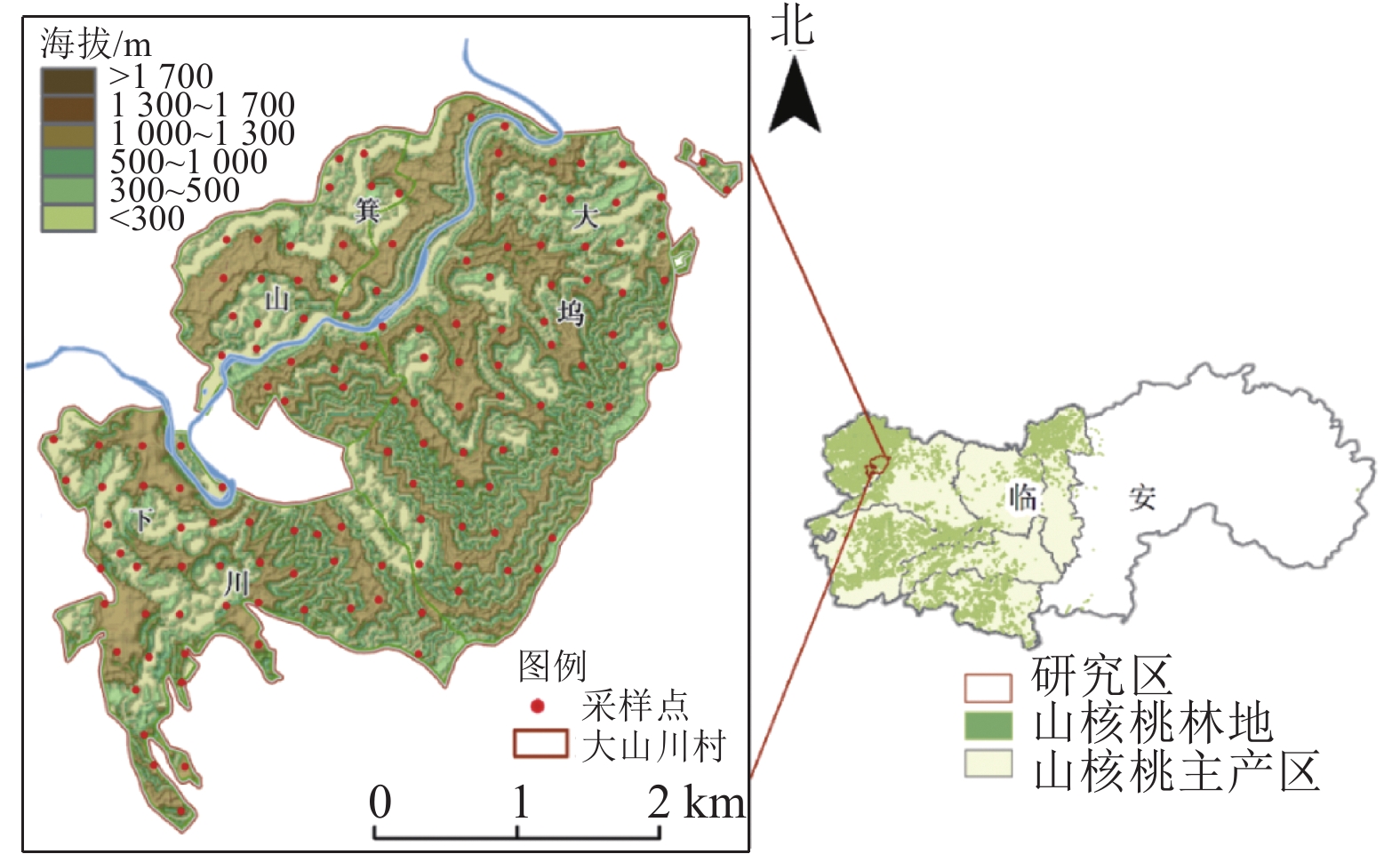
2023, 40(4): 811-819.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220544
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of a total of 134 topsoil samples (0−30 cm) systematically collected from Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis) plantation in Dashanchuan Village, Daoshi Town, Zhejiang Province, is aimed to provide scientific basis for rational soil fertility management of Chinese hickory plantation at village scale. Method GIS and geostatistics were utilized to reveal the spatial heterogeneity of soil fertility properties, whereas principal component analysis (PCA) was used to explore the main controlling factors affecting the soil fertility. Result Soil in Dashanchuan Village was acidic (pH 5.39) on the whole with the average of bulk density (BD) being 1.14 g·cm−3 while organic matter (OM), available nitrogen (AN), available potassium (AK) and total nitrogen (TN) were moderate with average concentrations of 42.13 g·kg−1, 115.89 mg·kg−1, 82.69 mg·kg−1 and 2.33 g·kg−1 respectively. Available phosphorus (AP) was low with average concentrations of 1.47 mg·kg−1 with the nugget coefficients of BD, TN, AP and AK below 25%, featured with a strong spatial autocorrelation. Soil pH and OM showed moderately spatial autocorrelation. AN fit the weak spatial autocorrelation, which indicated that random factors had a significant influence. The results of correlation analysis revealed that pH, OM, AK and AN had significant correlation with altitude and bulk density (P<0.05) while the integrated fertility index (IFI) of study area ranged from 0.20 to 0.90 with an average of 0.66, indicating moderate fertility level. Principal component analysis showed that OM and AN had a high load in PC1. Conclusion The study area suffered serious the soil acidification and nutrient imbalances with the soil fertility being high in the middle but low in the surrounding areas. Besides, OM and AN, are the main controlling factors affecting soil fertility quality of the study area, with their contents significantly affected by elevation and BD. Therefore, to improve soil acidification and soil fertility quality so as to better manage the soil, single element fertilizers including quicklime, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium could be applied under the principle of “large formula, small adjustment” based on formula fertilizer. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 28 ref.]
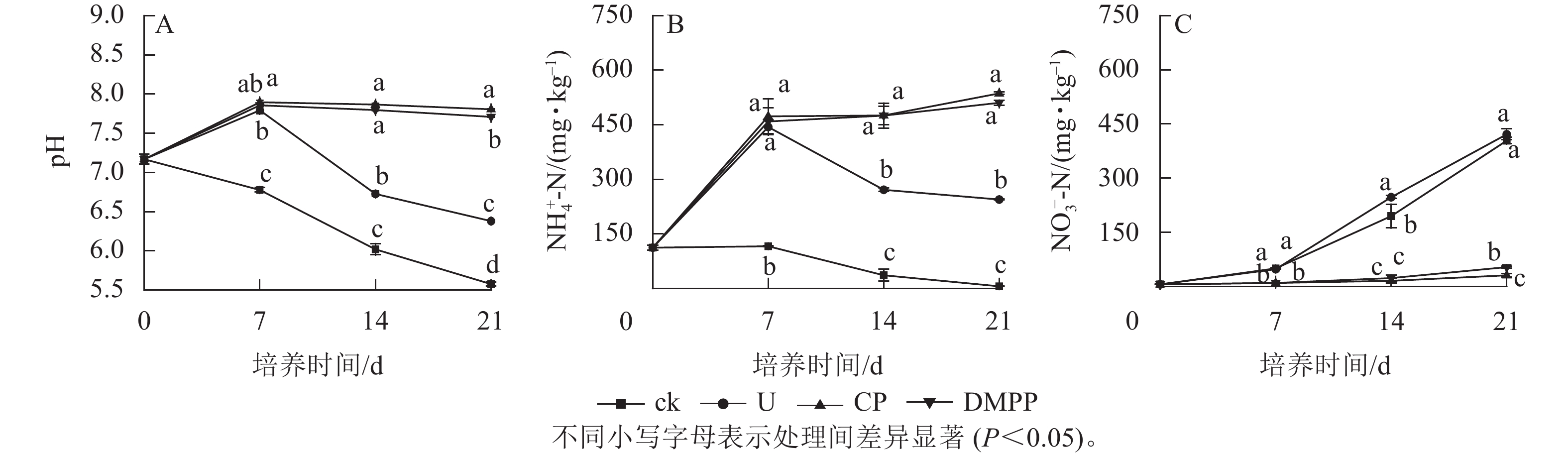
2023, 40(4): 820-827.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220605
Abstract:
Objective This study, with the conduct of a microcosm incubation using paddy soils, is aimed to investigate the effects of urea combined nitrification inhibitors 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) and 2-chloro-6 -trichloromethyl pyridine (CP) on pH, inorganic nitrogen, N2O emission and ammonia oxidizers with the ultimate purpose to explore the effects of nitrification inhibitors on soil nitrification and N2O emission. Method Four treatments were included in the whole process, namely no urea and nitrification inhibitor (ck), urea alone (N 200 mg·kg−1, U), urea + DMPP (1% of N, DMPP) and urea + CP (2% of N, CP). Result Addition of nitrification inhibitors significantly increased soil pH relative to ck and U with urea addition significantly enhancing soil NH4 +-N content (P<0.05) but having no effect on NO3 – -N content when compared with ck; The NO3 – -N contents and net nitrification rates were significantly lower under DMPP and CP treatments than those under ck and U treatments (P<0.05), indicating that nitrification inhibitors had an obvious effect of nitrification inhibition in paddy soils; Compared with ck, urea addition significantly increased soil N2O emission (P<0.05), while combined application of urea and nitrification inhibitors significantly reduced the cumulative N2O emission (P<0.05); Nitrification inhibitors decreased the amoA gene copy number of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), but had no effect on the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) when compared with U . Correlation analysis showed that soil N2O emission was significantly correlated with soil pH, AOB abundance and NO3 –-N content (P<0.05), indicating that soil pH, AOB abundance and NO3 –-N content were the key factors affecting soil N2O emission. Conclusion In neutral paddy soils, AOB rather than AOA dominated soil N2O emission and nitrification while DMPP and CP could inhibit soil nitrification and reduce N2O emission by decreasing AOB abundance. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 34 ref.]
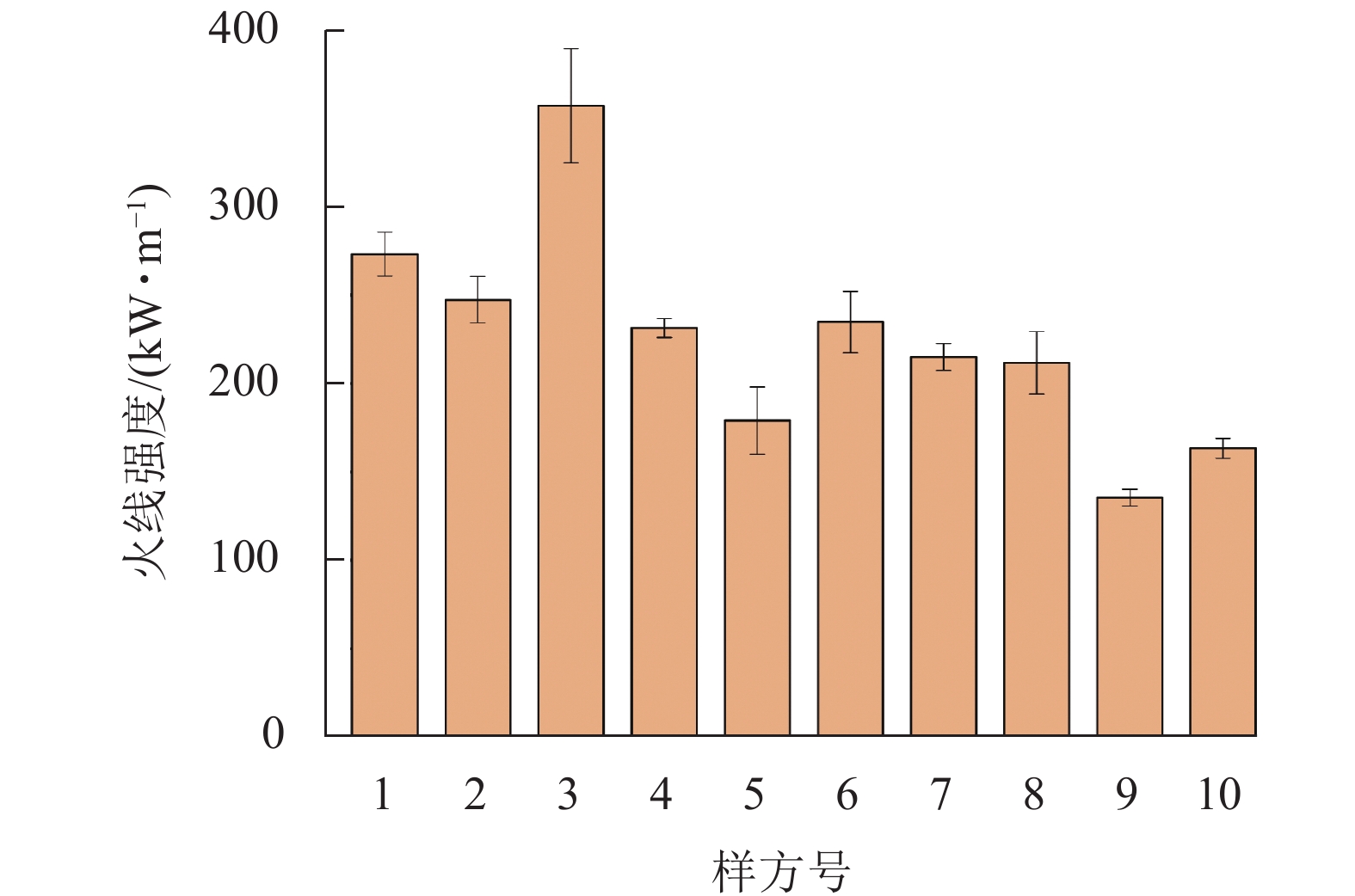
2023, 40(4): 828-835.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220560
Abstract:
Objective Prescribed burning is the most widely used and effective management measure for forest fuels. This study aims to reveal the behavior characteristics of prescribed burning in Pinus yunnanensis forest, so as to effectively clean up the forest land combustibles, reduce the possibility of forest fire, and realize the goal that forest fire management should focus on prevention. Method Downhill fire technology was employed as prescribed burning in P. yunnanensis forest. In the early stage of the fire prevention period, field investigation was conducted in the continuous distribution area of P. yunnanensis in Zhaobi Hill, Xinping County in central Yunnan Province, including sample plot setting and prescribed burning test to investigate the characteristics of fuels and record dynamic changes of fire behavior during the burning process, such as fire spreading rate, fireline intensity, flame temperature and height. Result In the early stage of fire prevention, the moisture content of surface fuels in the forest was 11.99%−12.06%, which was dry and flammable. The burning test showed that the fire spreading speed was 0.14−0.29 m·min−1, the fireline intensity was 147−332 kW·m−1, the flame temperature was 386−578 ℃, and the maximum flame height was 0.9 m. The parameters of fire behavior differed significantly among different surface fuels (P<0.05), but they were all low-intensity fires. The average under-branch height of P. yunnanensis forest was more than 7 m, and the vertical continuity of surface fuels was poor, so it was difficult for the understory burning flame to spread to the canopy. The unburned land rate accounted for 5.00% and the overall burning rate was 59.00%−75.00%, which achieved the expected effect and could effectively control combustibles. Conclusion The burning and fire spreading speed in P. yunnanensis forest is slow, belonging to stable surface fire, with spreading speed less than 4 km·h−1, and the surface combustibles burn thoroughly. Fireline intensity is less than 750 kW·m−1, which is a low-intensity fire and manually controllable. The average burning rate is 63.05% and the burning effect is good, and the load of flammable and combustible materials can be regulated to prevent forest fires. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 33 ref.]
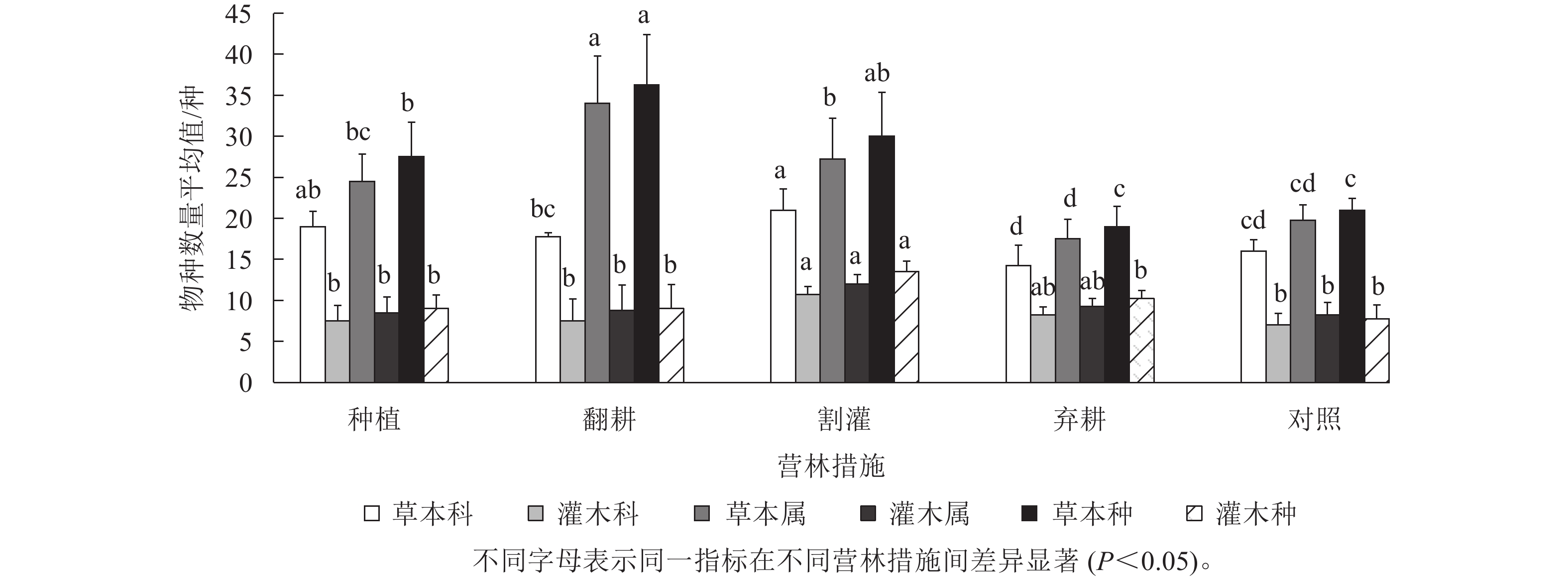
2023, 40(4): 836-847.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220604
Abstract:
Objective Expressway forest, as an important part of modern forestry, is undergoing common problems such as vulnerability and sensitivity. Therefore, this study, with an investigation into the effects of different forest management measures on the interspecific association of the under canopy planting and community stability, is aimed to put forward appropriate stand rearing measures for the Populus canadensis plantation in Chengdu ring expressway area so as to improve its overall ecological benefits. Method First, taking the P. canadensis plantation in the first expressway area of Chengdu as the research object, a total of 20 plots were set up by typical sampling method. Then, with the empployment of the variance ratio method (VR), χ2 test, connection coefficient (AC), Spearman rank correlation coefficient and M. Godron stability were measured before a comparative analysis was conducted of the effects of under canopy planting (UP), plow tillage (PT), swamping (SW), abandoned cultivation (AC) and control group (the sample land without any business activities after afforestation as a control group, CG) on interspecific association and community stability. Result The VR values of dominant herb species displayed a trend of UP>SW>PT>CG>AC under different management measures, and the VR (>1) values in UP and SW plots demonstrated positive correlation whereas the VR values of dominant shrub species showed a trend of PT>SW>CG>UP>AC and only the VR (<1) values in AC plots showed a negative correlation; Interspecific association analysis showed that the number of species of dominant species in shrub and herb layer with positive correlation displayed an opposite trend from that of those with negative correlation with managing methods PT and SW and the managing methods of UP and CG mainly affected dominant herb species; The stability analysis of M. Godron showed a relatively weak overall stability of the communities in the five forestry measures plots which were all in the primary stage of succession, with the UP and SW communities having the highest overall stability. Conclusion The interspecific association strength of the dominant shrub species is better in UP and SW which can help promote community succession and the overall stability of the under canopy planting community. [Ch, 5 fig. 5 tab. 29 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 848-858.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220570
Abstract:
Objective Chimonanthus nitens is a rare wild plant unique to China both for tea and medicine. The wild resources have been seriously damaged with the development of its medicinal function and the increase of market demand. This study aims to explore the structure characteristics and species diversity of the habitat community of C. nitens population, as well as its suitable living environment, so as to provide a scientific basis for the protection, development and utilization of C. nitens population. Method Based on the field survey, the typical community of C. nitens was selected in Wuxi River Basin of Suichang, and five 400 m2 plots were set up to investigate and analyze the flora, species composition, community structure and species diversity of the community. Result (1) The flora of C. nitens community was dominated by pantropical distributions, disjuncted distribution in East Asia and North America, and northern temperate distribution. The proportions of tropical and temperate genera were 50.70% and 40.85%, respectively, with typical characteristics of mid-subtropical flora. (2) There were 105 species in the 2000 m2 sample plots, belonging to 80 genera and 47 families. The families and genera were rich in species and dispersed in composition. The dominant families were Lauraceae, Rosaceae, Fagaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. (3) The diameter class structure of C. nitens population and habitat community was an inverted “J” type, indicating a growth type. The top 5 tree species with important values of the arbor layer were Cunninghamia lanceolata (11.67%), Chimonanthus nitens (11.63%), Castanopsis sclerophylla (9.05%), Loropetalum chinense (7.28%) and Lithocarpus glaber (7.08%). The vertical structure of the community was rich. K-means clustering showed that individuals with DBH≥1 cm in the tree layer could be divided into five forest layers according to the tree height. The main location of the community was in the tree layer Ⅰ [1.0, 4.5) m and tree layer Ⅱ [4.5, 7.0) m. (4) The species diversity index varied greatly in different regions. Margalef index, Shannon-Wiener index, Simpson index, Pielou index and Dominance index were 1.98−3.84, 1.56−2.37, 0.72−0.87, 0.69−0.86 and 1.98−3.85, respectively. Conclusion The community of wild Chimonanthus nitens in Wuxi River Basin of Suichang has rich species composition and complex vertical structure. Small and medium diameter trees account for the vast majority, which is an increasing community with high species diversity as a whole. Under the premise of protecting the existing community habitat, it is suggested to carry out experiments imitating wild cultivation to rationally develop and utilize the wild resources of Chimonanthus nitens. [Ch, 2 fig. 7 tab. 26 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 859-866.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220616
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to study and analyze the habitat characteristics of Emeia pseudosauteri in Kowloon National Wetland Park and the influence of relevant habitat factors on its population density (D), so as to understand the habitat requirements of E. pseudosauteri and provide scientific reference for future research on species resources conservation and utilization, population breeding, habitat protection and management. Method In early April 2022, taking Kowloon National Wetland Park and the surrounding habitat of E. pseudosauteri in Lishui of Zhejiang Province as the research area, 34 survey points were set up to obtain the population density of E. pseudosauteri and 12 habitat factors data at each survey point, and a multiple stepwise regression model was established to analyze the impact of different habitat factors on population density. Result Canopy closure [XCC, standardized coefficient (β)=0.505, P<0.001] and soil water content (XSWC, β=0.143, P=0.029) had a significant positive correlation with the population density of E. pseudosauteri. Wind speed (XWS, β=−0.424, P<0.001) had a significant negative correlation with population density. Stepwise regression equation: D=7.446XCC−1.666XWS+9.337XSWC−6.584. The adjusted R2 was 0.930, the Durbin-Watson test result was 1.615, the variance inflation coefficient was less than 5, and the significance P values were less than 0.05, indicating that the three habitat factors included in the analysis model were independent of each other, and there was no collinearity. The analysis result was statistically significant. Conclusion Higher canopy density, lower wind speed and higher soil water content are choices of environment made by E. pseudosauteri according to its own biological characteristics and living habits, reflecting its habitat needs in communication, mating, breeding and spawning. Therefore, in carrying out the breeding, protection and habitat management of E. pseudosauteri population, attention should be paid to increasing canopy closure, reducing the impact of environmental wind, and maintaining suitable soil and air humidity. [Ch, 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 867-874.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220518
Abstract:
Objective This study attempts to prepare ceramsite from slag and sludge, which is produced in the incineration of municipal solid waste, so as to achieve a reasonable disposal of the slag and sludge. Method The slag sludge separated from the slag according to the particle size was made into spherical particles with fly ash, quartz powder and kaolin in a mass ratio of 3∶3∶3∶1, and then sintered in a muffle furnace. The properties of ceramsite were tested according to GB/T 17342.1, and the microscopic morphology, crystal structure and heavy metal leaching of ceramsite were measured. Result Two heavy metals in slag sludge exceeded the standard, namely cadmium and zinc. At 1 175 ℃, the bulk density and compressive strength of the obtained ceramsite particles increased significantly, and the water absorption rate decreased in 1 h. When the sintering time was 10−15 min, the water absorption of ceramsite varied greatly in 1 h. Excessive preheating temperature and preheating time were not conducive to good expansion effect of ceramsite. Under the optimum firing conditions, the bulk density of the ceramsite obtained was 783 kg·m−3, the compressive strength was 7.9 MPa, and the water absorption rate in 1 h was 9.8%, conforming to the national standard of GB/T 17431.1 for lightweight aggregates. The leaching contents of cadmium and zinc in the ceramsite particles fired by the optimal process were 0.006 5 and 0.511 7 mg·L−1 respectively, which were far lower than the leaching contents of cadmium and zinc in the slag sludge itself. The cost of producing ceramsite from domestic waste incineration slag sludge in the laboratory was 28.0 yuan·m−3, and according to the market price of ceramsite, a profit of 102.0 yuan·m−3 of ceramsite could be generated. Conclusion The optimal sintering process includes a sintering temperature of 1 175 ℃, a sintering time of 15 min, a preheating temperature of 400 ℃, and a preheating time of 20 min. The properties and heavy metal leaching content of ceramsite meet national standards. [Ch, 6 fig. 5 tab. 28 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 875-882.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220662
Abstract:
Objective This study, with the establishment of the discrete element model of bamboo powder particles and the calibration of its related contact parameters, is aimed to provide a fundamental basis for the research of the interaction mechanism between biomass material particles and processing equipment. Method First, a physical test was conducted of the contact parameters with its results used as the basis for the selection of simulation parameters. Then, with the method of discrete element method (DEM) simulation combined with design of experiment (DOE) test, the quadratic polynomial regression model between the stacking angle and DEM parameters was obtained by Plackett-Burman (P-BD) test, climbing test and response surface test. At last, The optimal combination of contact parameters was obtained by using the physical stacking angle as the target value. Result The measured physical stacking angle was 49.29°. The rolling friction coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder, the restitution coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder and the static friction coefficient of bamboo powder-stainless steel plate had significant effects on the stacking angle as was shown in the P-BD test (P<0.05). The response surface test further confirmed the results of P-BD test, and showed that the interaction between the rolling friction coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder had significant effects on the stacking angle. It was proved that the interaction between the rolling friction coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder and the restitution coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder had significant effects on the stacking angle (P<0.05). The optimal combination was obtained with the restitution coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder being 0.44, the rolling friction coefficient of bamboo powder-bamboo powder being 0.22 and the static friction coefficient of bamboo powder-stainless steel plate being 0.45. Conclusion The quantitative simulation calibration and prediction platform of bamboo powder particle stacking angle is of high reliability in the range of 41.20°−55.27°and the DEM calibration method employed in this study is conducive to the subsequent establishment of material models to evaluate the motion behavior of lignocellulosic biomass pellet and their interaction with equipment. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 27 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 883-891.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230327
Abstract:
Objective Build a landscape performance evaluation system in line with the characteristics of the coordinated development of forest characteristic towns to provide a basis for the scientific evaluation of their construction benefits and development level. Method Taking Tianhuangping Forest Town in Anji County as the research object, through the questionnaire survey and field research, and the corresponding evaluation index system are used to construct the hierarchical analysis method and Delphi method, and its landscape performance is comprehensively evaluated. Result (1) Tianhuangping Forest Town with an forest ecological service value of 716 million yuan in 2022, its ecosystem service value per unit area is 76 000 yuan·hm−2·a−1, higher than the provincial average. Among them, the value of carbon fixation and oxygen release and water conservation accounts for a relatively large proportion, for 46% and 41%, respectively. (2) Good small town livable environment indicators, but the forest phase landscape is relatively single, and characteristic landscape construction needs to be improved. (3) The linkage of the three industries has achieved remarkable results, industrial structure has been effectively adjusted. The gross domestic product of forestry industry, per capita disposable income and other indicators are higher than the provincial average. (4) The ecological culture represented by the “Two Mountains” culture has been fully explored and carried forward. Conclusion The landscape performance evaluation of Tianhuangping Forest Town is “excellent”. Its planning and construction consider both ecological protection and economic development, realizing the effective transformation from clear water and green mountains to golden mountains and silver mountains, and can provide reference for the planning and construction of the same type of forest characteristic town. [Ch, 5 tab. 30 ref.]
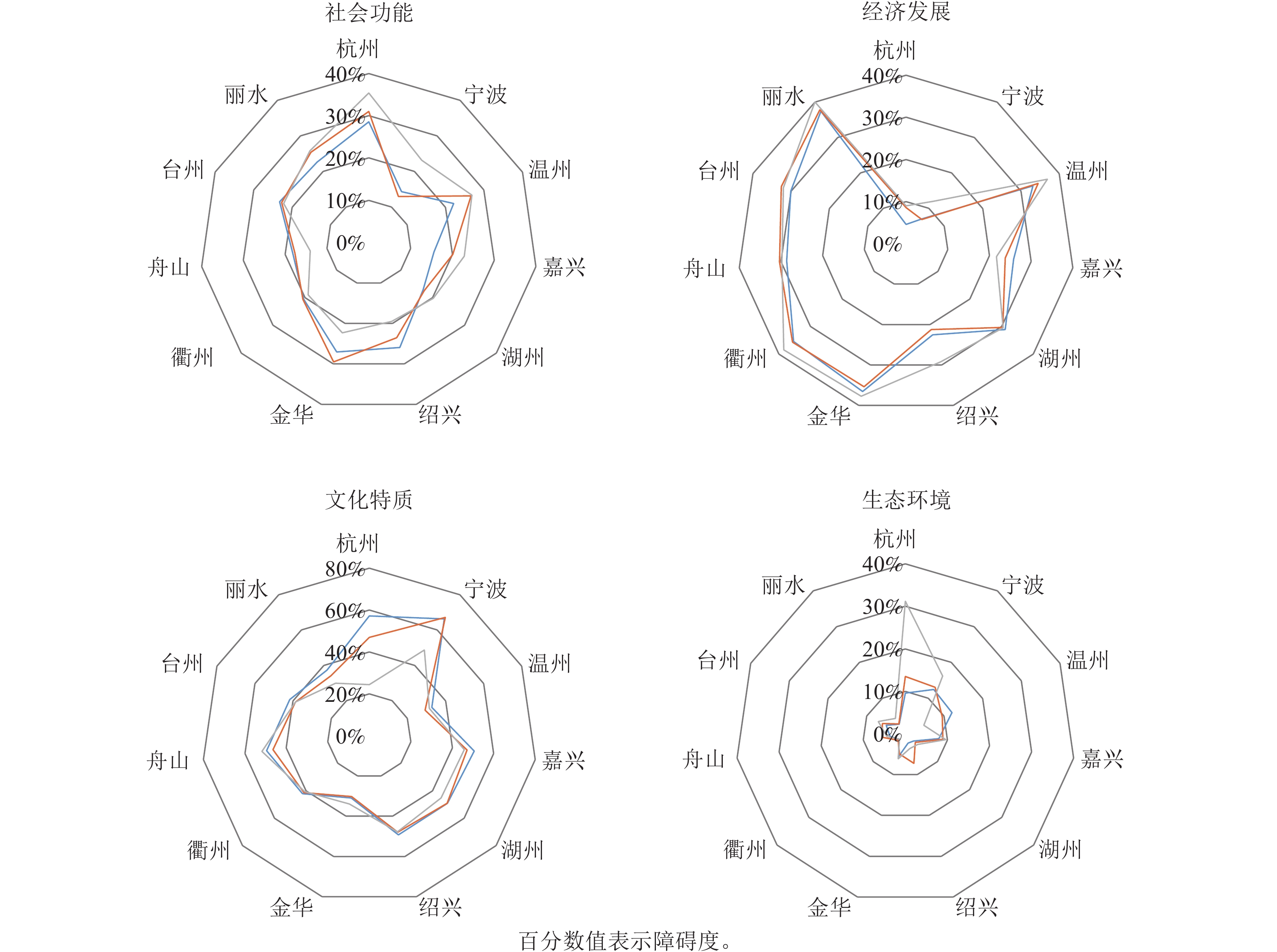
Spatiotemporal differences and influencing factors of urban development quality in Zhejiang Province
2023, 40(4): 892-900.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220623
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an exploration and evaluation of the spatiotemporal differences of the urban development quality in Zhejiang Province as well as an analysis of the influencing factors, is aimed to provide scientific basis for urban development. Method From the four dimensions of social function, economic development, ecological environment and cultural characteristics, the entropy weight TOPSIS model was used to evaluate the differences of urban development quality in Zhejiang province whereas the obstacle degree model was employed in the exploration of the main obstacle factors affecting the quality of urban development. Result In terms of temporal variation, the overall level of urban development quality in Zhejiang Province has steadily improved, and the city rank has been relatively stable though with differences expanding. From the perspective of spatial change, the urban development of Zhejiang Province has gradually formed a pattern of high-quality urban agglomeration around Hangzhou Bay with Hangzhou and Ningbo as the center. In accordance with the subsystem evaluation results, the development quality of each city is featured with an imbalance in social function, economic development, ecological environment and cultural characteristics, among which, the one in the economic development subsystem, though consistent with the comprehensive evaluation results of cities, is the most significant. Though the barriers vary from city to city in the high value areas and change trends at the subsystem level and indicator level, cultural characteristics and economic development are the main subsystems that restrict the high-quality development of each city while the ecological environment subsystem has the least impact on the quality of urban development. Conclusion The overall quality of urban development in Zhejiang Province is on the rise, with different cities displaying different development advantages and disadvantages, reflecting the current situation of imbalanced development, which calls for the formulation of differentiated development strategies so as to cope with the significant differences in obstacle factors. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 26 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 901-909.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220592
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation into the mechanism of county digitalization that has greatly contributed to the development of rural industries in Zhejiang Province, a pioneer in the promotion of common prosperity and agricultural and rural modernization via digital economy, is aimed to sum up practical experience that will help facilitate the development of counties, rural revitalization and common prosperity. Method With field interviews and investigations conducted in Changshan County, Suichang County and Chun’an County, an analysis was made of the impact of digital development on economic and social development from the county level. Then an investigation was carried out of three typical models including Suichang County rural e-commerce model, Changshan County Internet of Things model and Chun’an County Internet + characteristic agriculture model so as to analyze the mechanism of digitalization in the promotion of rural industry development. Result Digitization can promote the development of rural industry, from creating new business forms, promoting employment, reducing cost, expanding profit sources, improving human capital to attracting returning entrepreneurs, etc. Conclusion In the future, on the basis of fully considering the actual situation of the development of regional featured industries, efforts should be made in the optimization of digital infrastructure, cultivation of rural digital talents and development of regional characteristic resources for the goal of ensuring the leapfrog and high-quality development of counties. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 31 ref.]
2023, 40(4): 910-920.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220619
Abstract:
Soil extracellular enzymes play indispensable role in the driving of biogeochemical cycle of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and other elements in soil ecosystem. Therefore, under the background of global changes, disclosing the response of soil extracellular enzyme activity to variation of climate can improve the understanding of the mechanisms of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus key biogeochemical processes under climate change. However, the current understanding of the response mechanism of soil extracellular enzyme activities related to carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in different ecosystems to climate change still needs to strengthen. Thus, the sources, classification and regulatory factors of soil extracellular enzymes in the biogeochemical cycle of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, and the biogeochemical processes of soil extracellular enzymes were summarized. On this basis, the response rules and mechanisms of soil extracellular enzyme activity to nitrogen deposition, warming, precipitation and CO2 changes were discussed. The response mechanism of soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry to common global change factors was summarized. Therefore, in the context of global change, it is necessary to combine metabolome and molecular biology to strengthen the response mechanism of soil extracellular enzymes to climate change. This review provides a new perspective for further understanding the role of soil extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycles under climate change scenarios. [Ch, 112 ref.]
Soil extracellular enzymes play indispensable role in the driving of biogeochemical cycle of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and other elements in soil ecosystem. Therefore, under the background of global changes, disclosing the response of soil extracellular enzyme activity to variation of climate can improve the understanding of the mechanisms of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus key biogeochemical processes under climate change. However, the current understanding of the response mechanism of soil extracellular enzyme activities related to carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in different ecosystems to climate change still needs to strengthen. Thus, the sources, classification and regulatory factors of soil extracellular enzymes in the biogeochemical cycle of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, and the biogeochemical processes of soil extracellular enzymes were summarized. On this basis, the response rules and mechanisms of soil extracellular enzyme activity to nitrogen deposition, warming, precipitation and CO2 changes were discussed. The response mechanism of soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry to common global change factors was summarized. Therefore, in the context of global change, it is necessary to combine metabolome and molecular biology to strengthen the response mechanism of soil extracellular enzymes to climate change. This review provides a new perspective for further understanding the role of soil extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycles under climate change scenarios. [Ch, 112 ref.]