2020 Vol. 37, No. 6
2020, 37(6): 1027-1035.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190631
Abstract:
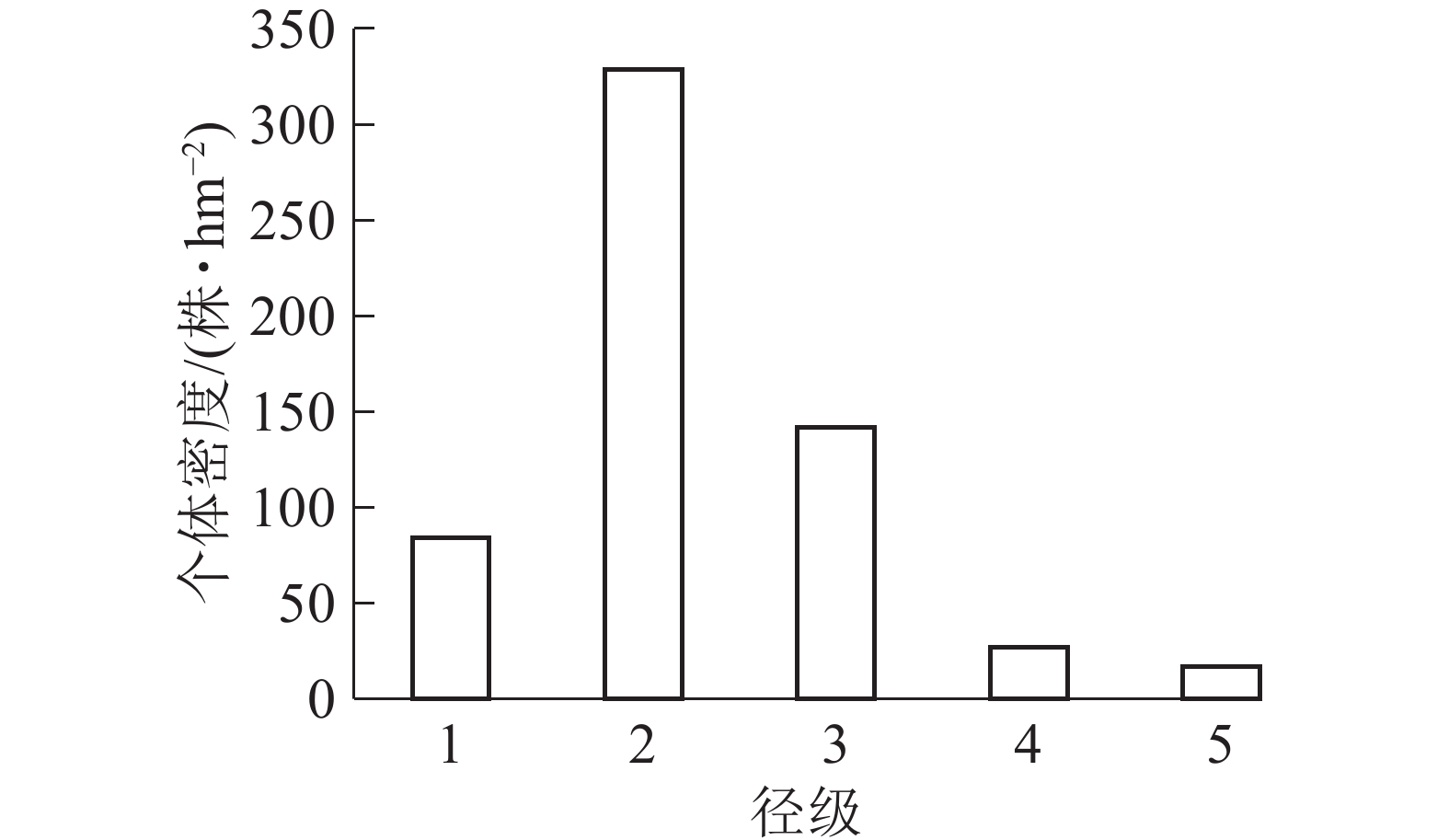
Objective This research aims to study the age structure and spatial pattern of Phoebe sheareri population in Mount Tianmu, so as to better protect the population and provide basis for forest management. Method Based on the survey data of 1 hm2 (100 m×100 m) of evergreen broad-leaved forests in Mount Tianmu of Zhejiang Province, the age structure of dominant species P. sheareri population was analyzed. According to the diameter at breast height(DBH), the population was divided into five diameter classes: diameter class 1 (1.0 cm≤DBH<2.5 cm), diameter class 2 (2.5 cm≤DBH<10.0 cm), diameter class 3 (10.0 cm≤DBH<20.0 cm), diameter class 4 (20.0 cm≤DBH<30.0 cm), diameter class 5 (DBH≥30.0 cm). The point pattern method was used to analyze the spatial distribution pattern of P. sheareri and spatial correlation of individuals of different diameter classes. Result (1) 68.95% were young individuals in diameter class 1 and diameter class 2, 23.71% in diameter class 3, 7.34% in diameter class 4 and diameter class 5. The survival curve of the population was close to Deevey type I, belonging to the growth-oriented development model. (2) The individuals of diameter class 1, diameter class 2, diameter class 3 and diameter class 4 were mainly distributed in clusters, and with the increase of research scale, the aggregation was more significant, and diameter class 5 was mainly of random distribution. (3) There existed a close relationship between diameter classes, displaying a dominant positive correlation. In small scale observation, diameter class 1 and diameter class 4 were negatively correlated in the scale of 0−5 m, diameter class 3 and diameter class 4 were negatively correlated in the scale of 0−8 m, and diameter class 3 and diameter class 5 were negatively correlated in the scale of 0−4 m. All other diameter individuals were positively correlated. From the large-scale observation, there was a significant positive correlation between individuals of different sizes in P. sheareri population. Conclusion The population of P. sheareri in Mount Tianmu belongs to the growth-oriented development model, and each diameter class is distributed in clusters. The relationship between different diameter classes is close, displaying a dominant positive correlation. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 24 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1036-1044.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190762
Abstract:
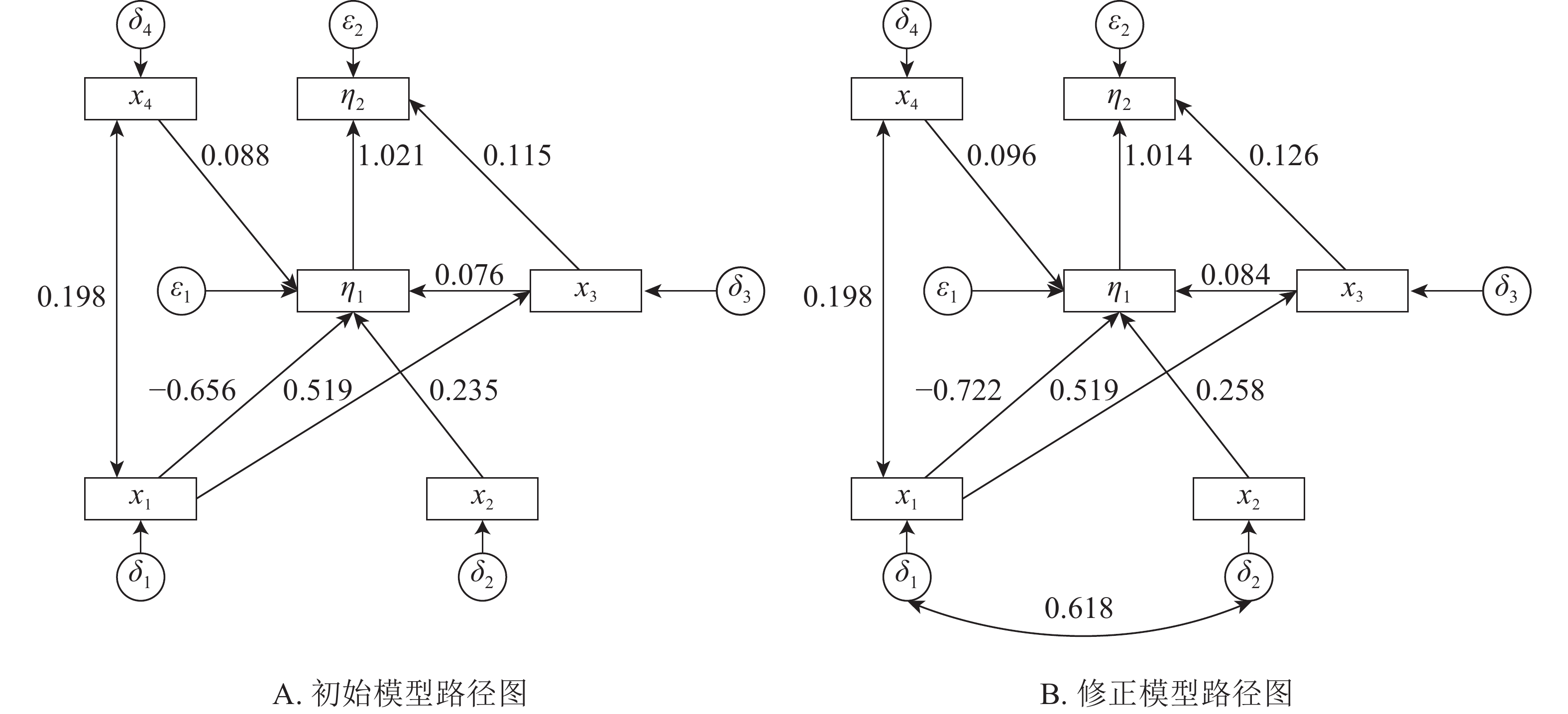
Objective This study aims to explore the dominant factors affecting the growth of different stands in the karst area at the headwaters of South-to-North Water Diversion Project, so as to provide scientific evidence for vegetation restoration, forest management and forest rehabilitation in such area. Method The karst area of Xichuan County, where the head of the middle channel of South-to-North Water Diversion Project is located, was taken as the research object. The models of tree layer biomass, bedrock exposure, soil thickness, tree species diversity and stand density were built, based on the structural equation model to carry out relational coupling. Result There existed a positive correlation between bedrock exposure and stand density (P<0.01), a very significant positive correlation with tree species diversity (P<0.01), and a very significant negative correlation with the biomass of constructive species (P<0.01). The direct impact coefficient of bedrock exposure on stand density was 0.198, the direct impact coefficient on tree species diversity was 0.519, the total, direct and indirect impact coefficients on biomass of constructive species were −0.659, −0.722 and 0.063, respectively, and the indirect impact coefficient on stand biomass was −0.604. There existed a significant positive correlation between soil thickness and constructive species biomass (P<0.05), and a positive correlation between tree species diversity, stand density and constructive species biomass. The direct and indirect impact coefficients of soil thickness on the biomass of constructive species were 0.258 and 0.262 respectively. The direct impact coefficient of tree species diversity on constructive species was 0.084, and the total, direct and indirect impact coefficients on total biomass of stand were 0.211, 0.126 and 0.085 respectively. The direct impact coefficient of stand density on constructive species was 0.096, and the indirect impact coefficient on total biomass was 0.098. There was a significant positive correlation between the biomass of constructive species and the total biomass of stands(P<0.01), and the total impact coefficient of constructive species biomass on the total biomass of stands was 1.014. Conclusion There are complex relationships between bedrock exposure degree, soil thickness, tree species diversity, stand density, and constructive species biomass and total stand biomass. Reducing bedrock exposure in karst area and increasing soil thickness (i.e. improving site conditions) can improve the stand structure, as well as the constructive species biomass and stand biomass. Biomass is positively correlated with site conditions, stand density, and tree species diversity. Improving site conditions, tending and changing stand structure can promote individual growth, increase the biomass accumulation, and improve the ecological environment in karst area. [Ch, 1 fig. 3 tab. 34 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1045-1053.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200136
Abstract:
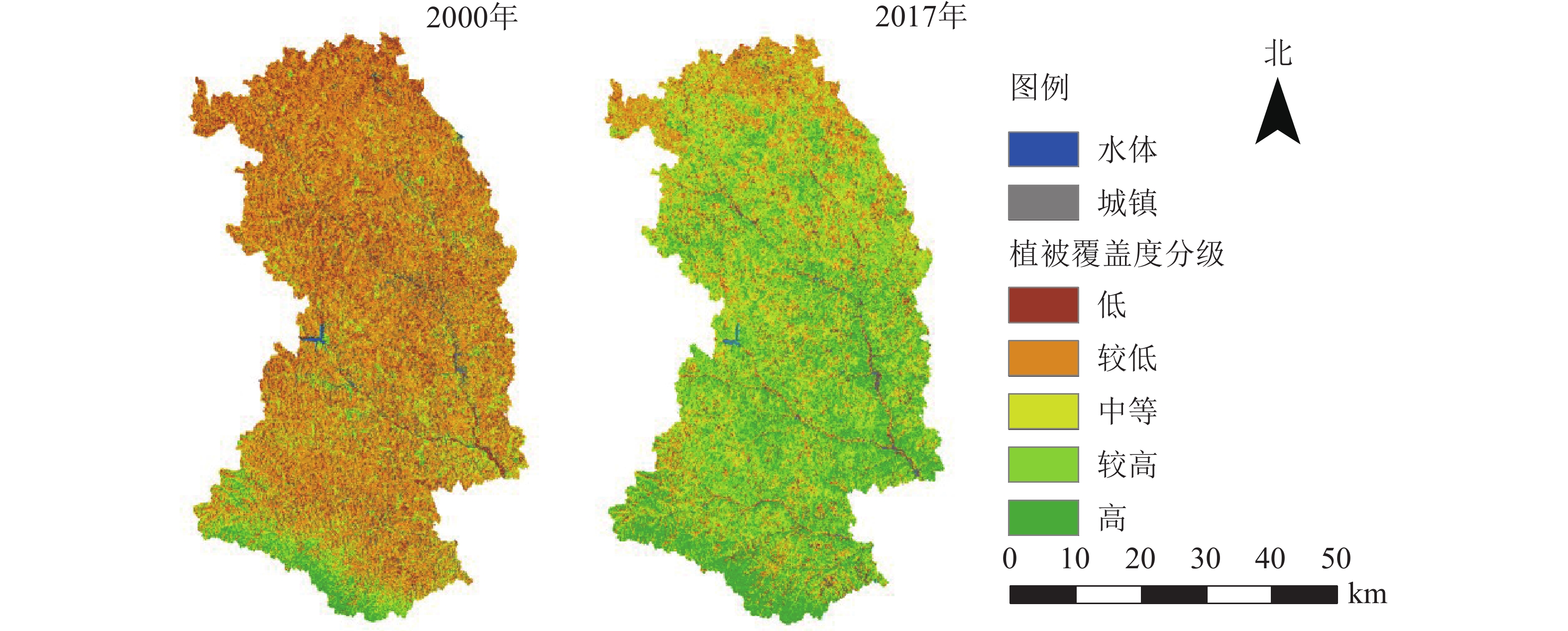
Objective The present study is to analyze the vegetation changes in areas with severe soil erosion on the Loess Plateau since the implementation of forestry ecological projects such as the Three-north (northwest, north and northeast) Shelterbelts and Conversion of Farmland to Forests, so as to provide basis for formulating reasonable ecological restoration and management countermeasures. Method Taking Ansai District of Yan’an City in Shaanxi Province as an example, the vegetation coverage in 2000 and 2017 was estimated by pixel dichotomy based on Landsat TM/OLI image, and topographic differentiation characteristics were analyzed in combination with altitude, slope and slope direction. Result (1)Vegetation coverage significantly increased from 24.98% in 2000 to 53.34% in 2017. (2)The proportion of vegetation coverage with extremely significant increase in the study area accounted for 44.70%, which was concentrated along rivers. (3)In 2000, the vegetation coverage gradually decreased with the increase of altitude. In 2017, the vegetation coverage increased first and then decreased with the increase of altitude. In 2000 and 2017, the vegetation coverage increased first and then decreased as the slope increased, and reached its maximum value at the slope of 25°−35°. The order of vegetation coverage from large to small with the change of slope direction was shady slope, semi shady slope, semi sunny slope, and sunny slope. (4)When the altitude was less than 1 300 m and the slope was 15°−35°, flat land, shady and semi shady slopes had good water and heat conditions, with easy vegetation recovery and the largest proportion of high vegetation coverage area. Conclusion The vegetation in Ansai District showed a trend of improvement from 2000 to 2017, with differences under terrain conditions such as altitude, slope, and slope aspects. Ecological restoration countermeasures should be formulated based on local conditions. [Ch, 2 fig. 6 tab. 27 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1054-1063.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190666
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the causes for the development of Dicranopteris dichotoma monodominant synusium, photoresponse process and primary photochemical reaction in D. dichotoma were studied. Method Different levels of light intensity (slight shade, L1, medium shade, L2 and heavy shade, L3) and soil moisture (sufficient moisture, W1, moderate drought, W2 and severe drought, W3) were set, compared with all light treatment, and the change characteristics of photosynthetic parameters and chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetic parameters of potted D. dichotoma were analyzed. Result (1) Under slight shading, severe drought significantly reduced Pn, YAQ and Pmax of D. dichotoma, and the Pn of sufficient moisture and moderate water control was approximately 34.4%−69.2% higher than that of ck; (2) Under medium and heavy shade, Pn between three water control treatments was similar and slightly higher than that of ck, and there was no significant difference in LCP and Rd (P>0.05), which indicated that the increase of shade degree could alleviate the negative effect of water deficit on the photosynthetic parameters of D. dichotoma; (3) Under the same soil moisture, the fluorescence parameters showed a change characteristic of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of shade degree; (4) Severe drought stress reduced the photosynthetic mechanism capacity of D. dichotoma under slight and medium shade; under heavy shade, the ψO, φEo, energy flow parameters and PIABS growed upward with the decrease of soil moisture, which showed that D. dichotoma had obvious drought resistance in low light environment; (5) Shade and drought did not significantly inhibit the PIABS and PItotal, indicating that PSⅡ of D. dichotoma was not seriously damaged. Conclusion It is considered that the combination of medium shade and sufficient moisture is more conducive for potted D. dichotoma to accumulate photosynthate. Under medium shade and moderate drought, potted D. dichotoma has the highest activity of PSⅡ, with a strong adaptability showed to the changes of shade environment and soil moisture. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 38 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1064-1070.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200121
Abstract:
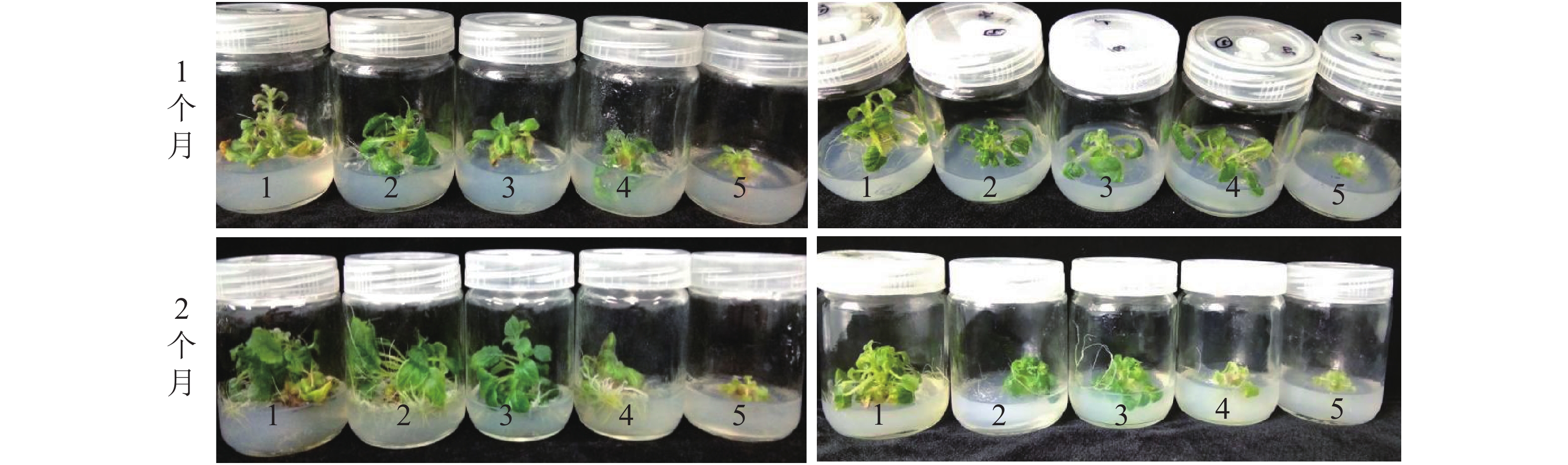
Objective The aim is to explore the aluminum tolerance of Hydrogena strigosa and H. longipes tissue culture seedlings, so as to lay a foundation for the application of aluminum resistant plants and the utilization of special acid soil resources. Method The effects of different concentrations of AlCl3 (0, 25, 50, 100, 200 mg·L−1) on the growth and physiological characteristics of H. strigosa and H. longipes tissue culture seedlings were studied. Result Under low concentration of aluminum stress (25, 50 mg·L−1), the growth of H. strigosa was normal and similar to that of the control group, while the growth of H. longipes was inferior to that of the control group. Under the medium and high concentration of aluminum stress (100, 200 mg·L−1), the growth of tissue culture seedlings was significantly reduced, and the average root length and root volume were lower than those of the control group, indicating that aluminum stress inhibited both the aboveground and underground parts of Hydrangea. With the increase of aluminum stress concentration, the chlorophyll mass fraction of H. strigosa increased at 50 mg·L−1, while the chlorophyll mass fraction of H. longipes decreased, which indicated that H. strigosa promoted chlorophyll synthesis under low aluminum stress, and H. longipes inhibited chlorophyll synthesis under aluminum stress. The content of malondialdehyde in H. strigosa and H.longipes decreased first and then increased. The catalase and peroxid activities increased continuously. The activities of superoxide dismutase were lower than those of the control group, but the difference was not significant. The proline mass fraction of H. strigosa was lower than that of the control group under the treatment of 25 mg·L−1, and higher than that of the control group under other aluminum concentration treatment. The proline mass fraction of H. longipes under aluminum stress was higher than that of the control group. Conclusion Hydrangea can make positive growth and physiological responses under aluminum stress, and different species of Hydrangea have different aluminum tolerance. In sum, H. strigosa and H. longipes are resistant to low concentration of aluminum.[Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 24 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1071-1079.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190687
Abstract:
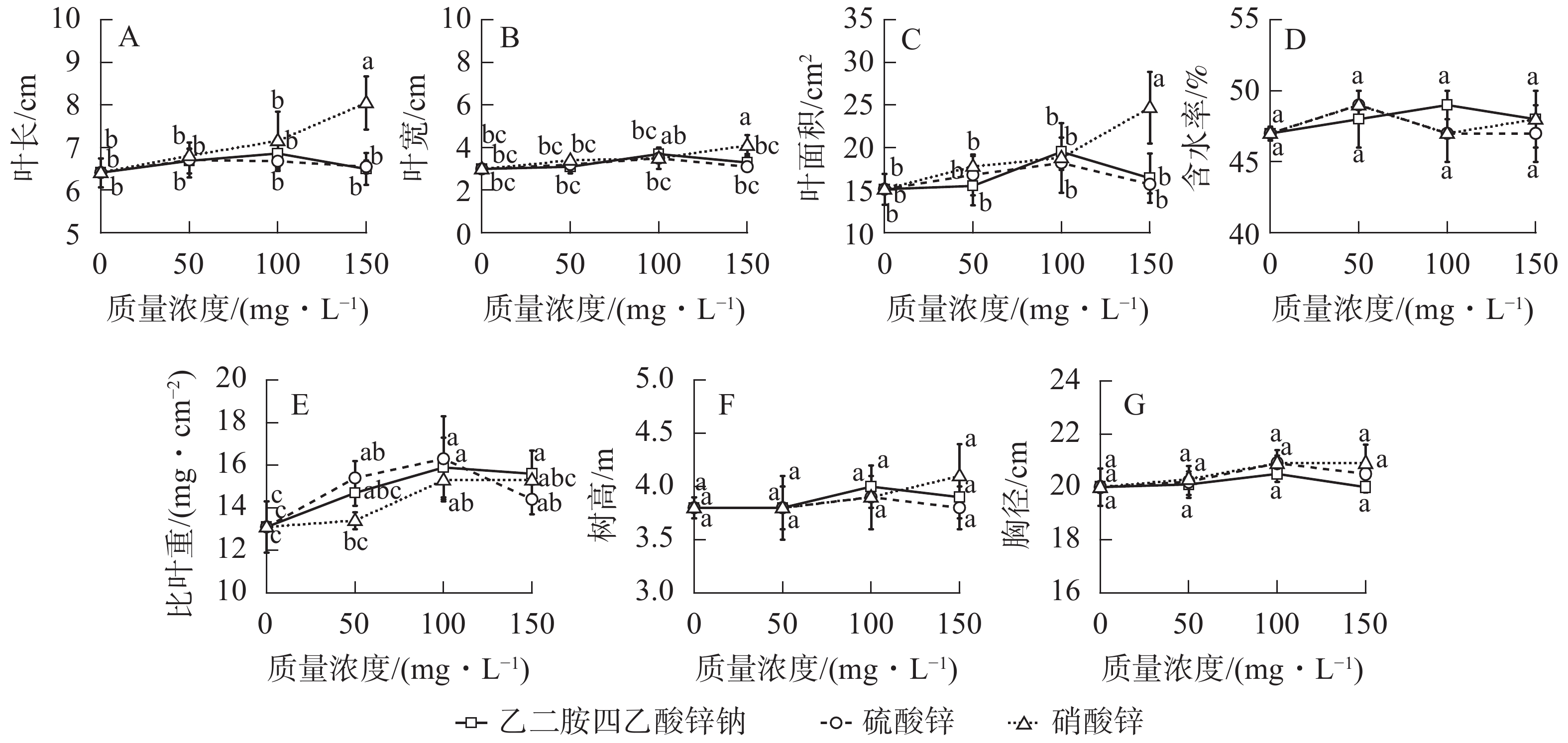
Objective With the effect of foliar spraying of zinc (Zn) on leaves growth and mineral elements of pecans (Carya illinoensis) explored, the study is aimed to provide scientific basis for the fertilizer control of fruit trees. Method Using 6-year-old ‘Pawnee’ pecans as the research material under field conditions, a field experiment was conducted with 3 types of zinc fertilizers, such as EDTA-Zn, zinc sulfate (ZnSO4·7H2O), zinc nitrate [Zn (NO3)2·6H2O)] sprayed at 3 levels of concentrations (50, 100, 150 mg·L−1 Zn) in terms of 10 treatments (with 0 mg·L−1 Zn as control). Treatments were replicated three times in a randomized complete block design to measure the growth parameters (leaf length and width and area, rate of water content, specific leaf weight, tree height and diameter) and leaf mineral elements [nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu)]. These parameters were initially evaluated with the employment of principal component analysis (PCA) and weight subordinate function (WSF). Result The leaf growth parameters and tree height and diameter increased to a certain extent with the increased concentration. The leaf length, width, area, specific leaf weight increased by 26%, 37%, 25%, 17% with the 150 mg·L−1 of zinc nitrate treatment respectively, which was significantly higher than that with other treatments (P<0.05). With the increased concentration, the N, K, Zn, Mn contents of pecan leaves increased and the P, Fe content decreased while the Ca and Mg contents first increased and then decreased. As was shown in the correlation analysis, the length, width, N, K were significantly and positively correlated (P<0.05) to Zn in leaves while the coverage, Ca, Mn were significantly and positively correlated (P<0.01) to Zn in leaves. Conclusion Foliar spraying of zinc has significantly improved the leaf growth of pecans (P<0.05) and increased the accumulation of mineral elements in leaves. Thus, it was suggested that 150 mg·L−1 of zinc nitrate or 100 mg·L−1 of zinc sulfate or 100 mg·L−1 of EDTA-Zn could be used for foliar spraying of zinc fertilizers in pecans. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 30 ref.]
Effects of nitrogen addition on decomposition and nutrient release of Cinnamomum migao litter leaves
2020, 37(6): 1080-1087.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200106
Abstract:
Objective This research aims to examine the effects of different nitrogen application levels on nutrient decomposition of Cinnamomum migao litter leaves. Method In January 2017, the litter leaves of the medicinal plant C. migao were taken as the research object. The leaves were washed, air dried and put into decomposition bags, 10.00 g each. Nitrogen treatments were designed as ck(0 g·m−2·a−1), N1(5 g·m−2·a−1), N2(15 g·m−2·a−1), and N3(30 g·m−2·a−1), and there were three repetitions for each treatment. The samples of litter leaves were collected in March, May, July, September and November, respectively. The quality and nutrient contents of the leaves were measured, and the dynamic effects of nitrogen deposition on nutrient release from the leaves were analyzed. Result At the end of litter decomposition experiment, the mass loss rate of litter leaves in all nitrogen application groups was lower than that of ck, the residue rate of litter was higher than that of ck. The difference between N2 and ck was not significant, but the difference between N2 and N3 was significant (P<0.05). The time needed for 95% decomposition of ck, N1, N2 and N3 was 2.973, 3.626, 3.285 and 3.671 a, respectively. In the leaves of all treatments, the content of C decreased and the content of total N increased first and then decreased, while the content of total P and total K was similar, which decreased at the initial stage of decomposition, then increased as a whole, and finally stabilized. The residual rates of C, total P, total K in the leaves decreased, while the residue rates of total N increased first and then decreased. The residual rate of C in each nitrogen treatment was significantly higher than that of ck (P<0.05). With the passage of time, the residue rate of N, which increased first and then decreased in ck treatment, showed an overall upward and then downward trend in each nitrogen application treatment. C/N ratio of each nitrogen application group was lower than that of ck in the whole decomposition process, and there was a significant difference between the early decomposition stage and ck (P<0.05). Conclusion Nitrogen addition is not conducive to the decomposition and nutrient release of litter leaves. The more nitrogen is applied, the more obvious the inhibition of decomposition is.[Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 33 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1088-1096.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190703
Abstract:
Objective This study aimed to determine the effects of different proportions of biochar and compost from Bos grunniens waste as well as the polyacrylamide (PAM) on nutrient leaching in desertified soil. Method Experiment were conducted in the laboratory by using soil column leaching method. All of treatments were divided into two groups, with and without PAM. Additionally, each group include four treatments, Bos grunniens biochar only, Bos grunniens biochar: Bos grunniens compost equal to 1∶1, bos grunniens compost only and the control treatment. Result (1) In general, the application of biochar or compost can enhance soil nutrients, and the effect of combined application of biochar fertilizer is significantly better than that of single application of biochar or compost. (2) Compared with the control group, the mixed application of biochar and compost (1∶1, w/w) with a rate of 3% of soil weight can significantly increase the soil pH and make the soil become weak alkalescent: the organic matter content increased by 530% with the addition of biochar and compost, the total nitrogen concentration increased by 255%, with the nitrate nitrogen concentration improved by 24.1% and the total and available phosphorus contents increased by 120% and 78% respectively, with no significant impact on the ammonium nitrogen content, though. (3) The addition of PAM can effectively reduce the leaching loss of exogenous nutrients with the total nitrogen leaching rate decreased by 9.6% in the presence of biochar and compost and the total phosphorus decreased by 7.1%. Conclusion The application of biochar and compost products with the addition of PAM can effectively increase the soil nutrient content while reducing nutrient seepage. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 38 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1097-1104.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200117
Abstract:
Objective As a factor affecting photosynthesis, light quality can influence the accumulation of secondary metabolites in plants. Cyclocarya paliurus is a medicinal and edible multifunctional plant unique to China, and the active substances (such as triterpenoids) in its leaves can promote and improve human health. The objective of this study is to investigate the effects of light quality on biomass and the accumulation of triterpenoids in C. paliurus leaves from different families to provide reference for environmental selection during the seedling stages and further development of health care products. Method Taking 1-year-old seedlings of C. paliurus as materials, four families (Muchuan 31, Anji 1, Jinzhongshan 6, Jinzhongshan 7) and four different light qualities (white light, blue light, green light and red light) were selected to examine the effects of different treatments on biomass, leaf triterpenoid content and yield per plant. Result Light quality and genetic factors had significant effects on biomass, triterpenoid content and yield in C. paliurus leaves (P<0.05). Compared with white light treatment, other light quality treatments significantly reduced total biomass accumulation of C. paliurus (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference between blue light treatment and white light treatment in Anji 1 family(P>0.05). The total triterpenoid content in C. paliurus leaves was the highest under white light treatment in Anji 1 and Muchuan 31 families, followed by blue light. Red light treatment significantly increased the content of unique triterpenoid individuals in C. paliurus leaves(P<0.05). Under white light treatment, the plants with higher level of leaf biomass accumulated more triterpenoids than those under blue and green light treatments. Conclusion Proper light quality treatment can be used to increase the contents of target compounds (e.g. triterpenoids) in medicinal plants. [Ch, 1 fig. 8 tab. 27 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1105-1111.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190722
Abstract:
Objective With succinic acid of fatty acids, cinnamic acid and vanillic acid sdanders of phenolic acids, three allelochemicals extracted from Pontederia cordata rhizomes used both alone and jointly. Method This paper is aimed at an investigation of the effects of organic acids on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Result (1) The growth of M. aeruginosa could be inhibited by succinic acid, cinnamic acid and vanillic acid either solely or jointly, with 92.78% as the inhibition rate achieved with the employment of 100 mg·L−1 succinic acid and cinnamic acid for seven days; (2) when used alone, cinnamic acid demonstrates the strongest inhibition ability with succinic acid and vanillic acid following behind, yet when used jointly, the inhibition ability weakens in the following order: succinic acid + cinnamic acid > cinnamic acid + vanillic acid > succinic acid + cinnamic acid + vanillic acid with vanillic acid weakening the inhibition effect of succinic acid and cinnamic acid on the growth of M. aeruginosa to a certain degree; (3) when succinic acid was combined with phenolic acid (cinnamic acid or vanillic acid), cinnamic acid was combined with vanillic acid or the three organic acids combined, their inhibition effect on M. aeruginosa was enhanced; (4) the combination of fatty acid and phenol acidification either in the same kind or among different kinds can enhance the effect of algal inhibition. Conclusion The three allelochemicals extracted from the rhizome of P. cordata might have good algae inhibition effect and the combined action of various allelochemicals might be the main mechanism of P. cordata inhibiting cyanobacteria bloom. Therefore, succinic acid, cinnamic acid and vanillic acid have the potential to be developed as algal inhibitors. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 26 ref.]
Preparation of magnetic sodium alginate composite gel balls and their adsorption properties for Pb2+
2020, 37(6): 1112-1119.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190751
Abstract:
Objective Magnetic gel balls are new adsorbents which can efficiently remove pollutants and can be reused. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare a new type of magnetic gel ball. Method Magnetic particles (MNP) prepared by the ion co-precipitation method were used as carries for silanization reaction to synthesize magnetic nanoparticles (AM) with amino terminals. A novel magnetic composite gel ball (SA@AM) containing amino, hydroxyl and carboxyl multifunctional groups was prepared by coating sodium alginate (SA) on the surface of magnetic particles with electrostatic effect. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), elemental analyzer, X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning/transmission electron microscope (SEM/TEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) were used to characterize the product, and the adsorption properties of the products for heavy metal ions were studied. Result The target functional composite gel ball (SA@AM) successfully prepared was of paramagnetic magnetite crystal type, and the size of the SA@AM gel ball was 1.5−2.0 mm. The magnetization values of MNP, AM, SA@AM were 13.8, 13.4, and 6.85 A·m2·kg−1, respectively. Adsorption experiments showed that the maximum adsorption capacity of heavy metal Pb2+ by SA@AM was 105.82 mg·g−1, and the adsorption mechanism was more in line with the Langmuir isothermal adsorption model. Repeated adsorption-desorption experiments showed that the removal rate of Pb2+ by SA@AM was more than 76%. Conclusion The new sodium alginate magnetic composite gel ball has excellent adsorption capacity for heavy metal ions Pb2+, and the magnetic gel ball has good regeneration properties. [Ch, 10 fig. 1 tab. 25 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1120-1127.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190676
Abstract:
Objective With the phenotypic diversity of male Torreya grandis populations explored and superior male individuals initially screened, this paper is aimed to provide a reference for the scientific configuration of superior pollinator trees so as to improve the actual yield and quality of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’. Method With 121 single plants selected from 5 natural male populations in T. grandis, an analysis was conducted of 10 phenotypic traits including single leaf weight, leaf shape index, weight of single male cone, cone shape index, percentage of pollen yield and pollen vitality, etc to study variation in phenotype, based on which superior male individuals were selected. Result (1) There were no significant differences (P>0.05) between populations in all the traits except leaf length and percentage of pollen yield (P<0.05), but there were significant differences in all 10 traits among individuals within each population, indicating that variation within a population is the main sources of phenotypic variation in male T. grandis and larger than that among populations, which means that artificial selection should be based on the selection of individuals. (2) Among the 10 phenotypic traits, coefficients of variation for male cones were larger than those for leaves with 42.36% and 34.13% as the coefficient of variation for the pollen vitality and pollen yield respectively, which indicates that the selection of superior male individuals should be based on the traits of male cones. (3) 36 superior early, interim and late flowering individuals were screened out according to traits of male cones, which could be used as reference for breeding and plantation in the future. Conclusion The phenotypic traits of male T. grandis demonstrate more significant genetic diversity within the populations, and the focus should be laid on the choice of superior individuals within populations in the attempt at the establishment of later genetic improvement strategy of T. grandis while cone shape index, percentage of pollen yield, pollen vitality are important phenotypic indexes for the primary selection of superior individual. [Ch, 1 fig. 7 tab. 26 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1128-1135.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190661
Abstract:
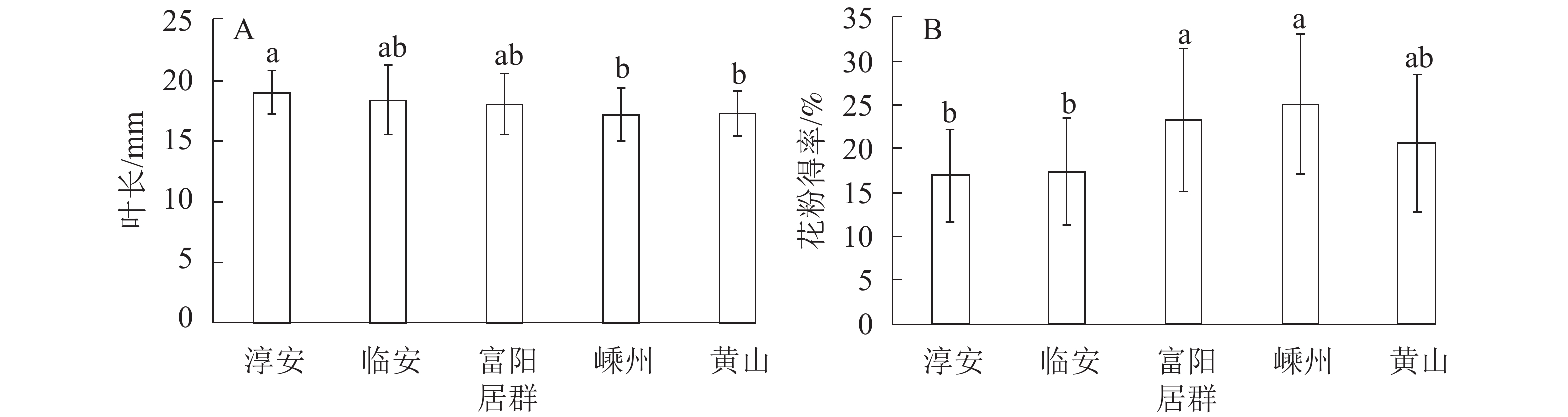
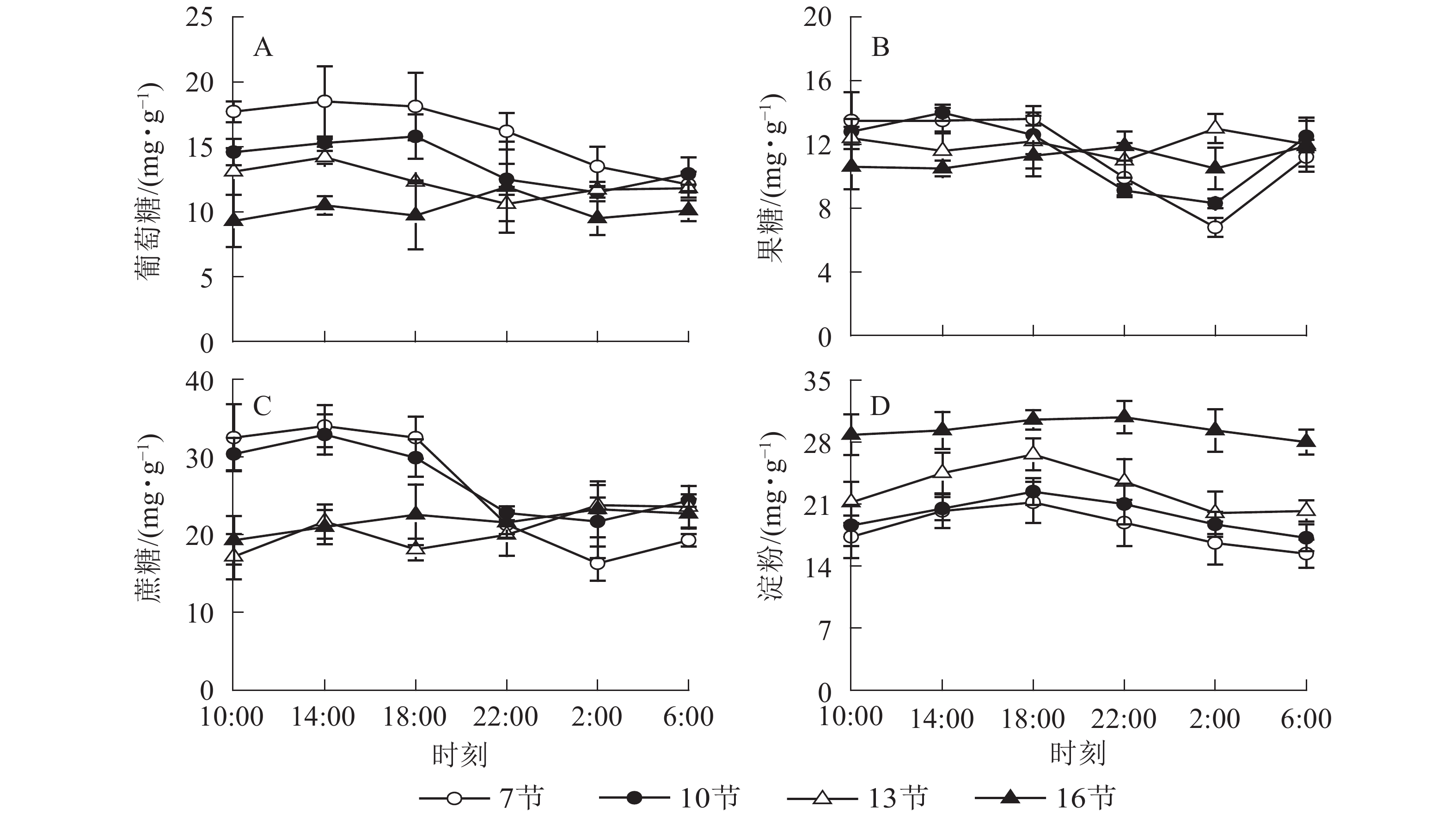
Objective The aim of this study is to reveal the regulating mechanism alpha amylase (AMY) and beta amylase (BAM) and related gene expression of Phyllostachys edulis in the rapid growth period. Method The stems of Ph. edulis shoots were used as materials, and the content of non-structural carbohydrates (NSC), AMY and BAM activity, and gene expression of PeAMY and PeBAM were measured at different time (10:00, 14:00, 18:00, 22:00, 2:00, 6:00) and different internodes (7, 10, 13, 16). Result The NSC content of bamboo stems was higher in the daytime, and gradually decreased after 18:00. At 2:00, the glucose content in the 7th and 10th internodes decreased by 25.4% and 27.2% (P<0.01), fructose by 50.0% and 34.1%, respectively (P<0.01), sucrose by 49.8% and 27.4%, respectively (P<0.01). Starch content at 6:00 decreased by 27.3% and 23.2%, respectively (P<0.01). The activity and gene expression of BAM were stable in the daytime, increased significantly after 18:00, and gradually decreased before dawn. BAM activity of the 7th, 10th and 13th internodes was 90.5%, 76.7% and 50.5% higher at 22:00 than at 18:00 (P<0.01). The PeBAM gene expression was 1.8, 1.8 and 1.7 times higher at 2:00 than at 18:00 (P<0.01). Conclusion During the period of rapid growth, the stem of Ph. edulis grows slowly in the daytime and quickly at night. The development and maturation of stems are promoted from bottom to top. The rapid growth of Ph. edulis is closely related to the expression of PeBAM gene. BAM may play a key role in starch degradation. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 38 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1136-1142.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190742
Abstract:
Objective The objective of this study is to explore the molecular evolution characteristics of P gene of peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) during an epidemic in China. Method Bioinformatics analysis on the sequences of P gene of PPRV strains from 37 epidemic sites in 21 provinces of China from 2013 to 2017 was carried out. Result The genetic distances among the nucleotide sequences of P gene of 37 strains was 0−0.0092, and the variation sites were distributed in 47 sites. The genetic distances among the amino acid sequences of P gene of these strains ranged from 0−0.0079, and the variation sites were distributed in 26 sites. Sequence comparison with 15 representative strains showed that nucleotide sequence mutations occurred at 10 sites of P gene of 37 PPRV epidemic strains in China since 2013, and 3 of them led to the change of amino acid sequence. Phylogenetic analysis of P gene using maximum likelihood method revealed that all the 37 PPRV strains prevalent in China from 2013 to 2017 could be grouped into an independent clade in lineageⅣ, different from the strain introduced into Tibet in 2007. Conclusion From 2013 to 2017, the P gene mutation of peste des petits ruminants virus in China was relatively large. With the increase of epidemic time, the mutation sites of P gene increased, but the mutation sites of different strains were different, showing a relatively random mutation. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 12 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1143-1148.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190723
Abstract:
Objective To further the relationship of Ceracris kiangsu with their host plants, an investigation was conducted of its feeding preferences and developmental status when living on three different host plants. Method The grid area calculation method was employed to determine the feeding selectivity of bamboo locust of different ages and observation was made of the effects of three different host plants on the body weight, body length, pre-laying period, spawning volume and survival rate of C. kiangsu. Result The feeding preference of host plants of C. kiangsu changes as its age accumulates; the average feeding area of first-instar nymphs was Zea mays (474.67 mm2±66.03 mm2)>Phyllostachys edulis (179.33 mm2±41.38 mm2)>Miscanthus sinensis (76.00 mm2±42.11 mm2) while the feeding area of the nymphs from the second to the fifth instar on M. sinensis was significantly larger than that on the other two host plants(P<0.05). The weight growth of different host plants was Z. mays (0.301 g±0.015 g)>M. sinensis (0.295 g±0.022 g)>Ph. edulis(0.229 g±0.027 g) whereas the length growth of different host plants was M. sinensis (25.120 mm±0.682 mm)>Z. mays (24.860 mm±1.436 mm)>Ph. edulis (22.910 mm±2.914 mm). When breeding on different host plants, C. kiangsu demonstrates significant differences in the pre-spawing period of the adults(P<0.05) and the average pre-spawning period of the three populations was M. sinensis (55.4 d± 6.9 d)>Ph. edulis (41.7 d±2.2 d)>Z. mays (41.2 d±3.7 d), and the pre-spawning period of the population feeding on M. sinensis was significantly longer than that of those feeding on the other two plants(P<0.05). The population of spawn per female was significantly different after feeding on different host plants, and the result was Ph. edulis (122.00 seeds±6.08 seeds)>Z. mays (121.00 seeds±12.70 seeds)>M. sinensis (21.00 seeds±2.89 seeds), yet there was no significant difference in the survival rate of C. kiangsu feeding on different host plants(P>0.05) with the survival rates as follows: Ph. edulis(88.33%±1.70%)>M. sinensis (86.67%±1.66%)>Z. mays (83.33%±1.60%). Conclusion With the difficulty of obtaining the host plants and the weight growth, body length calculation and reproductive capacity of C. kiangsu taken into consideration, corn leaves, compared with other two host plants which are not easy to obtain in large quantities, can be planted in large quantities, thus making the most suitable food source for artificial breeding of C. kiangsu. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 17 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1149-1158.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190738
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the electroantennogram and behavioral responses of Agrilus mali to the volatiles from Malus sieversii trees in different damaged states to provide reference for the research and development of highly effective attractants. Method The volatiles were collected by using dynamic headspace adsorption from branches and limbs of M. sieversii trees. Result There are total of 46 volatile compounds in 9 categories has been obtained, including alcohols, lipids, aldehydes, alkanes, alkenes, ketones, terpenes, ethers and others. Compared with healthy branches, the relative contents of eicosane and pentadecane increased in A. mali damaged branches, while the relative contents of 8 volatiles such as butenol, 2-methylacrolein, heptadecane, heneicosane, cycloheptatriene, cyclohexanone, α-pinene and chamomile decreased. Fourteen compounds were added such as cis-3-hexenol, hexanal, decanal, nonanal, (+)-limonene etc. In Valsa mali damaged branches, pentadecane, heptadecane, 3,7-dimethyldecane, eicosane and α-pinene increased, and heneicosane, cyclohexanone, cycloheptatriene, azulene decreased. Twelve compounds were added such as cis-3-hexenol, butyl butyrate, hexanal, (+)-α-pinene, (+)-limonene, etc. Compared with the volatilides released from healthy limbs, the relative contents of cis-3-hexenol, α-pinene, (−)-α-pinene and camphene were increased in A. mali damaged limbs, and hexanal, cycloheptane, β-pinene, cycloheptatriene, azulene contents decreased. Seventeen compounds were added such as 3-octene-2-alcohol, butyl butyrate, decanal pentadecane, (+)-aromadendrene, etc. In Valsa mali damaged limbs, hexanal increased, and cis-3-hexenol, acrolein, cyclohexanone, α-pinene, (−)-α-pinene, β-pinene and azulene decreased. Eleven compounds were added such as benzaldehyde, pentadecane, dipentene, etc. EAG responses and behaviour of A. mali towards volatiles released by host were tested. The results showed that strong EAG reactants could be produced in the antennae of male and female adults of A. mali, these compounds were (−)-α-pinene, nonanal, (+)-α-pinene, benzaldehyde, decanal, butyl acrylate. A. mali were attracted by (−)-α-pinene, α-pinene, (+)-β-pinene, β-pinene, decanal, nonanal in the behavior bioassay. Conclusion According to the results of EAG responses and behavioral orientation, the (−)-a-pinene, nonanal and decanal had good attraction to the adult of Agrilus mali.[Ch, 1 fig. 3 tab. 27 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1159-1166.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190752
Abstract:
Objective In view of the inconspicuous characteristics of poplar(Populus) scab and mosaic disease, this paper is aimed to propose a method to improve the disease recognition accuracy by means of the pre-treatment of the original image set. Method Firstly, the contour of the blade was extracted employing the improved Canny operator edge detection method combined with Hoss Transformation so as to remove the disturbance of the image background. After that, the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization was adopted to reduce the impact of local illumination unevenness. Thirdly, the OTSU segmentation algorithm with adaptive threshold was used to extract leaf lesion images. At last, the binarized images with lesion and the leaf lesion images were fed into the Alexnet which consists of 5 convolutional layers, 3 full-connection layers, 650 000 neurons and over 60 million learning parameters. Result Both groups came back with a significantly higher recognition accuracy rate than that of the the original image experiment group (93.56% and 98.05% VS 88.77%). The hybrid method proposed in this paper could help completely extract the images of the main body of the blade with different backgrounds and effectively avoid the background interference of the target blade. And the adaptive histogram equalization algorithm with limited contrast helped in dealing with the uneven light produced by natural environment and reducing the interference of reflective factors like reflected light. Conclusion The pre-treatment of the images of the above-mentioned diseases has significantly improved the recognition accuracy, and is highly recommended in future tasks. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 22 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1167-1176.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190737
Abstract:
Objective The investigation of biological resources is the basis of the management and protection in nature reserve. The objective of this study is to investigate and analyze bird resources in Jiulongshan National Nature Reserve and provide scientific basis for the protection and restoration of birds. Method The bird community in the research area was investigated and analyzed by integrating historical data, special bird survey and infrared camera survey. Result A total of 165 species were recorded, belonging to 15 orders and 49 families, among which resident birds had the highest proportion(56.36%). The dominant species were Alcippe morrisonia and Aegithalos concinnus. There were 37 species in need of special protection, among which there were 2 species of national class Ⅰ protection birds (Syrmaticus ellioti and Tragopan caboti), 26 species of national class Ⅱ key protected birds, 10 species listed in IUCN Red List, and 18 species listed in the red list of vertebrates in China. There were both Palaearctic and Oriental elements in the composition of avifauna, but the Oriental realm was dominant (89 species, 53.94%). Among 121 breeding birds (i.e. the sum of resident and summer birds), the most species were Oriental (69.42%). Palaearctic species occupied the highest proportion (84.62% and 100.00% respectively) of migratory and winter birds. Conclusion Jiulongshan National Nature Reserve is rich in bird resources, accounting for more than 30.00% of bird species in Zhejiang Province. The faunal composition is dominated by the Oriental fauna, and has the characteristic of transition to the Palaearctic fauna. [Ch, 4 tab. 13 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1177-1185.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200167
Abstract:
Objective Taking phaseⅠof the greenway around Qingshan Lake National Forest Park in Zhejiang Province as an example, this study aims to evaluate quantitatively and qualitatively the landscape performance from such aspects as environment, economy and society, so as to objectively reflect the comprehensive benefits of greenway construction. Method Corresponding evaluation index system was established. Ecological and economic methods were used for environmental performance evaluation. Market value method was used for economic performance evaluation, and post occupancy evaluation and questionnaire survey were used for social performance evaluation. Result The economic value of the environmental performance of the greenway was about 3 984 400 Yuan·a−1, of which the value of regulating the temperature and water conservation accounted for 74% and 18% respectively. In terms of economic performance, about 900 800 Yuan construction cost was saved. After the completion of the greenway, it provided new jobs, stimulated the development of tourism, and had a positive impact on the value of nearby real estate. In terms of social performance, the construction of the greenway improved the image of the city, reflected the history and culture of Lin’an District of Hangzhou City, enhanced people’s participation in outdoor activities, and changed people’s lifestyle to a certain extent. Most people visited the greenway because of the beautiful natural environment. More than half of the respondents said they had a deeper understanding of sustainable design. Conclusion Through quantitative and qualitative analysis and evaluation of the comprehensive value of waterfront greenway landscape performance, the comprehensive benefits of greenway construction can be presented objectively and clearly. [Ch, 9 tab. 35 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1186-1192.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190720
Abstract:
Objective With an analysis of the genetic variation of wood basic density and fiber morphology of Pinus massoniana among seed sources and clones within seed sources, this paper is aimed to provide high quality genetic material for the breeding and improvement of P. massoniana. Method Fifty clones from five seed sources of P. massoniana clones selected from 34-year-old experimental forests of different seed sources in Laoshan Forest Farm, Chun’an County, Zhejiang Province, were investigated to determine the wood basic density, fiber length, fiber width and fiber length-width ratio. Then variance analysis, correlation analysis and genetic parameter estimation were conducted to reveal the genetic variation while superior individuals were selected from the 50 P. massoniana with the employment of Independent Selection Standard Method. Result The results of ANOVA revealed that there were significant or extremely significant differences in the basic density and fiber morphology of the wood among seed sources and clones within seed sources. The variation of clones within seed sources with the variance components ranging from 19.37% to 28.26% was the main source of wood basic density, fiber length and fiber length-width ratio. The variation of seed sources with the variance components (45.57%) was the main source of fiber width. There is a significant phenotypic and genetic negative correlation between basic densities of wood and fiber length and fiber length/width, but the correlation coefficient is not high and the basic densities of wood is not related to fiber width. The fiber morphological indexes showed significant positive genetic correlation in the juvenile age and mature age, while the wood basic density showed no significant correlation in the juvenile age and mature age. A total of 12 clones of P. massoniana with excellent wood properties were selected. Conclusion More attention should be paid to the selection of superior trees within seed sources in the attempt to improve the three traits of wood basic density, fiber length and fiber length-width ratio. On the other hand, the fiber width can be better improved through the choice of seed sources. In view of the significant correlation of fiber morphology indexes between juvenile and mature timber, they can be selected as reference indexes in the early stage. [Ch, 4 tab. 25 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1193-1199.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190709
Abstract:
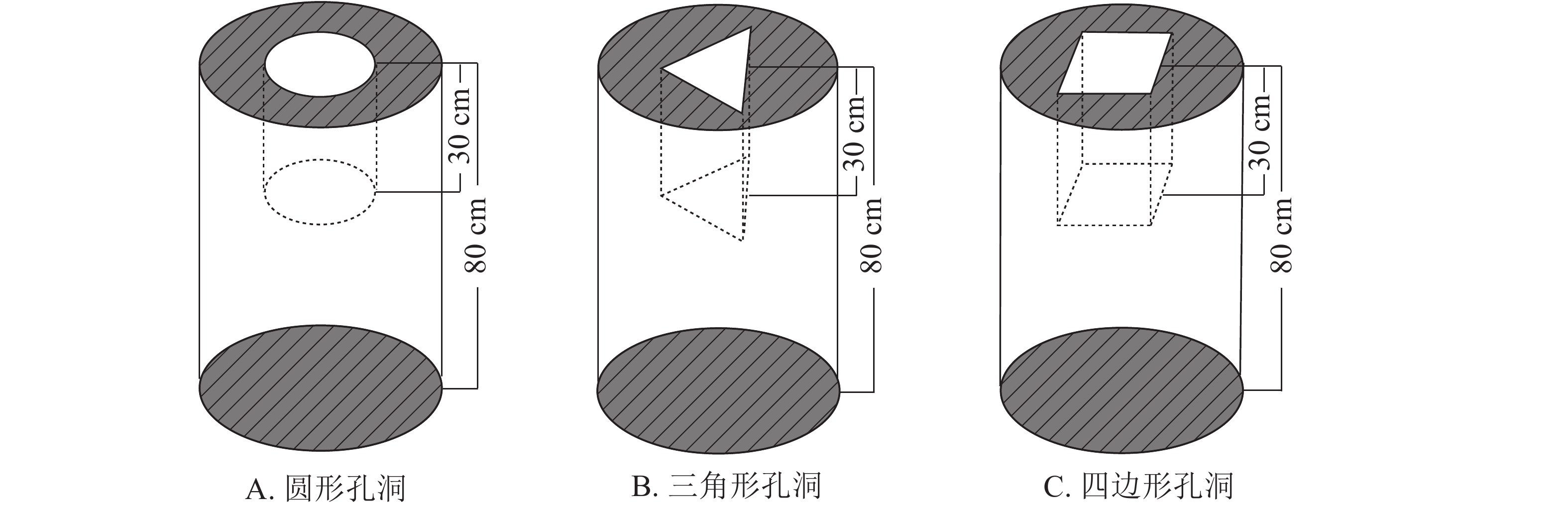
Objective The objective of this study is to realize the rapid recognition and quantitative characterization of the internal cavities in wood by evaluating the accuracy and precision of the cavity imaging under radar detection method. Method Pinus massoniana and Cunninghamia lanceolata, commonly used in ancient building timber structure, were taken as the research object. Artificial simulation was used to make special-shaped cavities at the end of the logs to simulate the internal damages, and then the radar scanner was used to detect the cavities. The differences between the visual imaging technology and the processing methods such as the Hilbert integral method, single path data extraction and synthesis, and the multi-parameter correction of the image contour were compared and analyzed. The calculation and feasible correction method of wood internal cavity area based on radar detection was proposed. Result The internal cavity of P. massoniana and C. lanceolata wood could be recognized rapidly by the radar nondestructive testing technology, but the visual imaging technology had a large error in quantitative evaluation, which required further relevant data processing and correction. The estimated cavity area of the unmodified radar image was smaller than that of the actual one. There was still a certain error between the actual cavity area and the estimated cavity area of the radar image calculated by Hilbert integral method or modified by dielectric constant. The distance between the wood edge and the cavity edge should be corrected according to the formula s3c=(sr−a)k1k2, that was to say, the dielectric constant obtained by tree species and moisture content in practical application was only one factor in the multi-parameter correction. Therefore, it was difficult for radar scanner to accurately recognize the specific shape of the cavity, regardless of data processing and correction, and further research should be carried out. Conclusion The radar detection and correction technology can be applied to the detection of cavities in wood and the error of cavity area identification can be less than 30% by integrating tree species and moisture content values. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 17 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1200-1206.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190672
Abstract:
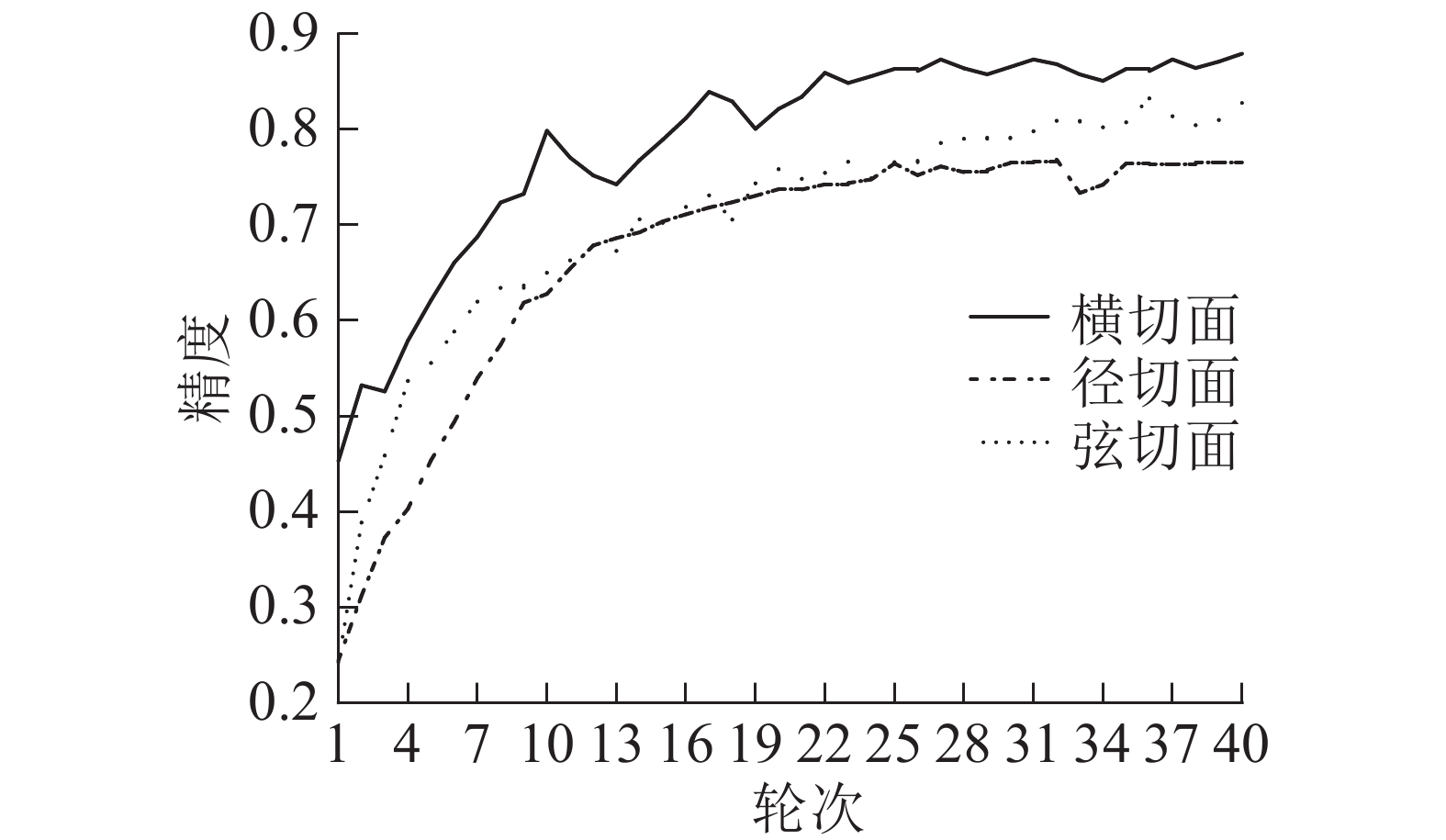
Objective Due to the differences in growth cycles and wood characteristics, the market price of rosewood species including some nationally protected species varies sharply. To prevent fraud and better protect tree species, this paper is aimed at the accurate identification of rosewood species. Method With 376 samples of 7 species of rosewood collected in the actual test by the National Forestry and Grassland Administration Center for Quality Supervision and Testing of Wood and Bamboo Products (Kunming) selected as the research subject, a convolutional neural network model for automatic recognition of redwood is proposed using the computer algorithm to expand the number of samples. Result This method can automatically identify features that fit with the model of classification and recognition, making it more convenient to utilize. Compared with traditional methods, it secures a more accurate identification with an average identification accuracy of 99.4%. Conclusion The self-built convolutional neural network can effectively identify redwood species. Although it takes a long time to achieve the parameter adjustment and train than VGG16 and other transfer learning methods, it shows stronger competence of generalization. It is proved that the self-built model is superior to the transfer learning model when applied in rosewood recognition. [Ch, 7 fig. 4 tab. 23 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1207-1215.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190745
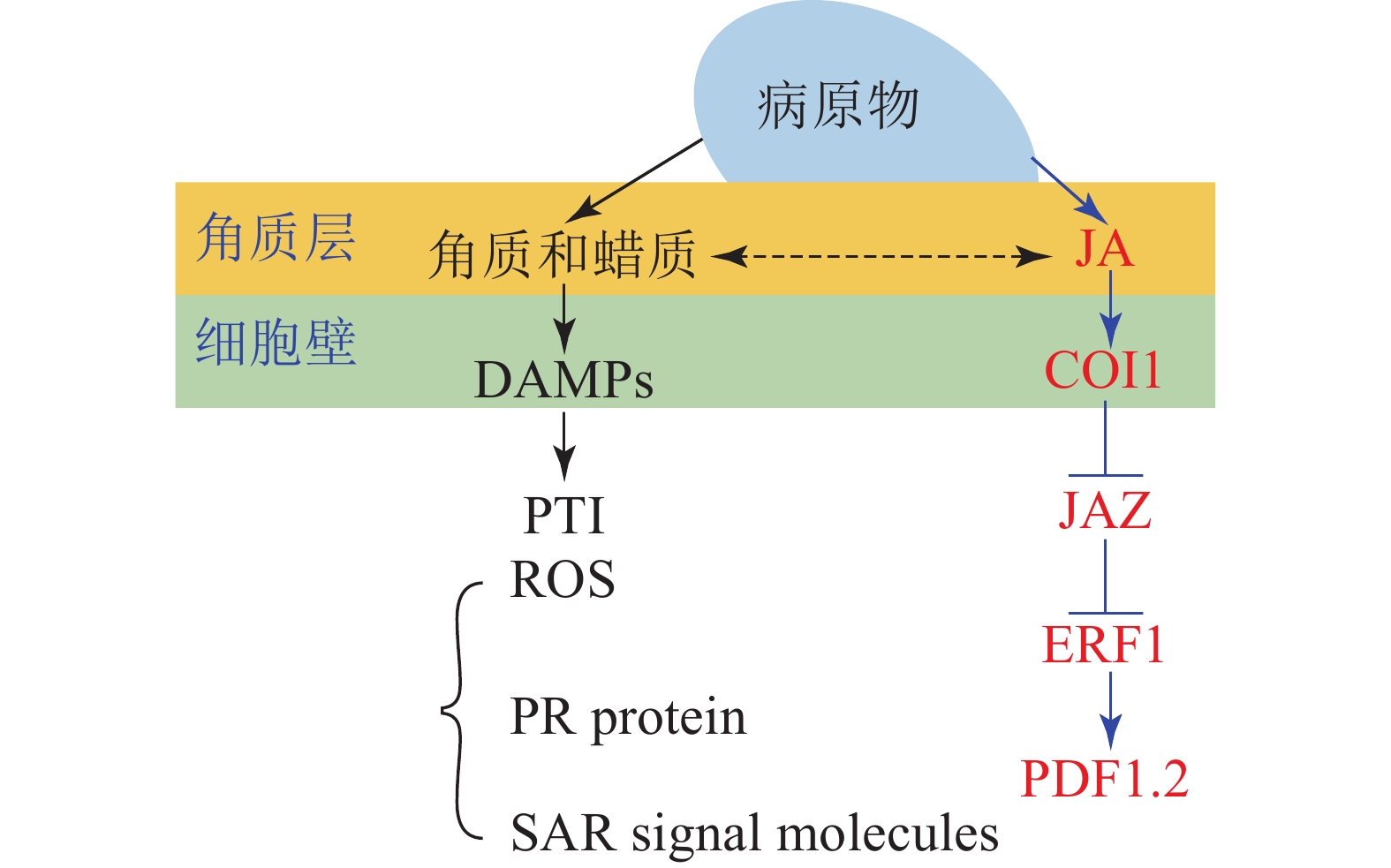
Abstract:
As a type of secondary metabolites produced by plants during long-term ecological adaptation, cutin and wax are widely involved in many resistance physiological processes including stress defense and resistance to pests and diseases, playing critical roles in the plant-pathogen interaction, thus becoming an important part of plant disease resistance mechanism. With the development of molecular biology, there is an increasing understanding on the cutin and wax metabolism and their mechanisms against fungal disease in plant. With prior researches mainly focused on the constitutive resistance and inducible resistance of plant cutin and wax, the present study, with a review of the research progress achieved on the plant cutin and wax biosynthesis and its disease resistance mechanism, is aimed to put forward prospects for future research. It was concluded that (1) as the main components of the cuticle, the first line of defense for plants against pathogen infection, cutin and wax play a critical role in physical resistance (physical barrier) and chemical resistance (bacteriostasis) as constitutive resistance components, (2) They can also play the role of inducible resistance components and (3) in addition to being the main component of the cuticle to exert physical resistance, the inducible cutin and wax component can also act as a signal molecule or inducer to activate downstream resistance reactions and exert its chemical resistance function. In the future, the research concerning cutin and wax can be focused on an in-depth explanation of the mechanism of cutin and wax inducible resistance, so as to further enrich the theoretical system of plant chemical ecology. In addition, cutin and wax biopesticides (plant immunity inducers) can be developed based on the inducible resistance of cutin and wax to provide new insight for the plant diseases control. [Ch, 1 fig. 71 ref.]
As a type of secondary metabolites produced by plants during long-term ecological adaptation, cutin and wax are widely involved in many resistance physiological processes including stress defense and resistance to pests and diseases, playing critical roles in the plant-pathogen interaction, thus becoming an important part of plant disease resistance mechanism. With the development of molecular biology, there is an increasing understanding on the cutin and wax metabolism and their mechanisms against fungal disease in plant. With prior researches mainly focused on the constitutive resistance and inducible resistance of plant cutin and wax, the present study, with a review of the research progress achieved on the plant cutin and wax biosynthesis and its disease resistance mechanism, is aimed to put forward prospects for future research. It was concluded that (1) as the main components of the cuticle, the first line of defense for plants against pathogen infection, cutin and wax play a critical role in physical resistance (physical barrier) and chemical resistance (bacteriostasis) as constitutive resistance components, (2) They can also play the role of inducible resistance components and (3) in addition to being the main component of the cuticle to exert physical resistance, the inducible cutin and wax component can also act as a signal molecule or inducer to activate downstream resistance reactions and exert its chemical resistance function. In the future, the research concerning cutin and wax can be focused on an in-depth explanation of the mechanism of cutin and wax inducible resistance, so as to further enrich the theoretical system of plant chemical ecology. In addition, cutin and wax biopesticides (plant immunity inducers) can be developed based on the inducible resistance of cutin and wax to provide new insight for the plant diseases control. [Ch, 1 fig. 71 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1216-1223.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190756
Abstract:
Cucurbitaceae is one of the important plant families in agricultural production, most of which are annual vines. The key morphological marker of Cucurbitaceae plants is tendril. This paper summarizes and analyzes the main research results on tendrils of Cucurbitaceae plants, and puts forward a prospect for future research. The present researches on tendrils of Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops mainly focus on the following aspects: (1) the origin of tendril; (2) the key gene regulating tendril development; (3) the genes specifically or highly expressed in tendrils; (4) the endogenous hormones regulating tendril development; (5) the influence of external environment on tendril development. The main conclusions are as follows: tendrils of Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops are identified as abnormal organs of lateral branches, and the key gene regulating tendril is TCP1. Tendril tissue-specific or high-level genes are mainly involved in morphological development, tropism, auxin polar transport, calcium ion transport, glutamate metabolism, lignin metabolism, which are closely related to tendril generation, development and coiling. Hormone (auxin, gibberellin) and environment factors (light, temperature and water) have been reported to affect tendril development, but the specific molecular mechanism remains unknown. Future research on tendrils of Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops should focus on the analysis of the upstream and downstream gene network of TCP1
Cucurbitaceae is one of the important plant families in agricultural production, most of which are annual vines. The key morphological marker of Cucurbitaceae plants is tendril. This paper summarizes and analyzes the main research results on tendrils of Cucurbitaceae plants, and puts forward a prospect for future research. The present researches on tendrils of Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops mainly focus on the following aspects: (1) the origin of tendril; (2) the key gene regulating tendril development; (3) the genes specifically or highly expressed in tendrils; (4) the endogenous hormones regulating tendril development; (5) the influence of external environment on tendril development. The main conclusions are as follows: tendrils of Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops are identified as abnormal organs of lateral branches, and the key gene regulating tendril is TCP1. Tendril tissue-specific or high-level genes are mainly involved in morphological development, tropism, auxin polar transport, calcium ion transport, glutamate metabolism, lignin metabolism, which are closely related to tendril generation, development and coiling. Hormone (auxin, gibberellin) and environment factors (light, temperature and water) have been reported to affect tendril development, but the specific molecular mechanism remains unknown. Future research on tendrils of Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops should focus on the analysis of the upstream and downstream gene network of TCP1
2020, 37(6): 1224-1229.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200124
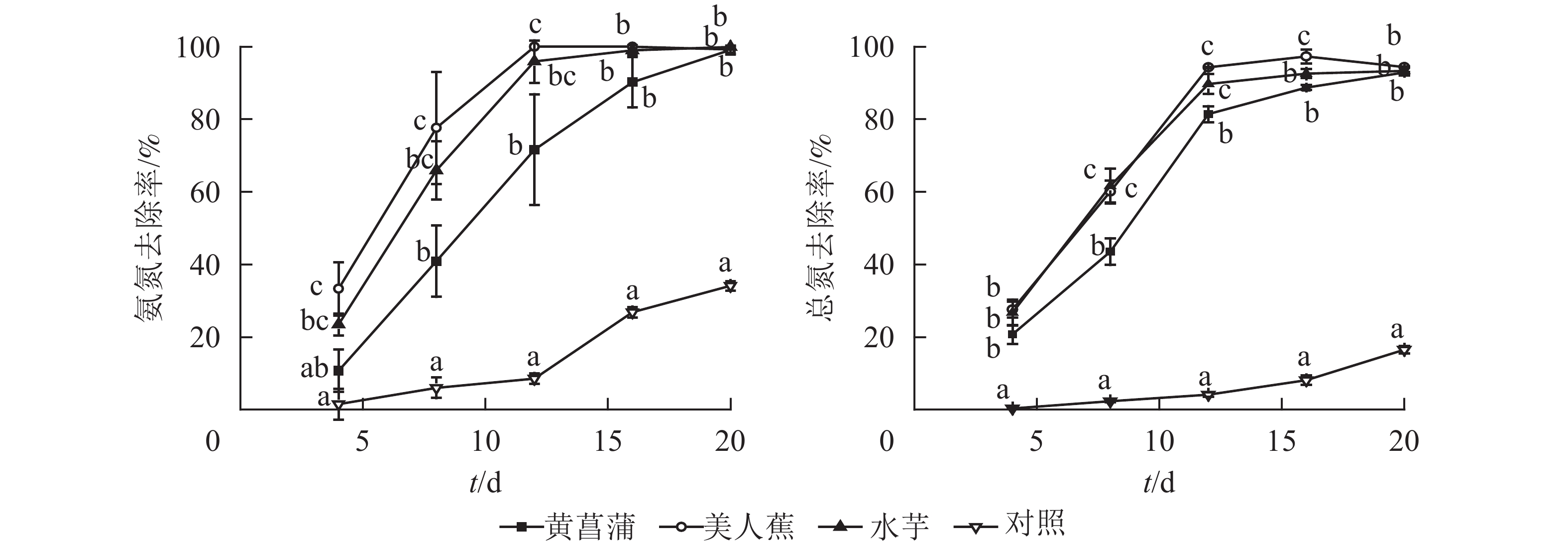
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to investigate the purification capacity for nutrients in polluted water and the yield of tuber starch of three common tuberous aquatic plants, and estimate the feasibility and potential risk of starch resource utilization. Method Purification efficiency of Iris pseudacorus, Canna indica and Calla palustris for polluted water body was compared using hydroponic experiment, and three replicates were set for each group. No plant treatment was used as control group. Removal efficiency of ammonium nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water was investigated. The contents of nitrogen and phosphorus in plant roots, stems, leaves and tubers were analyzed. The content of starch and heavy metals including Cu, Zn, Cr and Pb in plant tubers were measured. Result When initial concentrations of ammonium nitrogen and total phosphorus were 7.37−7.53 and 0.41−0.45 mg·L−1, concentrations of ammonium nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in plant treatment groups decreased to 0.01−0.07, 0.61−0.91, and 0.025−0.031 mg·L−1 respectively after 20 days of treatment, which met the Class Ⅲ standard for surface water environmental quality (GB 3838−2002). The starch extracted from tubers of I. pseudacorus, C. indica and C. palustris was 61.3, 14.1 and 64.0 g·kg−1, respectively. Starch yields of these plant species were 14.3, 1.2 and 2.6 kg·m−2 respectively in the 100 m2 trial plot. The tuber could accumulate heavy metals. As initial concentrations of Cu2+, Zn2+, Cr3+ and Pb2+ in water were 2.01−2.08, 2.56−2.87, 0.22−0.26, and 0.24−0.26 mg·L−1, the contents of Cu, Zn, Cr and Pb in tuber starch of I. pseudacorus were 10.30, 46.7, 12.03, and 1.74 mg·kg−1, respectively and those of C. indica were 12.68, 44.67, 8.15 and 1.32 mg·kg−1, respectively, while those of C. palustris were 19.28, 66.91, 9.63 and 3.97 mg·kg−1, respectively. Conclusion The three tuberous aquatic plants can effectively purify nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, and recover a considerable amount of starch. However if heavy metals coexist in the polluted water, plant tubers are not recommended for resource utilization. [Ch, 4 fig. 17 ref.]
2020, 37(6): 1230-1234.
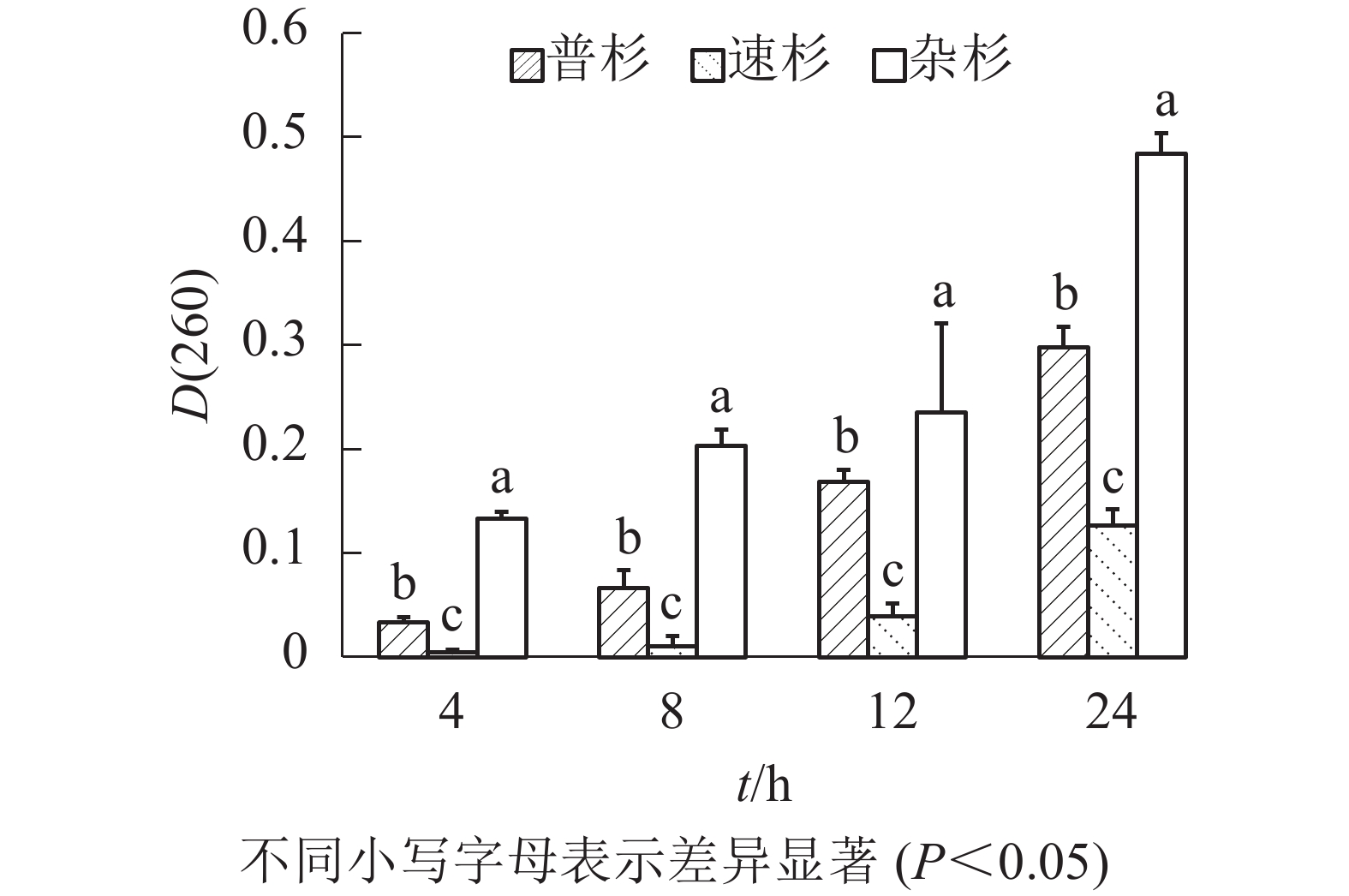
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190615
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to establish a quick and simple method for the determination of the seed vigor of Cunninghamia lanceolata. Method With the seeds selected from three different cultivars of C. lanceolata, a comparison was conducted of the accuracy and efficiency of triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) and ultraviolet spectrophotometer (UVS) methods with the standard germination test for reference. Result The standard germination test was the most accurate but most time-consuming method, which could not be performed on a large scale. TTC method was unstable and inaccurate with cumbersome operation for C. lanceolata seeds. UVS method displayed an estimated value quite close to the real germination rate and enjoyed advantages such as high reliability and simple operation. Conclusion UVS method could be taken as an efficient method for the rapid determination of seed vigor in C. lanceolata. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 21 ref.]