2024 Vol. 41, No. 4
2024, 41(4): 669-678.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240145
Abstract:
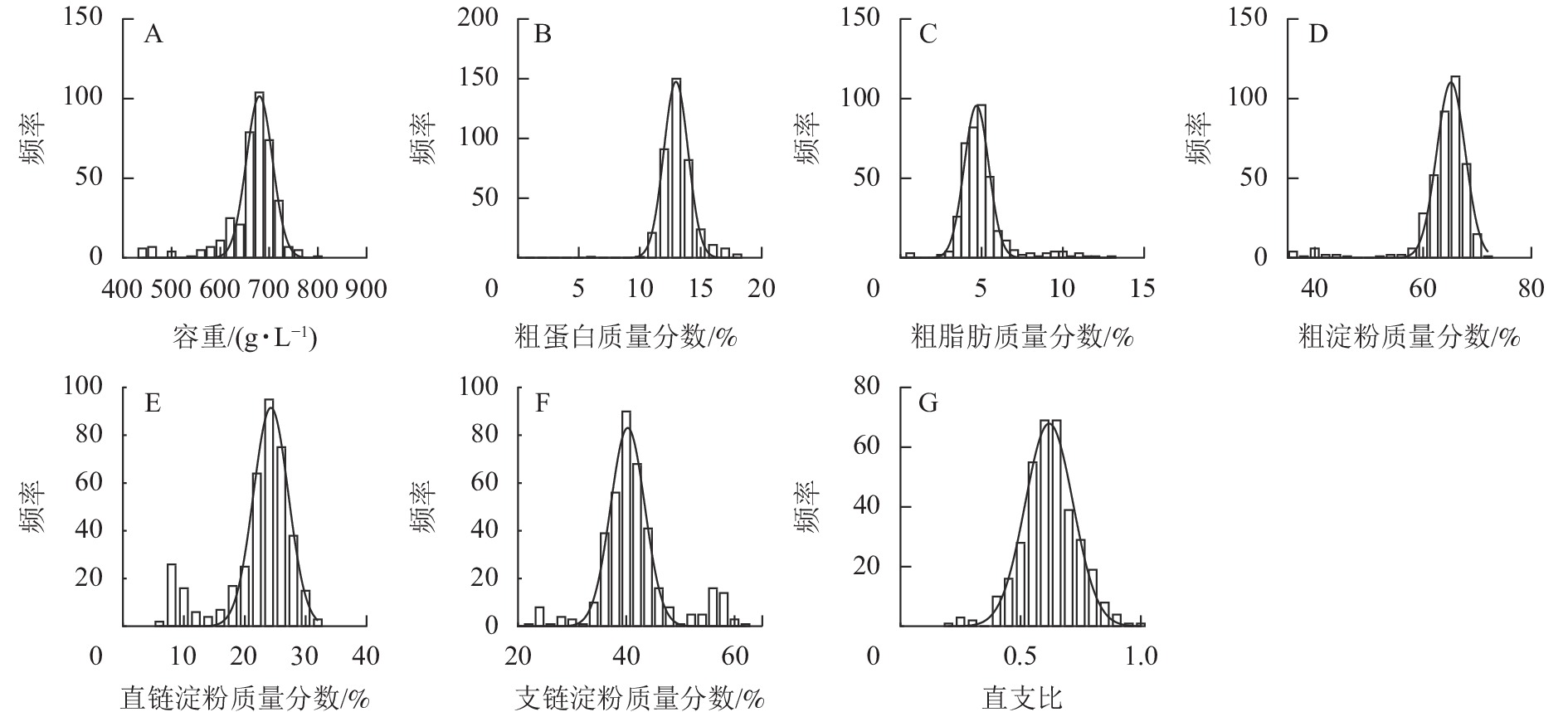
Objective As an important factor of quality traits in national maize standard regional tests, test weight is a complex quantitative trait, and its influencing factor and regulatory mechanism is still unclear. Quality traits such as starch, protein, and fat content are important factors affecting test weight, but the relationship between them is still unclear. Method This research determined the test weight, starch, crude protein, gross fat, and amylose content of 517 maize germplasms mainly composed of local maize germplasm resources in Zhejiang Province. On the basis of correlation analysis, the kernels of four germplasms with higher test weight, higher starch content, lower protein content, lower fat content, and four germplasms with opposite phenotypes were selected for RNA-Seq analysis. Result By correlation analysis, this research found there was a significant positive correlation between test weight and starch content, while a negative correlation was found between test weight and protein or fat content. RNA-Seq analysis was performed for the extreme germplasm, a total of 159 differentially expressed genes were screened between 2 groups, and 8 candidate genes related to carbon metabolism or amino acid biosynthesis were used for further analysis. The expression difference of these genes was consistent with the change of test weight in different inbred lines by RT-qPCR. Conclusion The correlation between test weight and other quality traits was preliminarily clarified, providing superior germplasms and 8 candidate genes that play important roles in carbon reduction, endosperm development, starch metabolism, cellular metabolism, and seed fat accumulation for the selection of new high-quality maize cultivars. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 40 ref.]
Correlation research between rice quality traits and seed vigor in different types of rice cultivars
2024, 41(4): 679-687.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240214
Abstract:
Objective The level of seed vigor is closely related to crop emergence performance, population quality, yield and quality potential. By studying the correlation between rice quality traits and seed vigor in different types of Oryza sativa cultivars, this research aims to preliminarily reveal the effect of seed vigor on rice quality, and screen out high-quality rice cultivars to provide guidance for agricultural production. Method 12 conventional japonica rice and 12 hybrid indica rice cultivars were used as test materials to determine seed vigor and quality indexes such as brown rice rate, whole semolina rate, chalky whiteness, transparency, gel consistency, straight-chain starch quality fraction and protein quality fraction under different germination conditions, and analyze their differences and correlations to investigate the relationship between seed vigor and quality traits. Result There were significant differences in seed vigor and rice quality among different rice types and cultivars, and cultivars with excellent quality had significant advantages in brown rice rate, whole semolina rate, chalky whiteness, transparency and gel consistency. Among them, ‘Shennong 702’ ‘Shennong 9816’ ‘Liangyou 0367’ ‘Y-liangyou 900’ ‘Jingliangyou Huazhan’ had germination indexes of 23.8 − 27.2, vigor indexes of 2.8 − 3.7, brown rice rates of 79.0% − 82.7%, and whole semolina rates of 54.4%−66.0%, which had higher seed vigor and better quality compared with other rice cultivars. There was a significant positive correlation between rice quality and vigor index, in which the correlation between the whole refined rice rate and vigor index reached a significant level in both conventional japonica and hybrid indica rice. Conclusion Rice cultivars with high seed vigor have better rice quality. Considering all the indexes, ‘Shennong 9816’ ‘Shennong 702’ ‘Liangyou 0367’ ‘Jingliangyou Huazhan’ ‘Y-liangyou 900’ can be promoted for cultivation and application. [Ch, 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 688-695.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230521
Abstract:
Objective The aim is to investigate the tolerance of weedy rice (Oryza sativa f. spontanea) seeds to different stress environments in Zhejiang Province, and to provide evidence for genetic improvement of rice varieties and prevention and control of weedy rice. Method The seeds of weedy rice and cultivated rice (O. sativa ‘Nangeng 46’) collected from the same field in Zhejiang Province were used as material. The germination of seeds and seedling quality were studied under indoor standard germination condition, salt stress (0.15 mol·L−1 NaCl), drought stress (simulated with 15% PEG 6000), flooding stress (simulated with 5 cm water depth), and low temperature stress (at 15 ℃). The antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde (MDA) content of seedlings under drought and salt stress were measured. Result Under standard germination conditions, the germination indicators of weedy rice seeds were significantly better than those of cultivated rice (P<0.05). Different environmental stresses inhibited seed germination and affected seedling quality. Under salt stress, the germination rate and germination index of weedy rice seeds were significantly higher than those of cultivated rice, and the seedling length was lower than that of cultivated rice (P<0.05). Under drought stress, the germination potential, germination rate, and germination index of weedy rice seeds were significantly higher than those of cultivated rice (P< 0.05). After drought and salt stress treatment, the activities of catalase, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase in weedy rice seedlings were significantly higher than those in cultivated rice , and the MDA content was significantly lower than that in cultivated rice (P<0.05). Under flood stress, the germination potential and germination index of weedy rice were significantly lower than those of cultivated rice (P<0.05). Under chilling stress, there was no significant difference in germination indicators between weedy rice and cultivated rice seeds, and the quality of weedy rice seedlings was better than that of cultivated rice. Conclusion The germination ability of weedy rice in Zhejiang Province is significantly stronger in suitable environments than that of cultivated rice in the same region, but it is sensitive to flooding stress. Compared with cultivated rice, weedy rice is more tolerant to drought and salt stress, which may be related to its stronger antioxidant activity. [Ch, 6 tab. 32 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 696-705.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230498
Abstract:
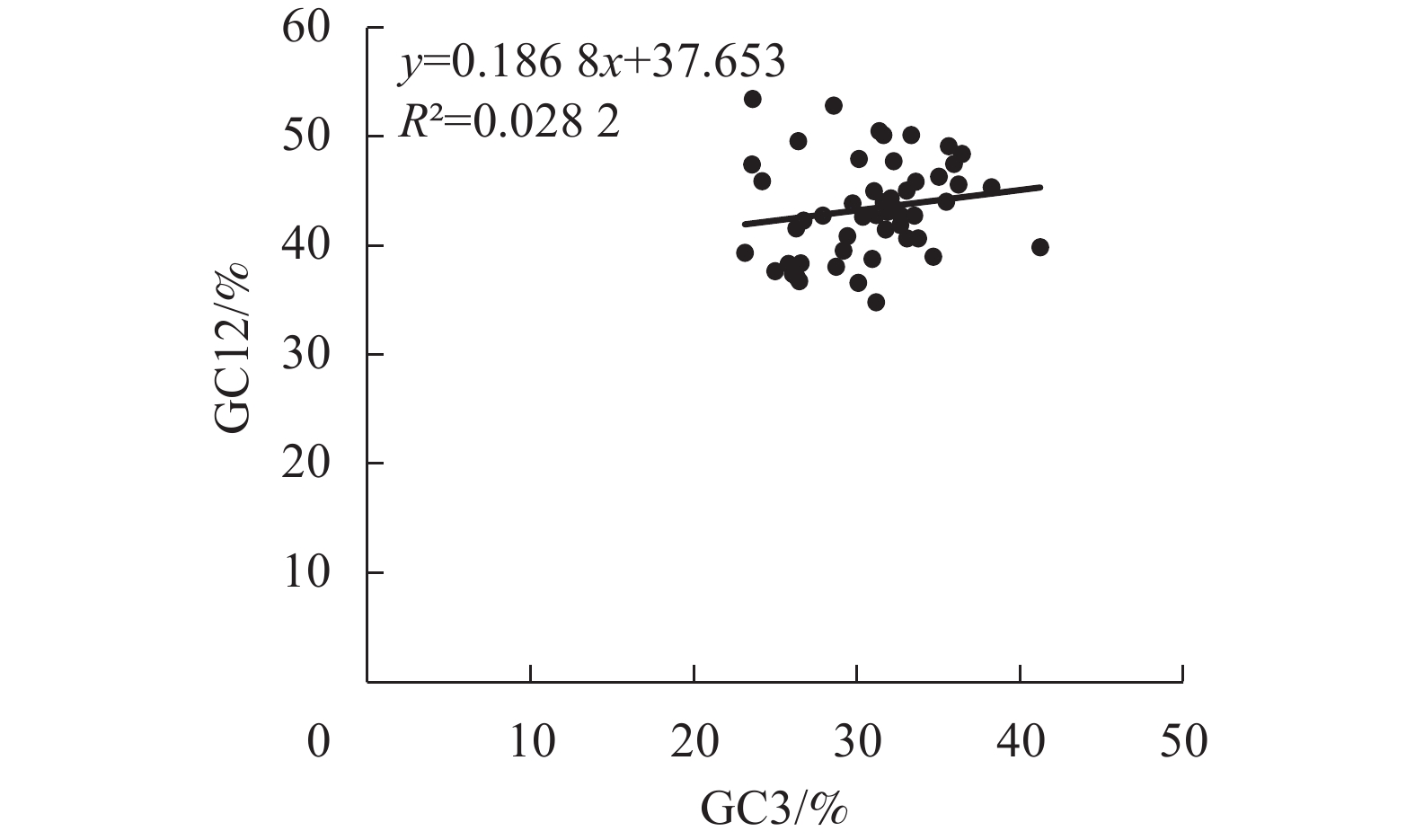
Objective The objective is to explore the preferred usage patterns of chloroplast genome codon in Dendrocalamus farinosus, analyze the main reasons affecting the codon usage preference of D. farinosus, and determine the optimal codon, so as to provide reference for chloroplast genomics research in Bambusoideae plants. Method According to the GenBank login number MZ681865.156, 85 chloroplast gene sequences of D. farinosus were downloaded from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database in the United States. CodonW, CUSP and R language software were used to analyze the effective number of codons (ENC), adaptation index (CAI) and relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU). Correspondence analysis of RSCU was performed and the codons were sorted based on ENC and RSCU values. Result The average ratio of guanine (G) and cytosine (C) in the chloroplast genome codon (GC ratio) was 39.48%, with GC1 (47.69%)>GC2 (39.70%)>GC3 (31.05%), and the last codon base preferred to end in A/U. The majority of ENC value was above 35, and CAI value was 0.167, so the codon preference was weak. Neutral plot analysis, ENC-plot and PR2-plot analysis showed that natural selection was the main factor affecting the codon preference of the chloroplast genome of D. farinosus. A total of 18 codons, including GCA, GCU, UUC, and GGU, were identified as the optimal codons for the chloroplast genome of D. farinosus. Conclusion Natural selection is the main factor contributing to the codon preference of the chloroplast genome in D. farinosus, and 18 optimal codons such as GCU, GAU, and GGU are screened for the chloroplast genome of D. farinosus. [Ch, 5 fig. 5 tab. 30 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 706-714.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230614
Abstract:
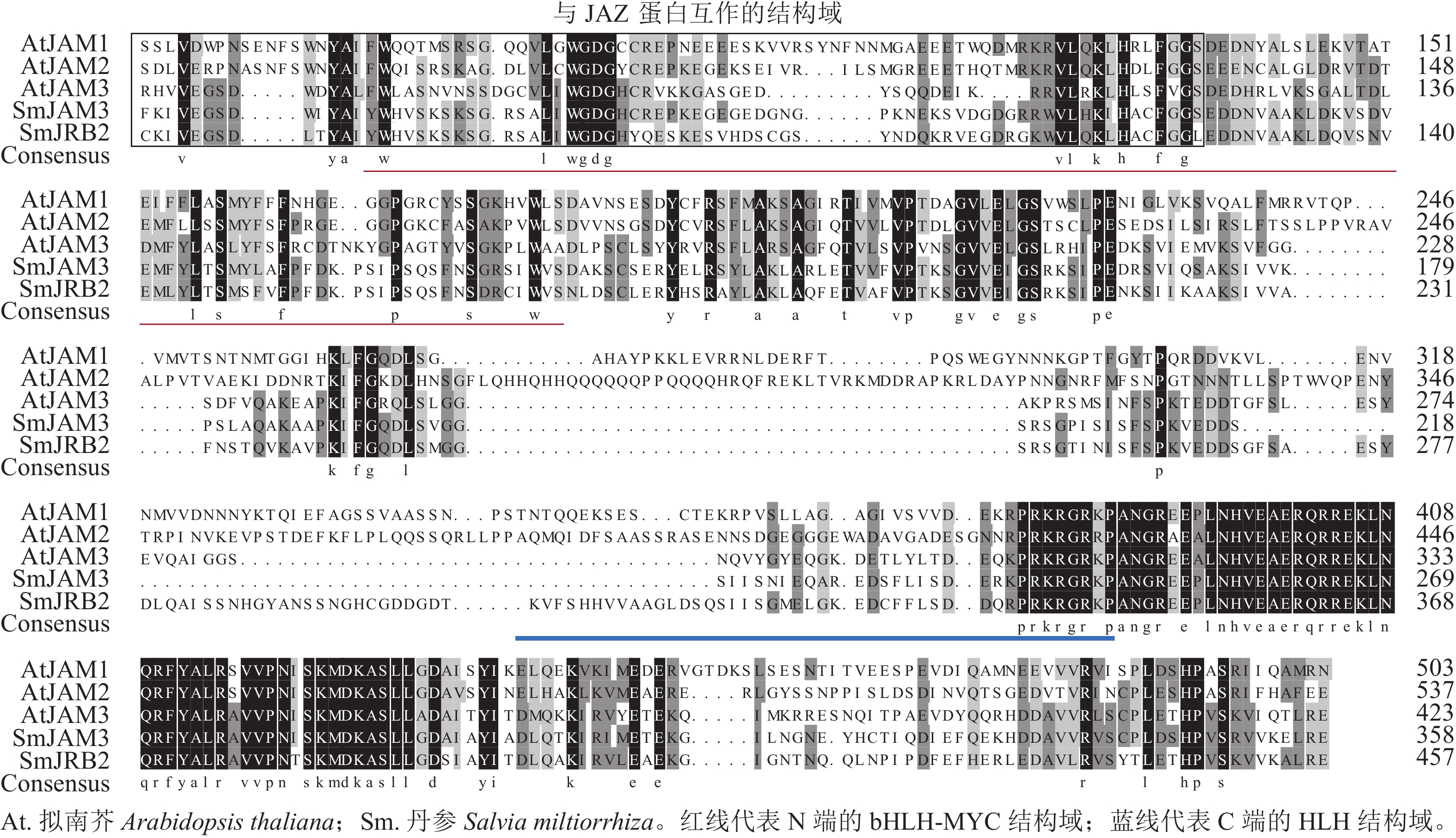
Objective Salvia miltiorrhiza is a traditional Chinese medicine used in clinical treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Elucidating the molecular regulation mechanism of metabolism and synthesis of pharmacophore of S. miltiorrhiza can provide scientific basis for breeding new varieties of S. miltiorrhiza with high quality. Method The transcriptional factor SmJRB2 in response to methyljasmonic acid (MeJA) induction was picked out based on comparative transcriptome mining. The coding sequence of this gene was cloned using homologous cloning technology and analyzed by bioinformatics. The tissue expression and MeJA induced expression of SmJRB2 gene were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The function of SmJRB2 gene was identified based on the genetic transformation technology of S. miltiorrhiza mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Result The results showed that SmJRB2 encoded 501 amino acids and belonged to the MYC transcription factor of bHLH transcription factor family. The expression of SmJRB2 gene was the highest in leaves and principal root. SmJRB2 gene was intensively induced by MeJA and its highest expression level peaked at the induction time of 4.0 h. Overexpression of SmJRB2 promoted the accumulation of tanshinones and suppression of SmJRB2 gene decreased the biosynthesis of tanshinones. Conclusion SmJRB2 is a positive regulator of tanshinone metabolic synthesis. [Ch, 8 fig. 1 tab. 40 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 715-723.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230567
Abstract:
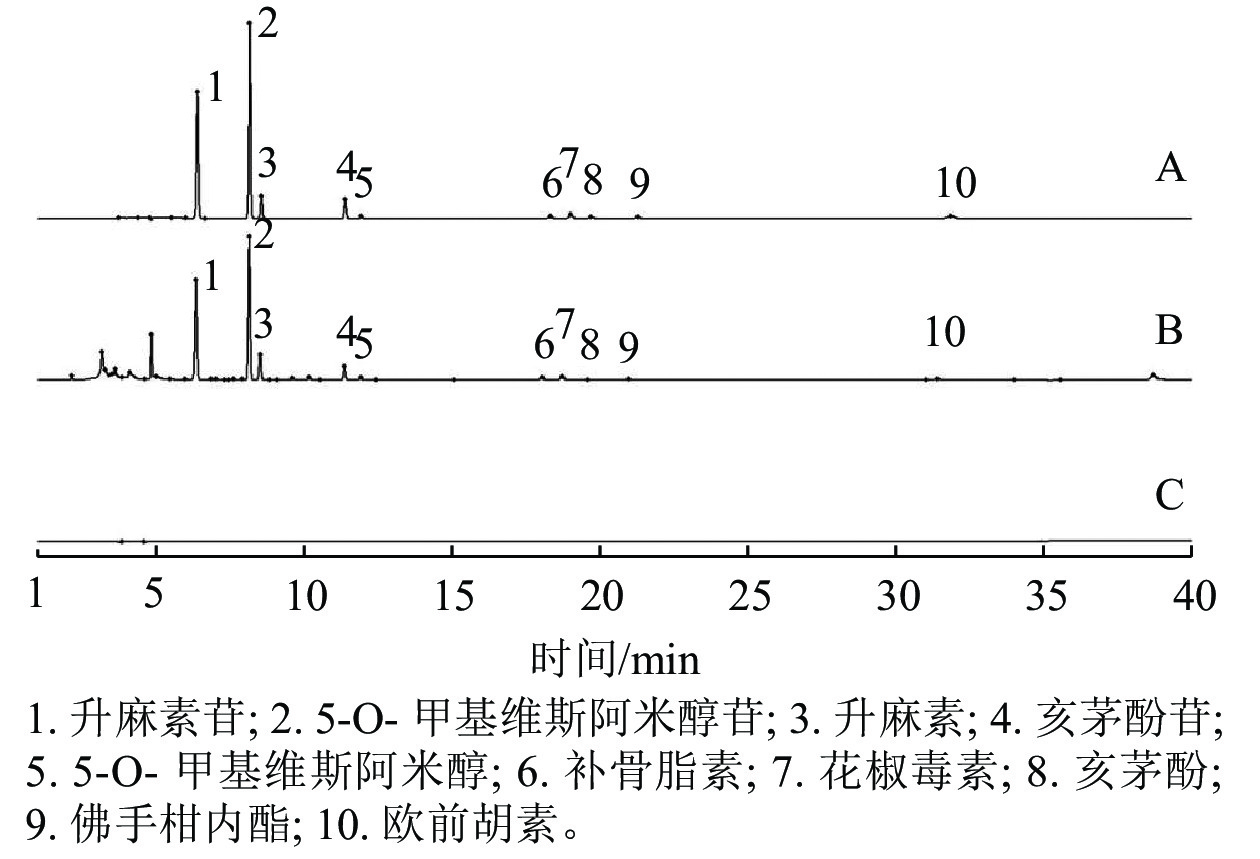
Objective To establish a method for quantitative analysis of multi-index components in Saposhnikoviae radix (Saposhnikovia divaricata), and for comprehensive quality evaluation of the medicinal materials from different areas, using the contents of multiple-index components as evaluation indexes, and the contribution of different components to the anti-inflammatory activity. Method The concentrations of 6 chromones and 4 coumarins from Saposhnikoviae radix were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The quality was comprehensively evaluated using cluster analysis and principal component analysis. The correlations between 10 chemical components and their anti-inflammatory activities were analyzed in a lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage inflammation model in RAW 264.7 mice. Result The 10 kinds of chemical components had good linear relationship, accuracy, and separation in their respective ranges, respectively. 17 batches of samples were grouped into 4 categories by cluster analysis and principal component analysis. The quality of 2-year-old S. divaricata grown in Inner Mongolia (S5) and Jilin (S8 to S11) were relatively better. 17 batches of S. divaricata alcohol extracts differentially inhibited NO, IL-6, and IL-1β secreted by lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin, 5-O-methylvisammioside, cimifugin, sec-O-glucosylhamaudol, 5-O-methylvisamminol, and imperatorin were positively correlated with anti-inflammation. The anti-inflammatory effect of S. divaricata is the result of the combined action of several components, and the correlation degrees among prim-O-glucosylcimifugin, 5-O-methylvisammioside, cimifugin, sec-O-glucosylhamaudol, and 5-O-methylvisamminol with three cellular indicators of inflammation (NO, IL-6, and IL-1 β) were over 0.8, which were the main material basis for the anti-inflammatory activity, according to the gray correlation analysis. Conclusion A comprehensive evaluation model of the quality of S. divaricata based on biological activity and combining the anti-inflammatory activity and gray correlation analysis was established, which provided a new method and scientific basis for the establishment of quality standards for a comprehensive evaluation of the quality of S. divaricata. [Ch, 3 fig. 7 tab. 30 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 724-734.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240138
Abstract:
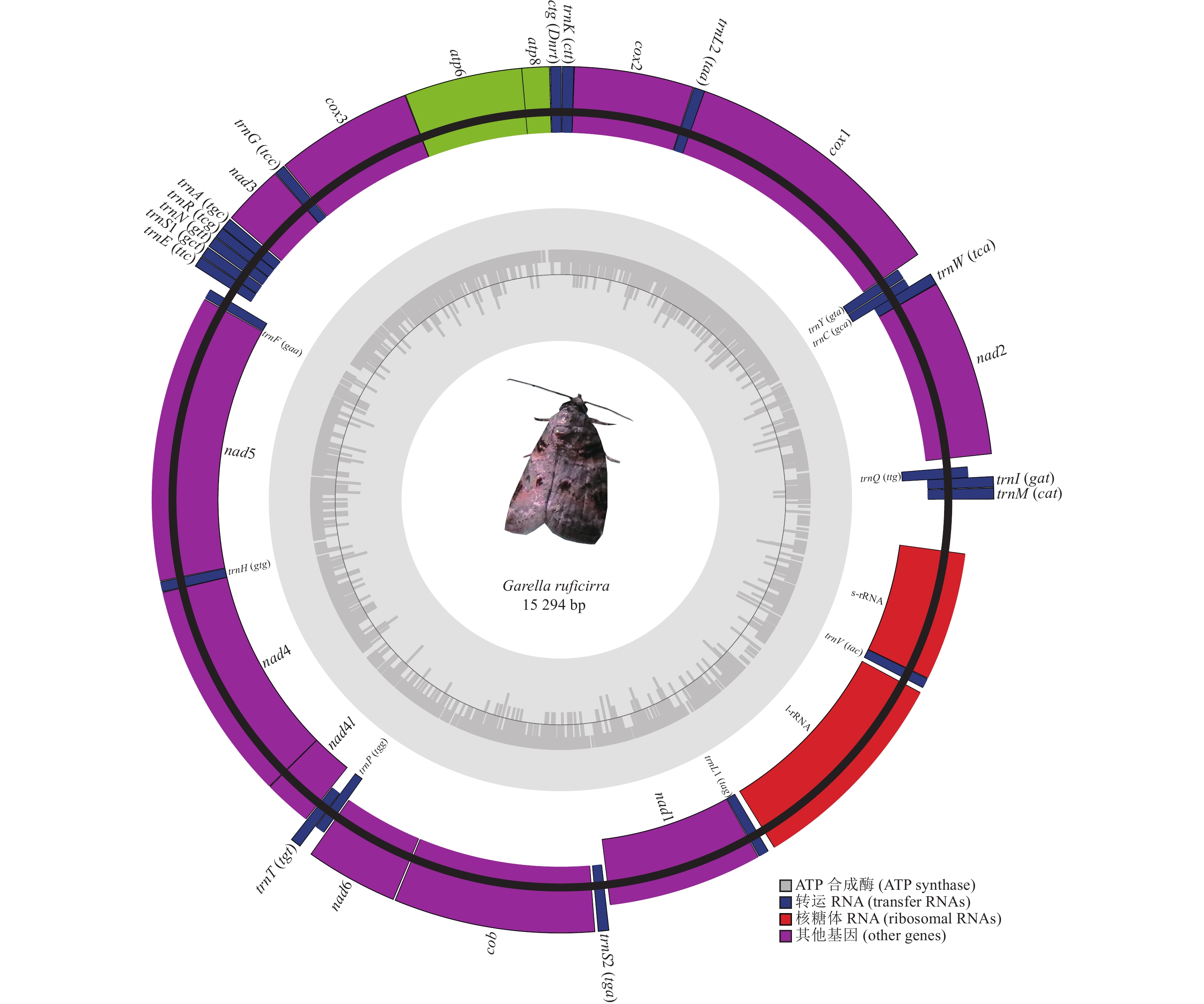
Objective This study, with a comprehensive sequencing and analysis of the mitochondrial genome of Garella ruficirra as well as an investigation into the phylogenetic position of Noctuidae through mitochondrial genome sequencing, is aimed to offer a valuable reference for delving into the phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary processes within the Noctuidae as well as exploring the phylogenetic relationship and evolutionary process of Noctuidae. Method First, the Illumina sequencing technique was employed to sequence the complete mitochondrial genome of G. ruficirra, allowing for the analysis of its overall characteristics and base composition. Subsequently, a phylogenetic tree encompassing mitochondrial genomes from 5 genera of Noctuidae, comprising 12 species, was constructed using both maximum likelihood and Bayesian methods so as to facilitate the examination of the phylogenetic relationships within the Noctuidae. Result The circular mitochondrial genome of G. ruficirra spanned 15 294 base pairs and encompasses 13 protein synthesis-related genes, 22 transfer RNA genes, and two ribosomal RNA genes and its gene arrangement conformed to the standard configuration observed in Lepidoptera mitogenomes, featuring a region rich in adenine and thymine, an A+T content of 80.53% and a significant AT bias. The gene order of trnM-trnI-trnQ in G. ruficirra aligned with other Noctuidae species and the majority of Lepidoptera with ATN sequences serving as initiation codons for all 13 protein-coding genes. While trnS1 lacked a DHU arm, the remaining tRNA genes exhibited a typical cloverleaf-shaped structure. According to the study of mitochondrial genome, Garella was most closely related to Nycteola and least closely related to Pseudoips among the 5 genera. Conclusion Gene rearrangement was evident in the mitochondrial genome of G. ruficirra. Phylogenetic analyses, indicating that the clustering of G. ruficirra and G. musculana samples was within a single clade. This study has furnished valuable insights into the evolutionary patterns of Garella and offered a foundational framework for investigating the phylogeny and evolution of Noctuidae within the Lepidoptera order. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 47 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 735-743.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230581
Abstract:
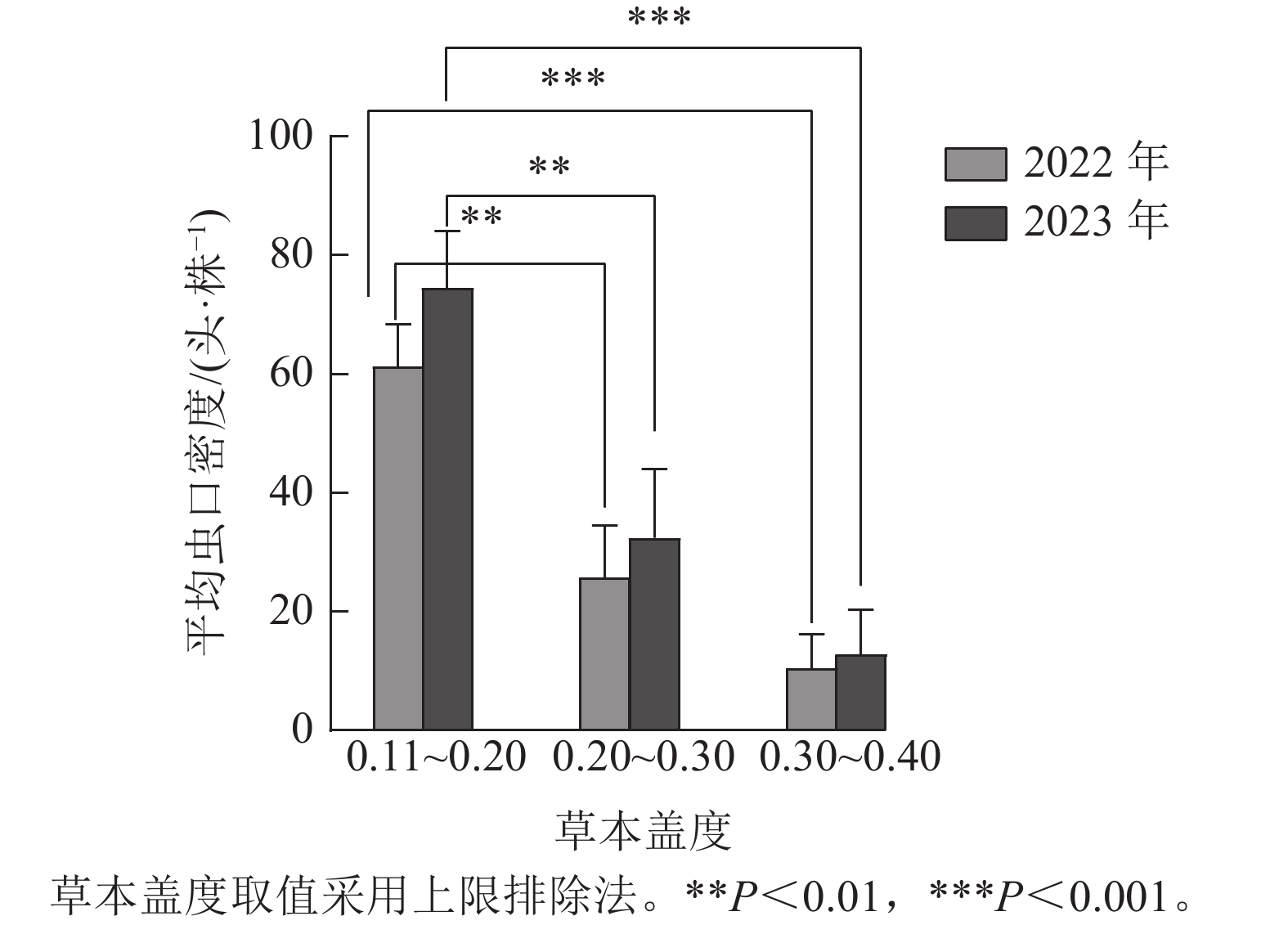
Objective The objective is to study the relationship between the occurrence of Acantholyda posticalis larvae and stand and site factors, and screen out the key factors affecting the occurrence of A. posticalis larvae. Method 21 sample plots were set up from 2022 to 2023 in the main occurrence areas of the larvae in Luoshan National Nature Reserve of Ningxia to investigate the larval population density of A. posticalis, stand factors and site factors. Using stepwise regression analysis, the key factors affecting the average population density of A. posticalis larvae were screened out. The relationship between mean population density and key factors was obtained by variance analysis and correlation analysis. Result By stepwise regression analysis, it was found that herb coverage, crown width, canopy density, and slope position were the key factors affecting A. posticalis larval occurrence. A linear prediction equation for the average larval population density was established based on the key factors. Among the 4 key factors selected, herb coverage and slope position inhibited the larval occurrence, while crown width and canopy density promoted the larval occurrence. Conclusion Larvae of A. posticalis are easy to occur in uphill forest areas with low herb coverage, high canopy density and crown width in the understory. It is suggested that these forest areas be taken as the key areas for prevention and control, and herb coverage be adjusted to above 0.3, crown width below 2.5 m and canopy density below 0.7, so as to realize the ecological control of the larval population of A. posticalis in this area. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 39 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 744-751.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230588
Abstract:
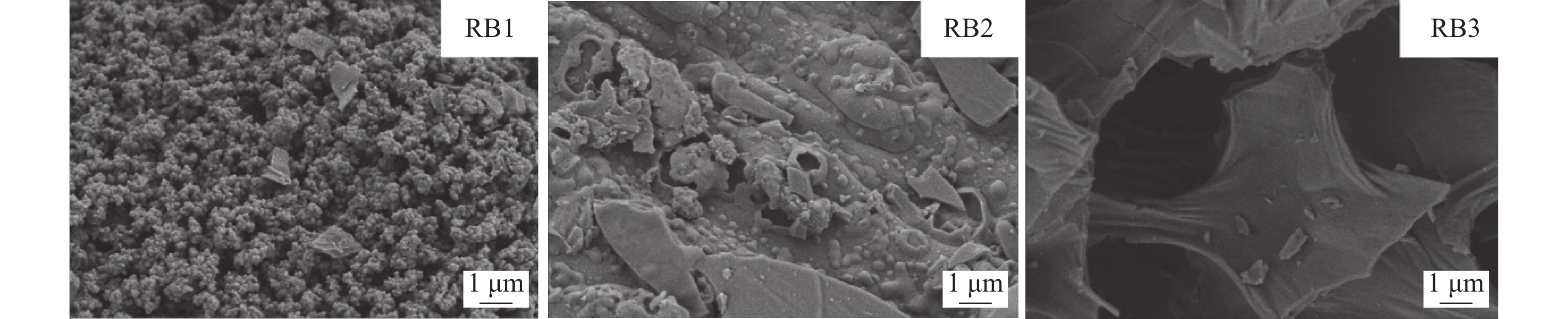
Objective The impact of different particle sizes of biochar on the physicochemical properties and its remediation efficacy in mercury-contaminated rice soil was investigated, aiming to establish a scientific foundation for mitigating methylmercury accumulation in rice within mercury-polluted regions and ensure food safety. Method Rice straw was utilized as the feedstock for biochar production. The rice straw biochar with different particle sizes (< 0.5, 0.5 − 1.0, 1.0 − 2.0 mm) were obtained through sieving, and the structural characteristics of various biochar were analyzed using element analyzer, specific surface analyzer, FTIR spectrometer and scanning electron microscope. The impact of different biochar particle sizes on the accumulation of methylmercury in rice was investigated through a rice pot experiment. Result (1) With the reduction of particle size, the surface morphology of biochar had significant changes. There was an increase in the specific surface area and pore volume of biochar, as well as an enhancement in the strength of C—O, —OH and —COO oxygen-containing functional groups. (2) Compared with the control group, the application of biochar with different particle sizes reduced the bioavailability of methylmercury in soil, and the enrichment of methylmercury in rice tissues decreased. The application of biochar with the smallest particle size demonstrated the most significant effect, the addition of biochar with particles <0.5 mm reduced the mass fraction of methylmercury in polished rice grain by 47.01% compared to the control. (3) The application of biochar increased the mass fraction of methylmercury in the rhizosphere soil of rice, and this positive promoting effect became more obvious with the decrease of the particle size of biochar. Conclusion The reduction of biochar particle size can enhance the remediation capacity of biochar in mercury-contaminated rice soil, decrease the accumulation of methylmercury in rice, and mitigate the exposure risk of methylmercury. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 34 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 752-759.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230630
Abstract:
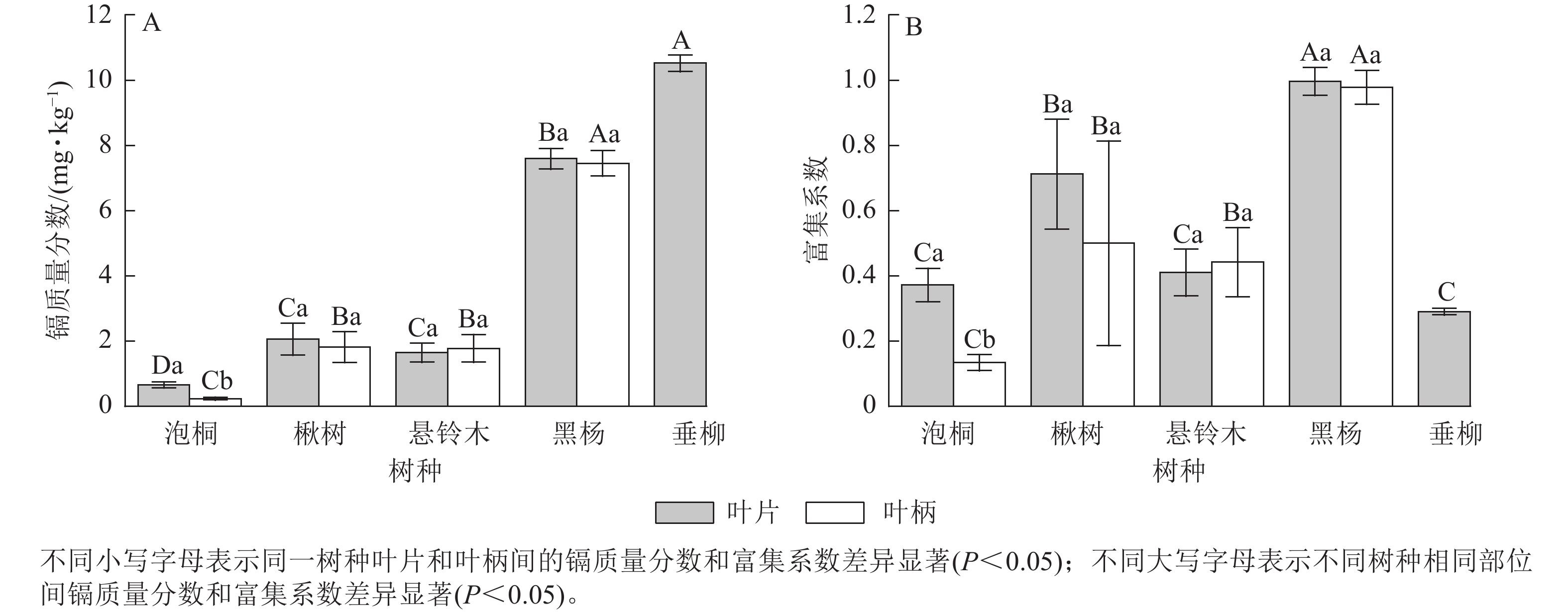
Objective While trees can accumulate heavy metals, their accumulation characteristics are currently unclear; this, to some degree, restricts the application of the technology of using trees to remediate heavy metal-contaminated soil. This study was designed to explore the cadmium (Cd) accumulation capacities of five greening tree species. Method The Cd accumulation characteristics of different parts of various greening trees (Paulownia fortunei, Catalpa bungei, Platanus acerifolia, Populus nigra, and Salix babylonica) planted in Cd-contaminated soil were analyzed, and the total amounts of Cd in the trees were determined. Result All the tested trees had a certain Cd accumulation capacity, and the cumulative amount of Cd per tree ranged from 43.01 to 886.28 mg·plant−1. Among the trees, S. babylonica had the highest accumulation amount of Cd (886.28 mg·plant−1), followed by Populus nigra (392.51 mg·plant−1). The Cd accumulation ability varied among different tree species and parts, with concentration coefficients ranging from 0.07 to 0.56, 0.10 to 1.24, 0.06 to 1.04, 0.32 to 1.58, and 0.06 to 0.97 for different parts of Paulownia fortunei, C. bungei, Platanus acerifolia, Populus nigra, and S. babylonica, respectively. The concentration coefficients of most parts (except for the stem bark) of Populus nigra were higher than those of the other trees. The Cd concentrations in the root bark, stem bark, and branch bark of all trees were significantly higher than those in their corresponding root wood, stem wood, and branch wood (P<0.05). A highly significant positive correlation was found between the Cd contents in different parts of trees and those in the soil (P<0.01). Conclusion The tested tree species accumulated Cd mainly in their branches and stems. Paulownia fortunei, C. bungei, and Platanus acerifolia accumulated Cd mainly in their branches, while Populus nigra and S. babylonica accumulated Cd mainly in their stems. Populus nigra and S. babylonica displayed higher Cd concentrations, which are the preferred tree species for the remediation of Cd-contaminated soil. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 23 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 760-768.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230522
Abstract:
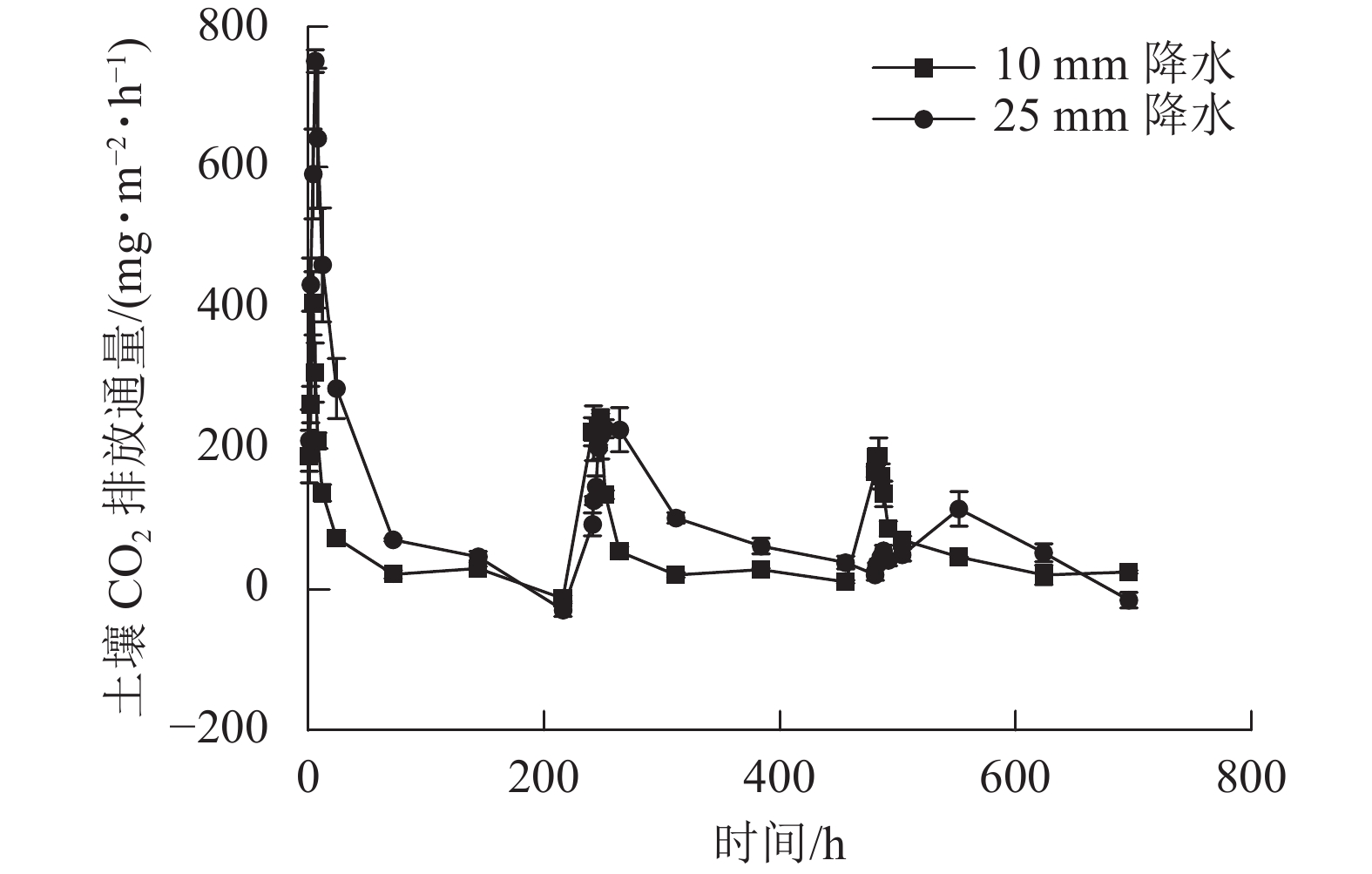
Objective The objective of this study is to explore the response of soil CO2 emission flux from calcareous soil to frequent dry-wet alternation in farmland of karst areas in southwest China. Method Taking calcareous soil in karst farmland as the research object, two dry-wet alternation intensities (simulated precipitation of 10 and 25 mm) were designed, with a dry-wet alternation cycle of 10 days as one cycle process, to investigate the response of soil respiration to dry-wet alternation in karst farmland. Result The intensity of dry-wet alternation significantly affected soil CO2 emission flux and total soil CO2 emissions (P<0.05). Under two different dry-wet alternation intensities, soil CO2 emission flux reached its maximum shortly after water was applied, and then gradually decreased. For the 10 mm dry-wet alternation intensity, there was no significant difference between soil CO2 emission flux and total soil CO2 emissions under different cycles. However, for the 25 mm dry-wet alternation intensity, the difference between soil CO2 emission flux and total soil CO2 emissions under most cycles was significant (P< 0.05). Correlation analysis revealed that the correlation between soil water content and soil CO2 emission flux decreased continuously under the multiple cycles of dry-wet alternation. Conclusion The intensity and process of dry-wet alternation are important factors affecting soil respiration release in karst farmland. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 64 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 769-777.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230545
Abstract:
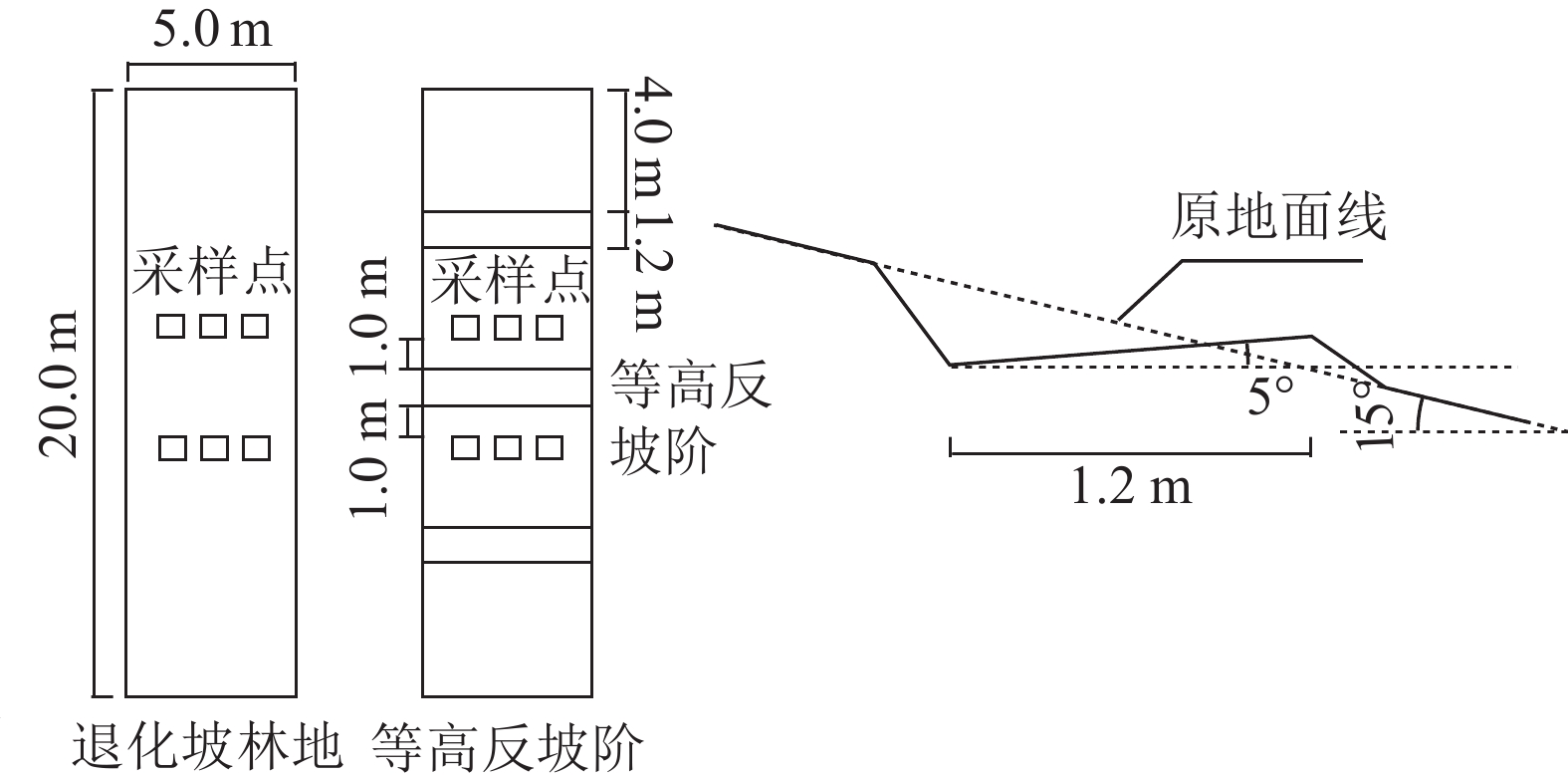
Objective The aim is to reveal the mechanism of ecological restoration by analyzing the effects of contour reverse-slope terrace on soil nutrients and enzyme activities during the restoration of degraded slope forest . Method The degraded Pinus yunnanensis slope forest land in Yizhe minor watershed of Songhuaba water source area in Kunming City was taken as the research object. 1-year and 10-year contour reverse-slope terrace preparation trials were set up, with the original slope as a control (ck). Soil nutrients contents and enzyme activities above and below the terrace, as well as those at different soil depths (0 − 10, 10 − 20, 20 − 30, and 30 − 40 cm) were systematically compared. Result (1) Contour reverse-slope terraces displayed a significant increase in soil nutrient contents (P<0.05), and the nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus increased by 15.3% − 236.2%. The nutrient levels below the terrace were higher than those above the terrace, and the increase in surface soil (0 − 10 cm) was the most significant. (2) The activities of soil urease, sucrase, acid phosphatase, and catalase in 10-year plots were significantly higher than those in ck (P<0.05), and the 4 enzyme activities increased by 3.7% − 587.5%. Soil enzyme activities below the terrace were still higher than those above the terrace. The increase in enzyme activity in the surface soil was significant (P<0.05). (3) Redundancy analysis showed that soil enzyme activities were better interpreted by soil nutrient indicators after soil preparation of contour reverse-slope terrace measures, with ck, 1-year plots, and 10-year plots accounting for 68.0%, 88.0%, and 92.7%, respectively. The positive correlation between soil nutrients contents and enzyme activities increased after soil preparation of contour reverse-slope terrace measures, and the range of correlation coefficients and the number of highly significant groups (P<0.01) increased from 0.26 − 0.99 and 1 group in ck to 0.78 − 1.00 and 15 groups in 10-year plots, respectively. Conclusion The implementation of contour reverse-slope terrace soil preparation in degraded slope forest can increase the accumulation of soil nutrient, stimulate soil enzyme activity, increase the coordination between the two in soil physiological and biochemical reaction, and ultimately improve soil quality. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 35 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 778-786.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230527
Abstract:
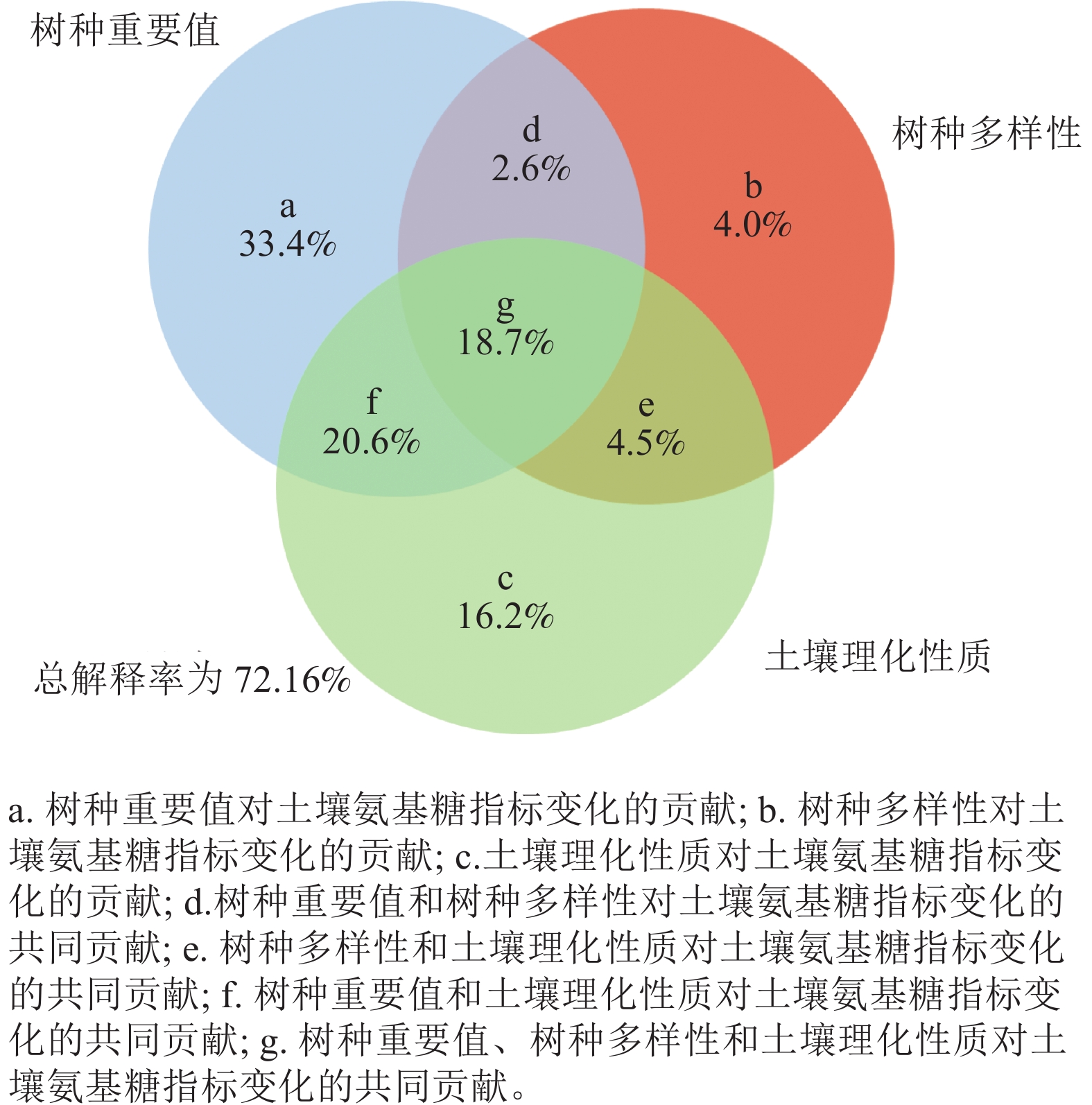
Objective Soil amino sugars are specific markers of soil microbial death residues, and play an important role in soil carbon and nitrogen sequestration. This study aims to explore the impact mechanism of tree species diversity and dominant tree species importance on soil amino sugars. Method The experimental forest farm of Northeast Forestry University was taken as the research sample, and 0 − 20 cm surface soil was used to measure glucosamine (Glu), galactosamine (Gal), muramic acid (Mur) and total amino sugar (TA). The diversity index of tree species and important values (IV) of dominant tree species were calculated. The main factors and contribution affecting soil amino sugars were determined through correlation analysis, redundancy analysis, and variance decomposition analysis. Result (1) The contents of Glu, Gal, Mur, TA were significantly positively correlated with those of total nitrogen (TN), electrical conductivity (EC), and organic carbon in soil (P<0.05). (2) The contents of Glu, Gal, Mur, TA were significantly negatively correlated with IV of Pinus tabulaeformis var. mukdensis (P<0.01). The contents of Glu, Gal, TA were negatively correlated with IV of Quercus mongolica (P<0.05). The contents of Glu and TA were significantly positively correlated with IV of Phellodendron amurense, Lonicera maackii, and Juglans mandshurica (P<0.05), while the contents of Ga, Mur and TA were significantly positively correlated with IV of Acer negundo (P<0.05). Redundancy analysis found that Pinus tabuliformis var. mukdensis and Q. mongolica were not conducive to the accumulation of amino sugars, while A. negundo, Phellodendron amurense, L. maackii, and J. mandshurica were conducive to the accumulation of amino sugars. (3) Variance decomposition analysis showed that the contribution of IV of tree species to changes in soil amino sugar content (35.4%) was significantly higher than that of tree species diversity (6.4%) and soil physical and chemical properties (17.2%). Conclusion The rich diversity of tree species maintained by increasing tree species such as A. negundo, L. maackii, Phellodendron amurense and J. mandshurica can better promote the accumulation of amino sugars in soil and improve soil carbon and nitrogen sequestration capacity. [Ch, 2 fig. 7 tab. 24 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 787-796.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230485
Abstract:
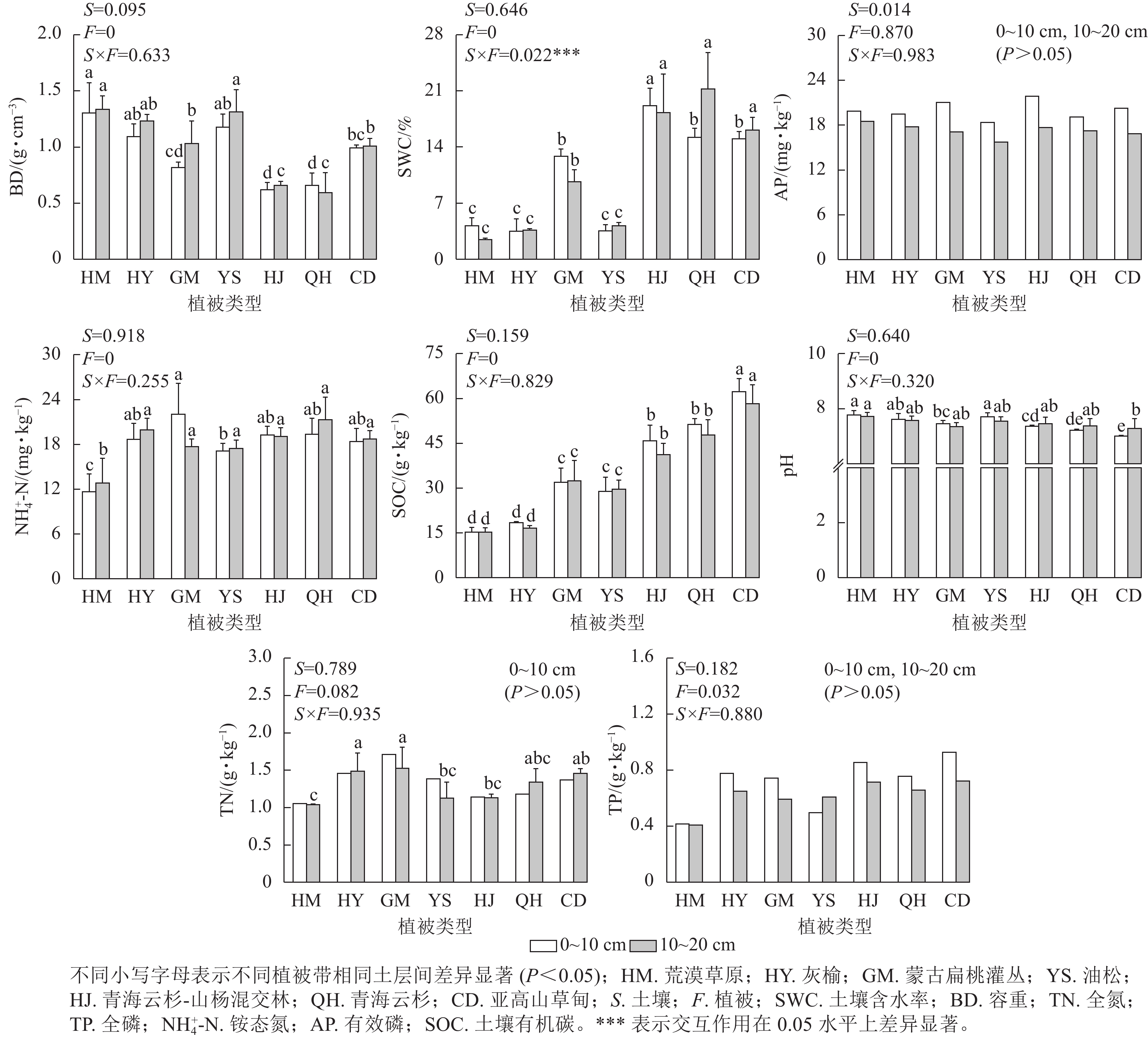
Objective The aim is to investigate the effects of soil physicochemical properties in different vegetation types on soil enzyme activity on the western slope of Helan Mountain, and to provide a reference basis for the changes of soil enzyme activity, nutrient cycling patterns and regulatory mechanisms in forest ecosystems in dry areas. Method The seven vegetation types on the western slope of Helan Mountain were selected as the research object, which were desert grassland, Ulmus glaucescens forest, Amygdalus mongolica shrub, Pinus tabuliformis forest, Picea crassifolia-Populus davidiana forest and Picea crassifolia forest and subalpine meadow respectively from 1 349 to 2 664 m. Three replicate plots were set up for each vegetation type, and soil physicochemical properties (water content, bulk density, pH, organic carbon, ammonium nitrogen, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and effective phosphorus) and enzyme activities (β-glucosidase, cellobiose hydrolase, α-glucosidase, β-xylosidase, sucrase, and amylase) were measured by field survey sampling and indoor analysis, with ANOVA and redundancy analysis. Result Soil water content and organic carbon mass fraction in the 0 − 10 and 10 − 20 cm soil layers of different vegetation zones at different altitudes showed an overall increasing trend with the rise in altitude; while soil bulk weight showed a decreasing trend with the rise in altitude in the 0 − 10 and 10 − 20 cm soil layers as a whole; soil total phosphorus, total nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, effective phosphorus, and pH did not show any significant change patterns in the 0 − 10 and 10 − 20 cm soil layers with the rise in altitude; soil enzyme activities in the 0 − 10 cm soil layer were higher than those in the 10 − 20 cm soil layer. The activities of soil enzymes were higher in the 0 − 10 cm soil layer than in the 10 − 20 cm soil layer in different vegetation zones; Soil cellobiose hydrolase and β-glucosidase showed an increasing trend with elevation in the 0 − 10 cm soil layer, amylase activity showed an increasing trend with elevation in the 0 − 10 cm soil layer, while α-glucosidase, β-xylosidase, and sucrase activities showed small and non-significant variations in different soil layers in different vegetation zones; Soil organic carbon, total phosphorus, ammonium nitrogen, and water content were the main factors affecting soil enzyme activities in the 0 − 10 and 10 − 20 cm soil layers. In the 0 − 10 and 10 − 20 cm soil layers, soil organic carbon, total phosphorus, ammonium nitrogen, and water content were the main influencing factors of soil enzyme activities. Conclusion Changes in altitudinal gradient caused significant changes in soil physicochemical properties on the western slope of Helan Mountain, which in turn regulated the changes in forest soil enzyme activity along the distribution of altitude and soil layers. Soil organic carbon, pH and water content were the main factors influencing soil enzyme activity, and could better explain the differences in the altitudinal gradient of soil enzyme activity. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 36 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 797-809.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230448
Abstract:
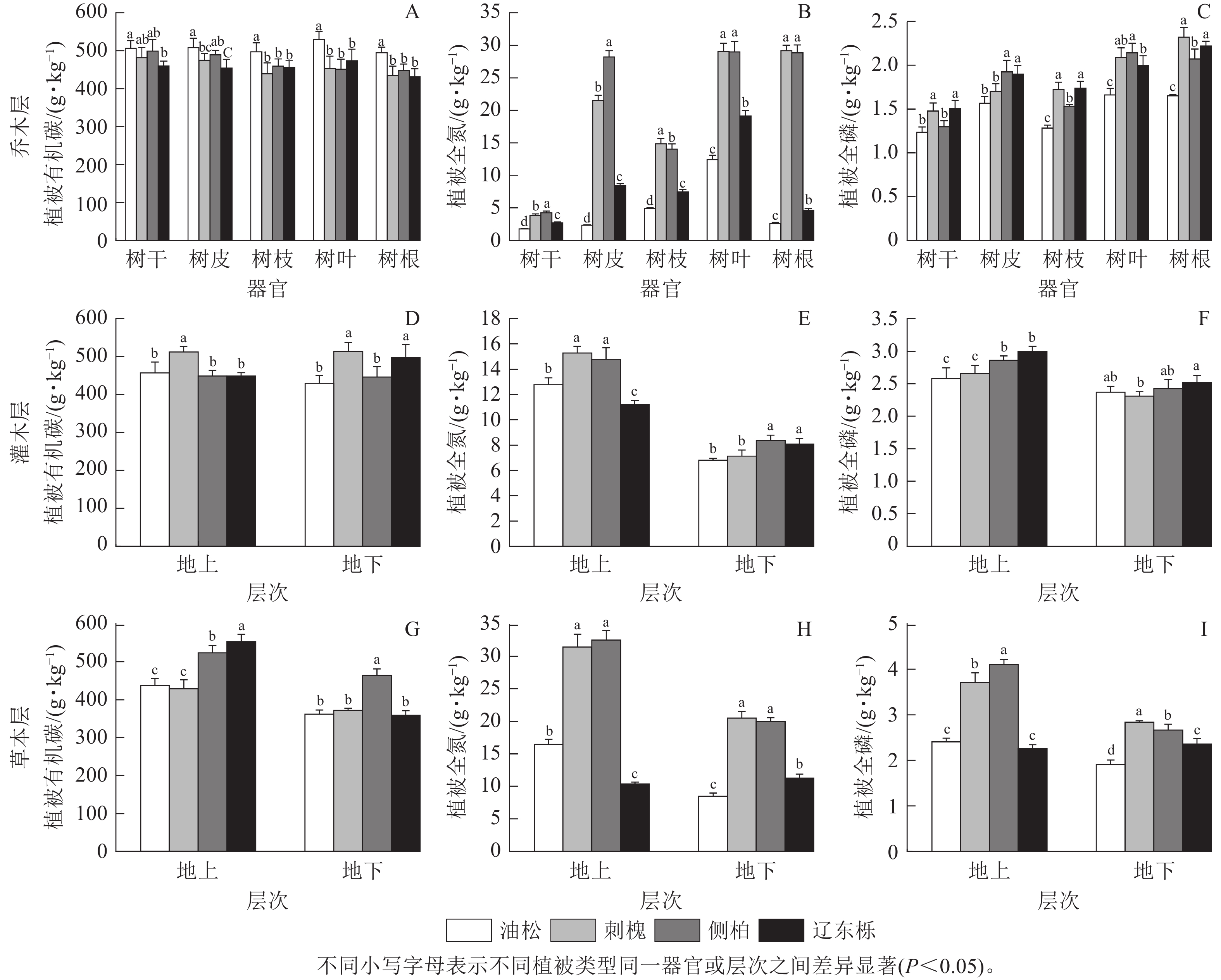
Objective Vegetation restoration is an important method of improving soil erosion and ecological environment in the Loess Plateau. This study aims to assess the impact of vegetation restoration on nutrient cycling and ecological service functions in ecosystem, and further clarify the stoichiometry and distribution characteristics of chemical elements in forest vegetation and soil, which is of great importance for selecting rational models of vegetation restoration. Method 4 typical vegetation restoration types were selected in the loess area of western Shanxi Province, namely Pinus tabuliformis plantation, Robinia pseudoacacia plantation, Platycladus orientalis plantation, and Quercus mongolica natural forest. The contents of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) in branches, leaves, trunks, barks, roots of the tree layer, as well as those in the aboveground and underground parts of the shrub layer, herbaceous layer, and 0 − 100 cm soil layers were determined respectively. The effects of vegetation restoration types on nutrient cycling and eco-stoichiometry were analyzed by single factor analysis of variance (ANOVA), minimum significant difference (MSD) and redundancy analysis (RDA). Result (1) Compared with other vegetation restoration types, the shrub layer and herbaceous layer in Q. mongolica forest had the highest biomass, with aboveground biomass of (8.62±0.78) and (5.91±0.18) t·hm−2 and underground biomass of (3.65±0.36) and (3.54±0.25) t·hm−2, respectively. (2) Q. mongolica natural forest had the highest C content, which was (552.90±19.33) g·kg−1, and the lowest N content, which was (10.36±0.30) g·kg−1. (3) There was a significant correlation (P<0.05) between C, N and P contents in plants and soil. Soil C and P ratio in Q. mongolica was the highest (15.22±0.28), while that in R. pseudoacacia was the lowest (8.28±0.26). (4) Mantel Test and RDA showed that there was a significant correlation between nutrients in soil and vegetation in plantation forests (P<0.05), but in Q. mongolica natural forest, the correlation was relatively small and the influence of tree layer on soil and vegetation stoichiometric characteristics was relatively weak. Conclusion Near natural afforestation can promote vegetation diversity and provide better ecosystem services. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 41 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 810-819.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230526
Abstract:
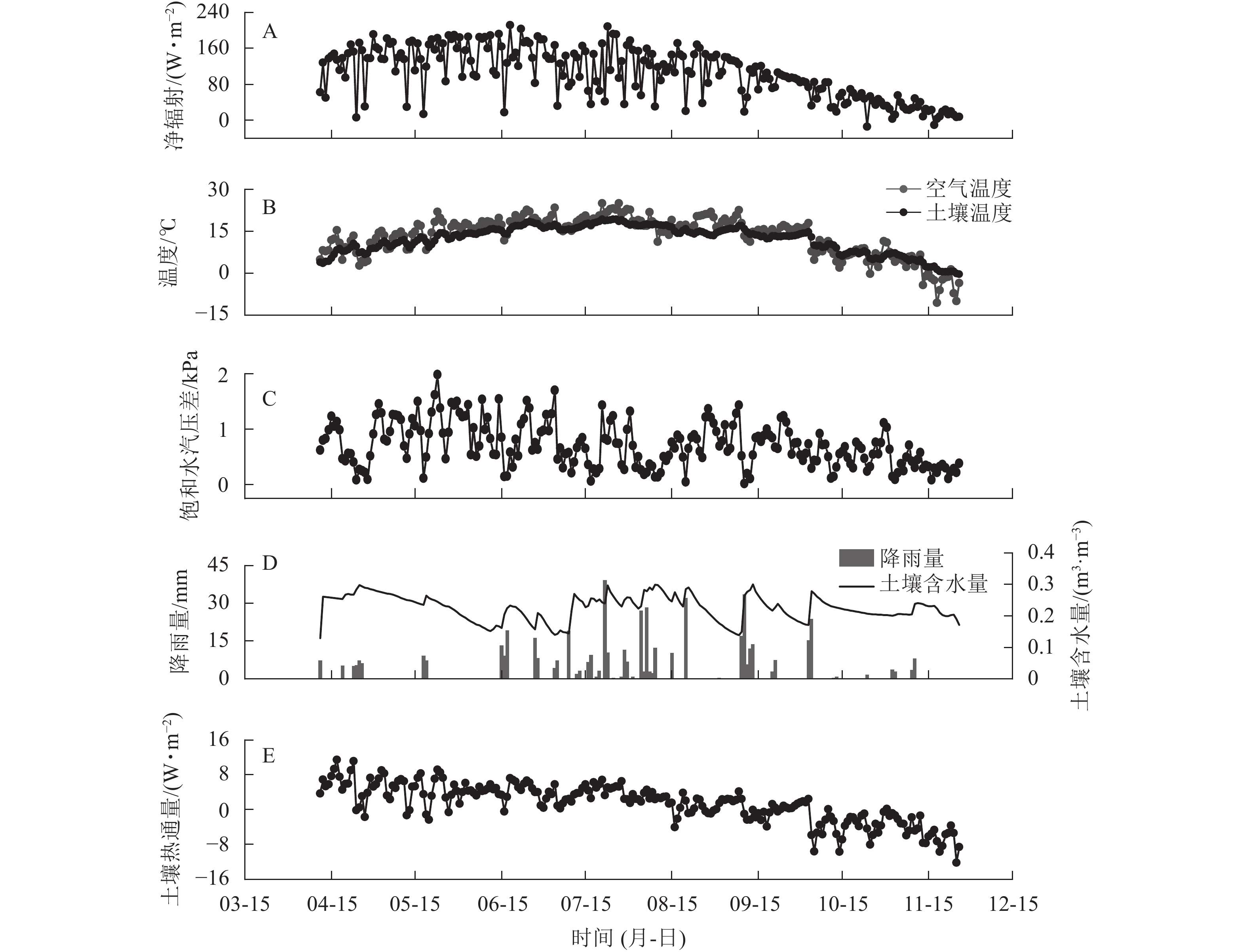
Objective The aim of this study is to analyze and compare the interpolation accuracy of different interpolation methods for missing latent heat flux value (FLE) in ecosystem. Method Eddy-covariance (EC) method was used to continuously monitor FLE and environmental factors of a typical natural deciduous broad-leaved forest ecosystem in Songshan National Nature Reserve, Beijing in 2019. Three interpolation methods, namely marginal distribution sampling method (MDS), linear regression method (REG), and artificial neural network method (ANN) were applied to interpolate the missing FLE data (randomly removed from 0.5 h data), and the relationship between measured FLE, interpolated FLE and environmental factors was analyzed. Result All the three interpolation results underestimated the measured FLE, among which ANN interpolation value was the closest to the measured one (R2=0.40). The measured FLE showed an exponential relationship with air temperature (Ta) and saturated vapor pressure deficit (DVP). MDS interpolated the relationship between FLE and Ta and DVP, and was the closest to the measured FLE. All the three interpolation methods changed the sensitivity of FLE to Ta and DVP to varying degrees. Conclusion The interpolation results of ANN are the closest to the measured values. The relationship between the results of MDS and environmental factors is the closest to the relationship between measured FLE and environmental factors. Therefore, appropriate interpolation methods should be selected in future research based on the research purpose. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 41 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 820-829.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230580
Abstract:
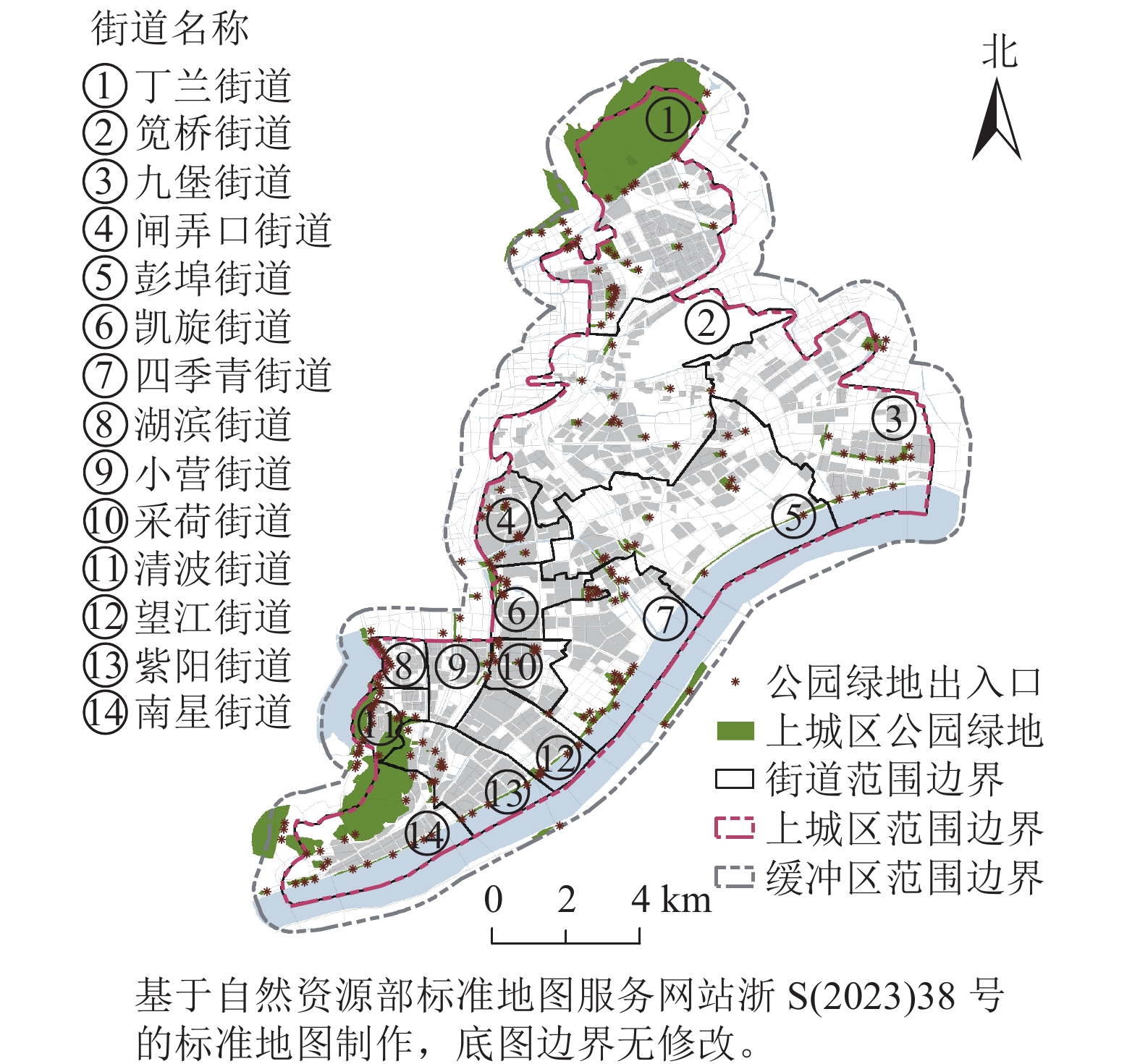
Objective To study the accessibility and social equity of urban park green spaces, and provide scientific basis for improving the quality of park green spaces and ensuring environmental justice for vulnerable groups. Method The park green spaces in Shangcheng District, Hangzhou City were chosen as the research object. By obtaining multi-source big data such as Mobile Signaling, the Public Comment, point of interest (POI) and so on, a database was constructed. The results of park quality evaluation, attraction algorithm, and Gaussian decay function were introduced to improve the two-step mobile search method, calculate the accessibility value of the elderly population at the residential community level to access park green spaces under the walking and public transportation modes. The Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze the differences in social equity and their causes. Result (1) There were significant differences in the quality of various types of parks in Shangcheng District, with 21.37% of park green spaces scoring higher than the average. (2) There were significant differences in accessibility levels among different transportation modes, with 65.98% of residential areas having extremely low accessibility levels under walking mode, while 33.81% had extremely low accessibility levels under public transportation mode. As the time threshold increased, there was a trend of high value diffusion and low value fading in accessibility. The accessibility of both types of transportation modes showed a clustering distribution, with a higher degree of clustering under public transportation modes. (3) There were social inequality in the park green spaces of Shangcheng District, with the highest level of unfairness in the walking mode, with a low fairness value of 74.8%. Overlay analysis showed that unfair areas were concentrated in the central part of the upper urban area, with a patchy distribution. Conclusion There is an imbalance between the supply of park green spaces and the demands of the elderly population. In the future, it is anticipated that during the planning and construction of urban green spaces, the quality of existing park green space services will be improved, transportation networks will be enhanced, the number of park green spaces will be moderately increased, and the living environment of residential communities will be improved. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 36 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 830-840.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230506
Abstract:
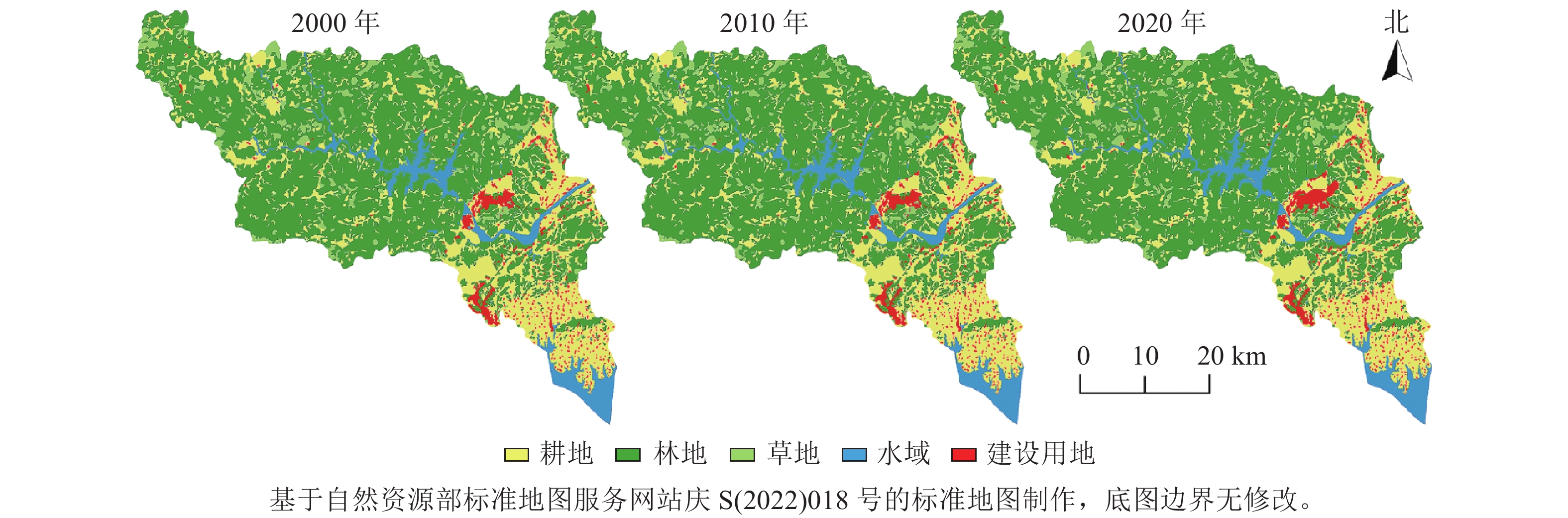
Objective This study, with an investigation into the impact of land use structure transformation in national key ecological functional areas on ecosystem service functions, is aimed to provide reference for the formulation of local economic and social development plans as well as the rational and effective allocation of land resources. Method With land use data collected of Taihu County in 2000, 2010, and 2020, a land use transfer matrix was established to analyze the law of land use changes whereas spatial quantitative calculations were performed based on the ecosystem service value (ESV) at the 600 m×600 m grid scale. Afterwards, spatial autocorrelation was employed to explore the spatiotemporal aggregation characteristics and hot and cold hot spot differentiation rules of ecosystem service value on land use changes. Result (1) The change in land use area in Taihu County from 2000 to 2020 was generally gradual with the proportion of construction land increasing by 1.43%, and the proportion of cultivated land decreasing by 1.00%; the area of grassland, forestland, and cultivated land from 2000 to 2020 was on the decline year by year while the construction land increased year by year. (2) The comprehensive land use change index was higher than 0 and the county’ s land use change structure was in the growth stage. (3) The past 20 years witnessed a decline in the ecosystem service value of all land use types in Taihu County with waters and forestland having the highest contribution rate to the total ecosystem service value of the study area. (4) Land use changes were positively correlated with the spatial distribution of ESV, mainly in low-low agglomeration areas and high-high agglomeration areas and such a correlation is enhanced with the changes in the land use structure, and in terms of the distribution of cold and hot spots in Taihu County, hot spots were mainly in the middle area while the cold ones are distributed in the northern area, with noticeable differentiation in the southern part. Conclusion Different land use types would cause significant differences in the quantity and spatial distribution of ESV in Taihu County, therefore, it is necessary to focus on the protection of water body area and the optimization of land resource allocation in the expansion of construction land in the south, and strengthen the optimization of land resource allocation for the sake of sustainable and effective ecological development of Taihu County. [Ch, 4 fig. 7 tab. 31 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 841-849.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230601
Abstract:
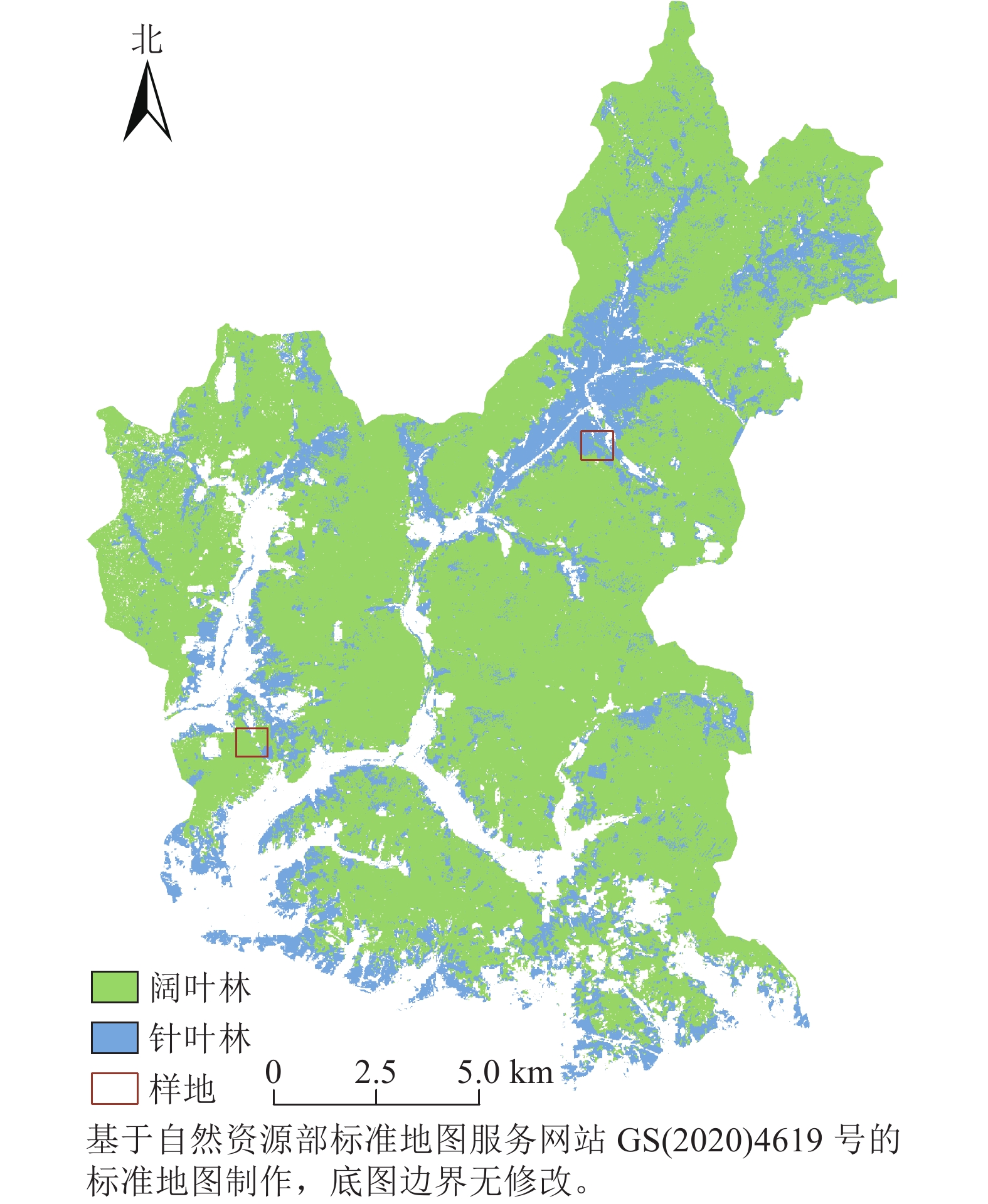
Objective Most of the existing leaf area index (LAI) products have some problems, such as low resolution, abnormal data and low accuracy, which are difficult to meet the requirements of some applications. Therefore, this study proposes a method of fusing multi-source LAI data to reduce the differences of data from different sources and improve product accuracy. Method The broad-leaved forest and coniferous forest in Maoershan experimental forest farm were taken as the research area. Based on MODIS LAI, VIIRS LAI and PROBA-V LAI products in 2017, the LAI background database was established to correct low-quality data by using years of LAI data as prior knowledge, and 3 LAI data sets were downscaled by mixed pixel decomposition. Based on Sentinel-2 reflectivity product coupling ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF) algorithm, LAI dynamic model and radiative transfer model, data assimilation was carried out. Finally, 3 LAI data after assimilation were weighted and fused, and the accuracy was evaluated by using measured data. Result In broad-leaved forest, the correlation coefficients between the assimilated MODIS, VIIRS and PROBA-V LAI and the measured data were 0.59, 0.56 and 0.62, respectively, which were 0.57, 0.52 and 0.57 higher than the original data. The root mean square error (ERMSE) were 0.37, 0.31 and 0.14 respectively, which were 1.23, 1.69 and 1.06 lower than the original data. In coniferous forest, the correlation coefficients between the assimilated MODIS, VIIRS and PROBA-V LAI and the measured data were 0.59, 0.49 and 0.56, respectively, which were 0.52, 0.30 and 0.40 higher than the original data. ERMSE were 0.24, 0.28 and 0.19 respectively, which were 1.22, 0.67 and 1.35 lower than the original data. Through the fusion method, the correlation coefficients of LAI in broad-leaved forest and coniferous forest were 0.83 and 0.76 respectively, which were higher than the data after assimilation. ERMSE were 0.15 and 0.13, respectively, which were smaller than the error of the assimilated data. Conclusion Through data assimilation, the accuracy of 3 LAI products is improved, and the fused LAI data has higher accuracy and reliability than the single LAI data after assimilation. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 30 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 850-860.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230478
Abstract:
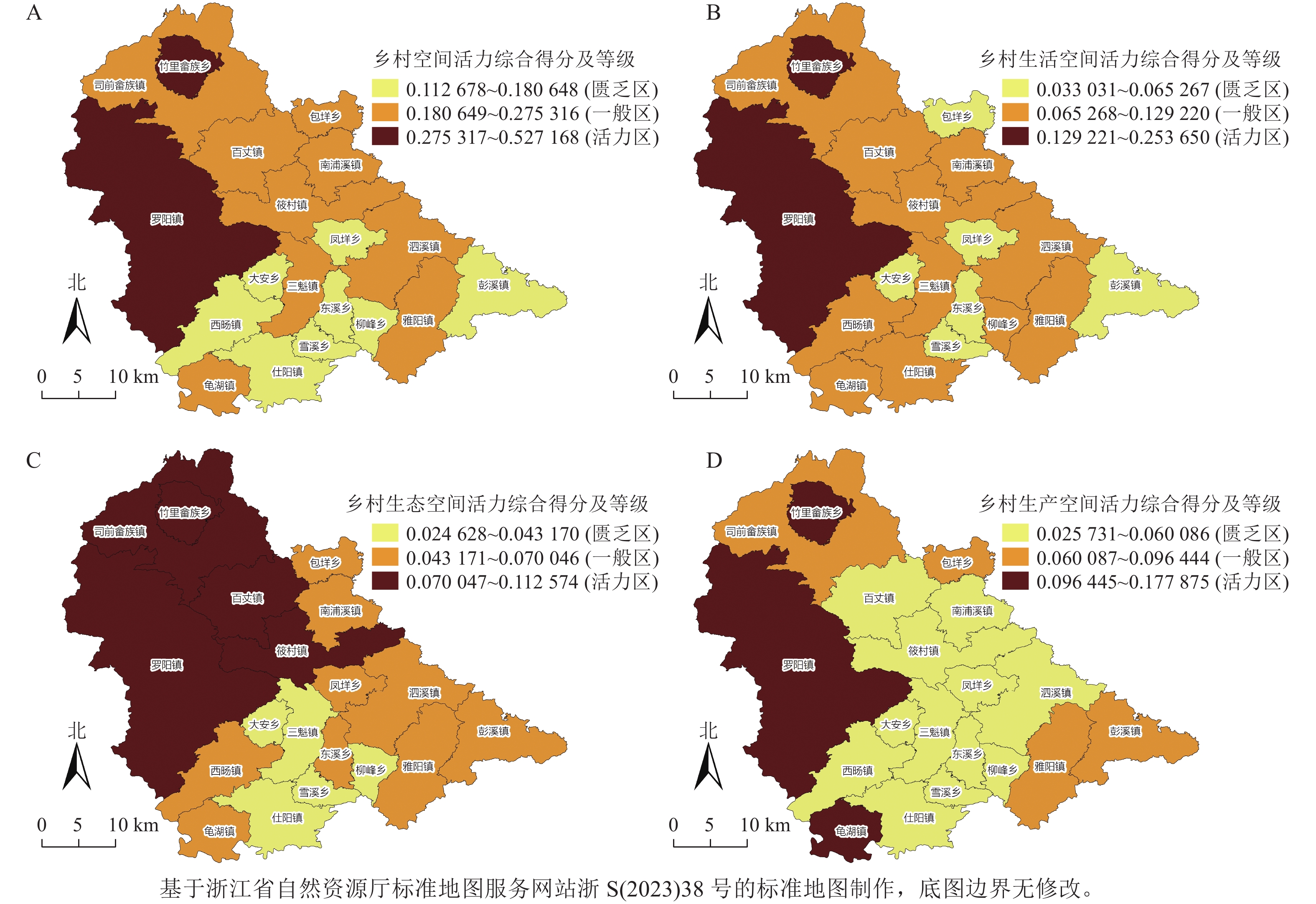
Objective This study aims to explore specific paths to improve the vitality of different regional types of rural areas in the context of rural revitalization and common prosperity, so as to provide scientific basis for rural development. Method Taking Taishun County in Zhejiang Province as the research object, a rural space vitality index evaluation system was constructed from the dimensions of rural life, ecology, and production vitality. The comprehensive evaluation method was applied to study the spatial differences in the development of rural spatial vitality, and the vertical and horizontal comparison method was used to identify leading and weak vitality of each township (town), and explore differentiated upgrading paths for various types of districts. Result (1) The spatial differentiation characteristics of rural spatial vitality in Taishun County were obvious, displaying an overall value of high in local areas, and high in the north and low in the south. The vitality level of most townships (towns) was relatively low. The vitality of each subsystem was different. The vitality of rural life, ecology and production space respectively showed the spatial distribution characteristics of locally low, high in the west and low in the east, high in the north and low in the south, locally prominent and high in the surroundings and low in the middle. (2) Based on the dividing principles of leading vitality and weak vitality, Taishun County was divided into four categories: comprehensive development, leading development, polarized development and underdevelopment, and the following vitality promotion strategies were proposed according to different regional types. The comprehensive development type should make full use of their respective advantageous resources to offer targeted assistance and form joint activation between the strong and the weak to promote a leap-forward improvement in rural spatial vitality. The leading development type should give full play to its own advantages and vitality to integrate and coordinate other vitalities. The polarized development should focus on exploring distinctive development path and filling gaps in vitality while enhancing the leading vitality. The underdevelopment type should deeply tap into core resources such as culture and ecology, and clarify the development orientation. Conclusion The overall level of rural vitality in Taishun County is low, and each township (town) also has different advantages and disadvantages, reflecting the unbalanced and inadequate development of vitality level. The proposed differentiated upgrading path is expected to have a certain guiding role in achieving rural revitalization and development in Taishun County. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 26 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 861-869.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230586
Abstract:
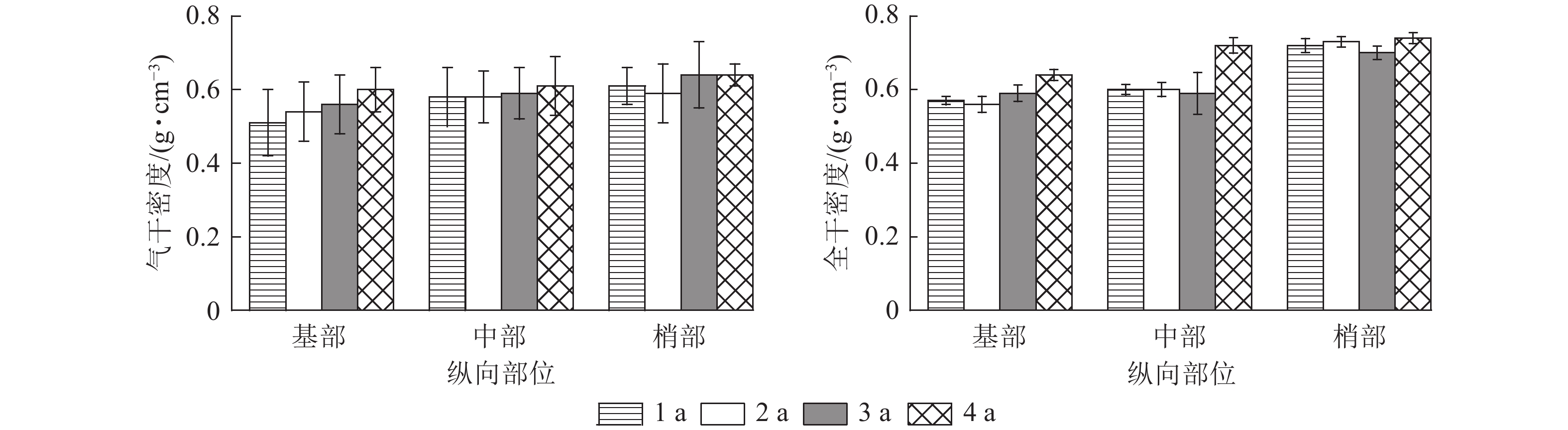
Objective This study aims to explore the effects of bamboo age and longitudinal position on wood and fiber properties of Bambusa blumeana, so as to provide theoretical and practical basis for the development and utilization of B. blumeana. Method The density, fiber morphology, chemical composition, mechanical properties and fiber bundle tensile properties of B. blumeana of different ages (1, 2, 3 and 4 years old) and different longitudinal parts (base, middle and tip) were analyzed by normal form washing, fiber segregation and microscopic observation and alkali boiling. Result With the increase of age, the air-dry density, total dry density, lignin mass fraction, tensile strength and longitudinal shear strength of B. blumeana increased, while the cellulose mass fraction gradually decreased. The average length difference of different longitudinal parts of B. blumeana aged 2, 3 and 4 were extremely significant (P<0.01). The fiber morphology of B. blumeana was significantly influenced by the longitudinal position. From the base to the tip of the longitudinal parts of B. blumeana, the air-dry density, total dry density, lignin mass fraction, bending strength, longitudinal shear strength, fiber bundle tensile strength and modulus all increased, while the cellulose mass fraction gradually decreased. The effects of bamboo age and longitudinal position on the mass fraction of semi fiber and benzenol extract were not obvious. Conclusion B. blumeana fiber has excellent properties and great potential in the development and utilization of fibrosis. There are significant differences in the properties of B. blumeana at different ages and longitudinal parts, among which B. blumeana of 3 and 4 years old can be used as the preferred material for processing and development. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 40 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 870-878.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230585
Abstract:
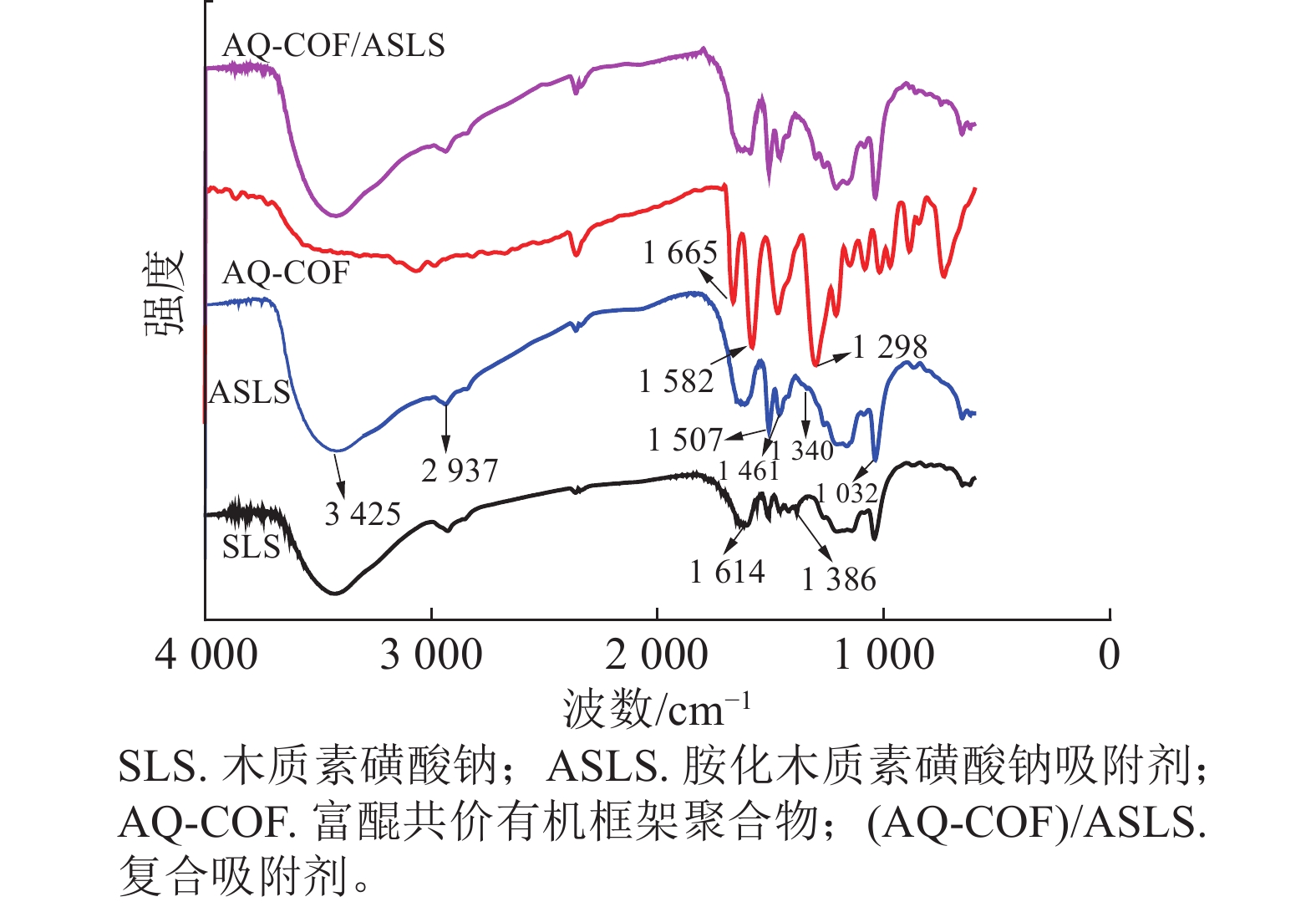
Objective Aminated sodium lignosulfonate (SLS) and covalent organic framework polymer/aminated sodium lignosulfonate composites were prepared with SLS as raw materials, and their adsorption properties for the Congo red (CR) were investigated. Method Aminated sodium lignosulfonate (ASLS) was prepared by Mannich reaction of sodium lignosulfonate with formaldehyde and diethylenetriamine. The surface functional groups and morphology of ASLS were characterized by infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The effects of initial concentration of CR, ASLS dosage, the pH value of the solution, and the adsorption time on the adsorption efficiency of the materials were investigated. The adsorption kinetics and regeneration performance of ASLS were analyzed. The AQ-COF was prepared, and the ASLS, AQ-COF, AQ-COF/ASLS on the adsorption for CR was compared. Result FTIR and SEM characterization results showed that sodium lignosulfonate was successfully aminated, and rod-like nanostructures were self-assembled after the combination of ASLS and AQ-COF. ASLS adsorption experiment showed that when the initial concentration of CR was 200 mg·L−1, the dosage of ASLS was 70 mg, and the pH was 1 − 5, the adsorption rate reached above 95%, and adsorption equilibrium was achieved within 80 minutes. The adsorption process was in line with the quasi second order adsorption kinetics model and Langmuir isotherm adsorption model, and the adsorption process was mainly chemical adsorption. When a small amount of AQ-COF (2 mg) was added to 30 mg ASLS, the adsorption rate of the composite adsorbent could reach more than 80%. Conclusion The modified aminated lignin has good adsorption effect on CR and excellent regeneration property, which can be used as an excellent adsorbent for CR. The composite adsorbent prepared by combining covalent organic framework polymer AQ-COF with ASLS can significantly improve the adsorption capacity of ASLS for CR, indicating that covalent organic frame polymers have good application prospects in the adsorption of organic pollutant CR. [Ch, 9 fig. 2 tab. 25 ref.]
2024, 41(4): 879-886.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230473
Abstract:
The vascular cambium is located between the xylem and phloem, which is responsible for many growth and development processes, and also plays an important role in wood production. In simulating cambium growth and potential molecular processes, deep imaging combined with gene expression analysis is a cutting-edge research direction, and mathematical modeling and simulation combined with real-time imaging have important application prospects. Based on this technique, some representative achievements at the molecular level of cambium activity are summarized, and the future research prospects are proposed. At present, molecular studies on cambium activity in plants mainly focus on: (1) cambium activity is regulated by plant hormone signaling; (2) cambium activity is regulated by transcription factors and peptide receptor signaling; (3) cambium activity is regulated by receptor kinase signals peptide receptor signaling. The main conclusions are that WOX4, WOX14, HB4, HB7, HB8 and ANT positively regulate the activities of tree cambium and can be used as the first choice for transgenic wood roughening breeding. In the future, the analysis of cell-to-cell communication connections in the cambium through computer models can better analyze the molecular mechanism of vascular cambium development in woody plants. [Ch, 3 tab. 68 ref.]
The vascular cambium is located between the xylem and phloem, which is responsible for many growth and development processes, and also plays an important role in wood production. In simulating cambium growth and potential molecular processes, deep imaging combined with gene expression analysis is a cutting-edge research direction, and mathematical modeling and simulation combined with real-time imaging have important application prospects. Based on this technique, some representative achievements at the molecular level of cambium activity are summarized, and the future research prospects are proposed. At present, molecular studies on cambium activity in plants mainly focus on: (1) cambium activity is regulated by plant hormone signaling; (2) cambium activity is regulated by transcription factors and peptide receptor signaling; (3) cambium activity is regulated by receptor kinase signals peptide receptor signaling. The main conclusions are that WOX4, WOX14, HB4, HB7, HB8 and ANT positively regulate the activities of tree cambium and can be used as the first choice for transgenic wood roughening breeding. In the future, the analysis of cell-to-cell communication connections in the cambium through computer models can better analyze the molecular mechanism of vascular cambium development in woody plants. [Ch, 3 tab. 68 ref.]