2022 Vol. 39, No. 6
2022, 39(6): 1155-1162.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220372
Abstract:
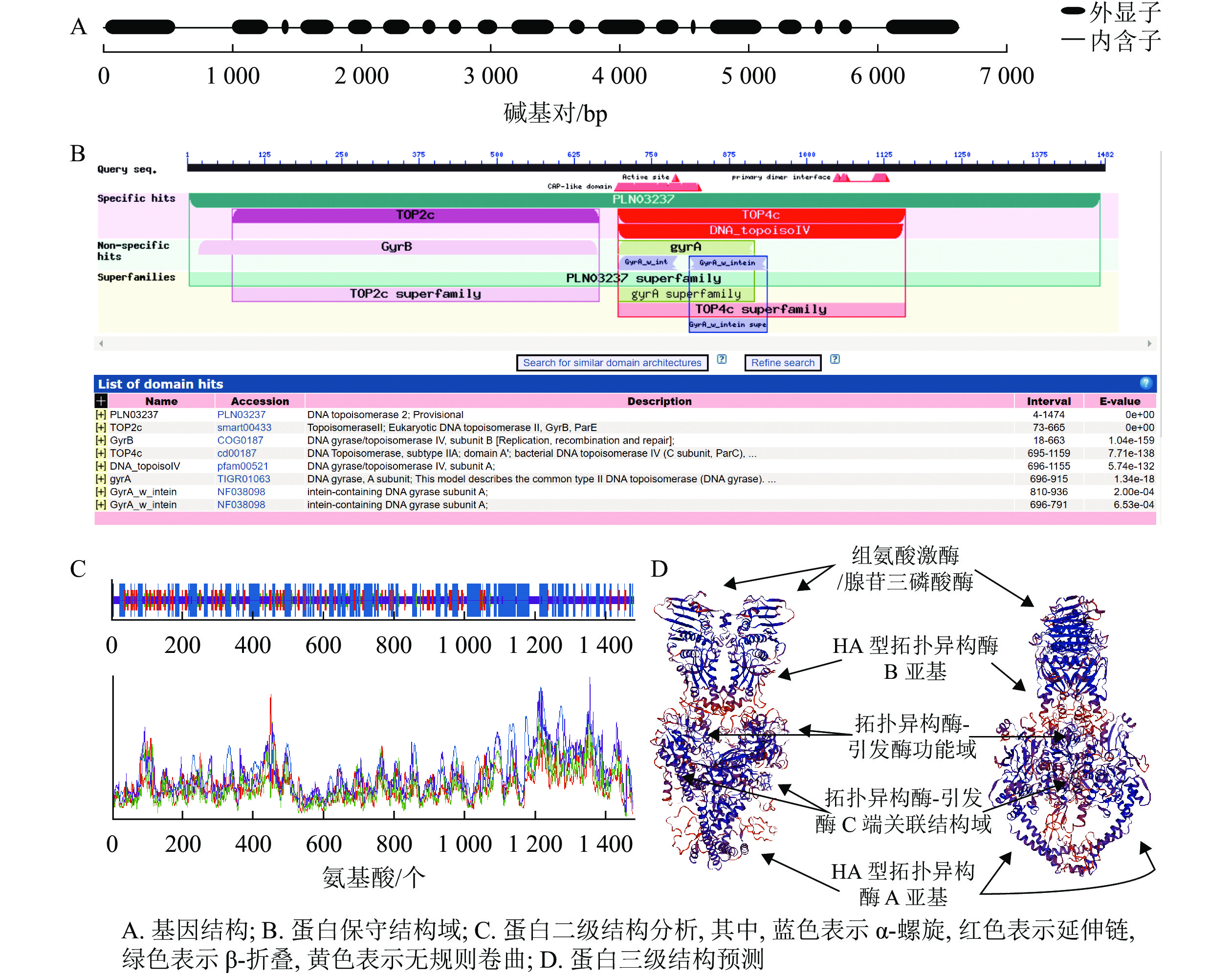
Objective DNA Topoisomerase, as a kind of enzyme that can change the topological structure of DNA, plays an important role in fundamental cellular activities such as DNA replication, transcription and mitosis, therefore, this study, with an investigtion into the effects of DNA topoisomerase genes on the growth and development of poplar, is aimed to lay a solid foundation for further understanding of the mechanism of DNA topoisomerase in woody plants and to evaluate whether it can be used as a target for molecular breeding. Method First, DNA topoisomerase gene PagTOP2b was cloned from poplar ‘84K’ (Populus alba × P. glandulosa ‘84K’) before an analysis was conducted of its sequence and the protein physicochemical properties and structure with the employment of Bioinformatic method. Then, with an exploration of the expression levels in different tissues of poplar by real-time quantitative PCR, Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated leaf disc transformation in poplar ‘84K’ was adopted to obtain PagTOP2b-overexpression transgenic plants with observations made of the effects of overexpression of PagTOP2b gene on the growth and development of plants employing a phenotypic and anatomic analysis. Result The coding sequence (CDS) length of the PagTOP2b gene cloned by using poplar ‘84K’ cDNA as the template was 4 449 bp, encoding 1 482 amino acids. According to protein domain analysis, it is classified as type ⅡA DNA topoisomerase. PagTOP2b was mainly expressed in immature and younger tissues of poplar. Overexpression of PagTOP2b gene resulted in a significant increase in height, basal internode diameter and xylem width of transgenic plants. Conclusion As an important functional enzyme involved in basic life activities, the overexpression of type ⅡA DNA topoisomerase gene PagTOP2b in poplar can significantly promote the longitudinal and radial growth in plant, thus increasing plant biomass. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1163-1172.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220387
Abstract:
Objective Salt damage, as an abiotic stress factor affecting plant growth and development, seriously threatens tree growth. Under salt stress, the level of endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants increases, resulting in oxidative stress and affecting the normal growth and development of plants. By enhancing the expression level of PRX family members and changing ROS levels, the salt tolerance ability of poplar can be enhanced, and the mechanism of PRX members involved in regulating salt stress response can be revealed. Method Poplar ‘84K’ (Populus alba × P. glandulosa ‘84K’) was used as material, and PagPRX19, a member of PRX family, was selected for cloning and construction of overexpression vector by bioinformatics analysis. Overexpressed plants were obtained by Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated leaf disk transformation. The tissue culture seedlings of non-transgenetic plants (the control) and PagPRX19 overexpressed plants growing for 45 days and the soil culture seedlings growing for 2 months were used as experimental materials for salt stress treatment. The plant phenotype was observed and the physiological indexes such as proline, malondialdehyde and electrolyte permeability were detected and analyzed. Result (1) PagPRX19 gene was cloned, overexpression vector was constructed, and transgenic positive plants were obtained. After molecular identification, 2 overexpressed lines OE#1 and OE#2 were used for further analysis. (2) Preliminary phenotypic observation showed that PagPRX19 overexpressed plants decreased in height and increased in ground diameter, compared with the control. (3) Compared with the control, the overexpressed plants showed lower leaf shrinkage and plant growth inhibition under salt stress. Tissue culture seedlings showed similar results under salt stress. (4) ROS level of transgenic plants decreased, and ROS level of leaves and roots of overexpressed plants remained lower than that of the control under salt stress. The content of proline in overexpressed plants increased, the water holding capacity of leaves increased, and the contents of malondialdehyde and electrolyte permeability were lower than those of wild type. The transgenic plants showed high salt tolerance from the physiological aspect. Conclusion Overexpression of PagPRX19 can reduce ROS level of transgenic poplar ‘84K’ plants under salt stress, alleviate oxidative stress, and enhance salt tolerance. [Ch, 11 fig. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1173-1182.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220351
Abstract:
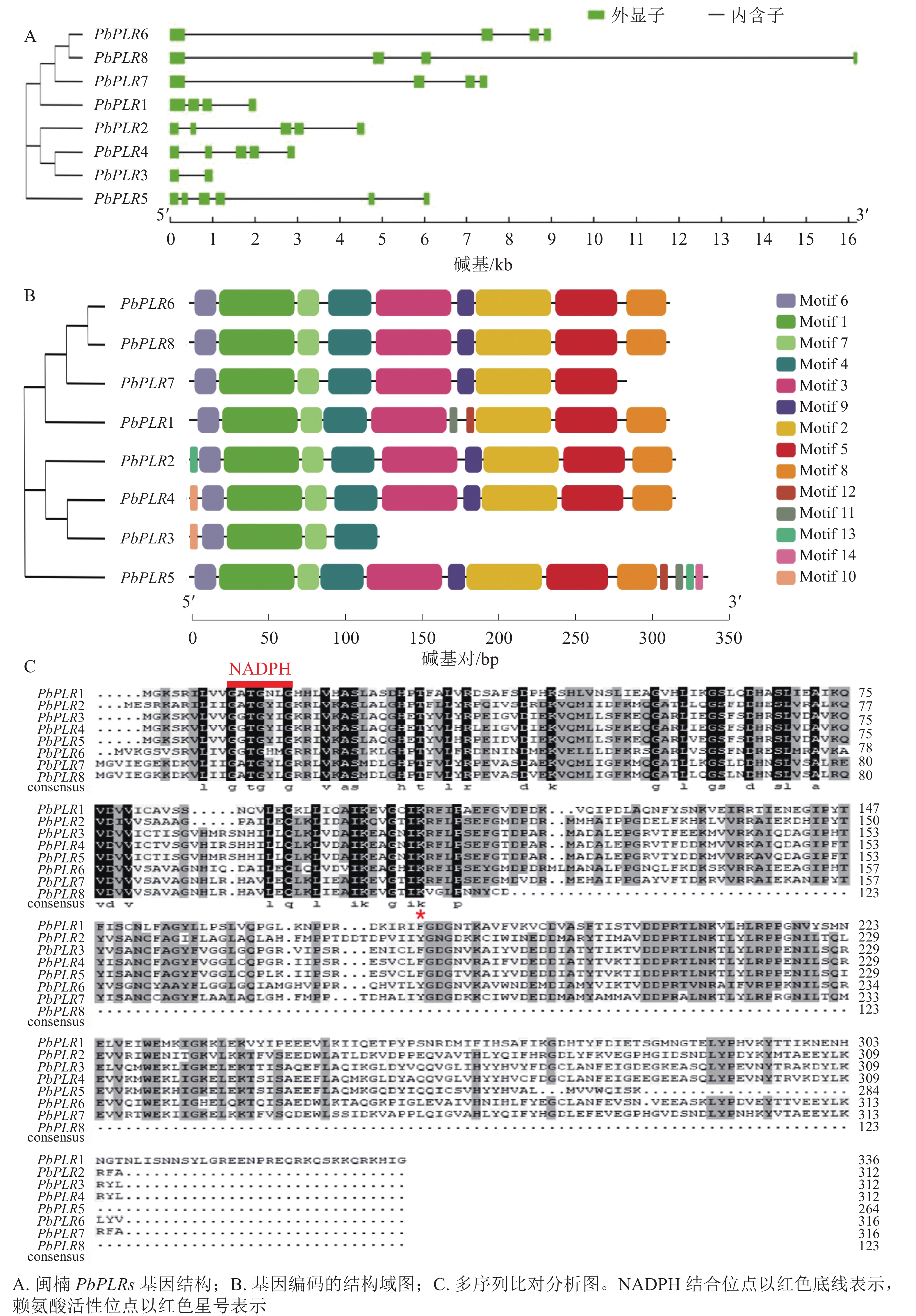
Objective Pinoresinol-laricisinol reductase (PLR) is a key enzyme gene involved in lignan biosynthesis. This study aims to clear the characteristics of PLR gene family in Phoebe bournei and the expression patterns under different hormone treatments, so as provide basis for further exploring the biological function of PLR gene family in P. bournei. Method The members of PLR gene family in P. bournei genome were identified by bioinformatics methods, and the gene structure, conserved motifs, chromosome location, phylogeny, cis acting elements of promoter and hormone response were analyzed. Result A total of 8 PLR (PbPLR) members were identified from the genome of P. bournei, which were unevenly distributed on chromosomes 1, 2, 5 and 10. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that PbPLR function may be related to substrate stereoselectivity. Promoter element analysis showed that there were hormone response elements such as bascisic acid (ABA), salicylic acid (SA), and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) in the promoter region of PbPLRs. Gene expression analysis showed that the expression of PbPLRs gene had the characteristics of tissue specificity and hormone response. The expression of PbPLRs gene was the highest in roots, followed by stems and leaves. The expression of PbPLR2 was the strongest when treated with 3 hormones. Conclusion The 8 PbPLRs gene identified from the genome of P. bournei have different gene characteristics, and different members may have different stereoselectivity of catalytic enzymes. The expression patterns of members are diverse, which may be induced by various hormones and have tissue specificity. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 25 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1183-1193.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220331
Abstract:
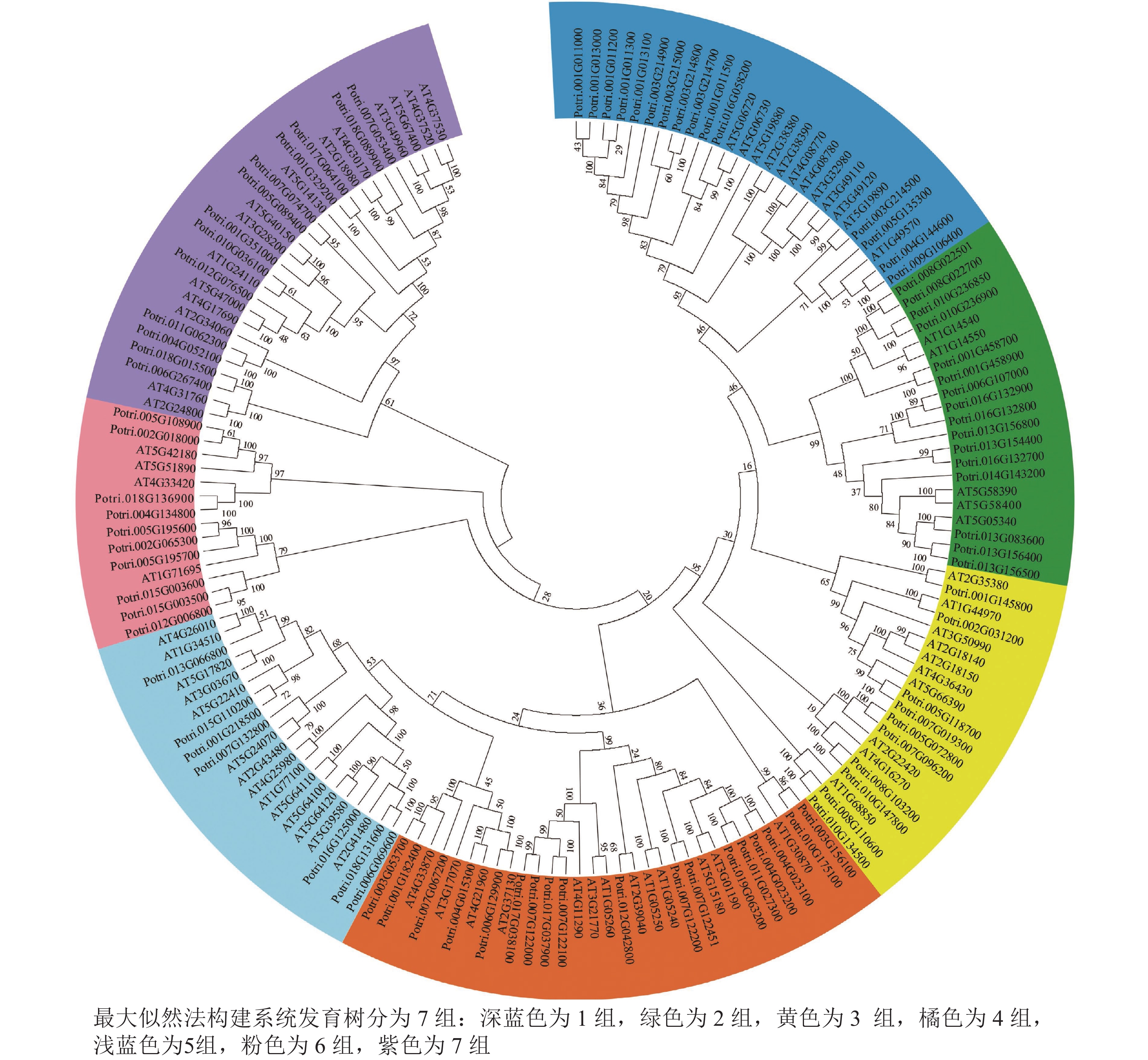
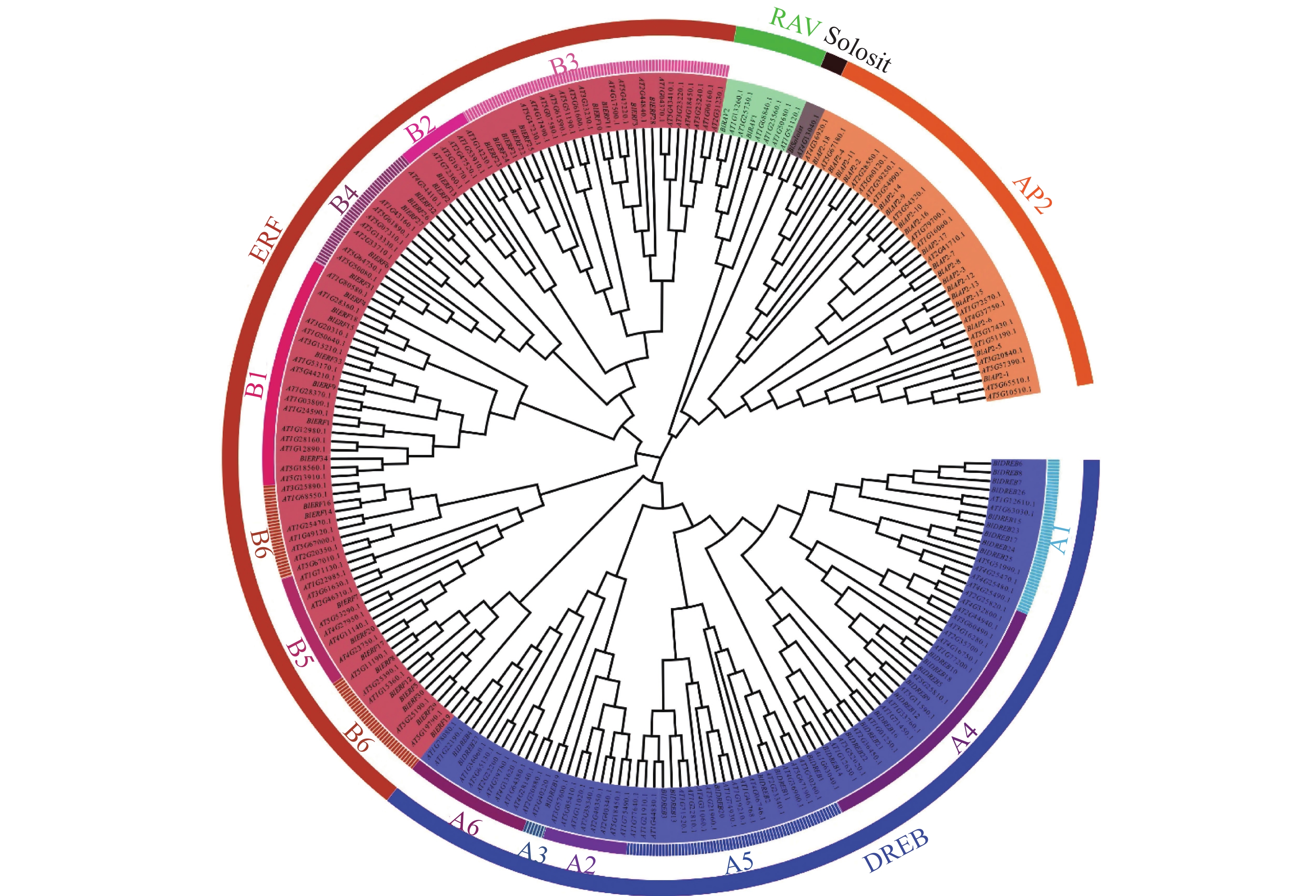
Objective This study aims to explore biological roles of AP2/ERF gene family in growth and development of Betula luminifera, and its responses to environmental stress. Method Based on the genome data of B. luminifera, AP2/ERF gene family were identified through bioinformatics method, and their gene features, phylogeny, gene structure, conserved motifs, cis-acting elements, protein interactions and expression pattern were analyzed. Result A total of 77 AP2/ERF genes were identified in the genome of B. luminifera. The physical and chemical properties of the encoded proteins were different, and the isoelectric points of most proteins (60) were less than 7.0. Phylogenetic analysis showed that these 77 AP2/ERF transcription factors belonged to 5 subfamilies, among which ERF subfamily was the largest, including 34 members. The gene structures of AP2/ERF subfamilies were quite different. The members of AP2 subfamily had 6−9 introns, while DREB subfamily gene had no introns. However, similar conserved motif types and distributions were observed in different members of AP2/ERF subfamilies. At the same time, there were a large number of cis acting elements related to hormone, regulation, stress responses, and growth and development in promoter of AP2/ERF genes. Protein interaction network analysis predicted that there were extensive interactions among different AP2/ERF subfamily proteins. Further expressions analysis showed that the expression of most AP2/ERF genes (71) had strong tissue specificity, and the expressions of most ERF or DREB genes changed significantly under heat stress, indicating that ERF and DREB genes might play an important role in the response to heat stress. Conclusion Through bioinformatics analysis, 77 AP2/ERF genes are identified in B. luminifera, which belong to 5 subfamilies. Different subfamily genes have similar gene structure and conserved motifs. The promoter region of the gene contains hormone, stress response and other related elements. Gene expression has strong tissue specificity, and most ERF and DREB genes have obvious response to heat stress. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 39 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1194-1202.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220348
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to analyze the sequence and expression characteristics of EgrCIN1 (Eucgr.B02882), a unique low temperature response gene in Eucalyptus grandis, and to explore its function in plant low temperature response, so as to enrich gene resources to cold resistance. Method Bioinformatics methods were used to analyze the characteristics of EgrCIN1 gene, protein sequence and cis-acting elements on the promoter. The expression pattern of EgrCIN1 in different tissues, at 4 ℃ in different time, under drought condition, under treatment of 300 mmol·L−1 NaCl, 100 μmol·L−1 ABA and 100 μmol·L−1 MeJA were analyzed by RT-qPCR method. Subcellular localization of EgrCIN1 was completed by transient transformation of Nicotiana tabacum with EgrCIN1::GFP vector. Besides, an overexpression vector driven by CaMV35S promoter was constructed and transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana. Three transgenic lines were obtained and treated with low temperature (−6 ℃) and ABA (0.5 μmol·L−1) to analyze the function of EgrCIN1 in response to low temperature stress. Result EgrCIN1 was a unique gene induced by low temperature in E. grandis. It did not contain introns and had no transmembrane structure. The promoter contained multiple cis acting elements related to stress response. The gene was mainly expressed in leaves and stems, but not in roots. Moreover, its expression in leaves was strongly induced by low temperature treatment. Meanwhile, abiotic stress factors such as drought, high salt and ABA could also induce EgrCIN1 expression in leaves. The encoded protein of EgrCIN1 was localized in chloroplasts. In Arabidopsis, EgrCIN1 overexpression transgenic lines were more tolerant to low temperature and more sensitive to exogenous ABA. Conclusion EgrCIN1 is expressed in chloroplasts and may participate in plant cold stress response possibly through ABA-dependent pathway to improve plant cold resistance. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1203-1211.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220145
Abstract:
Objective Based on the genome-wide expression profile of cotton seedlings under low phosphorus stress in the early stage of our research group, related genes were excavated and their preliminary expression analysis was conducted. Method Genomic DNA and cDNA sequence of the gene were cloned and analyzed by bioinformatics method. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR and fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) were used to detect the changes of gene expression in root, stem, leaf and flower tissues. The expression patterns of GhMGD3 under low phosphorus stress were analyzed by RT-qPCR technology. Result GhMGD3 gene was cloned. The coding sequence of GhMGD3 was 681 bp, encoding 226 amino acids and containing 3 introns. The molecular weight is 26 610.54 Da, isoelectric point is 8.74, it is a stable hydrophilic alkaline protein. The secondary structure is dominated by α-helix and random crimp. The protein does not have signal peptide, transmembrane domain and N-glycosylation site, but contains multiple acidification sites. Subcellular localization showed that the gene encoded a protein in chloroplast. GhMGD3 protein and Hibiscus syriacus protein amino acid sequence similarity is high, the most recent genetic relationship. The results of semi-quantitative RT-PCR and RT-qPCR showed that GhMGD3 gene was mainly expressed in root, medium expression in stem, and trace expression in leaf and flower, and its expression level reached the highest value at 72 h of low phosphorus stress. Conclusion The GhMGD3 gene was preliminarily obtained. The expression patterns of GhMGD3 in different tissues and under low phosphorus stress were analyzed. GhMGD3 gene has an important function in regulation of the efficient utilization of phosphorus in cotton. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1212-1220.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210751
Abstract:
Objective Molecular systematics have aroused a series of disputes on the classification of Cayratia s.l. (Vitaceae). Taking the species of Cayratia s.l. from Zhejiang Province as the research object, the present study aims to conduct a comprehensive classification research based on different evidences. Method The seed morphology and characteristics of stem and leaf indumentum were compared. Based on the phylogenetic analysis of four chloroplast gene fragments such as atpB-rbcL, trnC-petN, trnH-psbA and trnL-F, the classification of Cayratia s.l. from Zhejiang Province was discussed. Result The stem and leaf indumentum of Cayratia s.l. were different, and the type (glabrous, pubescent or multicellular-pilose) and density of the indumentum were different among species. There existed significant difference in the cross-sectional morphology and dorsal ventral infold morphology of endosperm between Causonis (M-shape in cross section, and ventral infolds narrowly obovate or obovate-elliptic, deeply concave) and Pseudocayratia (T-shape in cross section, and ventral infolds elliptic, shallowly concave). The phylogenetic tree supported the evidence that Cayratia s.l. in Zhejiang could be clearly divided into two genera: Causonis and Pseudocayratia. Conclusion Cayratia tenuifolia and C. japonica var. pseudotrifolia are treated as subspecies of C. japonica, and Pseudocayratia pengiana is treated as a subspecies of P. speciosa. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 16 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1221-1228.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220133
Abstract:
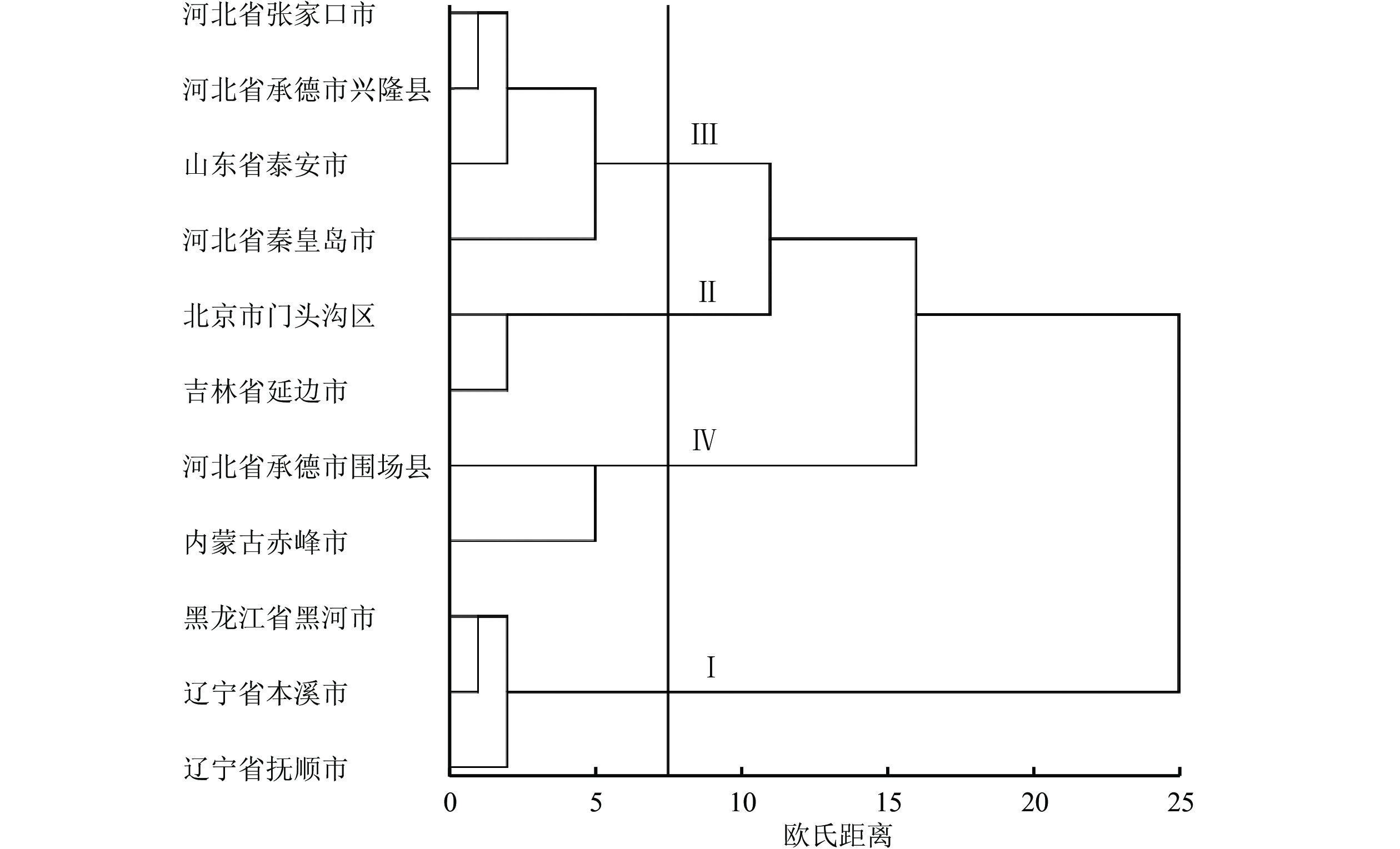
Objective The objective is to study the diversity of phenotypic characters of Quercus mongolica seeds from different provenances, so as to provide scientific basis for collection, evaluation and utilization of Q. mongolica germplasm resources. Method Seeds were collected from 11 provenances in natural distribution areas of Q. mongolica in China and 5 phenotypic characters were measured, including seed length, seed width, seed shape index, single grain weight, and thousand grain weight. SPSS software was used to analyze the character difference, correlation and principal component of Q. mongolica seeds from different provenances. Result (1) Seed length, seed width, seed shape index and single seed weight varied greatly among different provenances, and there were significant differences (P< 0.05) in thousand grain weight among different provenances. (2) There was a significant positive correlation (P<0.01) between seed length and seed width, single grain weight and thousand grain weight among different provenances. (3) There was a significant negative correlation (P< 0.05) between altitude and seed width, and a very significant negative correlation (P<0.01) with single grain weight and thousand grain weight. (4) According to the importance, the factors affecting seed characteristics in descending order were single grain weight, thousand grain weight, frost-free period and north latitude. According to the results of cluster analysis, the 11 provenances can be divided into 4 categories: Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ respectively. Among them, the provenances from Heihe City in Heilongjiang Province, Benxi City and Fushun City in Liaoning Province were grouped into Class Ⅰ, whose single grain weight and thousand grain weight were significantly higher (P<0.05) than those of other provenances, and they were the best provenances. Conclusion The phenotypic characters of Q. mongolica seeds vary significantly with geographical gradient, and the quality of provenances decreases gradually from northeast to southwest. Single grain weight and thousand grain weight can be used as the priority screening index for rapid screening of provenances. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 37 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1229-1237.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220164
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to establish a comprehensive evaluation system for ornamental quality of Clematis cultivars, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the rational introduction and utilization of Clematis cultivars. Method The growth phenological periods of plant, leaf, flower and fruit traits of 20 Clematis varieties were investigated. The ornamental value was evaluated using analytic hierarchy process and grey correlation analysis. Result (1) The 20 Clematis cultivars could be divided into 2 ecotypes: evergreen and deciduous. (2)The budding stage, branching and leaf spreading stage of plants in Hangzhou were mostly in early and mid-February to mid-March and late March. The flowering period was usually from April to June, and 7 cultivars including ‘Bagatelle’ and ‘Blue Light’ could bloom twice from July to December. (3) Sepals were mostly purplish red, blue purple or polychromatic with more than 2 colors. Conclusion Through ornamental evaluation and cluster analysis, ‘Bagatelle’and ‘Madame Julia Correvon’ have the highest comprehensive evaluation scores (Grade Ⅰ). Grade Ⅱ includes 4 cultivars such as ‘Innocent Blush’. Grade Ⅲ contains 3 cultivars including ‘Utopia’, and Grade Ⅳ contains 9 cultivars including ‘Julka’ and Grade Ⅴ includes ‘Blue Light’ and ‘Daniel Deronda’. 6 varieties of Grade Ⅰ and Ⅱ can be preferentially popularized and applied in Hangzhou. [Ch, 12 tab. 17 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1238-1246.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220159
Abstract:
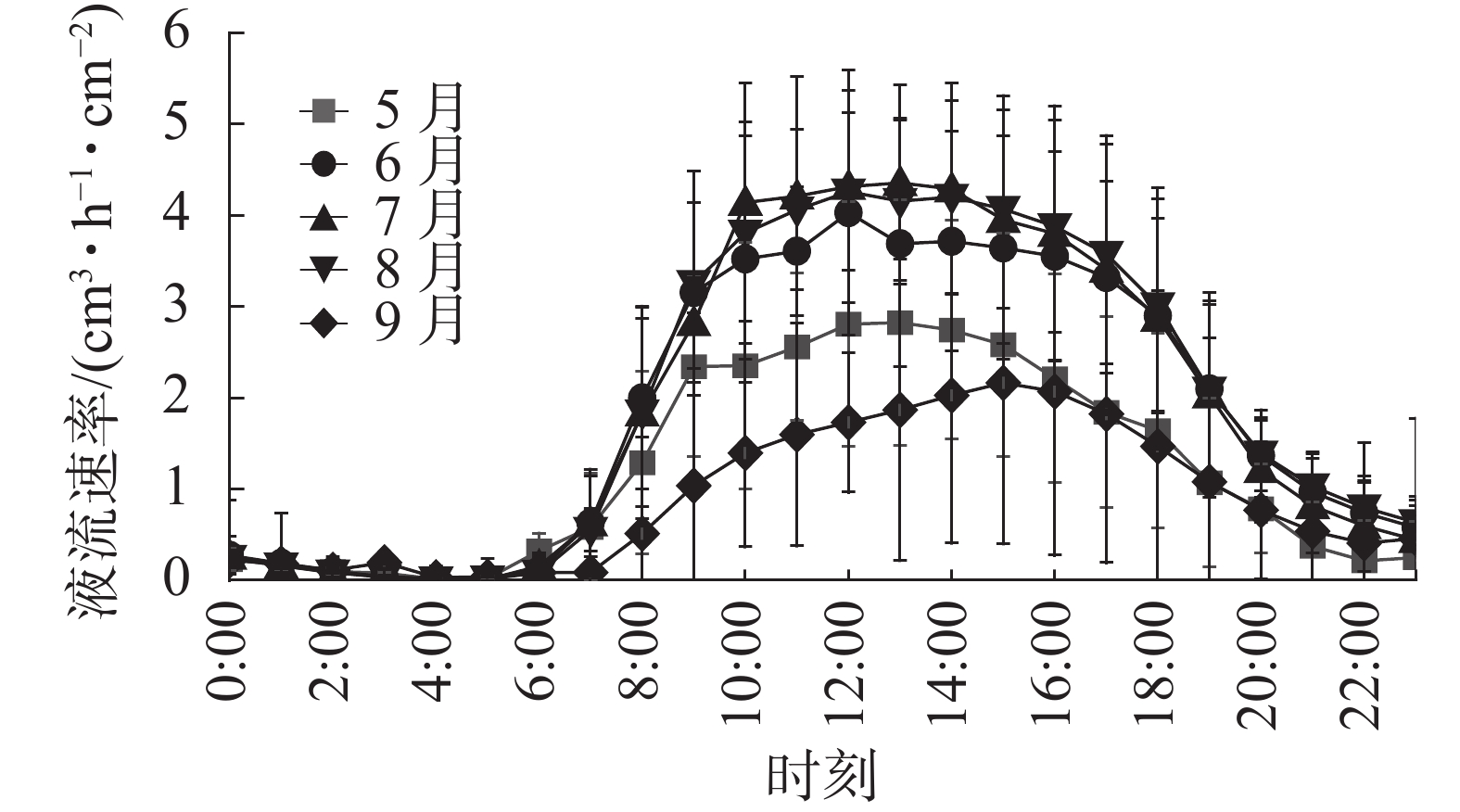
Objective The objective is to analyze the diurnal and nocturnal changes in stem sap flow of Robinia pseudoacacia in the growing season and explore the impact of meteorological factors on transpiration of R. pseudoacacia , so as to provide theoretical basis for estimating forest water consumption and forest water resource management. Method Eight sample trees were selected from R. pseudoacacia sample plots in Caijiachuan watershed, Ji County of Shanxi Province. From May to September 2021, thermal diffusion probe (TDP) was used to continuously observe stem sap flow of sample trees, and meteorological factors such as solar radiation, air temperature, soil temperature, wind speed and relative humidity were monitored simultaneously. Random forest and stepwise linear regression were used to analyze the influence of meteorological factors on stem sap flow. Result (1) The order of diurnal sap flow rate from small to large in the growing season was September, May, June, August and July, and the contribution rate of diurnal sap flow to full-day sap flow was 88%−93%. The nocturnal sap flow rate ranging from small to large was September, May, August, July and June, and the contribution rate of nocturnal sap flow to full-day sap flow was 7%−12%. (2) The main meteorological factors affecting the diurnal sap flow rate were basically the same, mainly solar radiation and air temperature. The dominant meteorological factors affecting nocturnal sap flow were different in each month. The main factors were soil temperature and water vapor pressure deficit in May and June, air temperature in July, water vapor pressure deficit and relative humidity in August, and wind speed and water vapor pressure deficit in September. (3) The fitting degree of the monthly day-night flow rate model constructed by random forest regression method was better than that by stepwise regression method. Conclusion There are obvious differences in diurnal and nocturnal sap flow rate in each month. The effect of nocturnal sap flow on water consumption of R. pseudoacacia should not be ignored, and the effect of meteorological factors on diurnal and nocturnal sap flow rate is different. Daytime and nighttime should be distinguished when simulating water consumption of tree transpiration according to meteorological factors. [Ch, 3 fig. 6 tab. 24 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1247-1256.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210771
Abstract:
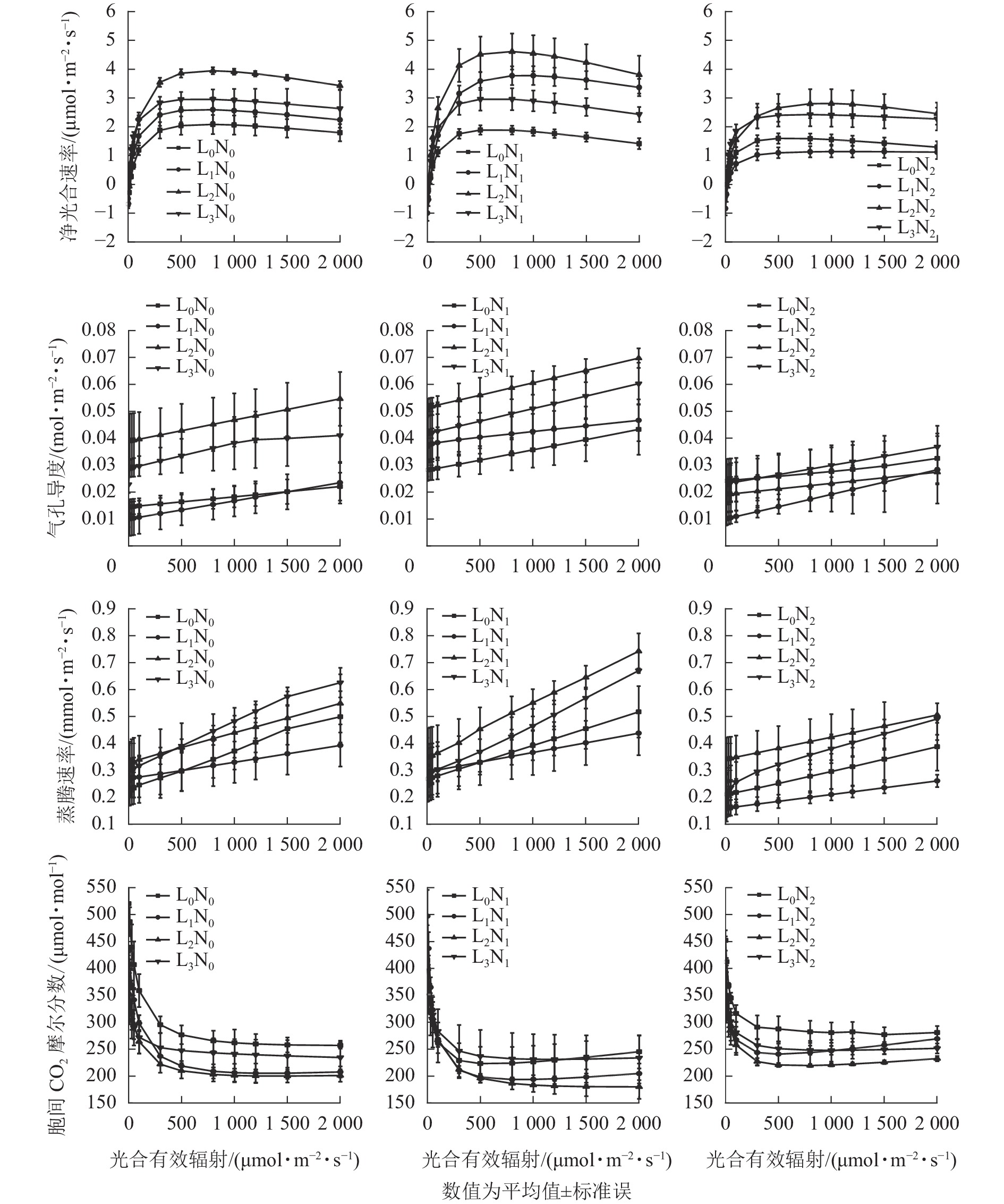
Objective This study, with an investigation of the differences in the hotosynthetic hysiological and ecological adaptation of Stewartia sinensis seedlings to different light intensity and soil nitrogen content, is aimed to select combinations of light intensity and nitrogen treatment that are conducive to the cultivation of S. sinensis seedlings. Method With S. sinensis seedlings used as test materials, efforts were made to set four light intensity gradients, namely full light (L0), light light (44.79±0.51)% (L1), moderate light (19.60±0.23)% (L2), high light (7.25±0.10)% (L3), and three nitrogen application rates, i.e, low nitrogen 0.2 g·kg−1 (N1), high nitrogen 0.6 g·kg−1 (N2) and no nitrogen application (N0) before the light response process, photosynthetic pigment mass fraction and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters were recorded and measured upon 90 d treatment. Result Light intensity, nitrogen and their interaction displayed significant effects on photosynthetic pigment and chlorophyll fluorescence of S. sinensis seedlings (P<0.05). Chl a/b values of S. sinensis seedlings varied from 2.0 to 2.5, the LSP of S. sinensis seedlings varied from 571.3 to 931.4 μmol·m−2·s−1 whereas LCP varied from 4.8 to 26.0 μmol·m−2·s−1. With the increase of shading degree, the Chl, Car, Fo, Fm, AQY of S. sinensis seedlings tended to increase, the Chl a/b and Car/Chl tended to decrease while the Pmax, Fv/Fo, Fv/Fm and PIABS increased first and then decreased. With the increase of nitrogen application rate, the PIABS of S. sinensis seedlings tended to increase, the Chl a/b, Fo and Fm tended to decrease and the Chl, Car, Pmax and AQY increased first and then decreased; With L1 and L2 light intensity, Pn, Gs and Tr of S. sinensis seedlings were higher and Ci was lower and the application of low nitrogen significantly promoted Pn, Gs and Tr. The Pmax of L1N1 increased by 45.21% compared with L1N0 with the Pn and Pmax of L2N1 being the highest. Conclusion S. sinensis seedlings had the best photosynthetic capacity when grown with moderate shading and low nitrogen treatment whereas photosynthetic inhibition occurred with full light or high nitrogen treatment. [Ch, 1 fig. 6 tab. 34 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1257-1266.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220139
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the key stand spatial structure factors that influence the understory plant diversity in Pinus taiwanensis plantations and provide a scientific basis for constructing healthy and stable P. taiwanensis plantations. Method Three analysis methods were used (grey correlation analysis, Pearson correlation analysis, and canonical correlation analysis) to discuss the effects of stand spatial structure on understory plant diversity in a 40-year-old P. taiwanensis plantation. We selected uniform angle index, mingling degree, spatial density index, storey index, opening degree index, Hegyi competition index as stand spatial structure parameters, and Simpson dominance index, Shannon diversity index, Pielou uniformity index, Margalef richness index as plant diversity indexes. Result Grey correlation analysis showed uniform angle index had the highest grey correlation with herb plant diversity; while mingling degree had the highest grey correlation with shrub and regeneration plant diversity. Pearson’s correlation analysis indicated that uniform angle index was extremely significant positively correlated with herb Shannon diversity index, herb Margalef richness index, and shrub Simpson dominance index (P<0.01); mingling degree was significantly positively correlated with herb Pielou uniformity index, shrub Shannon diversity index and shrub Margalef richness index significantly (P< 0.05); while spatial density index was extremely significant positively correlated with the Margalef richness index of understory regeneration tree species (P< 0.01). Canonical correlation analysis suggested that the six stand spatial structure parameters had a strong overall canonical correlation with herb and shrub plant diversity with corresponding coefficients of 0.998 5, and 0.999 5, respectively. Especially, uniform angle index and mingling degree had a greater impact. Conclusion Stand spatial structure significantly impacted understory plant diversity in P. taiwanensis plantations. Therefore, it’s a feasible way to improve understory plant diversity by adjusting stand horizontal spatial structure, optimizing stand competitive condition, and regulating stand vertical spatial structure. [Ch, 6 tab. 34 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1267-1277.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210820
Abstract:
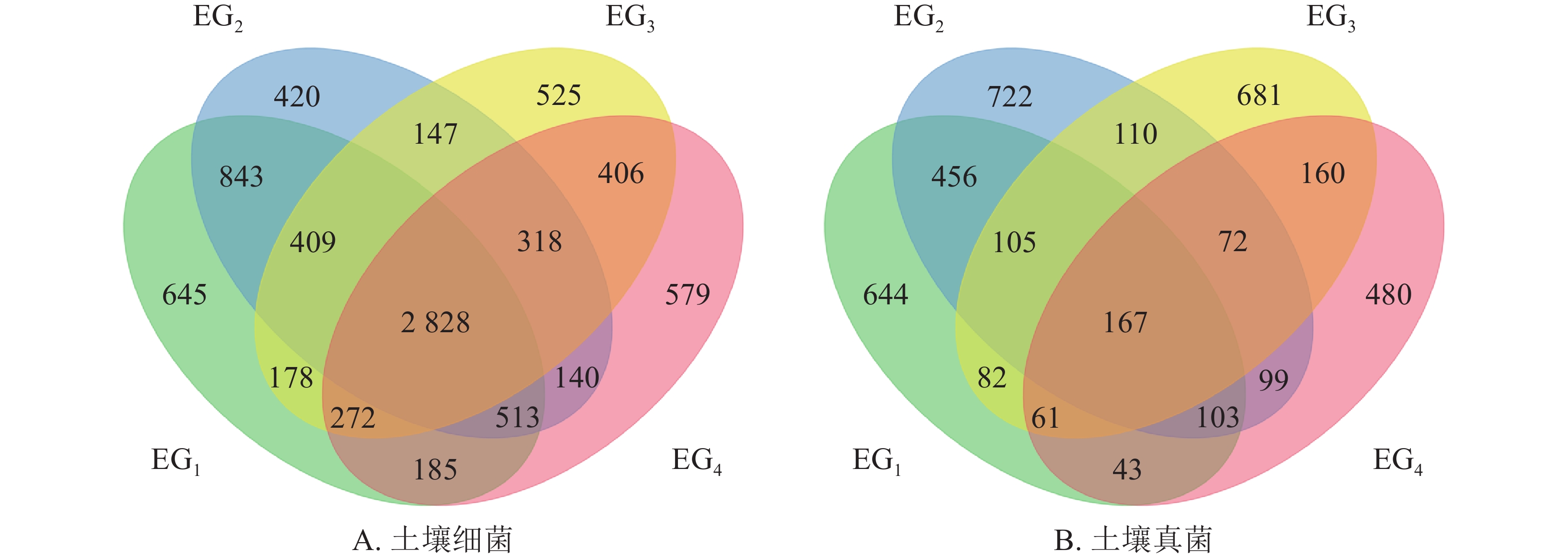
Objective The objective is to explore the characteristics of soil microbial community of zonal vegetation in evergreen broad-leaved forest in Fengyang Mountain, Zhejiang Province, and to clarify the changes of soil microbial community along the elevation gradient and the main factors affecting structure and diversity of microbial community. Method Soil samples were collected at 343, 765, 1364 and 1611 m above sea level. High-throughput sequencing technology was used to explore the relationship between soil microbial community and altitude. Result The number of OTU of bacteria was more than that of fungi, and middle and low altitudes (343 and 765 m) displayed more OTUs. Chao 1 index decreased with the increase of altitude, while Shannon index had no obvious trend. The dominant taxa of bacteria at the phylum level were Acidobacteria (43.77%−51.55%), Proteobacteria (31.18%−35.77%) and Actinobacteria, (5.24%−7.99%), while the dominant groups of fungal community were Basidiomycota (33.16%−67.35%) and Ascomycota (22.98%−46.78%). Among the top 10 bacterial phyla in relative abundance, Gemmatimonadetes, Nitrospirae and Verrucomicrobia were significantly negatively correlated with altitude (P<0.01). There were no altitudinal taxa in the fungal community at the phylum level. LefSe (LDA Effect Size) analysis exhibited more different taxa in the fungal community. In addition, PCoA showed that the soil microbial community had the characteristics of altitudinal differentiation bounded by 765 m, and the first axis of this PcoA (PC1) was significantly correlated with temperature, total phosphorus, total kalium and pH(P<0.05). Conclusion The change of altitude leads to the change of soil microbial community characteristics in Fengyang Mountain, and temperature is the main driving factor. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 41 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1278-1288.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220132
Abstract:
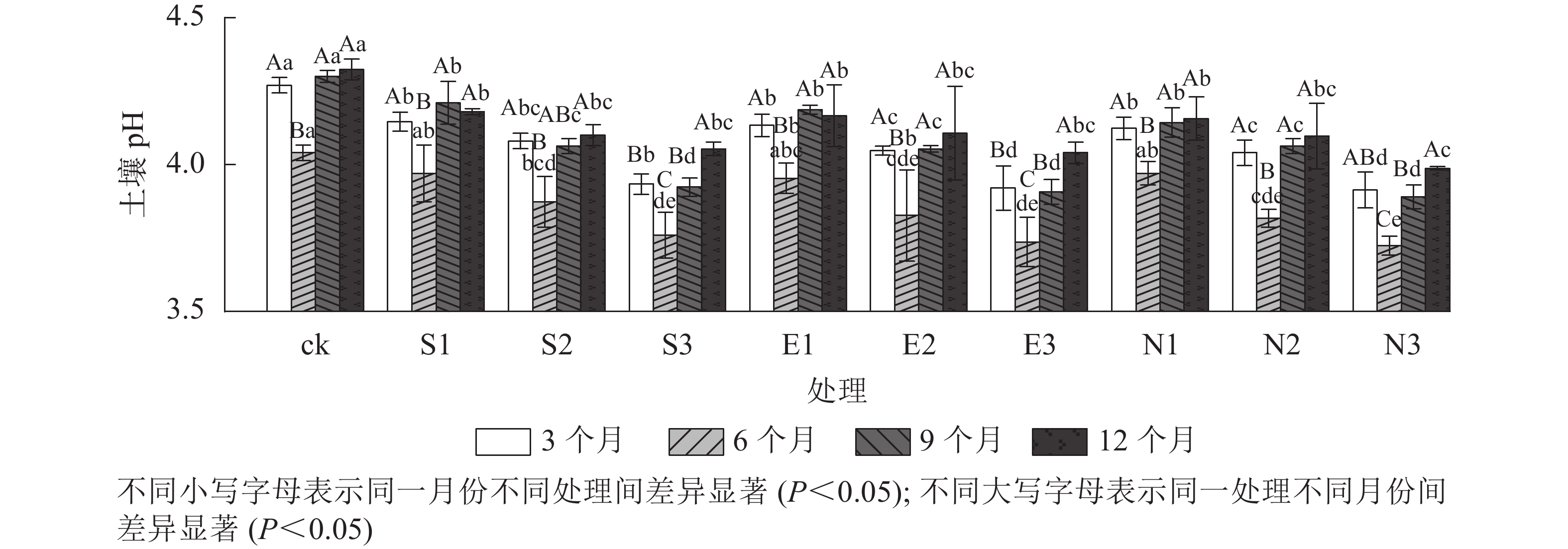
Objective The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of acid rain type change on soil nutrients and microbial C and N of the Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation, with a view to providing a theoretical basis for sustainable management of the C. lanceolata plantation in areas with different types of acid rain. Method Taking C. lanceolata plantation in Dongshanqiao Forest Farm in Nanjing as the research object, a control treatment (ck, mountain fire pool water, pH 6.6) was set. After 1 year of stress of different types of acid rain (sulfuric acid type, nitric acid type and mixed type) and acid rain acidity (simulated solution pH 4.5, 3.5 and 2.5), the effects of acid rain type change on soil nutrients and microorganisms in the C. lanceolata plantation were explored. Result With the increase of acid rain acidity, soil pH value of different types of acid rain treatment decreased significantly (P<0.05), while soil exchangeable hydrogen ions (H+) and aluminum ions (Al3+) increased significantly (P<0.05). Compared with the control (ck), when the pH value of acid rain was 2.5, the mean values of soil exchangeable H+ and Al3+ increased by 275% and 240% under sulfuric acid rain treatment, 254% and 246% under mixed acid rain treatment, and 246% and 249% under nitric acid rain treatment, respectively. In addition, the time of acid rain stress significantly affected the contents of soil total carbon, total nitrogen, total sulfur, available phosphorus and microbial C and N (P<0.05), but the type of acid rain had no significant effect on soil microbial C and N. After acid rain stress for 1 year, soil microbial C and N contents were the lowest under the treatment of pH 2.5 nitric acid rain, which were (378.89±60.69) and (38.67±4.10) mg·kg−1 respectively. According to the structural equation model, the effect of acid rain acidity on soil microbial C and N in the C. lanceolata plantation was stronger than that of acid rain type, which indirectly influenced microbial C and N mainly by affecting soil pH, available phosphorus and total carbon. Conclusion After 1 year of short-term acid rain stress, acid rain acidity is still the main factor affecting soil characteristics of C. lanceolata, and the change of acid rain type will intensify the inhibition effect of acid rain acidity on soil characteristics of C. lanceolata plantation. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 29 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1289-1295.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220122
Abstract:
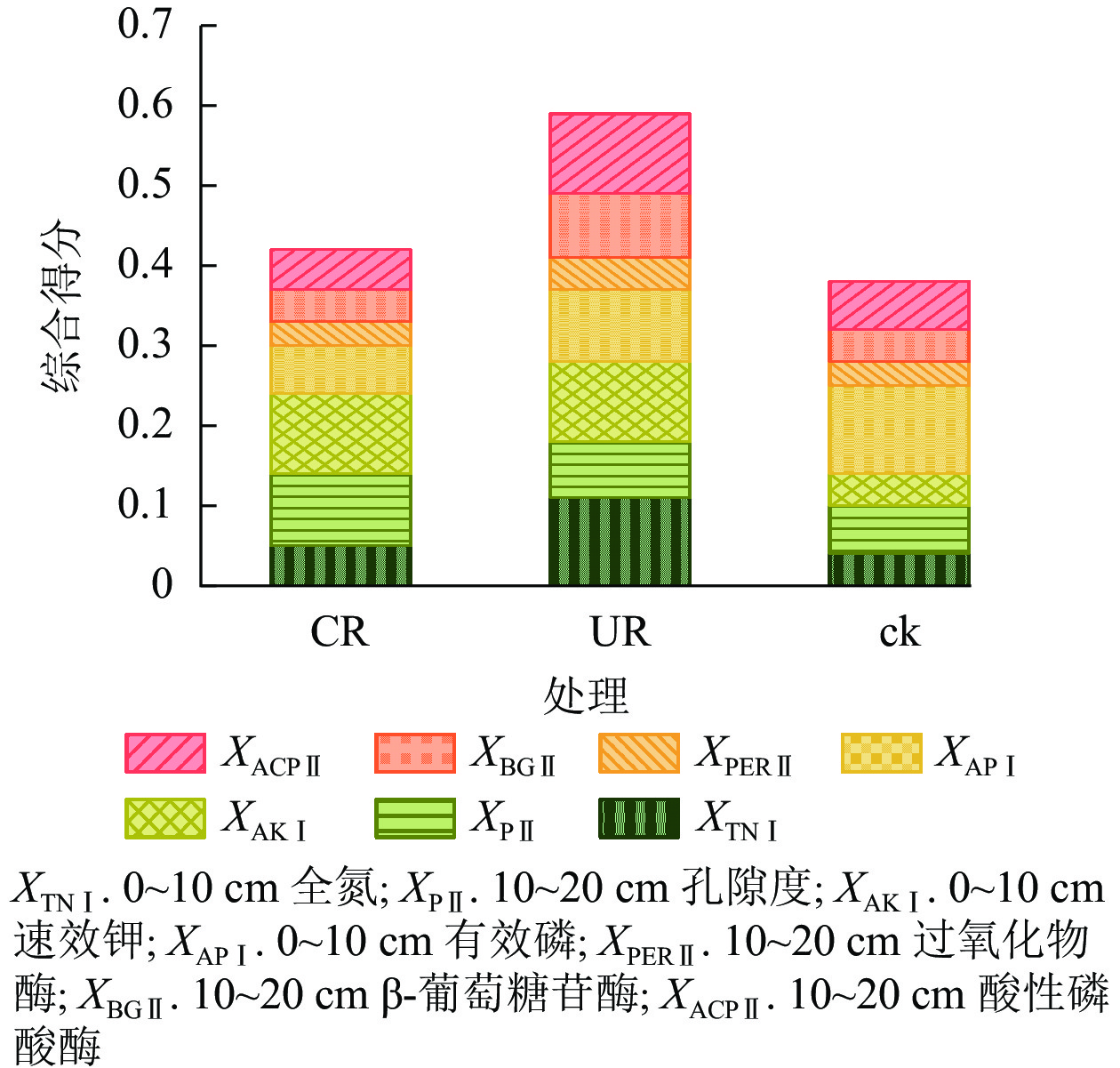
Objective Ecological restoration of Phyllostachys edulis forest is a challenge in subtropical regions of China. This study aims to understand the natural restoration status of the soil after clear-cutting and residue retention of Ph. edulis forest, so as to provide guidance for ecological restoration of forest. Method In the clear-cutting sites, 3 treatments were set up, i.e. cutting residue reserved (UR), cutting residue removed (CR), and uncut Ph. edulis forest as the control (ck). The changes of soil indexes under different treatments were analyzed and compared through soil survey and measurement 5 years later, and fuzzy mathematical discrimination and principal component analysis were used to quantitatively evaluate the natural restoration effect of Ph. edulis forest after clear-cutting. Result (1) The soil bulk density of CR and UR decreased by 31% and 14% respectively compared with ck (P<0.05). Soil total porosity, capillary water holding capacity, field water holding capacity and saturated water holding capacity were higher than those of ck. The water holding capacity of UR soil was better than that of CR. (2) The contents of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen and available potassium in CR and UR were higher than those in ck, and each index increased by 17%−123%. Available phosphorus showed that CR was significantly lower than UR and ck (P<0.01). Due to the retention of cutting residues of Ph. edulis forest after clear-cutting, the soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen and available phosphorus in UR were significantly higher than those in CR treatment by 33%−99% (P<0.05). (3) The activities of urease, β-glucosidase and peroxidase in CR, UR soil were higher than those in ck. The activities of 3 extracellular enzymes in UR soil were 46%−98% higher than those in CR treatment. (4) The comprehensive evaluation results showed that the soil quality had been well restored, and the comprehensive scores ranging from high to low in the restored site soil of Ph. edulis forest after clear-cutting was sample area with cutting residue reserved, sample area with cutting residue removed, Ph. edulis forest sample area. Conclusion After 5 years of natural recovery, the soil of Ph. edulis forest after clear-cutting can be restored faster than that in Ph. edulis forest land, and the retention of the cutting residues after clear-cutting of Ph. edulis forest is more conducive to soil restoration. [Ch, 1 fig. 4 tab. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1296-1302.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210607
Abstract:
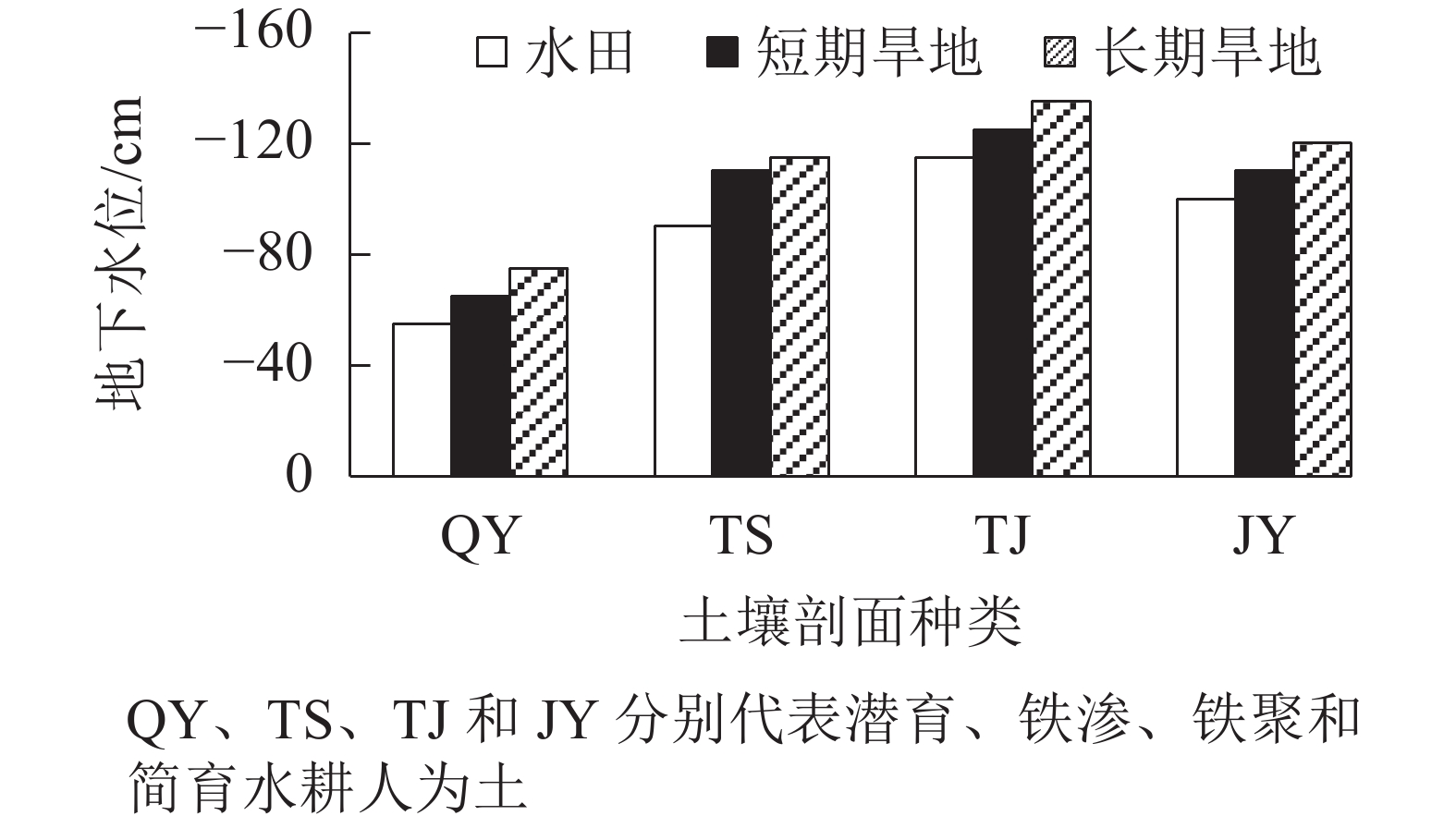
Objective This paper, with an exploration of the spatiotemporal differentiation of soil organic carbon (SOC) in such upland as nurseries of flowers and trees as well as orchards, which have been converted from paddy field in Zhejiang Province under the background of leisure agriculture tourism, is aimed to better understand the carbon sequestration in soils after the land-use conversions. Method With soil samples selected from paddy field and the converted upland as the research objects, combined methods of field investigation and laboratory analysis were employed, on the basis of “trading space for time”, to investigate the spatiotemporal changes in the density and storage of SOC in 1 meter depth soil before a comparison was conducted of the differences of SOC among different types of upland converted from paddy fields and an estimation was made of the storage changes of SOC after the land-use conversions in Zhejiang Province. Result Soil organic carbon on four types of stagnic anthrosols (hap-stagnic, Fe-leachi-stagn, iFe-accumuli-stagnic and hapli-stagnic anthrosols) in 1 meter depth upland soils decreased by 13.9%, 34.9%, 18.9% and 23.9% respectively after 15 to 20 years with the loss of SOC density being 2.06, 2.92, 1.14 and 1.54 t·hm−2·a−1, respectively. There was a significant positive correlation (P<0.01) between the decline rate of SOC and the decline depth of groundwater level in the upland soils. Conclusion Paddy field is a better choice for the storage of SOC whereas the conversion from paddy field to upland decreases the storage of SOC and affects regional carbon balance. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 16 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1303-1312.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210721
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to investigate the soil heavy metal pollution and its ecological risk in Diospyros kaki main producing areas in Henan Province, so as to provide scientific basis for evaluation of soil environmental safety and heavy metal prevention in the main producing areas. Method 450 soil samples were collected from 90 D. kaki plantations in 3 major producing areas, including Anyang, Jiyuan and Sanmenxia, and the contents of 6 heavy metal elements such as As, Hg, Pb, Cd, Cr, and Cu were determined. Pollution load index (IPL), potential ecological risk index (IR) and ecological risk warning index (IER) were used to evaluate the heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in D. kaki orchard. Result The average contents of As, Hg, Pb and Cu in soil were 1.26, 2.01, 1.86, and 1.64 times of the background values, respectively. The soil in D. kaki orchard was moderately polluted by Hg, slightly polluted by As, Pb and Cu. Cd and Cr were pollution-free. Soil As, Hg, Pb and Cu in the main producing areas were greatly affected by human activities, among which As was mainly affected by agricultural activities, while Hg, Pb and Cu were greatly affected by industrial activities. The average values of IPL, IR and IER were 1.08, 136.95 and 2.33, respectively, showing mild pollution, slight risk and mild warning grade. Jiyuan producing area had the most serious pollution, and the highest IR and IER level, with IPL, IR and IER reaching 1.32, 154.10 and 3.79, respectively. 13.33% of the orchards were moderately or severely polluted, and 33.33% were in moderate or strong IR level. 66.67% and 26.67% of orchards showed moderate and severe warnings respectively. Among the 6 heavy metals, Hg had the highest single factor pollution index (CF), IR and IER, which were 2.01, 80.31 and 1.01, respectively. Conclusion Hg is the heavy metal element with the highest IR and IER level in the soil of the main D. kaki producing areas. Jiyuan has the highest IPL, IR and IER among the 3 producing areas, all reaching the medium level. [Ch, 2 fig. 8 tab. 30 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1313-1320.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210828
Abstract:
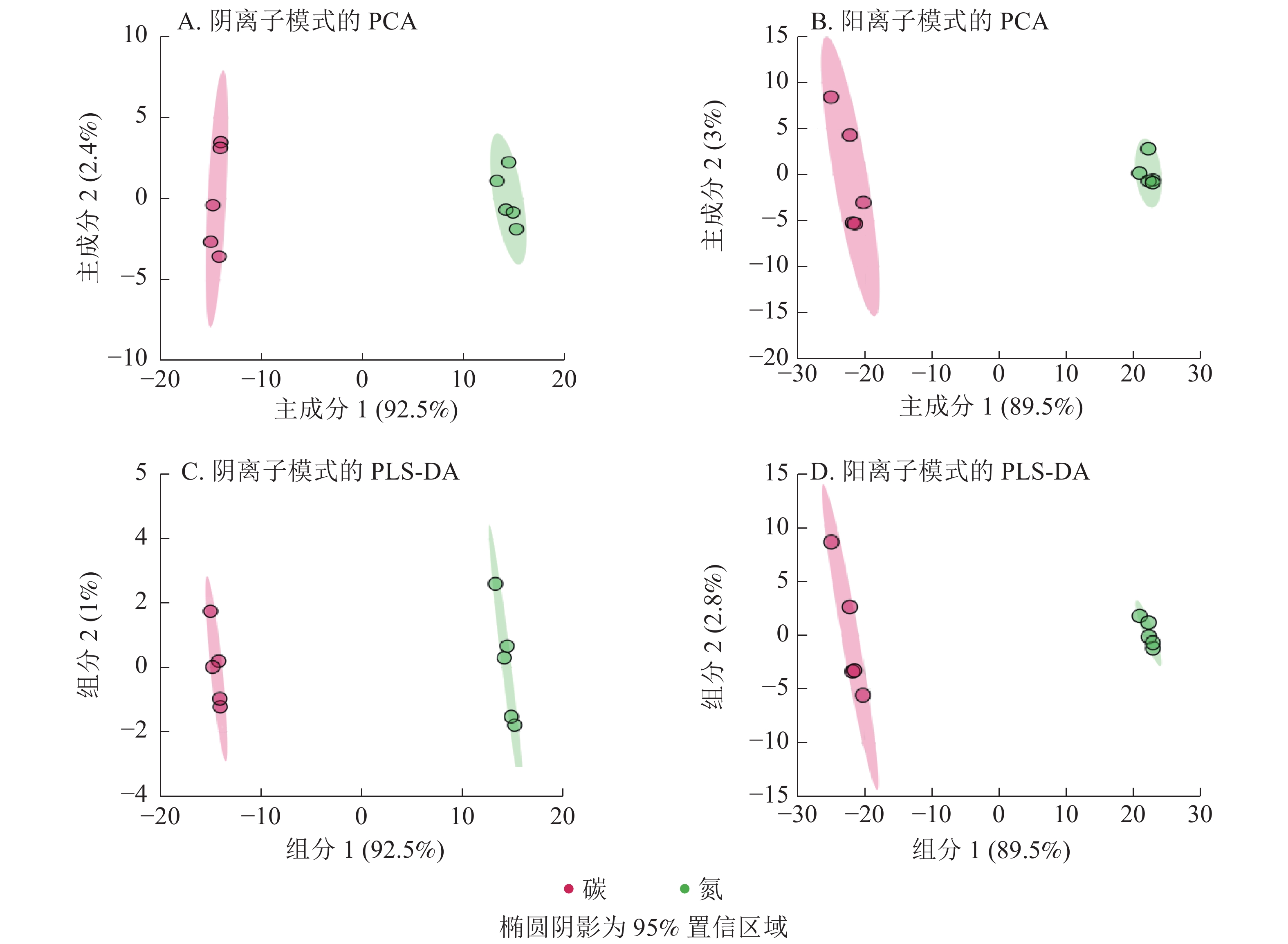
Objective The objective is to compare the metabolic differences of the nematode-killing fungus Esteya vermicola (EV) cultured in carbon and nitrogen nutrient sources and to identify key metabolites or signal molecules. Method The carbon medium (mainly composed of PDB) for culturing fungi and the nitrogen medium (mainly composed of yeast powder) for culturing bacteria were selected. EV bacteria were cultured on two kinds of culture media at 25 ℃ for 7 days. The mycelia were harvested and the metabolites were extracted. Non-target high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) was used to analyze and identify metabolite components in both positive and negative ion modes. The metabolic pathways of metabolites with significant differences were analyzed. Result A total of 498 metabolites were identified, including 176 negative and 362 positive ion modes and 40 metabolites in both modes. There were 444 metabolites with significant differences, accounting for 89.2% of the total, among which 162 were negative and 310 were positive, and 28 were common to the two modes. Both principal component analysis and partial least square discriminant analysis could cluster the metabolites into different clusters and separate them significantly in carbon and nitrogen culture. In nitrogen culture, guanidine phosphate acetate and p-cresol sulfate were abundant and unique metabolites, and the yield of allantoin, photopigment, indole, and trehalose were significantly up-regulated. Pathway analysis enriched the significantly up-regulated and down-regulated metabolites into the metabolic pathways related to amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism, respectively. Conclusion EV bacteria showed significant metabolic differences in carbon and nitrogen culture. The metabolic pathway mainly involves carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism. The important metabolites will provide a theoretical basis for efficient culture and application of EV. [Ch, 3 fig. 2 tab. 31 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1321-1329.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210819
Abstract:
Objective This study, with the main pathogens of Pleurotus geesteranus after harvest isolated and identified, is aimed to investigate the antibacterial activities of plant essential oil that effectively prevent and control fungal diseases so as to provide reference for the development of preservation technology of P. geesteranus after harvest. Method With major pathogenic fungi isolated and identified from P. geesteranus as the research objects of prevention and control, the most effective essential oils were screened out from 13 kinds of common essential oils before an analysis was conducted of their effects on the mycelial growth, conidia germination, mycelial morphology and structure, membrane lipid peroxidation and leakage of cell contents of the main postharvest pathogens in order to study the mechanism of prevention and treatment. The control group was treated without essential oil. Result Among the 13 alternative essential oils, Acorus tatarinowii essential oil had a good inhibitory effect on Fusarium fujiuroi and the growth of F. fujikuroi could be completely inhibited by 1 000 μL·L−1 A. tatarinowii essential oil with the concentration of essential oil positively correlated with the antifungal effect. After the treatment with 1 000 μL·L−1 essential oil for 3 h, the relative conductivity, MDA and cell contents in the cultured liquid of F. fujikuroi were 2 times, 5 times and 3 times of those in the control group, respectively. According to the results of scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy, the essential oil of A. tatarinowii could change F. fujikuroi mycelium morphology and destroy its cell structure. Conclusion A. tatarinowii essential oil could accelerate the membrane lipid peroxidation of mycelia cells, increase the permeability of cell membrane, destroy the normal physiological function of cells and cause cell death, thereby inhibiting the growth and reproduction of F. fujikuroi. [Ch, 9 fig. 26 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1330-1339.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220108
Abstract:
Objective LiDAR, as an active remote sensing technology, has proven to be an effective and efficient means for large-scale dynamic monitoring and investigation for forest resources. With an analysis of the airborne LiDAR data and ground survey data collected of Guangxi state-owned Gaofeng forest farm from January to February 2018, this paper is aimed to establish a regression model by using parametric and nonparametric methods to inverse the forest volume of Eucalyptus plantation. Method First, point cloud characteristic variables such as point cloud height parameters, point cloud density parameters and stand canopy density were extracted from point cloud after which parametric methods (stepwise regression, partial least squares regression) and nonparametric methods (random forest regression and support vector machine regression) were used to construct stand volume. Then the prediction performance of model regression is evaluated by comparing the estimated data of sample plot with the measured ones so that the optimal volume inversion model could be selected. Result After being verified by leaving one method, results are as follows: for the stepwise regression model, R2=0.85, RMSE=23.93 m3·hm−2 and MAE=18.18 m3·hm−2; for the partial least squares regression model, R2=0.81, RMSE=26.52 m3·hm−2 and MAE=19.94 m3·hm−2; for the support vector regression model with RBF kernel function, R2=0.88, RMSE=21.35 m3·hm−2, MAE=16.62 m3·hm−2 whereas for the random forest regression model, R2=0.84, RMSE=24.53 m3·hm−2 and MAE=17.41 m3·hm−2. Conclusion After variable screening with random forest; the RBF-SVR model has demonstrated the best fitness and generalization ability, followed by the stepwise regression model of optimizing variables by stepwise screening method combined with variance inflation factor (VIF) method whereas the random forest regression model and partial least squares regression model came last. It was also shown that nonparametric method is a better choice in the construction of RBF-SVR model in solving the problem of regression prediction in the field of forestry LiDAR and that the volume models of four forest types established in this study have high accuracy and met the requirements of relevant technical regulations of forest resources investigation. [Ch, 6 fig. 6 tab. 25 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1340-1349.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220109
Abstract:
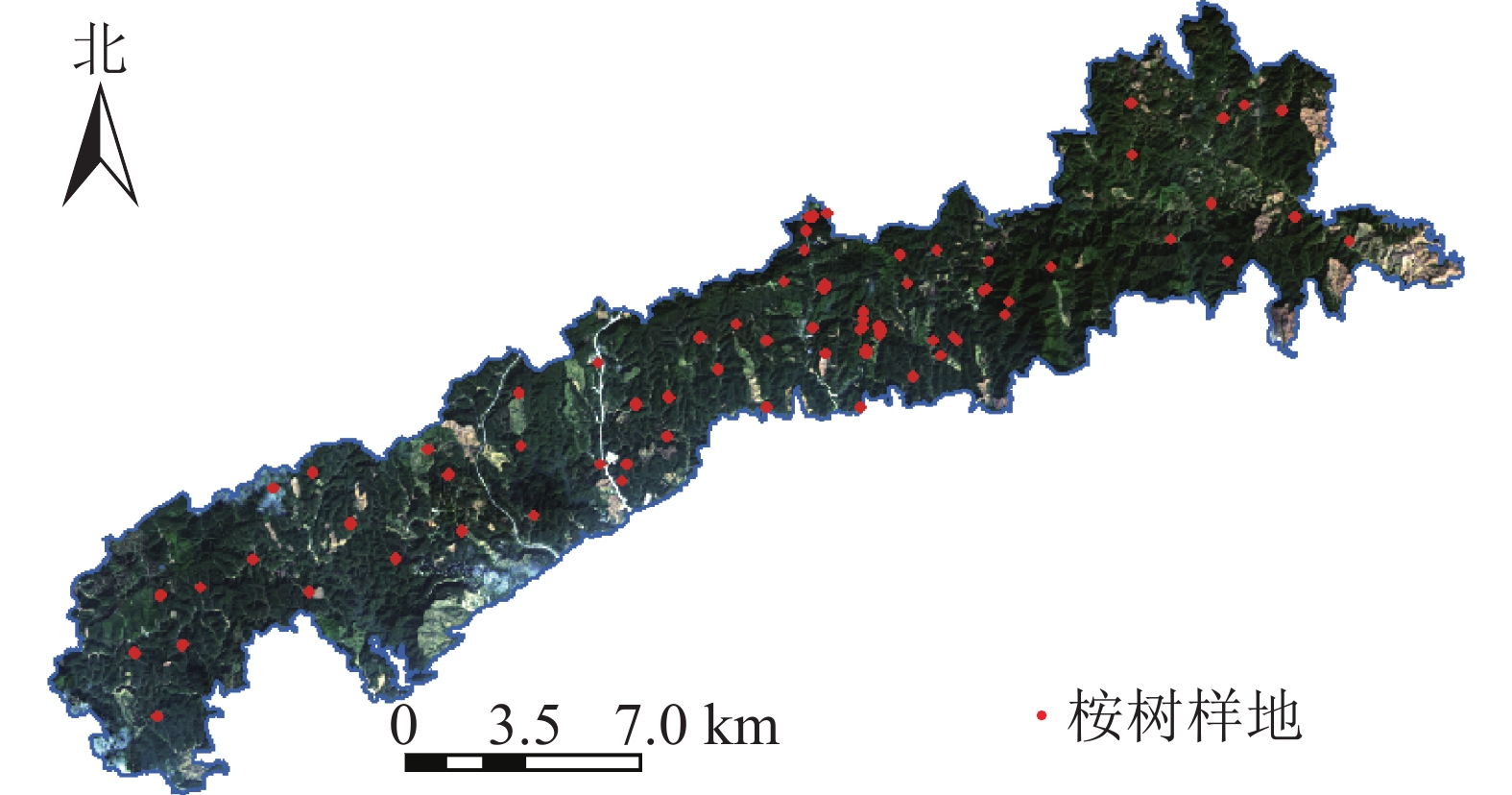
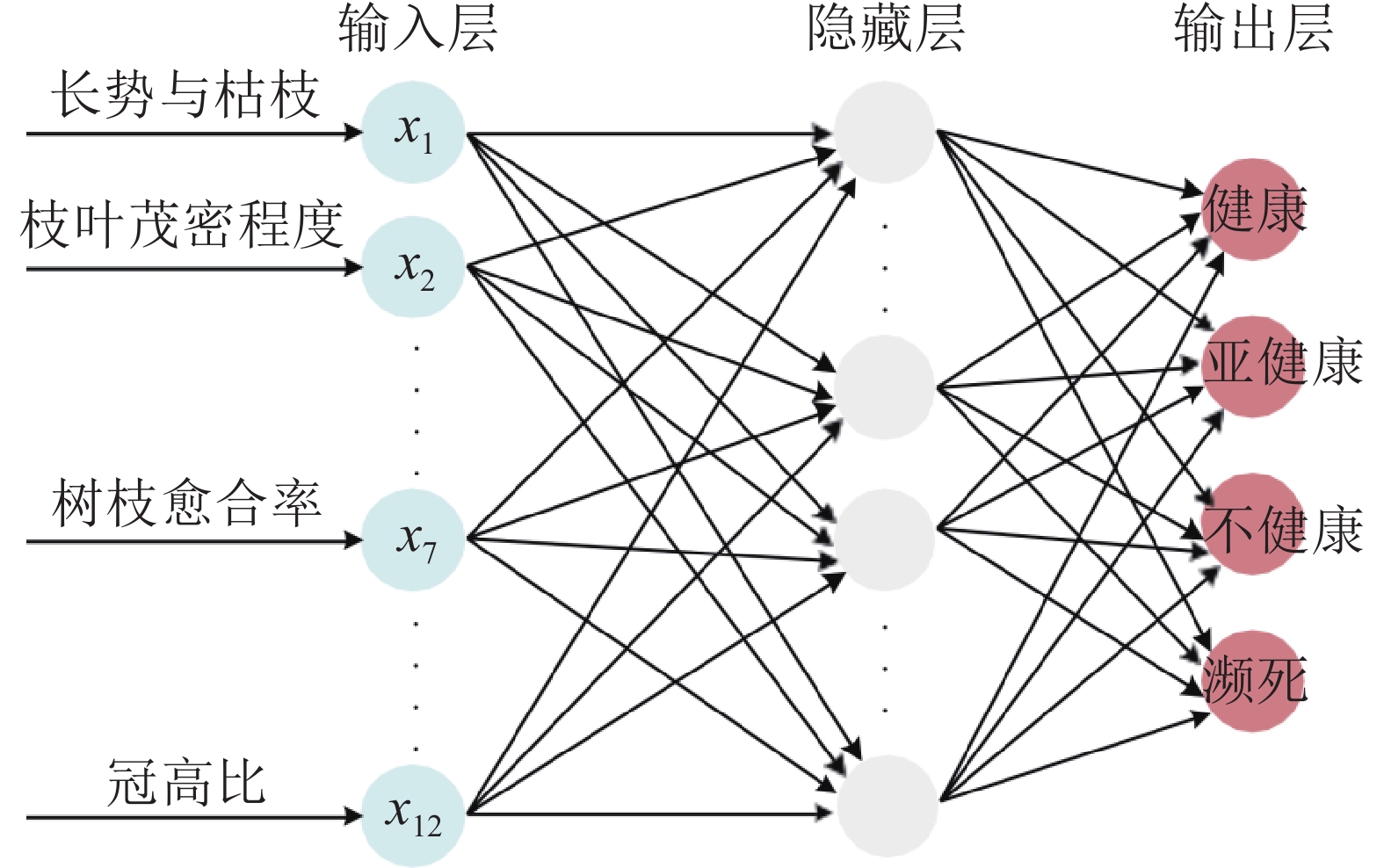
Objective For the rapid, accurate, and productive assessment of urban tree health, this study aims to investigate and analyze the growth, health, and management status of Fraxinus pennsylvanica in Beijing core functional area, so as to provide a scientific basis for comprehensive health assessment and technical measures for management and protection. Method Taking street trees of 11 main streets in the core area of Beijing as the research object, the health assessment model of F. pennsylvanica was constructed by principal component analysis and K-means clustering. The results were verified by discriminant analysis, and the BP neural network health prediction model was established by combining the assessment results with the assessment indexes. Meanwhile, the effects of DBH, tree height, the number of pruning stubble, anti-trampling pavement etc. on the health status of F. pennsylvanica were analyzed. Result The results indicated that healthy, sub-healthy, unhealthy, and dying plants accounted for 39.20%, 41.26%, 16.78%, and 2.76%, respectively. In the BP neural network health prediction model, the correlation coefficients between expected value and predicted value of the training set, verification set, test set, and total set were 0.9997, 0.9720, 0.9976 and 0.9953 respectively, all greater than 0.9500, indicating that the model could accurately reflect the relationship between 12 evaluation indexes and health assessment categories of F. pennsylvanica and could be used to predict the health status of other Conclusion F. pennsylvanica street trees in the study area are in a sub-health state on the whole, with good conservation and maintenance potential. However, some of them are seriously damaged and need to be dealt with urgently. In planting and management process, important measures should be taken to ensure the good status of F. pennsylvanica, such as standard pruning, strong water permeability of pavement materials, 5−10 m plant spacing, 1−2 m2 tree pool area, and suitable road conditions .
2022, 39(6): 1350-1358.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220134
Abstract:
Objective The purpose of this study is to obtain more efficient and accurate automatic land use classification methods, so as to provide theoretical support for the follow-up study of land use classification in plateau mountainous areas. Method Taking Dali City, a typical plateau mountainous area of Yunnan Province in China, as the research area and Sentinel-2A image as the object, an object-oriented decision tree classification method was proposed and compared with traditional ISODATA classification method and maximum likelihood method. Result (1) The classification results of object-oriented decision tree method were better than those of ISODATA classification method and maximum likelihood classification method in terms of spatial distribution and area statistics of various classes, and were closer to the actual land use area data of the study area. (2) In Dali, the maximum likelihood classification method had better applicability in the extraction of water body and forest land, while the object-oriented decision tree classification method had stronger applicability in the extraction of farmland, grassland, construction land and other land types, and had better extraction effect in the extraction of glacier snow. (3) Compared with the traditional ISODATA method and maximum likelihood method, the object-oriented decision tree classification method could further improve the classification accuracy. The overall classification accuracy could reach 90.20% and the Kappa coefficient was 87.95%. Conclusion Compared with the traditional classification methods, the idea of coarse classification before fine classification can avoid the confusion between regions. The combination of object-oriented features and decision tree has better applicability in plateau mountainous areas, and can effectively improve the classification accuracy. [Ch, 3 fig. 7 tab. 26 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1359-1368.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220359
Abstract:
Objective Analyzing the fruit characteristics and investigating the correlation between bird feeding behavior and fruit characteristics in autumn and winter aims to provide theoretical insights for urban bird-attracting plant landscape construction and biodiversity planning. Method The periodic investigation of birds feeding behavior was carried out at three sites in the East Lake campus of Zhejiang A&F University. The spatial environments that fruits located in and the changes of fruit external morphology about 10 common landscaping tree species were recorded. The contents of fruits including titratable acid, soluble sugar, starch and soluble protein were gauged during the birds feeding period. Result The spatial environments that fruits located in could be divided into three categories: (1) evergreen trees that inner and outer space could be distinguished easily with hard and spreading branches; (2) evergreen trees that inner and outer space could be distinguished slightly with soft and dense branches; (3) deciduous trees that inner and outer space could not be distinguished with hard and spreading branches. The security and concealment of spatial environments that fruits located in and the convenience for bird landing and taking-off would directly affect the tendency of bird feeding, and the internal characteristics of spatial environment would affect approaches of bird feeding. When it came soft branches and complex spatial environment, larger birds such as Spizixos semitorques chose to feed on the top of plants , while smaller birds such as Parus major chose to feed inside. Fruits’external morphological characteristic could be divided into two categories: (1) the fruits with unchanged external morphology within 60 days; (2) the fruits that external morphology gradually withered as time flowed within 60 days. Fruit hanging status affected the feeding tendency of birds as fresh and plump fruits were more attractive to birds. Fruits that were poorly maintained, such as Malus halliana, were only eaten by Pycnonotus sinensis at the early stage of fruit ripening, while fruits that were well maintained, such as Cinnamomum camphora, were continuously eaten by P. sinensis and Turdus merula for a long time. The contents of the fruit affected the feeding tendency of the birds. Fruits with high sugar content were more attractive to P. sinensis and T. merula, while the P. sinensis prefered fruits with higher acid content and the T. merula prefered fruits with higher protein content. Conclusion In order to improve bird diversity in urban green space, the concealing of food source tree should be ensured, and the tall evergreen trees owning fruits with high retention ability and high sugar content should be selected as the food source trees. [Ch, 9 fig. 5 tab. 27 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1369-1377.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220155
Abstract:
Since salinity is one of the major restraints for agricultural production, and plants are sensitive to the general heterogeneous variability in salt over time and space, it is of great importance to investigate the response patterns of plants to heterogeneous salt stresses which can shed some light on the improvement of plant resistance under nonuniform salt stress. However, studies conducted on plant salt stress so far have mainly focused on homogeneous salt stress, which is very different from the heterogeneous salt stress phenomenon in soils in actual agricultural production. In view of this, this paper is aimed at a review of the causes of soil salinity heterogeneity distribution and recent research progress on plants under salinity spatial heterogeneity, including: (1) the causes and distribution of soil salinity spatial heterogeneity; (2) effects of soil salinity spatial heterogeneity on plant above-ground growth; (3) plant root system response to soil salinity spatial heterogeneity and (4) the relationship between plant growth and root zone salt concentration under soil salinity spatial heterogeneity. This paper provides an insight into the feasibility study of the effects of spatial heterogeneity of soil salinity on plant growth for the subsequent research on heterogeneous salt stress. [Ch, 65 ref.]
Since salinity is one of the major restraints for agricultural production, and plants are sensitive to the general heterogeneous variability in salt over time and space, it is of great importance to investigate the response patterns of plants to heterogeneous salt stresses which can shed some light on the improvement of plant resistance under nonuniform salt stress. However, studies conducted on plant salt stress so far have mainly focused on homogeneous salt stress, which is very different from the heterogeneous salt stress phenomenon in soils in actual agricultural production. In view of this, this paper is aimed at a review of the causes of soil salinity heterogeneity distribution and recent research progress on plants under salinity spatial heterogeneity, including: (1) the causes and distribution of soil salinity spatial heterogeneity; (2) effects of soil salinity spatial heterogeneity on plant above-ground growth; (3) plant root system response to soil salinity spatial heterogeneity and (4) the relationship between plant growth and root zone salt concentration under soil salinity spatial heterogeneity. This paper provides an insight into the feasibility study of the effects of spatial heterogeneity of soil salinity on plant growth for the subsequent research on heterogeneous salt stress. [Ch, 65 ref.]
2022, 39(6): 1378-1387.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220180
Abstract:
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are lipophilic liquids with low molecular weight and high vapor pressure. According to the source, VOCs can be divided into anthropogenic sources and plant sources, and plant sources are the largest source of VOCs in the global atmosphere. VOCs release from plants is obviously affected by biological and abiotic factors, which play an important role in atmospheric chemical reactions, human health and plant physiology and ecology. However, the effects of complex environmental conditions on VOCs release from plants and their physiological and ecological roles are still not fully understood. In this paper, the synthesis pathways of VOCs in plants are summarized, the effects of single and compound environmental factors on VOCs species and release amount are emphasized, and the role of VOCs in physiology and ecology is summarized. In conclusion, the synthesis pathway of VOCs in plants has been clarified, but the molecular mechanism of VOCs regulation needs to be further explored. Insect feeding, high temperature, drought and high CO2 concentration can reduce the release of constituent VOCs (such as isoprene), increase the release of storage VOCs (such as pinene and limonene), and induce the synthesis and release of new compounds (such as GLVs). However, the effects of complex environment on VOCs release are complex and need to be further explored. VOCs play a role in plant defense against herbivores or attracting herbivores’ natural enemies, mediating interplant signal transduction, anti-oxidation, drought resistance and enhancing plant heat resistance, etc. It is predicted that more roles of plant VOCs in ecosystem will be explored in the future. [Ch, 96 ref.]
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are lipophilic liquids with low molecular weight and high vapor pressure. According to the source, VOCs can be divided into anthropogenic sources and plant sources, and plant sources are the largest source of VOCs in the global atmosphere. VOCs release from plants is obviously affected by biological and abiotic factors, which play an important role in atmospheric chemical reactions, human health and plant physiology and ecology. However, the effects of complex environmental conditions on VOCs release from plants and their physiological and ecological roles are still not fully understood. In this paper, the synthesis pathways of VOCs in plants are summarized, the effects of single and compound environmental factors on VOCs species and release amount are emphasized, and the role of VOCs in physiology and ecology is summarized. In conclusion, the synthesis pathway of VOCs in plants has been clarified, but the molecular mechanism of VOCs regulation needs to be further explored. Insect feeding, high temperature, drought and high CO2 concentration can reduce the release of constituent VOCs (such as isoprene), increase the release of storage VOCs (such as pinene and limonene), and induce the synthesis and release of new compounds (such as GLVs). However, the effects of complex environment on VOCs release are complex and need to be further explored. VOCs play a role in plant defense against herbivores or attracting herbivores’ natural enemies, mediating interplant signal transduction, anti-oxidation, drought resistance and enhancing plant heat resistance, etc. It is predicted that more roles of plant VOCs in ecosystem will be explored in the future. [Ch, 96 ref.]